Nosocomial Infections
Ass.Prof. Dr. Wijdan AkramCommunity Medicine Consultant
These infections occur:
up to 48 hours after hospital admissionup to 3 days after discharge
up to 30 days after an operation
in a healthcare facility when a patient was admitted for reasons other than the infection
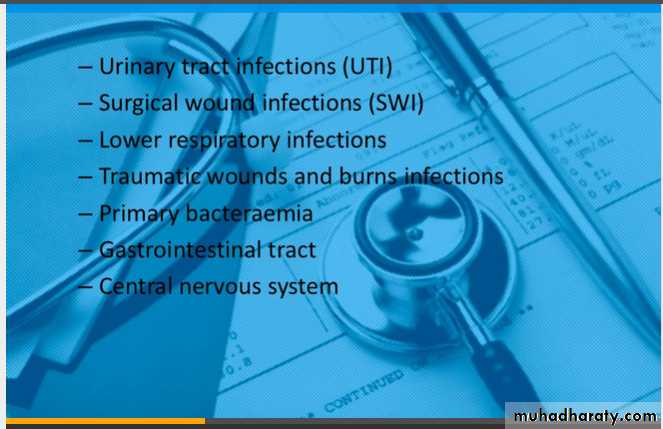
Types of Nosocomial Infections
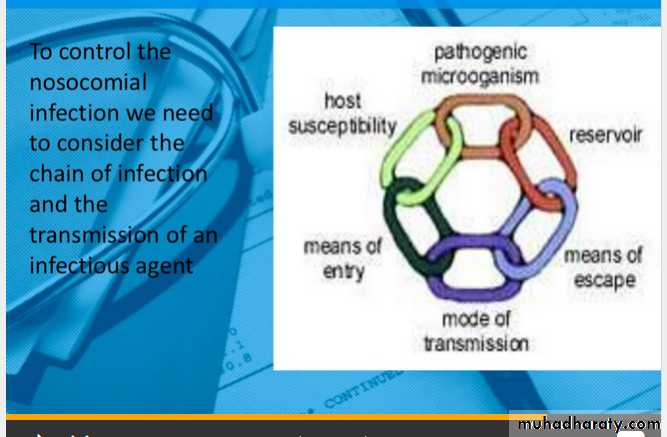
Mode of transmission
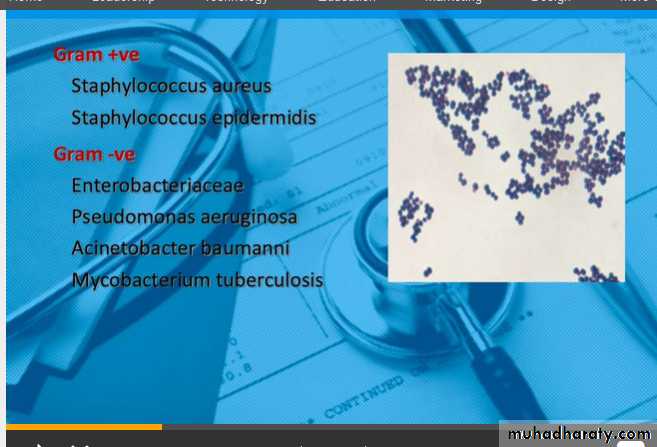
What Causes Nosocomial Infections?
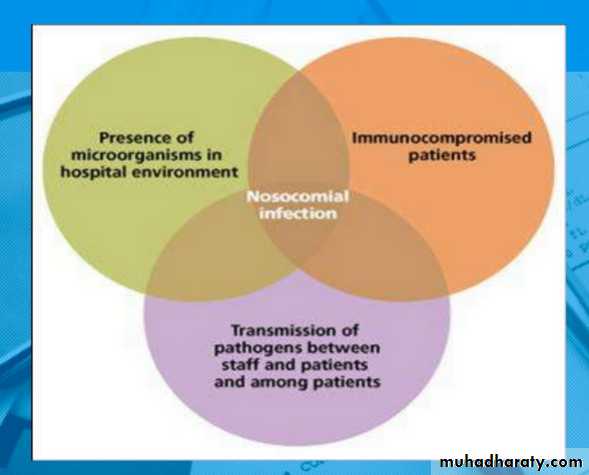
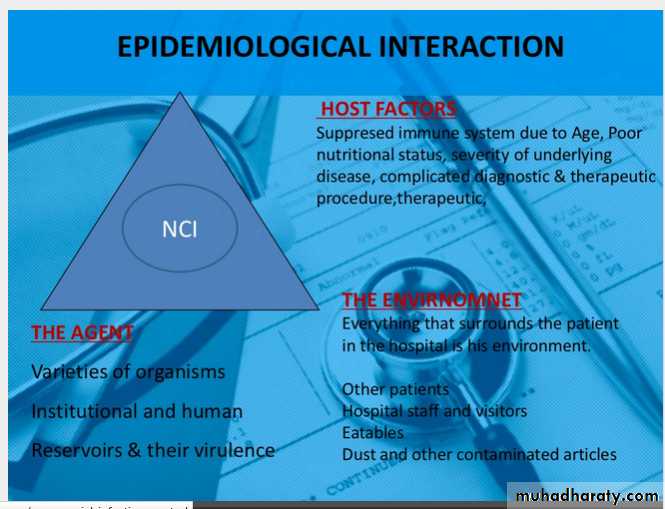
Nosocomial infections are caused by pathogens that easily spread through the body.Many hospital patients have compromised immune systems, so they are less able to fight off infections. In some cases, patients develop infections due to *poor conditions at a hospital or a healthcare facility, or due to *hospital staff not following proper procedures.
Some patients acquire nosocomial infections by *interacting with other patients. Others* encounter bacteria, fungi, parasites, or viruses in their hospital environment.
Who Is at Risk for Nosocomial Infections
Prevalence of Infection in Intensive Care Study, up to 20.6 percent of ICU patients acquire nosocomial infections during or after their stay.On average, nosocomial patients stay in the hospital 2.5 times longer than patients without infection. Patients with highly compromised immune systems are easily infected. This is because their bodies are not able to control the infections on their own
What Are the Symptoms of Nosocomial Infections?
Symptoms of nosocomial infections vary by type. They include inflammation, discharge, fever, and abscesses. Patients may experience pain and irritation at the infection site, and many experience visible symptoms.How Are Nosocomial Infections Diagnosed?
Many forms of nosocomial infections can be diagnosed through sight alone. Pus, inflammation, and rashes may all be indications of infection. Blood and urine culture tests can identify the infection.
How Are Nosocomial Infections Treated?
Treatments for nosocomial infections depend on the infection type. If the infection occurs at the site of a catheter or other inserted line, the line should be removed immediately.Antibiotics can combat symptoms of many infections. A healthy diet, fluid intake, and rest can encourage natural healing processes and prevent dehydration.
What Is the Outlook for Nosocomial Infections?
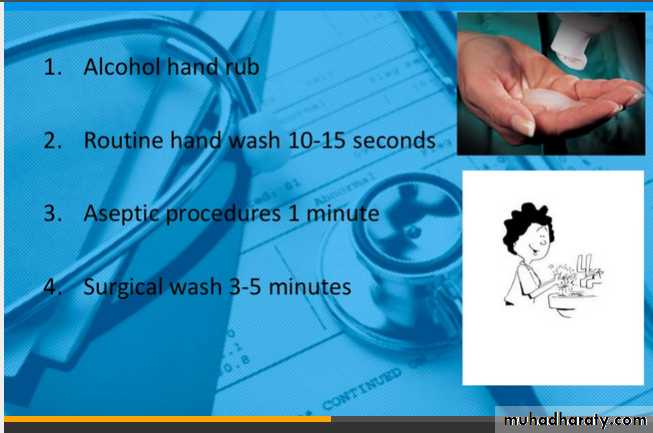
Most cases of nosocomial infection are resolved with treatment, but some can be fatal. Early detection and treatment are vital. Under the right conditions, most patients are able to make a full recoveryGENERAL PRINCIPLES Good general ward hygiene: - No overcrowding - Good ventilation - Regular removal of dust - Wound dressing early in day - Disposable equipment HAND WASHING most important - Before and after patient contact before invasive procedures
Why
Don’t Staff Wash their Hands(Compliance estimated at less than 50%)
Why Not?Skin irritation
Inaccessible hand washing facilities
Wearing gloves
Too busy
Lack of appropriate staff
Being a physician
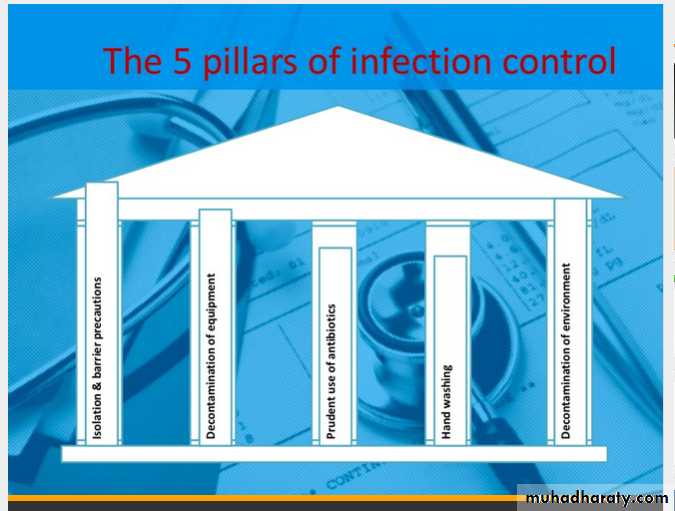
What to do to decrease NCI:
Hand Care
SURVEILLANCE DEFINITION
A dynamic process of gathering, managing, analyzing and reporting data on events that occur in a specific populationOBJECTIVES OF THE SURVEILLANCE
• Reducing the infection rate within a hospital.• Establishing baseline rates.
• Identifying outbreaks.
• Comparing infection rates among hospitals.
FIVE COMPONENTS OF SURVEILLANCE
• Case Definition: Define the health problem to be surveyed as precisely as possible.• Data Collection: Systematic and valid.
• Data Presentation in a useful manner.
• Data Analysis and interpretation.
• Feed Back to bring about the change in causative factors.
FEEDBACK
“Surveillance is not complete until the results are disseminated to those who use it to prevent and control”COST-EFFECTIVE CONTROL
Reducing incidenceReduce morbidity
Shorten hospital stay
Reduce cost of treating infections
Reduce cost of preventive measures
measures