
88Lec.3
Pediatrics
6
th
stage
Session Notes
د.اوس حازم
Notes :
Blood group taking in the history is important in hemolytic diseases such
as :-ABO incompatibility & Rh incompatibility(mother:Rh-ve,baby:Rh+ve)
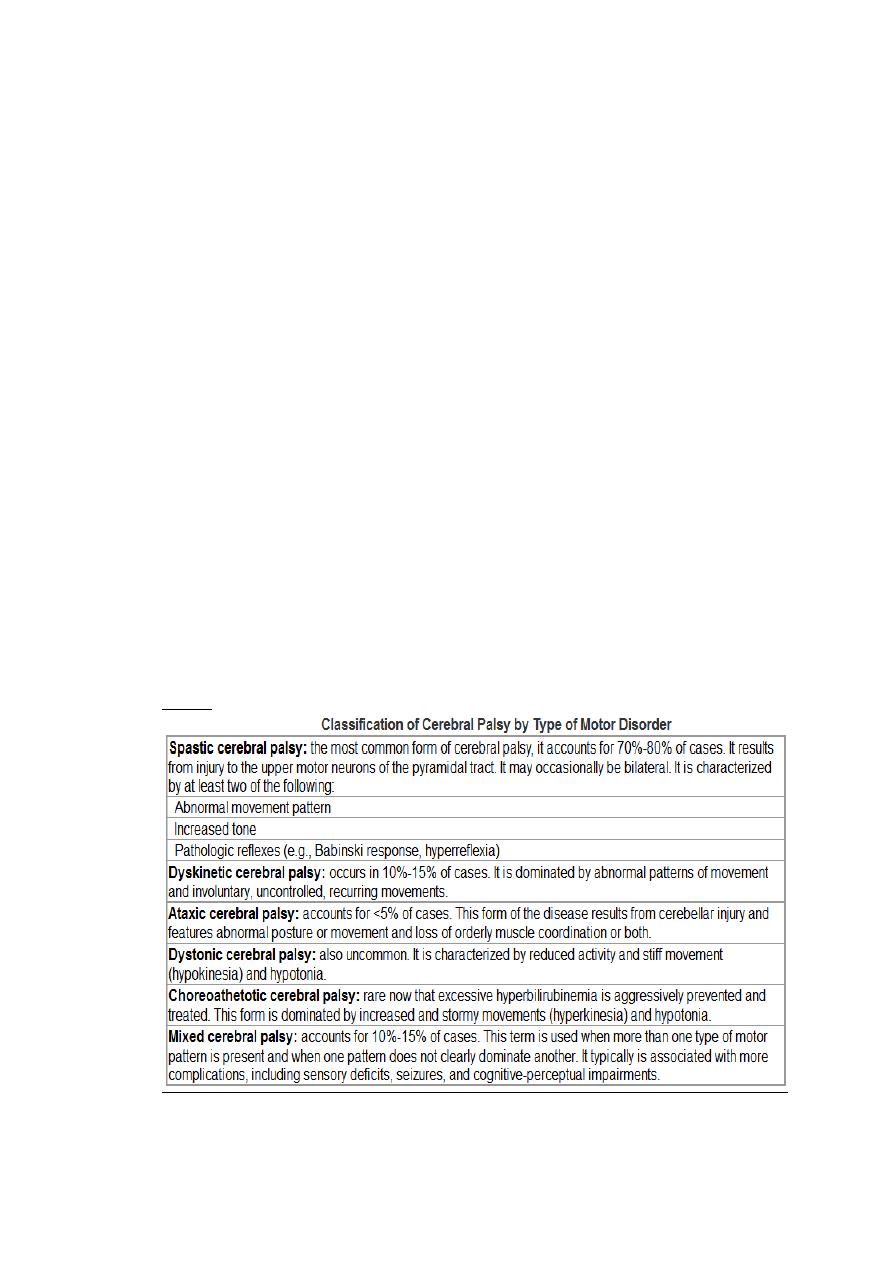
Cerebral palsy :
In general means disorder of posture & motion.
Causes
1) Prenatal
o Prematurity
o LBW
o Intrauterine exposure to maternal infection
o Maternal medical problems
o Sever toxemia and eclampsia
o Bleeding in the 3rd trimester
o Drug abuse, drug therapy and toxic exposure
o Trauma
o Multiple pregnancies
o Placental insufficiency
o Congenital malformations
. Perinatal
• Prolonged and difficult labor
• Premature rupture of membrane
• Presentation anomalies
• Vaginal bleeding at the time of admission for labor
• Bradycardia
• encephalopathy
3. Postnatal
o CNS infection: encephalitis and meningitis.
o Hypoxia.
o Seizure.
o Coagulopathies.
o Neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia (kernicterus):stormy event.
o Head trauma
النقاط السابقة كلها نسأل عنها لتحديد سببCP
Types

Topographic subclassification of spastic CP
hemiplegic CP :the cause may be emboli or CVA in the
intrauterine life.
in case of CP :concentrate on prenatal Hx,developmental
Hx(Global or in certain parts),family Hx is also important.
Grasping :- begins in (3)mo.

Grasp reflex :-hold the rattle.) (خشخاشة
Don't forget hearing & vision,ask about them.
He developed well for some periods of time then till
(6)months he begin to regress ,this is typical Hx of pt with
degenerative disease,also called lysosomal storage disease.
Ex:-Gaucher's disease/
Meningitis & CP:-
o CP : insult to brain during its development.
o CP is one of the complication of meningitis , they are :
1) Deafness/blindness.
2) Mental retardation
3) epilepsy
4) Hemiplegia/monoplegia
5) Hydrocephalus
Rx of CP:-multidisciplinary team ((very important))
1) Physiotherapist
2) Orthopedic surgeon
3) Pediatric surgeon
4) Ophthalmologist
5) Occupational therapist :-trying to make the child adapt.

Consanguinity is important in autosomal recessive
disorders(galactosemia,Glycogen storage disease,
mucopolysacridosis
We share eighth of the genes (1/8 of the genes),especially if 1
st
degree relative.
General exam of the child with CP (**we saw in the
ward**).
o are there any dysmorphic features?
o How is the body built?
o He looks ill or healthy?
o Dyspneic or NOT?
o Cyanosed ?
o Dehydrated ?
o Posture ?
o Instruments ?
o Abnormal body movement?(flexed spastic all joints
are contracted for example).
Hands exam
Face exam
Legs exam

Malnutition
Kwashiorkor
1. This disease is caused by the deficiency of protein in the diet of child.
2. Kwashiorkor occurs in children in the age group 1-5 years.
3. The disease is more common in villages where there is small gap
period between successive pregnancies.
4. In this disease, swelling of body is observed due to retention of fluids.
5. Wasting of muscles is not evident.
6. Skin changes color and become broken and scaly.
Marasmus
1. This disease is caused by deficiency of protein as well as energy
nutrients (that is carbohydrates and fats) in the diet.
2. Marasmus occurs in children below the age of 1 year.
3. This disease is more common in towns and cities where breast-
feeding in discontinued quite early.
4. No swelling of body takes place in Marasmus.
5. In Marasmus, wasting of muscles is quite evident. The child is reduced
to skin and bones.
6. Skin does not change color and does not break.

Kwashiorkor
Oedema
Psychomotor changes
Growth retardation
Muscle wasting
Usually present signs :
Moon face
Hair changes
Skin depigmentation
Anaemia
Occasionally present signs :
Hepatomegaly
Flaky paint dermatitis
Cardiomyopathy & failure
Dehydration (diarrh. & vomiting)
Signs of vitamin deficiencies

signs of infections
Clinical features of marasmus
Severe wasting of muscle & s/c fats
Severe growth retardation
Child looks older than his age
No edema or hair changes
Alert but miserable
Hungry
Diarrhoea & dehydration
Investigations
are usually guided by history and examination. Routine
tests may include:
FBC.
Urinalysis.
Urine culture.
U&E and creatinine.
LFTs, including total protein and albumin.

Coeliac screen.
Prealbumin which may be used as a nutritional marker.
The following tests are not usually routine but may be indicated by
history and examination:
Testing for HIV infection.
Sweat chloride test.
TFTs.
Stool studies for parasites or malabsorption.
Immunoglobulins.
Purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test (for tuberculosis).
Radiological studies (bone age may be helpful to distinguish genetic
short stature from constitutional delay of growth).
Special tests may be used for coeliac disease or to detect growth
hormone deficiency
Teartment :
Normal formula contain 100 ml = 67 Kcl
In malnuritition this formula changed to F100 = 100 Kcl ( high calories )
Start at F75 milk to avoid vomiting and diarrheoa
We can commence from 50% of the expected feeding at that age of child
Until reach 150 % of the expected

Developmental assessment :
Development occurs in four areas namely:
-Gross motor.
-Fine motor.
-Language
. -Social.
Gross Motor:
A newborn has head lag on pulling to sitting position. In ventral
suspension, the head and the limbs are flexed.
By 3 months, the head lag is minimal when pulled to sitting position. The
baby can raise the chin in prone position. On ventral suspension, the
head are in line with the body.
By 4 months, the baby has head control when held up. In prone position,
the baby can raise the head and shoulder.
By 5 months, the baby bears weight on the forearm in prone position
and can bear weight on standing, also rolling over can be seen at this
age.
By 6 months, the baby bears weight on hands in prone position.
By 7 months, the baby can sit with support and lean forward and also
bounce on standing.
By 8 months, the baby crawls on the abdomen, and can sits without
support.
By 10 months, most of the babies pull to standing posture and walk
holding on to a piece of furniture. This is called “cruising”, they can
crawl.
يمسك االثاث اثناء المشي
By 1 year, the baby can make a few steps with support.

By 15 months, the baby can walks alone.
By 18 months, the baby can runs.
By 24 months, the baby can climb stairs two feet per step and the baby
can also kick a ball.
By 3 years, the baby can climb stairs 1 foot per step and can ride a
tricycle.
By 4 years the baby can climb down stairs one foot per step.
By 5 years, the child can skip.
Fine Motor:
The newborn can focus on objects.
By 1 month, the baby can follow objects for up to 90º and for 180
degrees
by 2 months.
5 By 4 months the baby can hold objects with both hands and take them
to the mouth.
By 5 months, the baby can take the feet to the mouth.
By 7 months, the baby can transfer objects from hand to hand and
having a palmar grasp.
By 9 months, the baby can hit two cubes together, can drink by a cup
By 10 months, the baby has a “pincer grasp” by approximating the
thumb and the index finger and can uncover hidden things.
By 1 year, the baby can release objects on request and can make a tower
of two cubes.
By 13 months, the baby can turn pages of a book, two to three pages at
a time.

By 15 months, the baby can feed self with a spoon without much
spilling.
By 18 months the baby can build a tower of 3 cubes.
By 2 years, the baby can turn page by page, and can build a tower of 6
cubes also he can scribble lines ( horizantal line ) .
The baby can draw a circle by 3 years, a square by 4 years and a triangle
by 6 years.
Baby can dress and undress alone by 4 years.
-suquare , traingle , cycle drawing is called coping if more than 6 mo.
If less than 6 mo. Is called Emitate
-seizuring
حركة المقص
حركة مسك او عد الخرز
beating
- Language Development:
Baby makes cooing sounds by 3 months.
By 4 months, the baby can babble.
By 7 months the baby responds to his/her name. By 7-8 months, baby
vocalizes monosyllables.
By 10 months combines monosyllables, and understands spoken
speech.
By 1 year, the baby speaks 2-3 words with meaning. By 18 months, one
can speak 20 words.
By 2 years baby can speaks about 200 words and can make a 2 words
sentence.
Personal Social Development:

The baby regards faces by 1 month, has social smile by 6 weeks and
recognizes the mother and caretakers by 3 months, can laugh loudly by 4
months.
The baby enjoys looking at the mirror by 6 months and imitates other by
1 year.
By 6 months, the baby shows sadness when mother leaves and has
stranger anxiety by 8 months.
By 9 months, the baby can drink from a cup and by 15 months the baby
can self feed with a cup and a spoon with little spilling.
By 10 months baby can wave bye bye.
The baby starts toilet training by around 2 years, being dry during day by
around 3 years.
Bowel control is before urine control, and girls can control before boys.
By 2 years of age, baby refers to self as “ I “ By 3 years, the baby also has
gender identity.
#hearing :
At birth startle
Ask mother about hearing problem ?
Distraction test at 6 mo.
Hearing test at birth till 3mor 6 mo
9 mo. Listen to his / her name
PTA ( pure tone audiometry )
ABR ( auditory brain stem response )
Autoacustic machine
