WHO Partograph
Partograph
•
A partograph is a graphical record of the observations made of
a women in labour
•
For progress of labour and salient conditions of the mother
and fetus
•
It was developed and extensively tested by the world health
organization WHO.
History Of Partogram
•
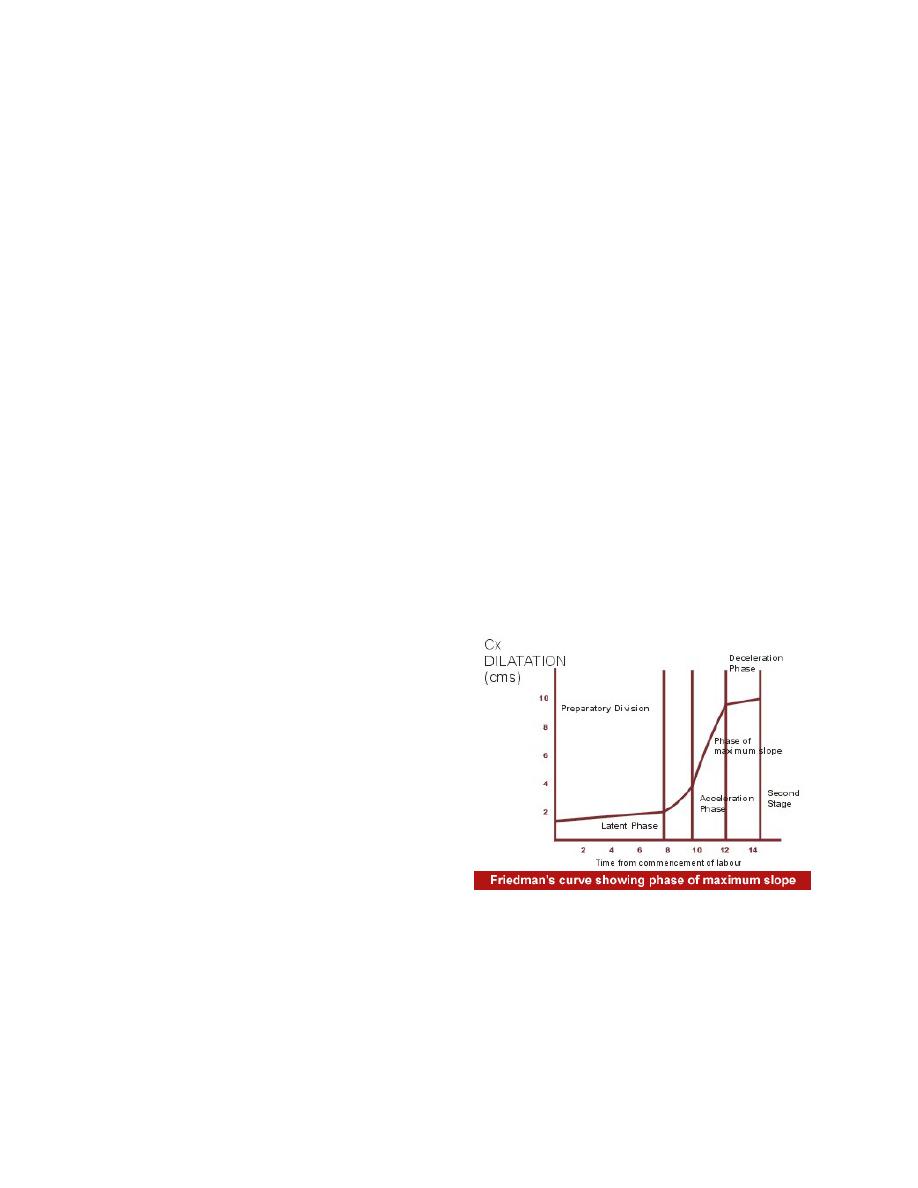
Friedman's partogram devised in 1954 was based on
observations of cervical dilatation and foetal station against
time elapsed in hours from onset of labour. The time onset of
labour was based on the patient's
subjective perception of her
contractility. Plotting cervical
dilatation against time yielded
the typical sigmoid or 'S' shaped
curve and station against time
gave rise to the hyperbolic curve.
Limits of normal were defined
Philpott and Castle
•
in 1972 introduced the concept of "ALERT" and "ACTION"
lines. The aim of this study was to fulfill the needs of
paramedical personnel practising obstetrics in Rhodesian
African primigravidae. The alert line represented the mean
rate of progress of the slowest 10% of patients in the African
نسائية
د. احمد جاسم
(10) ﻋﺪﺩد ﺍاﻻﻭوﺭرﺍاﻕق
!1

population whom they served. Alert line was drawn at a slope of
1 centimetre/hr for nulliparous women starting at zero time i.e.
time of admission . Action line drawn four hours to the right of
the alert line showing that if the patient has crossed the alert
line active management should be instituted within 4 hours,
enabling the transfer of the patient to a specialised tertiary
care centre.
•
The action line was subsequently drawn two hours to the right
of the alert line
WHO partograph
Overview
•
The partograph can be used by health workers with adequate
training in midwifery who are able to :
- observe and conduct normal labour and delivery.
- Perform vaginal examination in labour and assess cervical
diltation accurately
- plot cervical diltation accurately on a graph against time
•
There is no place for partograph in deliveries at home
conducted by attendants other than those trained in midwifery
•
Whether used in health centers or in hospitals , the
partograph must be accompanied by a program of training in its
use and by appropriate supervision and follow up
Objectives
•
early detection of abnormal progress of a labour
•
prevention of prolonged labour
•
recognize cephalopelvic disproportion long before obstructed
labour
•
assist in early decision on transfer , augmentation , or
termination of labour
•
increase the quality and regularity of all observations of
mother and fetus
!2
•
early recognition of maternal or fetal problems
•
the partograph can be highly effective in reducing
complications from prolonged labor for the mother (postpartum
hemorrhage, sepsis, uterine rupture and its sequelae) and for
the newborn (death, anoxia, infections, etc.).
Partograph function
•
The partograph is designed for use in all maternity settings ,
but has a different level of function at different levels of
health care
•
in health center, the partograph,s critical function is
to give early warning if labour is likely to be prolonged and to
indicate that the woman should be transferred to hospital
(ALERT LINE FUNCTION )
•
in hospital settings, moving to the right of alert line serves as
a warning for extra vigilance , but the action line is the critical
point at which specific management decisions must be made
•
other observations on the progress of labour are also recorded
on the partograph and are essential features in management of
labour.
Components of the
partograph
•
Part 1 : fetal condition
( at top )
•
Part 11 : progress of labour
( at middle )
•
Part 111 : maternal condition
( at bottom )
•
Outcome ……………… :
!3
Part 1 : Fetal condition
•
this part of the graph is used to monitor and assess fetal
condition
•
1 - Fetal heart rate
•
2 - membranes and liquor
•
3 - moulding the fetal skull bones
•
Caput.
Fetal heart rate
Basal fetal heart rate?
•>
160 beats/min =tachycardia
•
120 < beats/min = bradycardia
•
<100 beats/min = severe bradycardia
Decelerations? yes/no
Relation to contractions?
•
Early
•
Variable
•
Late – -----Auscultation - return to baseline
> 30 sec ! contraction
----- Electronic monitoring
peak and trough (nadir)
!
> 30 sec
membranes and liquor
•
intact membranes ……………………………………….I
!4
•
ruptured membranes + clear liquor …………………….C
•
ruptured membranes + meconium- stained liquor ……..M
•
ruptured membranes + blood – stained liquor …………B
•
ruptured membranes + absent liquor…………………....A
moulding the fetal skull bones
•
Molding is an important indication of how adequately the pelvis
can accommodate the fetal head
•
increasing molding with the head high in the pelvis is an
ominous sign of cephalopelvic disproportion
•
separated bones . sutures felt easily ……………….….O
•
bones just touching each other ………………………..+
•
overlapping bones ( reducible 0 ……………………...++
•
severely
overlapping
bones ( non –
reducible )
……..+++
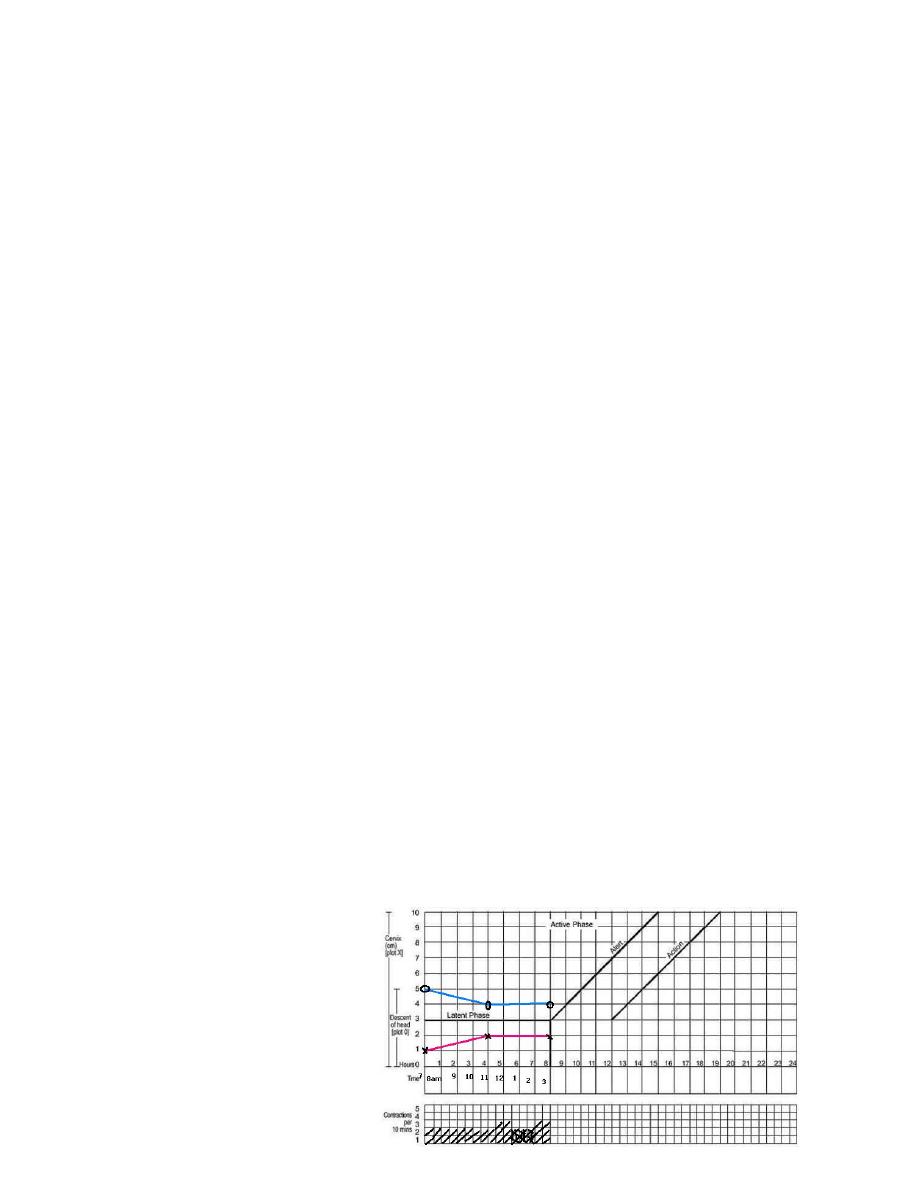
part11 – progress of labour
. Cervical diltation
•
Descent of the fetal head
•
Fetal position
•
Uterine contractions
•
this section of the paragraph has as its central feature a
graph of
cervical
diltation
against time
•
it is divided
!5

into a latent phase and an active phase
latent phase :
•
it starts from onset of labour until the cervix reaches 3 cm
diltation
•
once 3 cm diltation is reached , labour enters the active phase
•
lasts 8 hours or less
•
each lasting > 20 sceonds
•
at least 2/10 min contractions
Active phase :
•
Contractions at least 3 / 10 min
•
each lasting > 40 sceonds
•
The cervix should dilate at a rate of 1 cm / hour or faster
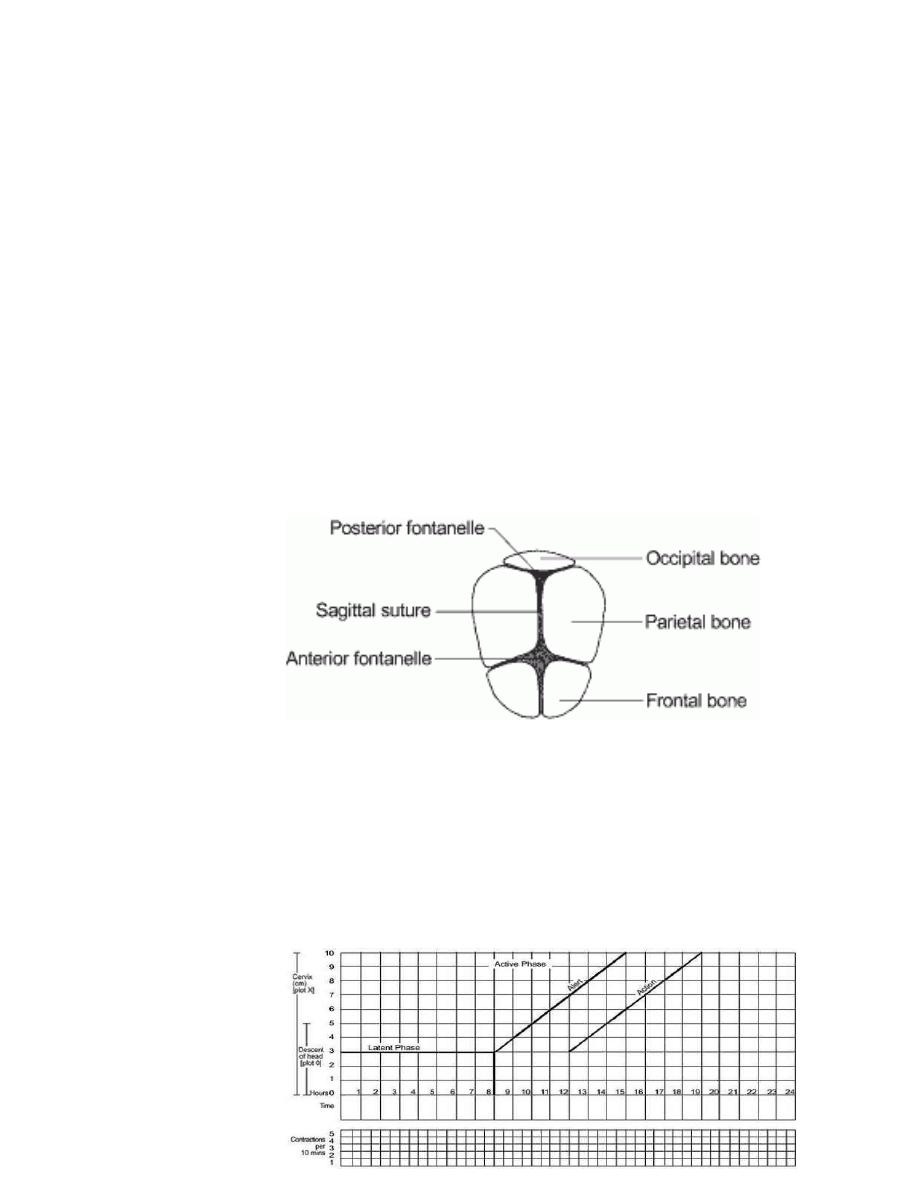
Alert line ( health facility line )
•
The alert line drawn from 3 cm diltation represents the rate
of diltation of 1 cm / hour
•
Moving to the right or the alert line means referral to hospital
for extra vigilance.
Action line ( hospital line )
•
The action line is drawn 4 hour to the right of the alert line
and parallel to it
•
This is the critical line at which specific management decisions
must be made at the hospital
Cervical diltation
•
It is the most important information and the surest way to
assess progress of labour , even though other findings
discovered on vaginal examination are also important
•
when progress of labour is normal and satisfactory , plotting of
cervical diltation remains on the alert line or to left of it
!6
•
if a woman arrives in the active phase of labour , recording of
cervical diltation starts on the alert line
•
when the active phase of labor begins , all recordings are
transferred and start by pltting cervical diltation on the alert
line
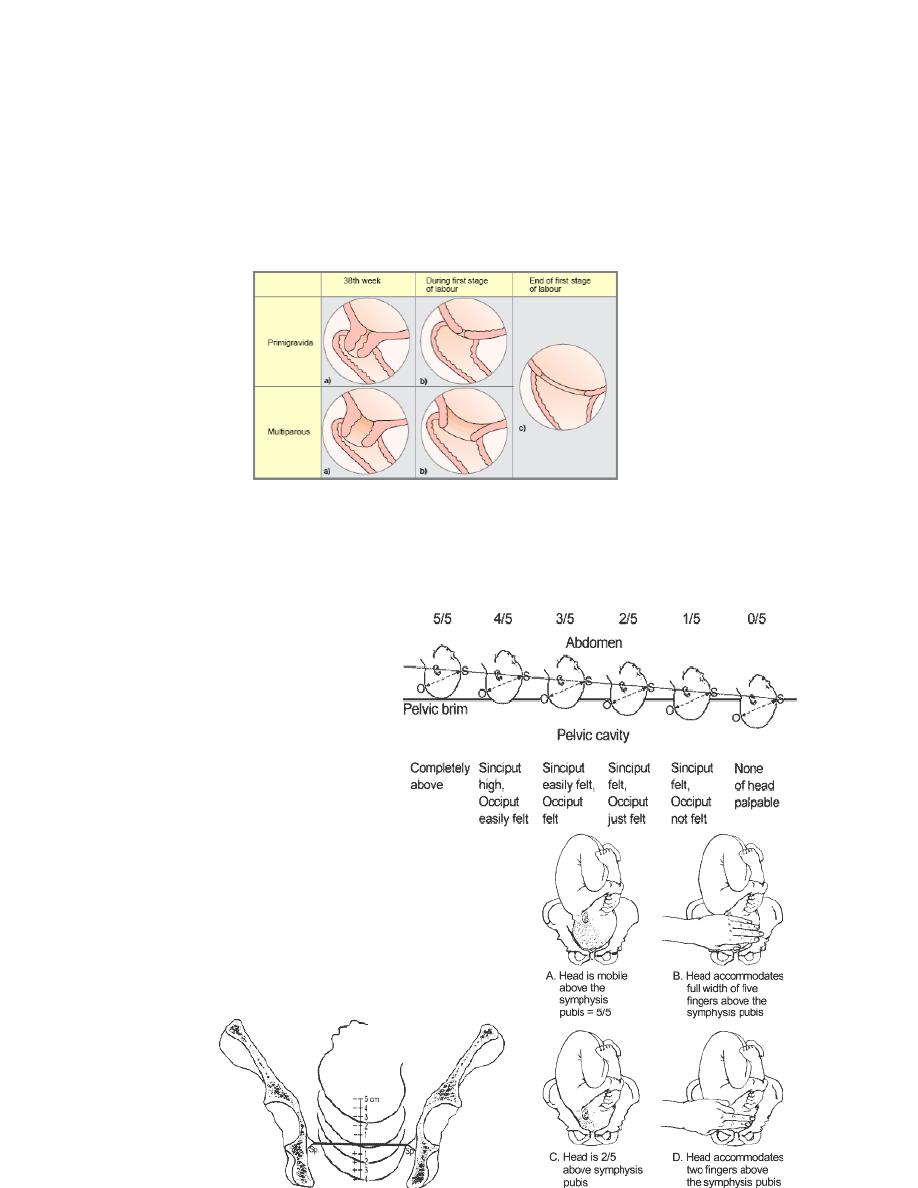
Descent
of the fetal
head
•
It should be assessed by abdominal examination immediately
before doing a vaginal
examination, using the
rule of fifth to assess
engagement
•
The rule of fifth means
the palpable fifth of the
fetal head are felt by
abdominal examination to
be above the level of
symphysis pubis
•
When 2/5 or less of fetal head is felt
above the level of symphysis pubis , this
means that the head is engage , and by
vaginal examination , the lowest part of
vertex
has
passed
!7
or is at the level of ischial spines
Assessing descent of the fetal head
by vaginal examination;
0 station is at the level of the ischial
spine (Sp).
Uterine contractions
•
Observations of the contractions are made every hour in the
latent phase and every half-hour in the active phase
•
frequency how often are they felt ?
•
Assessed by
number of
contractions in
!8
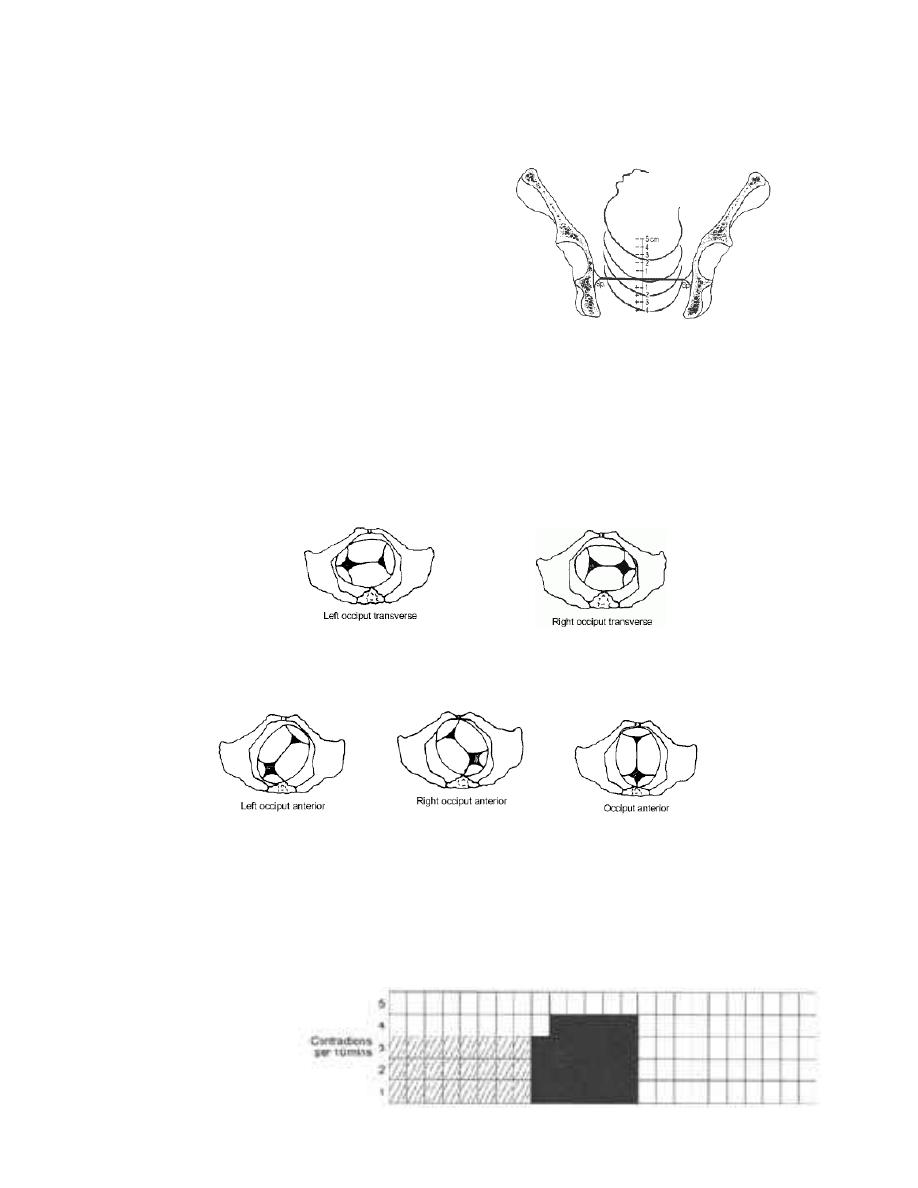
Occiput transverse positions
Occiput anterior positions
Fetal position
a 10 minutes period
•
duration how long do they last ?
Measured in seconds from the time the contraction is first
felt abdominally , to the time the contraction phases off
•
Each square represents one contraction
Palpate number of contraction in ten minutes and duration
of each contraction in seconds
•
Less than 20 seconds:
•
Between 20 and 40 seconds:
•
More than 40 seconds:
Part111: maternal condition
Name / DOB /Gestation
Medical / Obstetrical issues
Assess maternal condition regularly by monitoring :
•
drugs , IV fluids , and oxytocin , if labour is augmented
•
pulse , blood pressure
•
Temperature
•
Urine volume , analysis for protein and acetone
!9

Management of labour using the partograph
- latant phase is less than 8 hours
- progress in active phase remains on or left of the alert line
•
Do not augment with oxytocin
if latent and active phases go
normally
•
Do not intervene unless
complications develop
•
Artificial rupture of
membranes
( ARM )
•
No ARM in latent phase
•
ARM at any time in active
phase
Between alert and action lines
•
In health center , the women must be transferred to a hospital
with facilities for cesarean section , unless the cervix is almost
fully dilated
•
Observe labor progress for short period before transfer
!10
•
Continue routine observations
•
ARM may be performed if membranes are still intact
At or beyond action line
•
Conduct full medical assessement
•
Consider intravenous infusion / bladder catheterization /
analgesia
•
Options
- Deliver by cesarean section if there is fetal distress or
obstructed labour
- Augment with oxytocin by intravenous infusion if there are no
contraindications.
ABNORMAL PROGRESS OF LBOR
•
One of the main functions of the partograph is to detect early
deviation from normal progress of labor
Moving to the right of alert line
•
This means warning
•
Transfer the woman from health center to hospital
•
reaching the action line
•
This means possible danger
•
Decision needed on future management (usually by obesteritian
or resident )
Prolonged latent phase
•
If a woman is admitted in labor in the latent phase ( less than
3 cm diltation ) and
remains in the latent
phase for next 8 hours
•
Progress is abnormal
and she must br
transferred to a
hospital for a decision
!11

about further action
•
This is why there is a heavy line drawn on the partograph at
the end of 8 hours of the latent phase
Polonged Active phase
•
In the active phase of labor , plotting of cervical diltation will
normally remain on or to the left of the alert line
•
But some cases will move to the right of the alert line and this
warns that labor may be
prolonged
•
This will happen if the rate of
cervical diltation in the active
phase of labor is
not 1 cm / hour or faster
•
A woman whose cervical
diltation moves to the right of
the alert line must be
transferred and manged in a
hospital with adequate
facilities for obstetric
intervention unless delivery is
near
•
at the action line , the woman
must be carefully reassessed
for why labor is not progressing
and a decision made on further
management
!12
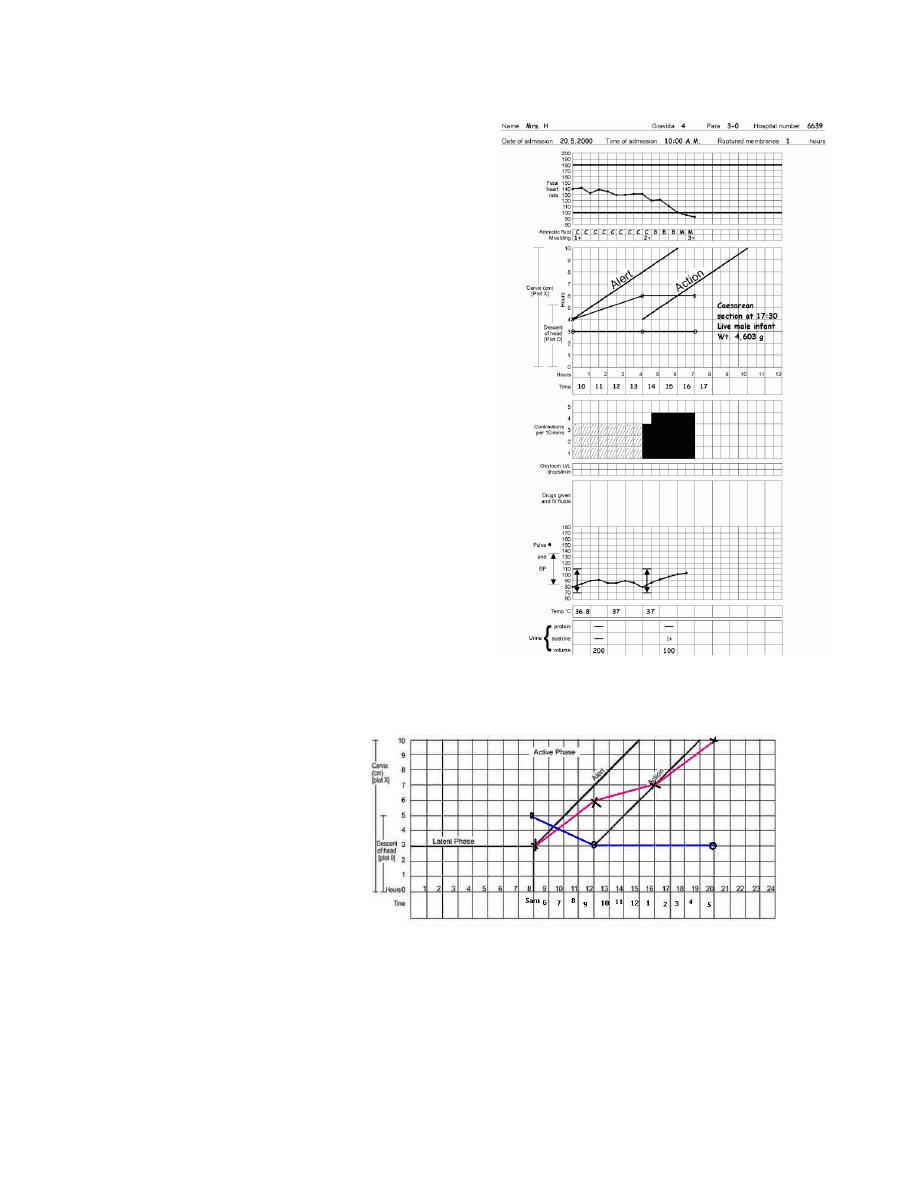
Secondary arrest of cervical
diltation
•
Abnormal progress of labor may
occur in cases with normal progress
of cervical diltation then followed
by secondary arrest of diltation
Secondary arrest of head
descant
•
Abnormal progress of labor may
occur with normal progress of
descent of the fetal head then
followed by secondary arrest of desscent of fetal head
Precipitate Labour
- Maximum slope of dilatation of 5 cm/hr or more
USING THE PARTOGRAPH POINTS TO REMEMBER
!13
•
It is important to realize that the partograph is a tool for
managing labor progress only
•
The partograph does not help to identify other risk factors
that may have been present before labor started
•
only start a partograph when you have checked that there are
no complications of pregnancy that require immediate action
•
a partograph chart must only be started when a woman is in
labor,-- be sure that she is contracting enough to start a
partograph
•
if progress of labor is satisfactory , the plotting of cervical
diltation will remain or to the left of the alert line
•
when labor progress well , the diltation should not move to the
right of the alert line
•
the latent phase . 0 – 3 cm diltation , is accompanied by
gradual shortening of cervix . normally , the latent phase should
not last more than 8 hours
•
the active phase , 3 – 10 cm diltation , should progress at rate
of at least 1 cm/hour
•
when admission takes place in the active phase , the admission
diltation, is immediately plotted on the alert line
•
when labor goes from latent to active phase , plotting of the
diltation is
immediately
transferred from
the latent phase
area to the alert
line
•
diltation of the cervix is plotted ( recorded with an X , desent
of the fetal head is plotted with an O , and uterine contractions
are plotted with differential shading
!14

•
desent of the head should always be assessed by abdominal
examination ( by the rule of fifths felt above the pelvic brim )
immediately before doing a vaginal examination
•
assessing descent of the head assists in detecting progress of
labor
•
increased molding with a high head is a sign of cephalopelvic
disproportion
•
vaginal examination should be performed infrequently as this is
compatible with safe practice ( once every 4 hours is
recommended )
•
when the woman arrives in the latent phase , time of admission
is 0 time
•
a woman whose cervical diltation moves to the right of the
alert line must be transferred and manged in an institution with
adequate facilities for obstetric intervention , unless delivery
is near
•
when a woman ,s partograph reaches the action line , she must
be carefully reassessed to determine why there is lack of
progress , and a decision must be made on further management
( usually by an obesterician or resident )
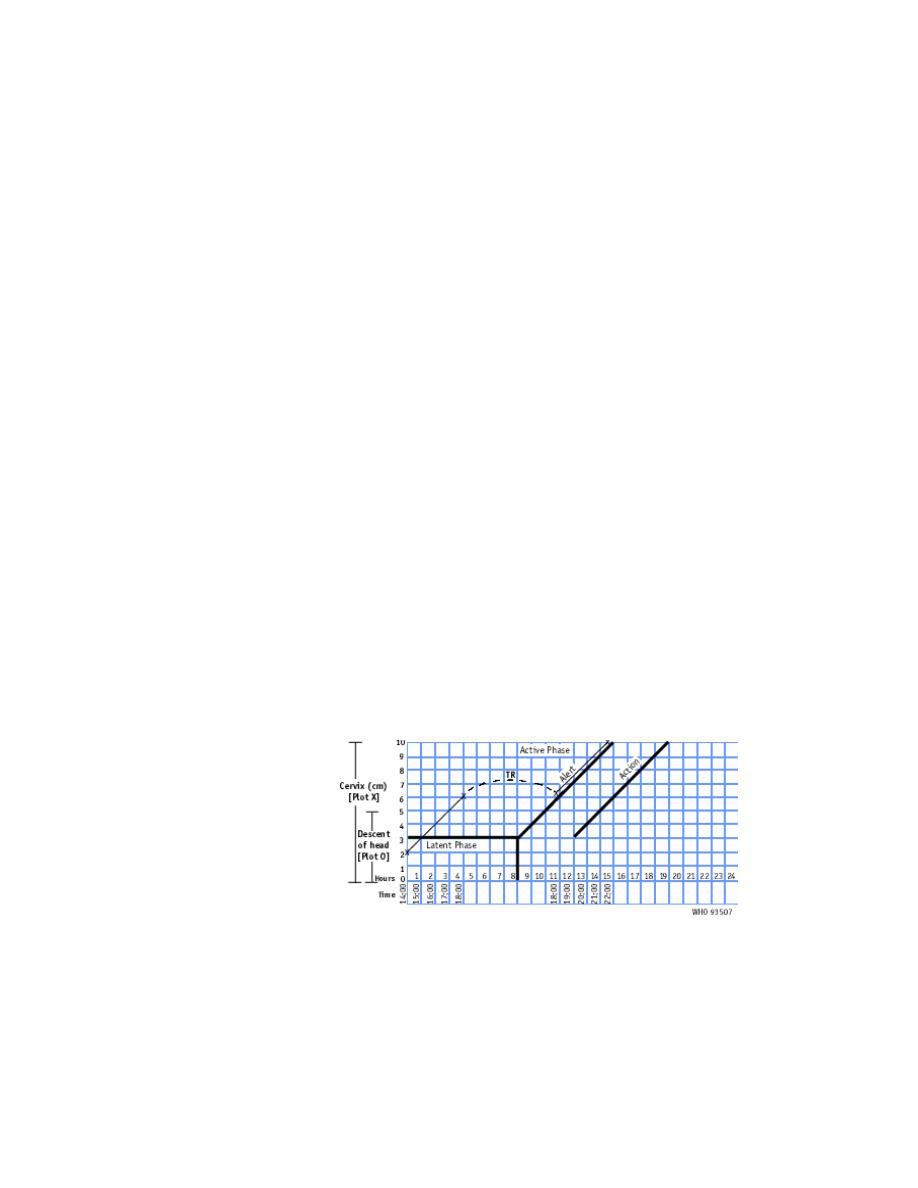
•
when a woman in labor passes the latent phase in less than 8
hours i.e., transfers from latent to active phase , the most
important feature is to transfer plotting of cervical diltation to
the alert line using the letters TR,
•
Leaving the area between the transferred recording blank.
The broken transfer line is not part of the process of labor
•
do not forget to transfer all other findings vertically
IMPORTANT COSIDERATIONS
OXYTOCIN
•
Oxytocics must be preserved in a cool , dark place
•
A local regime may be used
!15

•
Oxytocin should be titrates against uterine contractions and
increased every half- hour until contractions are 3 or 4 in10
minutes , each lasting 40 – 50 seconds
•
It may br maintained at the rate thoughout the second stage
of labor
•
Stop oxytocin infusion if there is
evidence of uterine hyperactivity
and / or fetal distress
•
Oxytocin must be used with
caution in multiparous women and
rarely , if at all , in women of para
4 or more
•
Augment with oxytocin only after
artificial rupture of membranes
and provided that the liquor is
clear
MEMBRANES
•
if membranes have been ruptured
for 12 hours or more , antibiotics
should be given
•
As a first defense against serious infections, give a
combination of antibiotics:
- ampicillin 2 g IV every 6 hours;
- PLUS gentamicin 5 mg/kg body weight IV every 24 hours;
- PLUS metronidazole 500 mg IV every 8 hours.
Note:
!16

If the infection is not severe, amoxicillin 500 mg by mouth
every 8 hours can be used instead of ampicillin. Metronidazole
can be given by mouth instead of IV.
FETAL DISTRESS
•
If a woman is laboring in a health center . transfer her to a
hospital with facilities for operative delivery
•
In a hospital , immediately :
- Conduct a vaginal examination to exclude cord prolapse and
observe amniotic fluid
- Provide adequate hydraion
- Administer oxygen , if avaliablestop oxytocin
-Turn the woman or her left side
Diagnosis of labour
Regular painful contractions resulting
in progressive change of the cervix
+/- show
+/- rupture of membranes
Components of normal labour
Patient
pain , bladder empty , dehydration , exhaustion
Powers
Uterine contractions
Maternal effort
Passages
Maternal pelvis ( Inlet - Outlet )
Maternal soft tissue
Passenger
Fetal ( size - presentation -
position – Moulding)
cord
placenta
!17

membranes
The partograph in the management of labor following
cesarean section.
•
In women undergoing a trial of labor following cesarean
section, the partographic zone 2-3 h after the alert line
represents a time of high risk of scar rupture. An action line in
this time zone would probably help reduce the rupture rate
without an unacceptable increase in the rate of cesarean
section
ELECTRONIC PARTOGRAPH
•
Full electronic capture of patient information during childbirth
including,
•
CTG's,
•
partograms,
•
all labour events,
•
outcome information,
•
fetal blood sampling results and cord blood gases direct from
the blood gas analyser
This information can be shown in real time to enhance
communication within and outside the delivery suite to improve
patient care and reduce human error.
•
It can be accessed over the anywhere, anytime, from within a
hospital or from a home..
COMPUTERIZED LABOR MANAGEMENT
To accurately and continuously measure cervical dilatation and
fetal head station in labor and the fetal monitoring and the
mother monitoring
!18
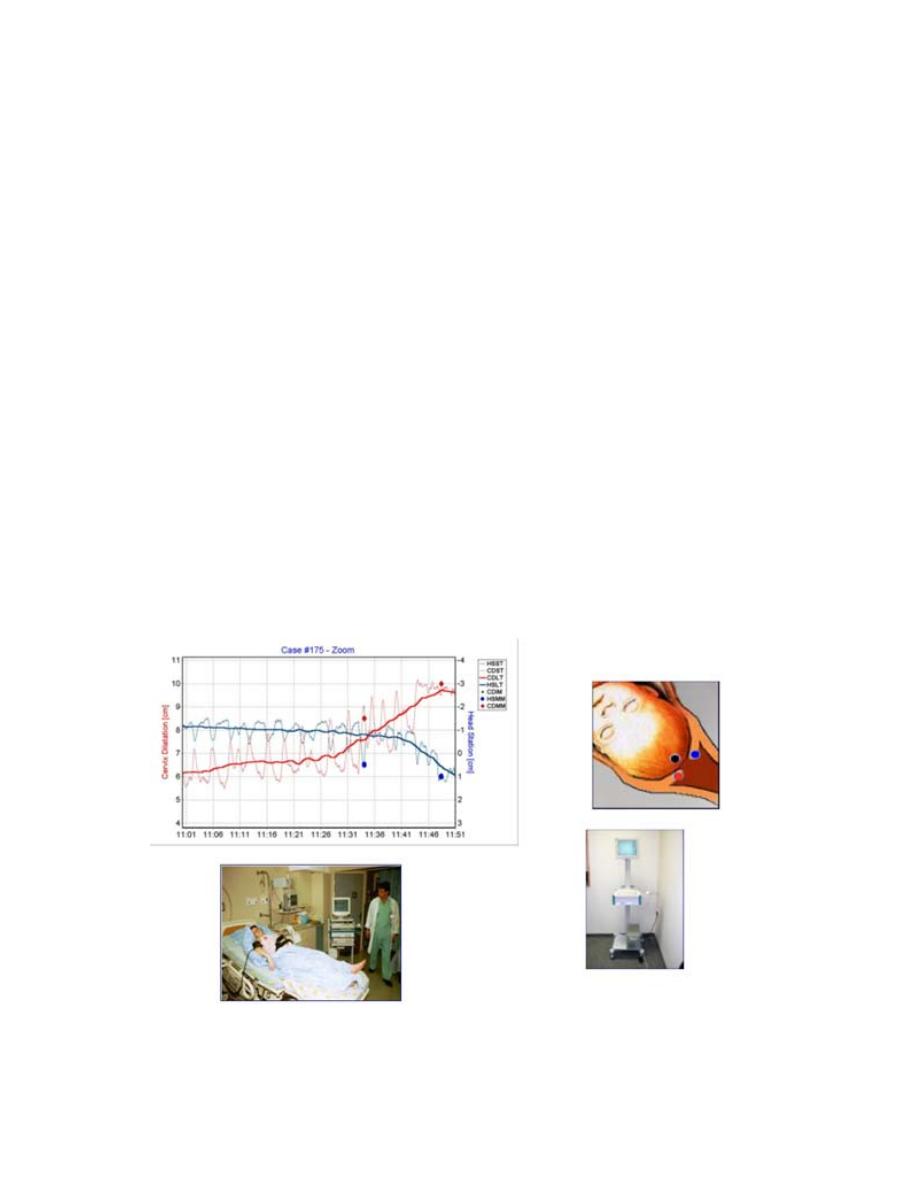
A ultrasound–based computerized labor management system was
designed
The Fetal Monitoring System and
The mother Monitoring System with
The system´s in-vivo generated individual Partograms
with real time dilatation and head station measurements.
The measurements had accuracy of < 5mm =
all parturients were comfortable throughout the insertion and
the testing period.
There was no infection, bleeding or any significant local
complication at any attachment site
•
This system provides accurate continuous measurements of
dilatation and station.
•
The method is superior to digital examination and provides real
time diagnosis of non-progressive and precipitous labor.
•
The system is likely to reduce discomfort and infections
associated to multiple vaginal examinations..
!19
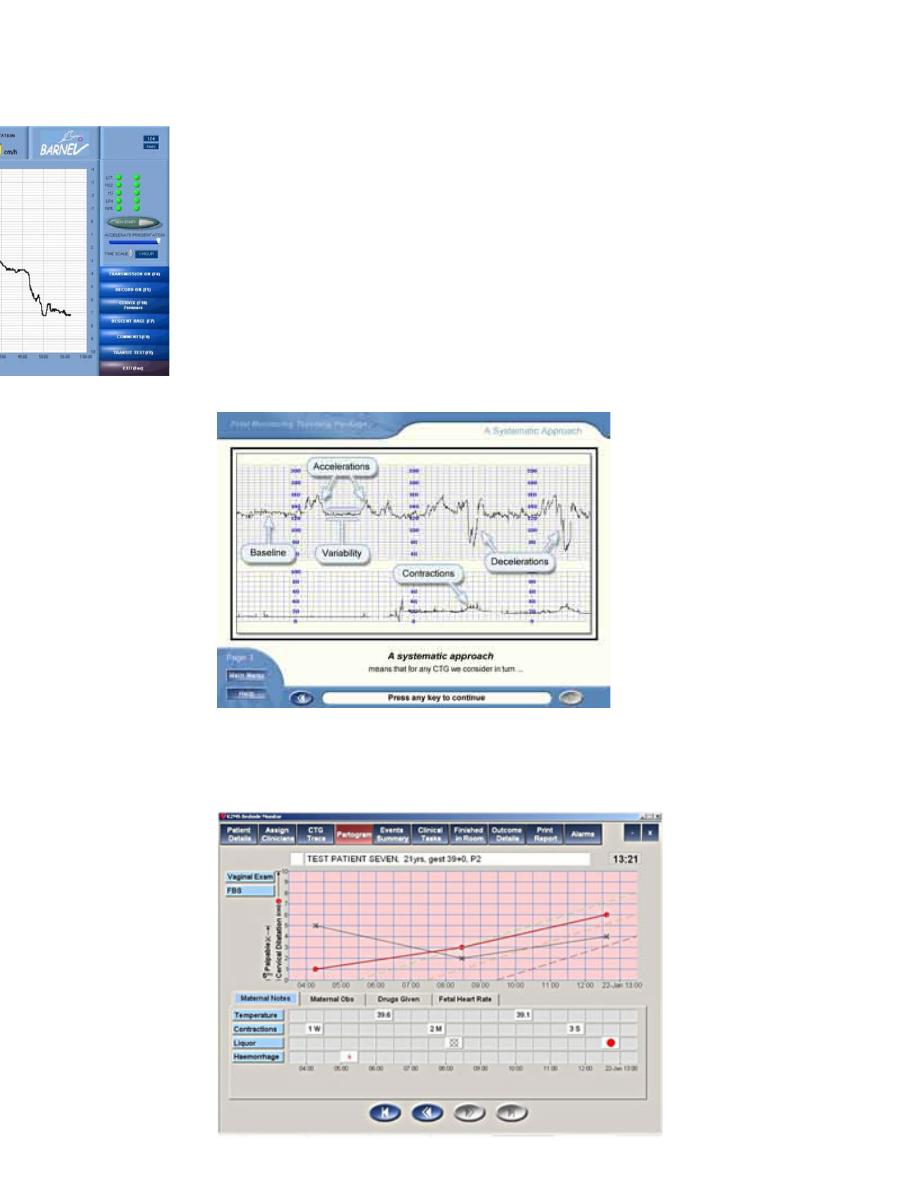
The Fetal Monitoring System
is a computer based training system that can be accessed
over the anywhere, anytime, from within a hospital or from a
home.
The Mother Monitoring System
!20
