Deep Vein Thrombosis
Low risk: young, with minor illnesses, who are to undergo operations lasting 30 min or less.Moderate risk: over 40 or with a debilitating illness who are to undergo major surgery.
High risk: over 40 who have serious medical conditions, or undergoing major surgery with an additional risk factor.Prophylaxis:
Risk factors:
Patients factors:• Age
• Obesity
• Varicose veins
• Immobility
• Pregnancy
• Puerperium
• Oral contraceptive pills
• Previous deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism
• Trauma or surgery,
• Malignancy,
• Heart failure
• Recent myocardial infarction
• Paralysis of lower limb(s)
• Infection
• Inflammatory bowel disease
• Nephrotic syndrome
• Polycythaemia
• Paraproteinaemia
Mechanical methods:
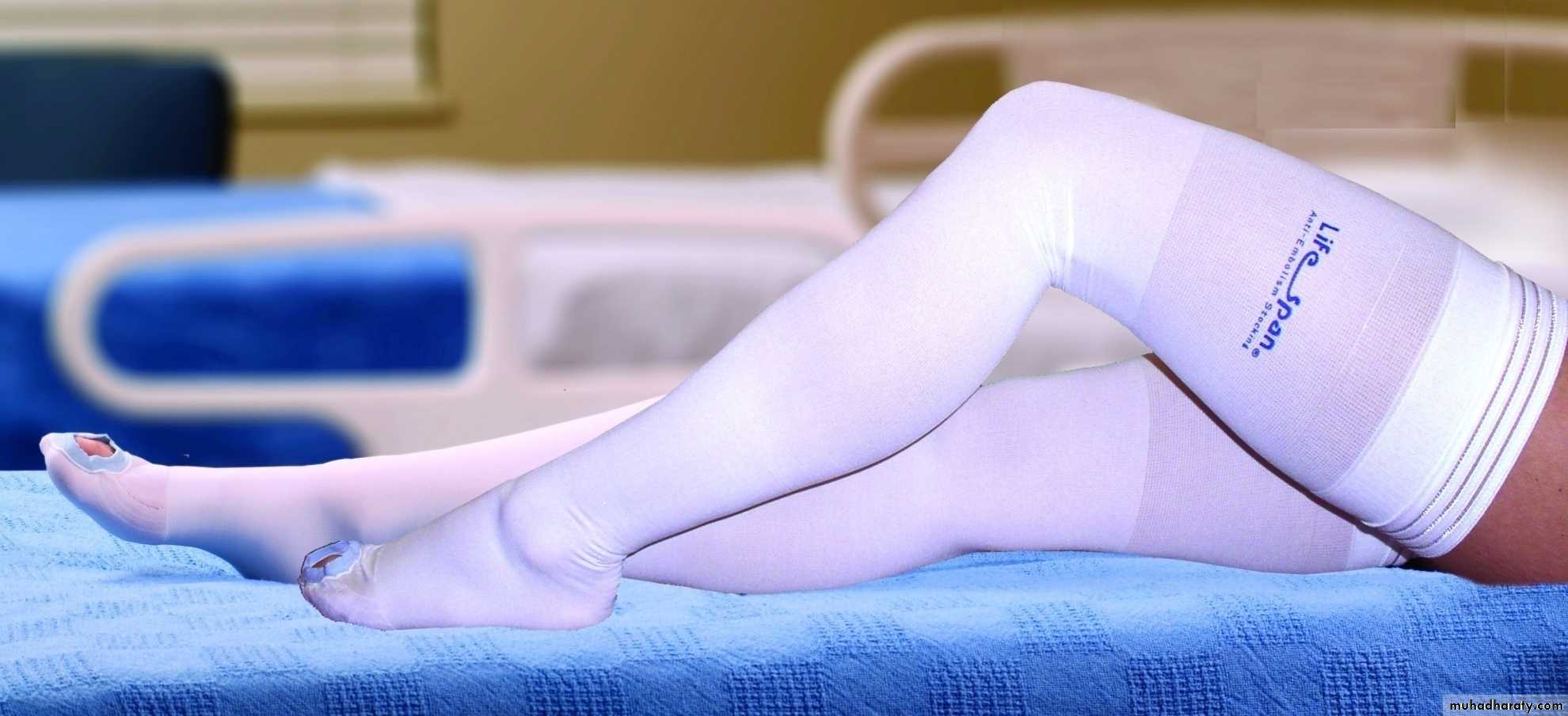
• graduated elastic compression stockings• external pneumatic compression
• passive foot movement (foot paddling machine)
• simple limb elevation
Pharmaceutical methods:
• low molecular weight heparin
• unfractionated heparin
• warfarin
Methods of prophylaxis:
Graduated elastic compressive stocking
External pneumatic compression
Foot Paddling Machine
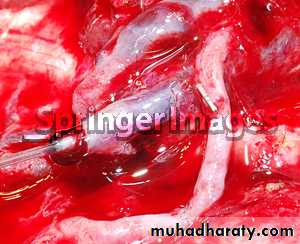
Venous thrombectomy:
Phlegmasia cerulea dolens with contraindication to thrombolyticsInferior vena cava filter:
Recurrent thromboembolism despite adequate anticoagulationProgressing thromboembolism despite adequate anticoagulation
Complication of anticoagulants
Contraindication to anticoagulants
Surgical treatment:
Venous thrombectomyIVC filter:
Lymphatic Disorders
Acute Lymphangitis:Infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes or Staphylococcus aureus that spreads to the draining lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes (lymphadenitis)
Treatment:
Rest and elevationi.v. antibiotics
Related to lymphoedema
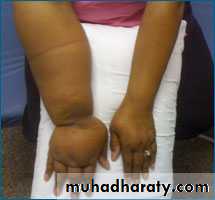
Lymphedema:
Edema due to high protein ISF secondary to defective lymphatic drainage in the presence of normal capillary filtrationPathophysiology:
Edema high capillary filtration normal but overwhelmed venous and lymphatic system protein low edemaLymphedema normal capillaries defective lymphatics protein rich edema
Sometimes high capillary filtration + defective lymphatics both types of edemaLymphedema is confined to the epifascial space
Classification:Primary lymphoedema, :
Congenital lymphoedema (Millroy's disease)
Lymphoedema praecox (Meige's disease)
Lymphoedema tarda
Secondary or acquired lymphoedema,
Infection (fungal, parasitic, bacterial ..etc.)
Exposure to foreign body material (silica particles)
Malignancy (primary or metastatic)
Trauma (surgery, radiotherapy, penetrating injury,…etc.)
Venous disorders (DVT, thrombophlebitis, …etc.)
Clinical presentation:
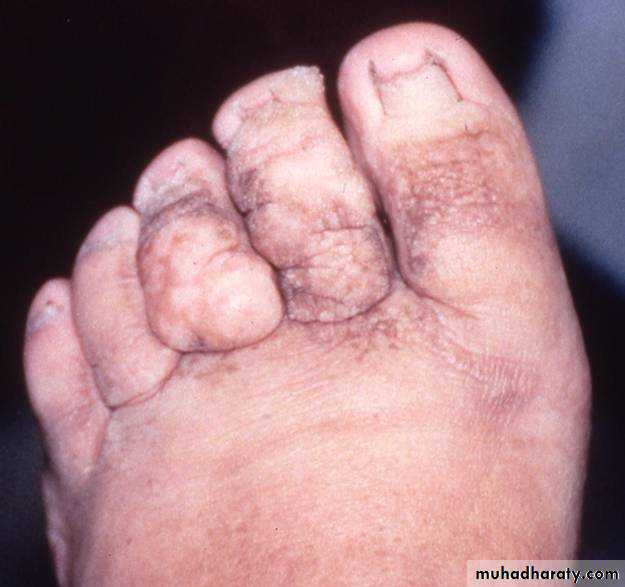
Lymphoedema characteristically involves the foot
May spread to knee, rarely to the thigh
Early it is pitting, later on it becomes non-pitting
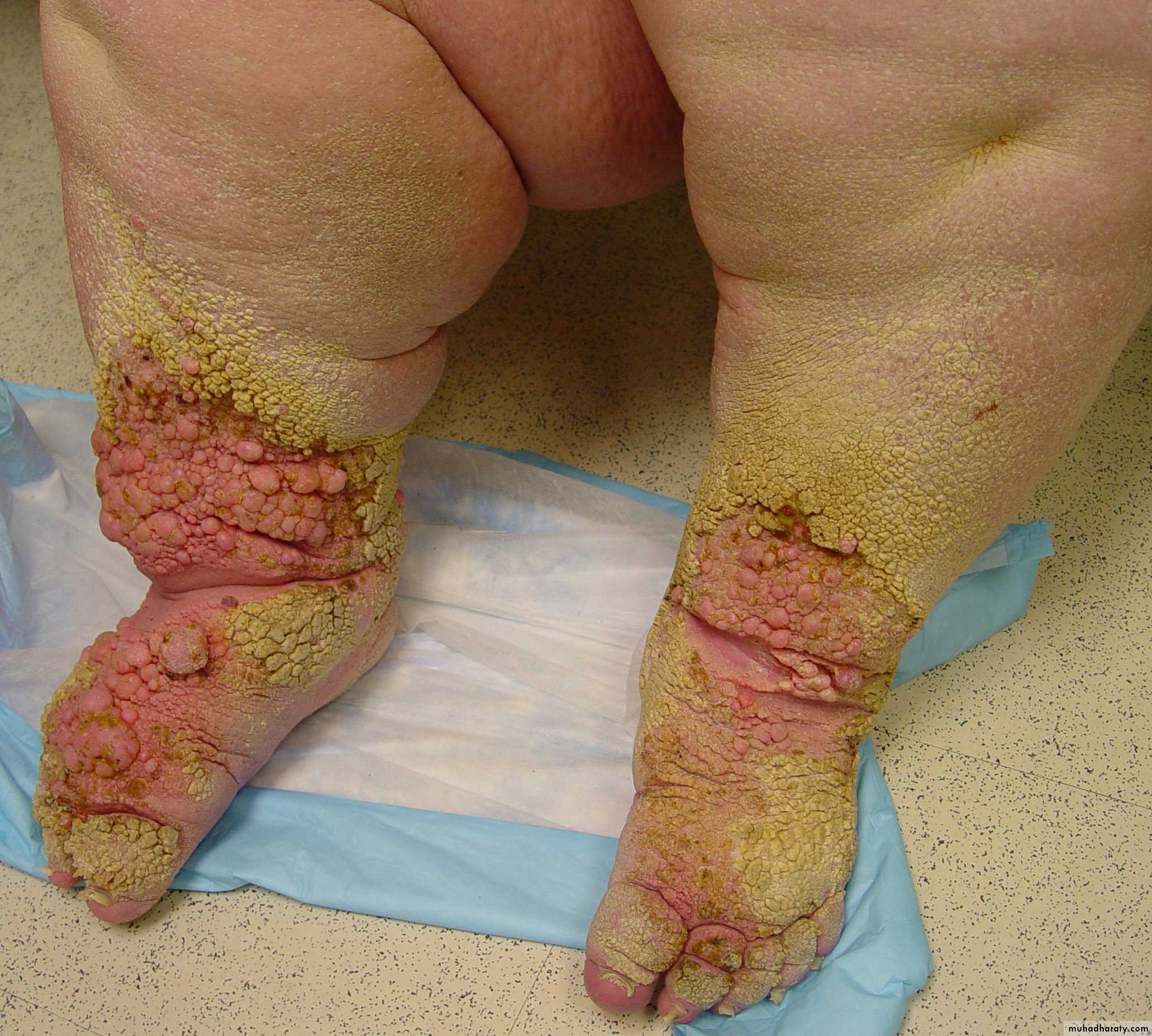
Skin problems (fungal, viral or bacterial infection)
Ulceration is unusual
Lymphangiomas
lymphangiosarcoma
Investigations:
• MRI• Lymphangiography
• Duplex ultrasound
Treatment:
• Pain relief• Skin care
• Control of swelling (decongestive lymphatic edema therapy)
• Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD)
• Multilayer lymphedema bandaging (MLLB)
• Exercise
• Drugs
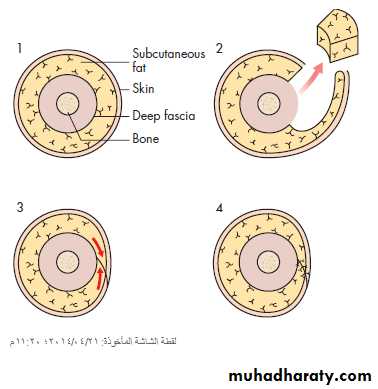
• Surgery (lymphatic bypass procedures or limb reduction procedures)
MLD