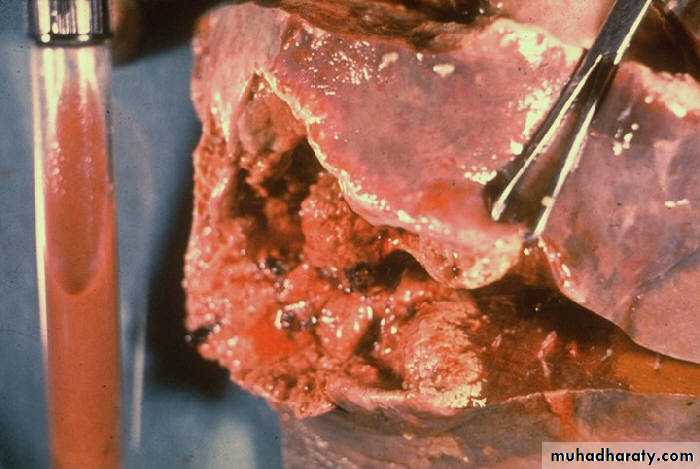
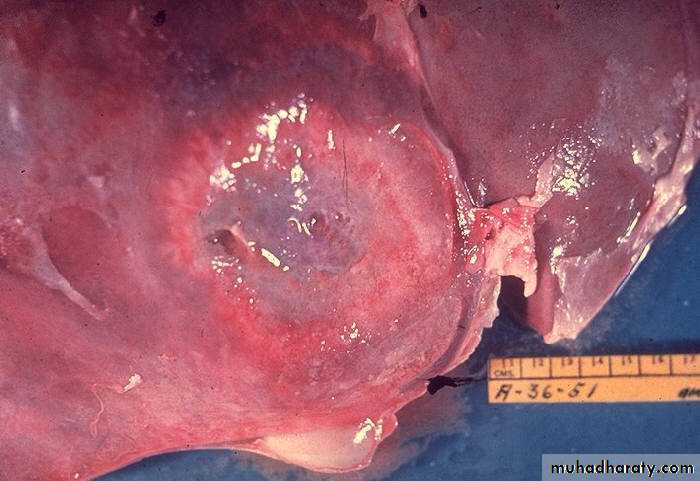
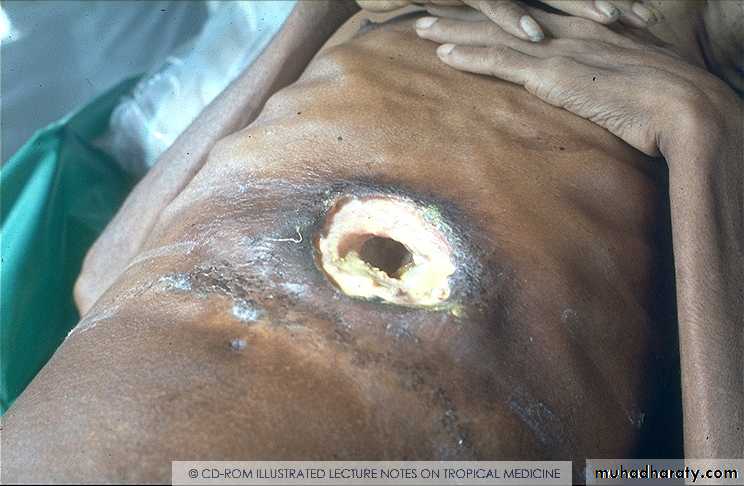
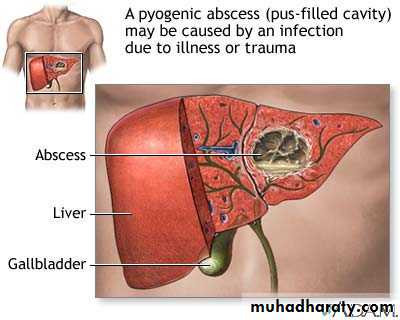
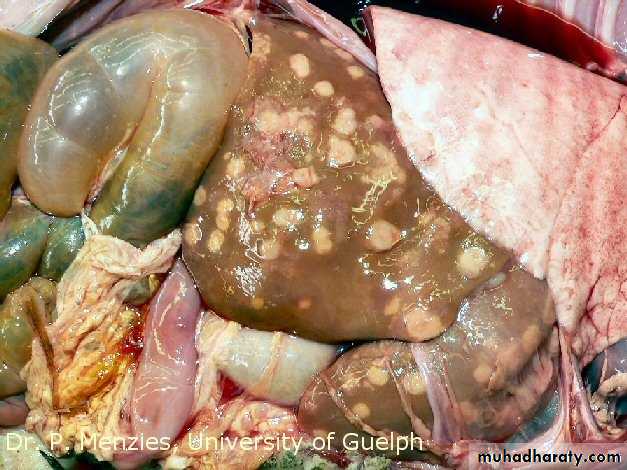
Liver Abscess
• common in developing countries• usually pyogenic multiple, small abscesses (E. coli, P. vulgaris, Enterobacter aerogenes, anaerobes)
• parasitic – usually solitary amebic & echinococcal
Liver Abscess
• Reach liver via:• Portal vein
• Arterial supply
• Ascending infection in biliary tract ascending cholangitis
• Direct invasion from nearby source
• Penetrating injury
• Clinical: RUQ pain, fever, tender hepatomegaly
Liver Abscess
• Abnormalities of liver function tests:• Dec. serum albumin (50%); inc. serum globulin
• Inc. serum ALP (75%)
• Inc. serum bilirubin (20-25%) >10 mg/dL usually indicates pyogenic rather than amebic origin poorer prognosis because of greater tissue destruction
• Inc. wbc (70%)
• Anemia (60%)
• Laboratory findings due to complications: R pleural effusion (20%), subphrenic abscess, pneumonia, empyema, bronchopleural fistula