Pericardial diseasesDr .Ghazi F. HajiSenior lecturer of cardiology Al-Kindy College of Medicine
introduction
Pericardial diseases is potentially curableIn westerian countries – idiopathic
In developing countries ---tuberculosisWhat is Pericardium ?
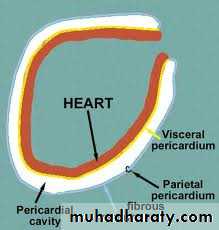
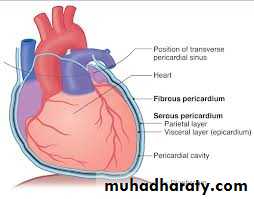
*fibrous sac suround heart*Serous membrane-two layers covering of the heart and root of great vessels
*Two layers : parietal (outer)and visceral (inner)with potential spacing between
*parietal layer sensitive to pain
Function
1-Stabilize the heart in it is position2-Lubricate surface of the heart
Allows smooth and controlled movement of the heart in the thorax
3-Barrier of the infectionPericardial Diseases
-Acute Pericarditis-Pericardial effusion
-Constrictive pericarditisMr X 55 y old man ,diabetic for 10y ago with regular therapy on metformine and glyberid ;presented with history of fever and tiredness for 4 days duration ,his illness associated with progressive chest pain ,in the left side ,increase with respiration and change in posture, He has family history of treatable tuberculosis.
On examination ;Pt .Conscious ,no pallor, not cyanosis.his puls was 66b/m BP 124/80 ,RR 18 ,normal S1S2 no added sound, no murmur ,but there is high pitched-scratching over pericordium .
What is the diagnosis ?
What are the suspected causes?
How confirm your diagnosis?
How manage ?
What are the prognosis?
Pericarditis
Inflammation of pericardiumPericardium ; thick and fibrous exudates in between –bread and butter appearance
May develop pericardial effusion later
Nature of fluid :serous ,purulent and hemorrhage
Sequelae-cardiac tamponada
constrictive pericaditis
recurrent pericarditis
Clinical classification
@Acute pericarditis : less than 6 wk
Fibrinous
Effusive
@Subacute pericaditis : 6wk-6month
Effusive / constrictive@Chronic pericarditis :more than 6 month
Constrictive
Effusive
Adhesive
Causes
#idopathic# following Myocardial infraction or cardiac surgery
#Infection :Viral –Coxsacki B,mump-Flue-Epstian –Barr- Hepatitis-HIV-Mycobactruim Tuberculosis
Staphylococcus /H. influenza
#Connective tissue diseases:Rheumatoid arthritis- Rheumatic fever
#Traumatic
#Post irradiation
#Malignancies- Breast 0 lung 0 lymphoma
#Drugs –penicillin –INH-hydralazine
#Metabolic :Uremia .Myxoedema
Clinical features and diagnosis
Pain – anterior ,sudden -central chest Pain- ,may radiated to back
@Pleurtic in nature ,change with position ,relive with sitting up and leaning forward
@ fever
@No pain in- uremia ,tuberculous ,neoplastic ,post irradiation pericarditis
Pericardial friction rub
Classically triphasic –high pitched-scratching
@Practically- to and fro sound ,may confuse with murmur
@Patient sitting leaning, in expiration –best heard
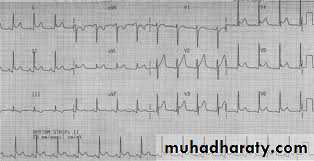
ECG
Differential diagnosis ;Acute myocardial infarction
1-Diffuse ST elevation in all leads except Avr + PR segment depression (80%) with upright T (concave) in all leads except aVR
2-normalization of ST-PR segments
3-Widspread T wav inversion
4- normalization of T wav
T inversion starts only after ST becoming iso-electiric
Blood
Blood picture-CRP,ESR,LEUKOCYTOSISCardiac enzymes
Blood cultureVirology –serelogy
Thyroid function tests
ANF,RF
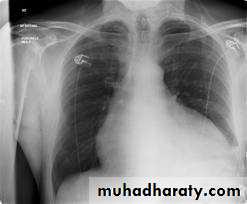
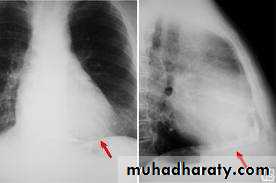
CXR – ECHO
CXR: Useful if there is effusionECHO :can detect even small amount
Treatment
-Treat underlying cause-Bed rest
-Analgesic –NSAID –indomethacin- ibuprofen –
-Colchicines
-steroid /immunosuppressant
.Mr X during treatment , 10 days later ;He developed progressive SOB and tachypenic but the pluertic pain suddenly subside, on examination ;JVP elevated and kuassmoul signs, pulsus paradoxis ,BP 90/50 ,Puls 100b/m
What new event happen?
What are useful investigation?Pericardial effusion
Collection of fluid in pericardial spaceNormally 15-20 ml
Echo :50 ml detected
CXR : 250 ml positive
Clinically : 500 ml
Rapid development of pericardial effusion if called tamponade
Diagnosis of pericardial effusion
*Pain – subside when effusion develop*Usual presentation as dyspenea
*Pulse –pulsus paradoxis (Normally during inspiration systolic Bp decrease up to 10 mmhg
Exaggeration of normal fall in systolic BP during inspiration)
*JVP elevation
*Apex – fainting not palpaple
*Percussion –widening of cardiac borders
*Auscultation –muffled heart sound
Ecg + CXR + ECHO
-ECG-low voltage
-CXR-Increase cardiac sillhoutte
Flask shaped enlargement
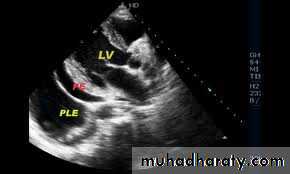
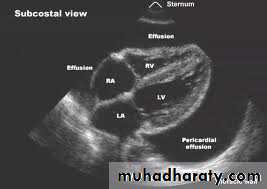
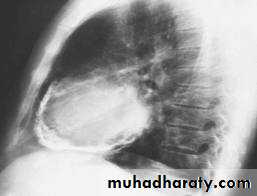
-Echo free zone surround the heart
-Fluid aspiration-Pericardial protein /serum protein > o.5 exudateAdenosine deaminases –sensitive and spesefic in TB
Treatment
Treated the causePericardiocentesis(diagnostic and therapeutic )
Culture .
ZN stain .
cytology .
Temponada
Rapid Accumulation of fluid lead to obstruction of ventricular filling even 200 ml but the heart can accumadate 2000ml if slowly accumulatedPhysiology :
Increase intra cardiac pressure
Decrease ventricular filling
Decrease cardiac output
CAUSES
Any pericarditis
Aortic dissection
Haemodialysis
Warfarin therapy
Cardiac surgery
Post cardiac cathetrization
Uremia
Connective tissue diseases –SLE.RA
Manifestation
-Dyspnea – orthopenia-Tachycardia , Pulsus paradoxis
-Hypotension
-Raise JVP and prominent descend of x wave
Kussmual s- absent (normaly inspiration cause decrease in chest pressure ,increase in venous return-JVP fall )
In constractive pericadritis –increase venous return cannot accommodate in RV because of end diastolic pressure so JVP rises in inspiration
-Wideness of cardiac dullness-percussion
Beck s triad (fall BP+raise JVP+ quite heart)
INVESTIGATION S
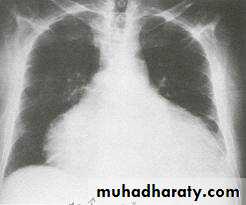
-CXR- cardiomegaly
-ECG-small QRS+may be - electric alternant
ECHO-
Free zone surround heartRT atrial and ventricular collapse
Dilated inferior vena cava
Treatment
Drainage *pericadrocentesis* and cultureXyphisternum puncture site-large needle with syringe
Mr X, After complete his treatment ,His general health became well,vital signs normal ,echo finding normal
5years later ;he suffer from progressively increase SOB ,fatigability ,ascites and leg swelling. On examination JVP elevated
What is the cause of these finding?
What is the underlying cause?
What is the diagnosis ?
What is the important tool in diagnosis?
What is the differnitional diagnosis?
Constrictive pericarditis
Pericardium undergo thickening ,fibrosis and calcification(rigid pericardium)
Restrict diastolic filling
LV systolic function preserve till late
causes
@Unknown-Usually secondary to chronic inflammation
Tuberculous pericarditis
Hemopericardium
Pyogenic -uremia -rheumatoid disease –rare
@May be late complication of open heart surgery
Manifestation
Typical features of systemic venous congestionIncrease JVP and prominent y wave descend
Hepatosplenomegaly – AScite –pedal edema
Impaired filling of ventricle :
Pulsus paradoxus-kussmaul sign
Heart sounds muffled
Radiological features
ECG –Low voltage –diffuse T wave changes
CXR- small heart -Calcification
ECHO – impaired diastolic relaxation
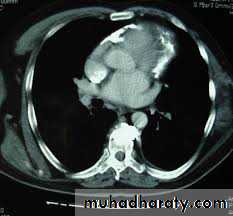
CT scan,MRI – pericardial thickness /calcification
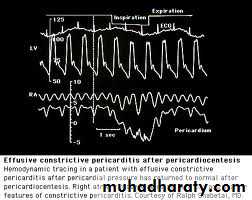
Catheterization – dip and plateau curve