Venous Disease
Varicose VeinDilated tortuous veins
5% of adult populationEqual gender prevalence
Family historyIntroduction:
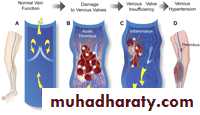
Incompetence of the venous valves
Primary venous incompetenceSecondary venous incompetence
Pathology:
Unsightly appearance
Discomfort and aching at the end of the dayAnkle swelling towards the end of the day
Complications:
Itching and eczema
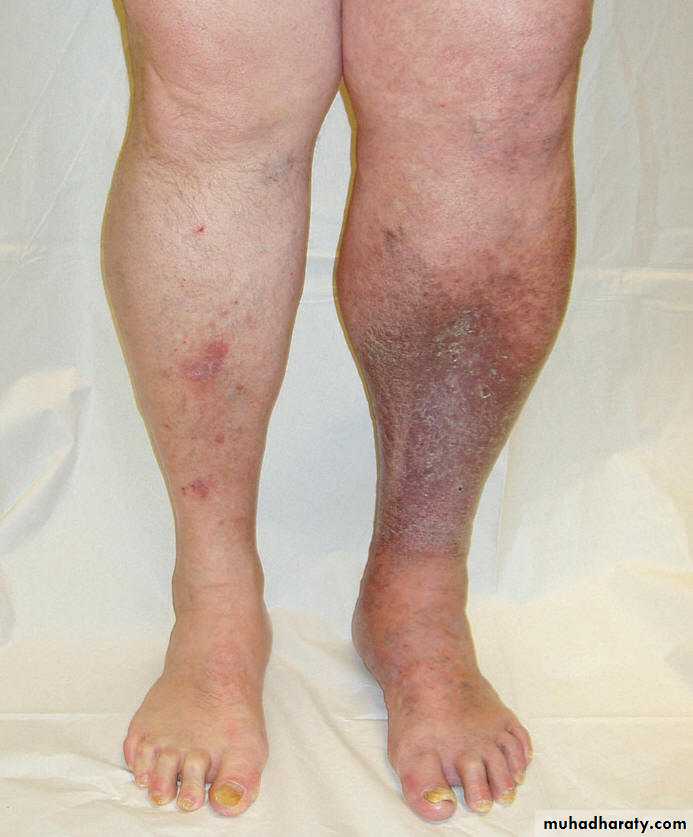
Lipodermatosclerosis
Venous ulceration
Clinical manifestations:
Venous Eczema (stasis dermatitis):
Lipodermatosclerosis:
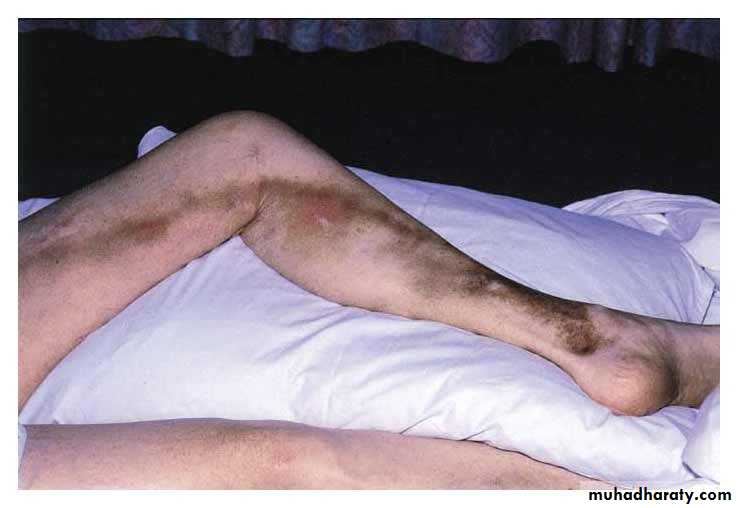
Venous Ulcer:
On examination:Great or small saphenous vein
• Incompetent saphenofemoral junction or incompetent perforators
Exclude DVT or deep vein incompetence
Usually diagnosed clinically
Investigations done to confirm and exclude• Duplex ultrasound
• Venography
• Abdominal and/or pelvic imaging
Investigations:
• Reassurance
• Elastic compression stockings• Avoid prolong standing and change of occupation may be required
• Periodic elevation of the feet
Treatment:
• I- Conservative Treatment:
Sodium tetradecyl sulfate (STD)
II- Injection sclerotherapy:
Indications for surgery:
Symptomatic varicose veinsComplicated or bleeding varicose veins
Large varicose veins
Cosmetic purposes
Surgical options include:
Ligation and stripping of the saphenous vein
Multiple subfacial perforator ligation
Combination of both.
Complications of varicose vein surgery:
Nerve injury (saphenous nerve and sural nerve)
Recurrence
III- Surgical Treatment:
Varicose vein stripping:
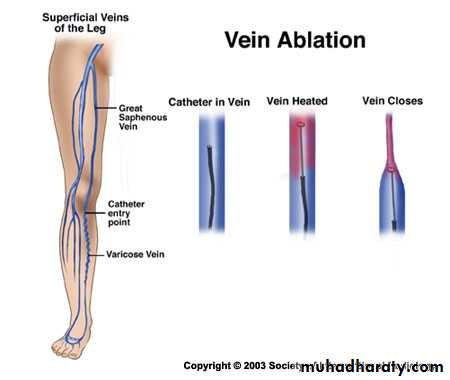
Radiofrequency AblationEndovascular laser ablation.
IV- New Techniques:
Deep Vein Incompetence
Pathology:
Leg swelling,Discomfort on walking,
Edema,
Varicose veins (which may not be present),
Ankle flare (small varices),
Lipodermatosclerosis
Ulceration
Clinical presentation
Post Phlebetic syndrome:
• Duplex ultrasound• Venography.
Investigations:
• Elastic compression stockings
• Avoid prolong standing and change of occupation may be required• Periodic elevation of the feet
• Exercise of the calf muscles
Treatment:
• I- Conservative Treatment:
• Venous bypass procedures (e.g. Palma procedure)
• Venous valve reconstruction• Venous valve transposition
II- Surgical Treatment:
Venous Ulceration
Venous disease: deep vein incompetence
Arterial ischemiaRheumatoid ulcer
Traumatic ulcer
Neuropathic ulcer (diabetic)
Neoplastic ulcer (squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma).
Differential diagnosis of leg ulcers:
Not fully understoodAmbulatory venous hypertension
Due to valve incompetence:
Incompetent superficial veins
Incompetent perforator veins
Incompetent or obstructed deep veins
Etiolgy:
Site: gaiter region (between calf and ankle)
Size: usually largeDepth: usually superficial
Edges: gently sloping edges
Base: granulation tissue + slough and exudates
Discharge: pus occasionally blood
Surrounding tissue: features of chronic venous disease
Local lymph nodes: enlarged (superadded infection)
Movement of ankle joint: restricted due to pain
Clinical examination
Venous Ulcer:
• Swab and culture from the ulcer• Duplex ultrasound
• Venography
Investigations:
multilayered elastic compression bandaging system,
avoid prolong standing,periodic leg elevation
Treatment:
• I- conservative Treatment:
Multilayer elastic compression
• Surgery for the cause of the venous ulcer (varicose vein, DVT or chronic venous insufficiency)
• Perforator vein subfacial ligation
• Skin graft to the ulcer after dealing with the underlying cause
II- Surgical Treatment:
Superficial Thrombophlebitis
External trauma,Venepunctures and infusions of hyperosmolar solutions and drugs.
Intravenous cannula
Some systemic diseases: buerger’s disease, and malignancy,
Coagulation disorders: polycythaemia, thrombocytosis and sickle cell disease
Etiology:
• Treatment::• Reassurance
• NSAIDs
• Warm massage