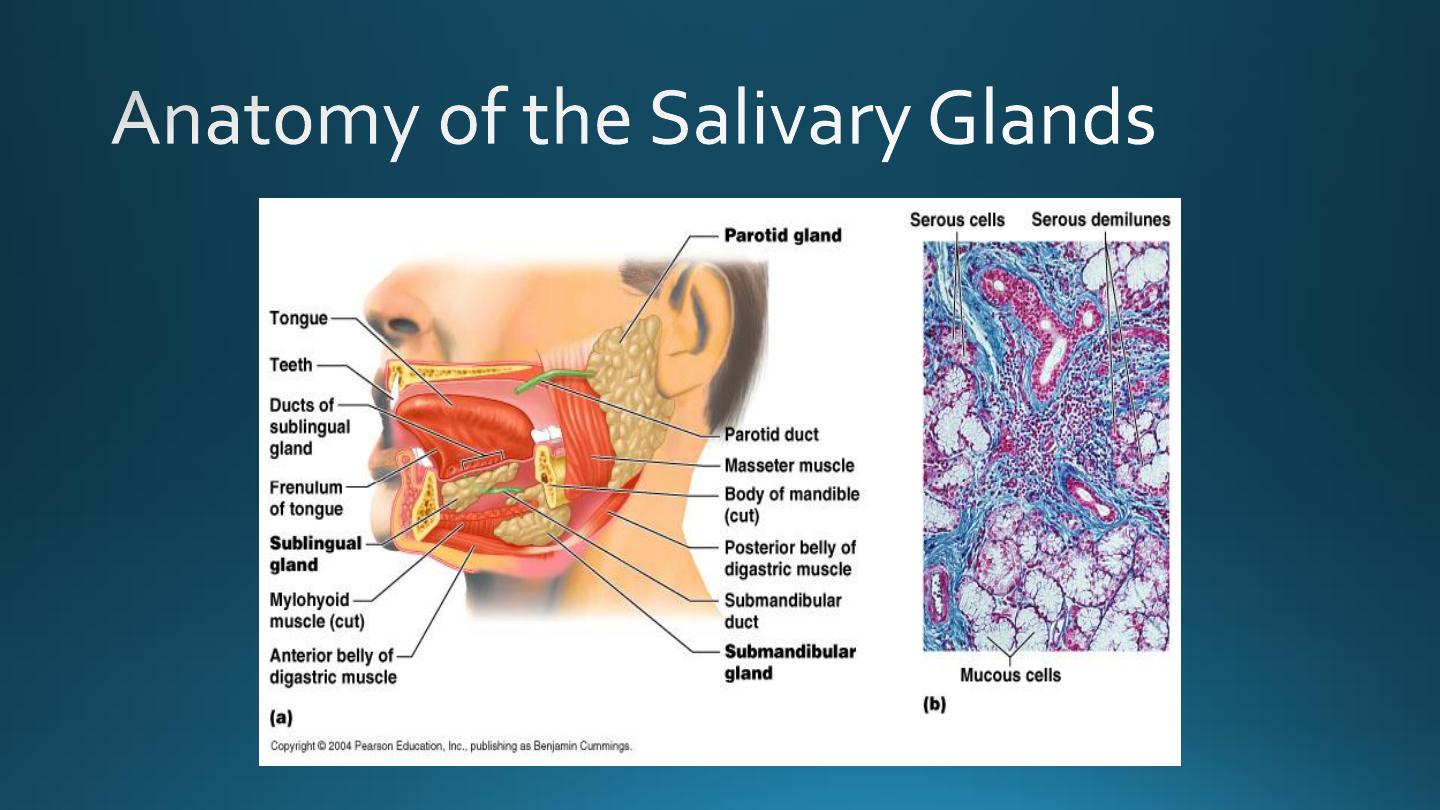

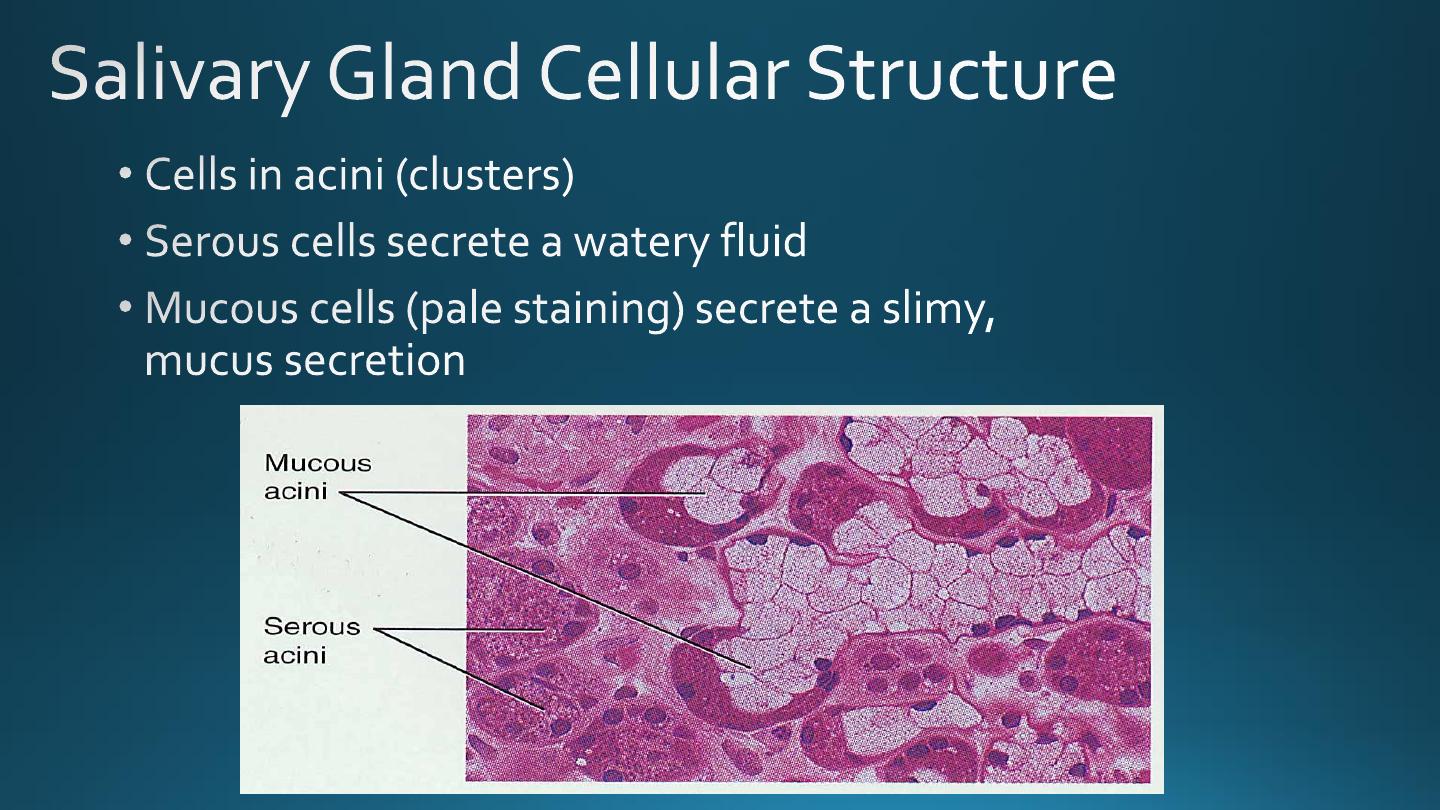
Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e
14
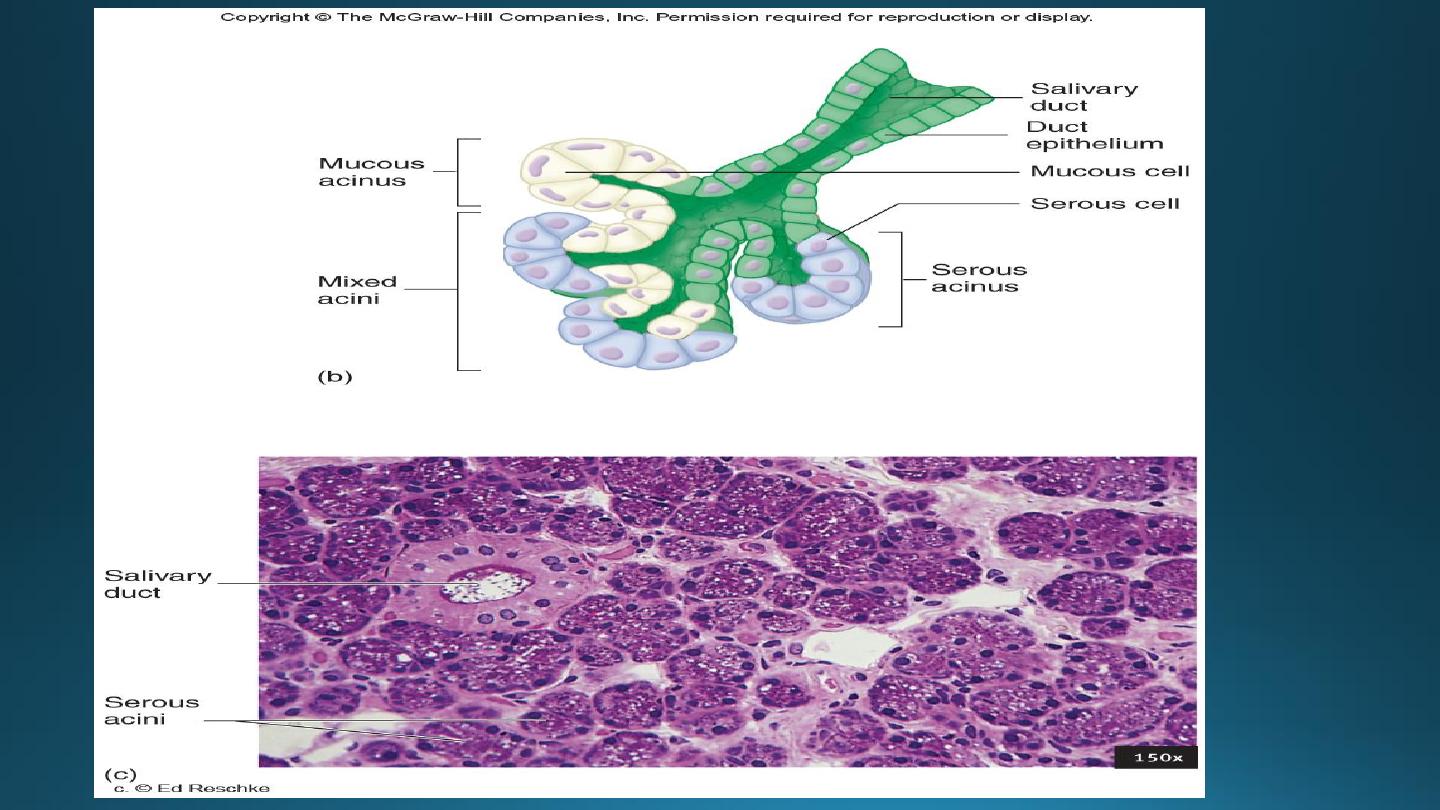

16
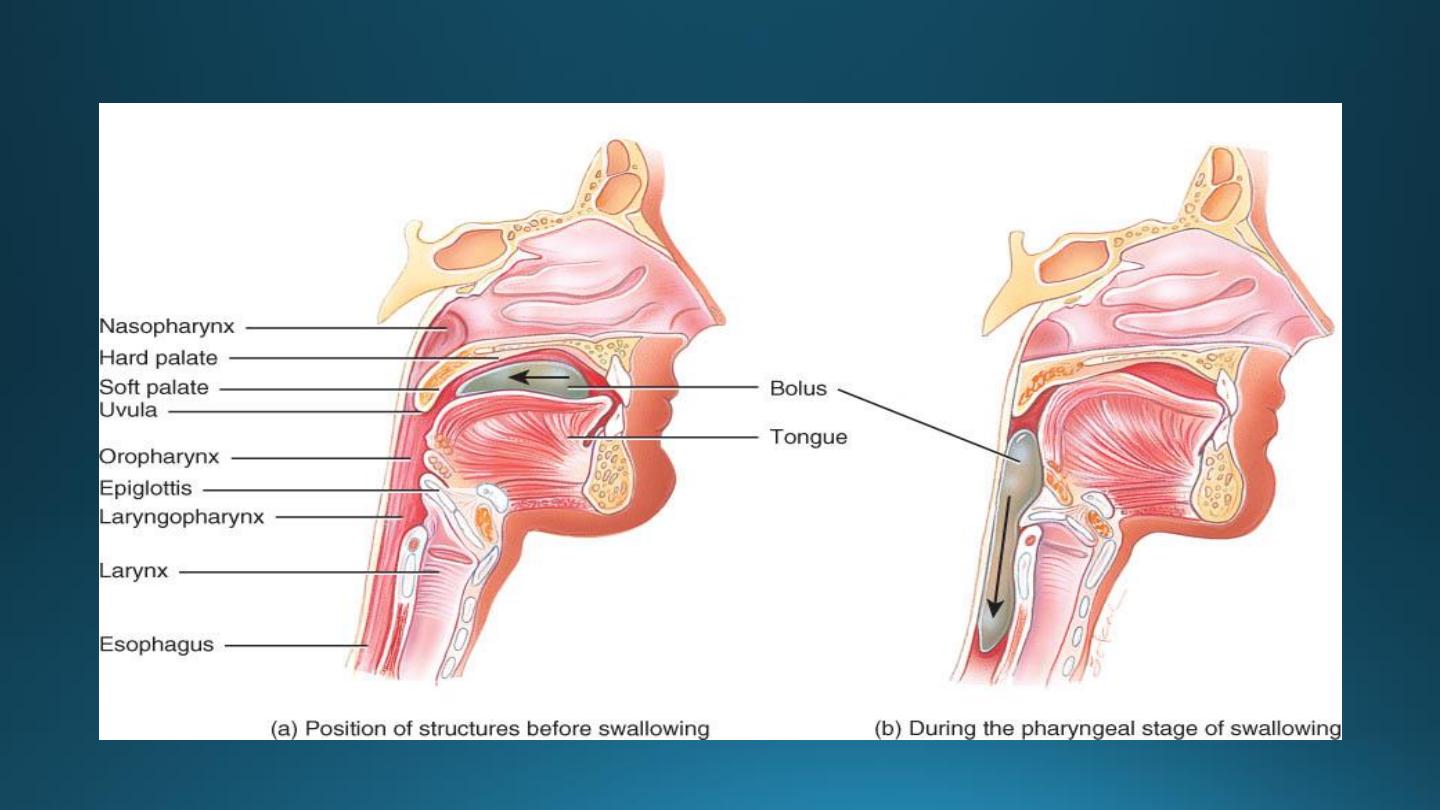

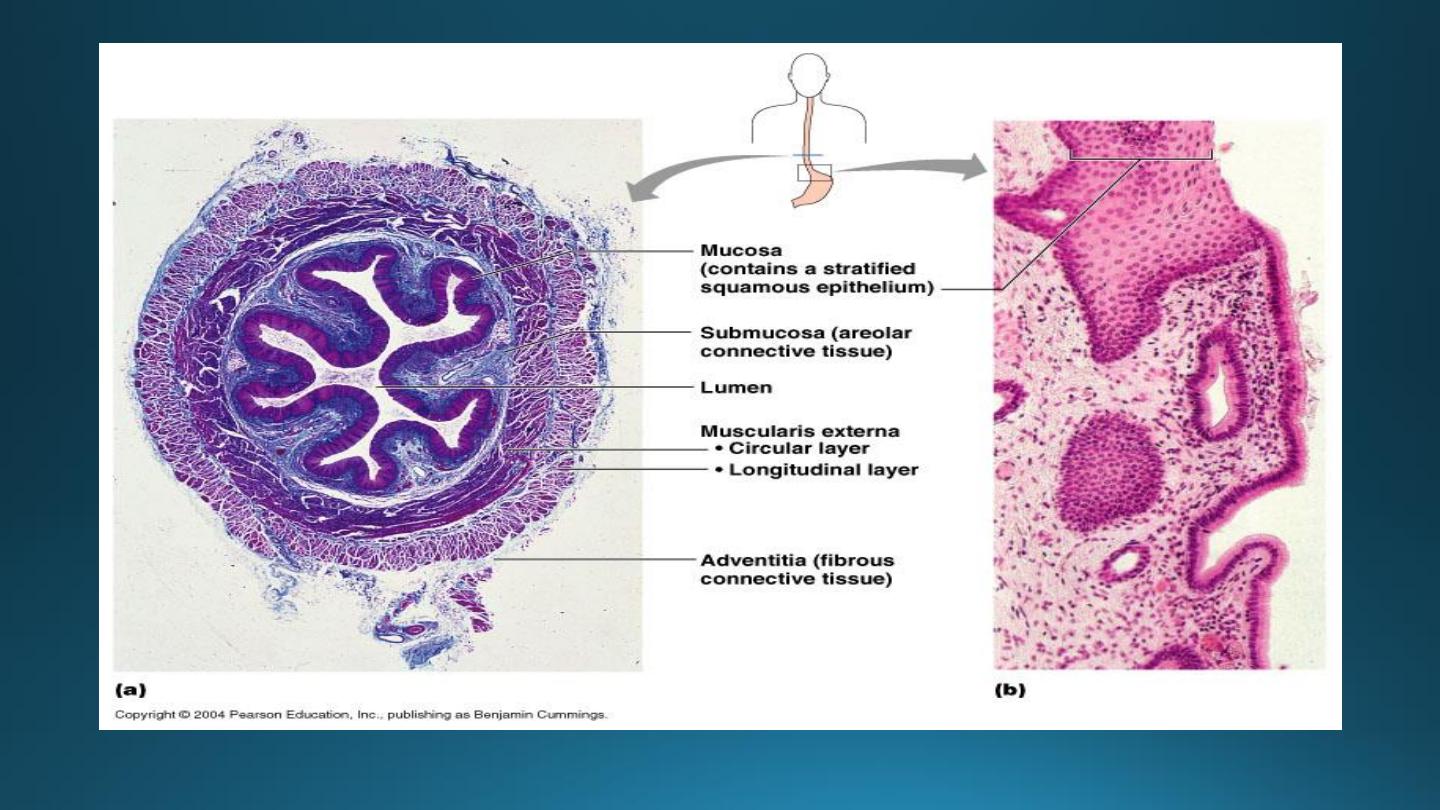
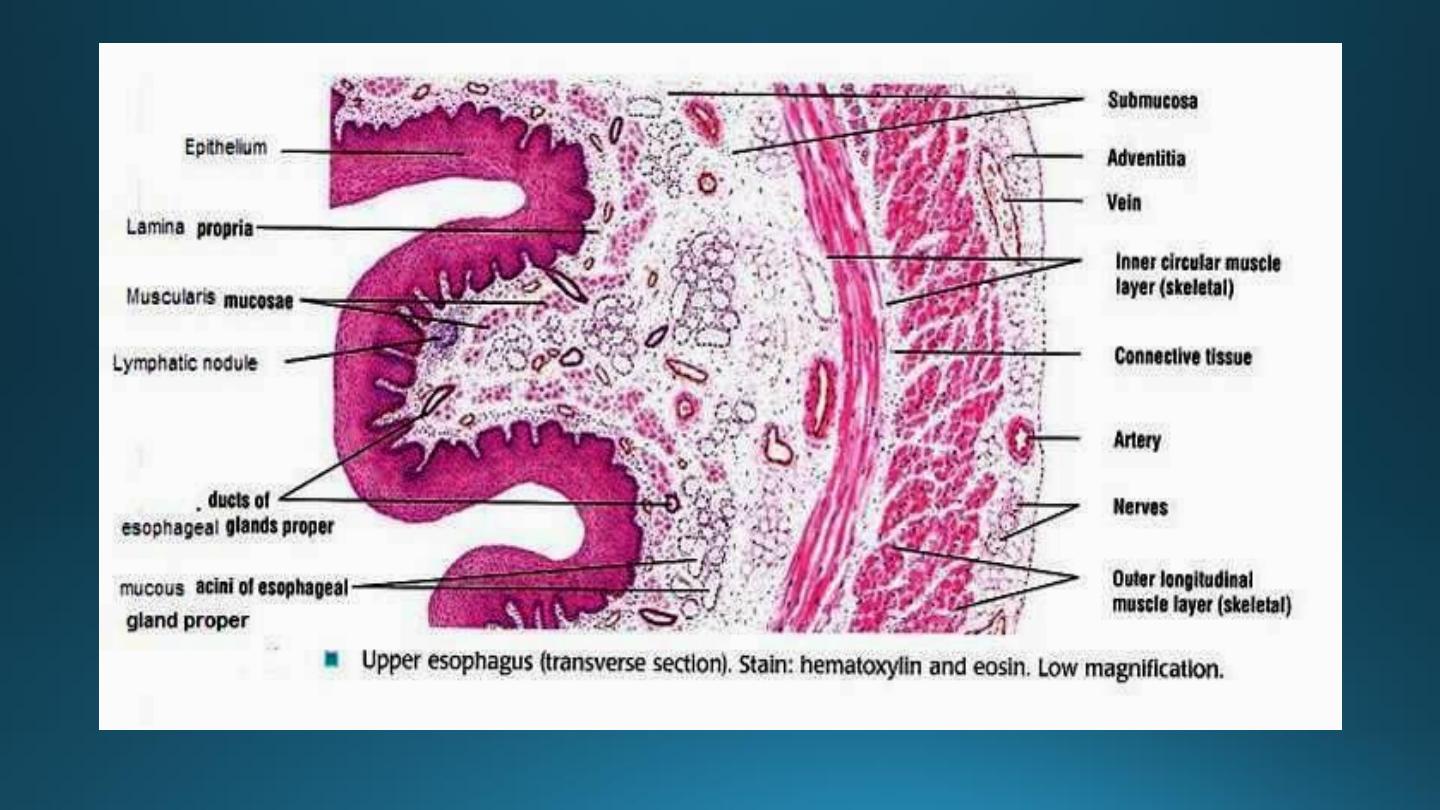
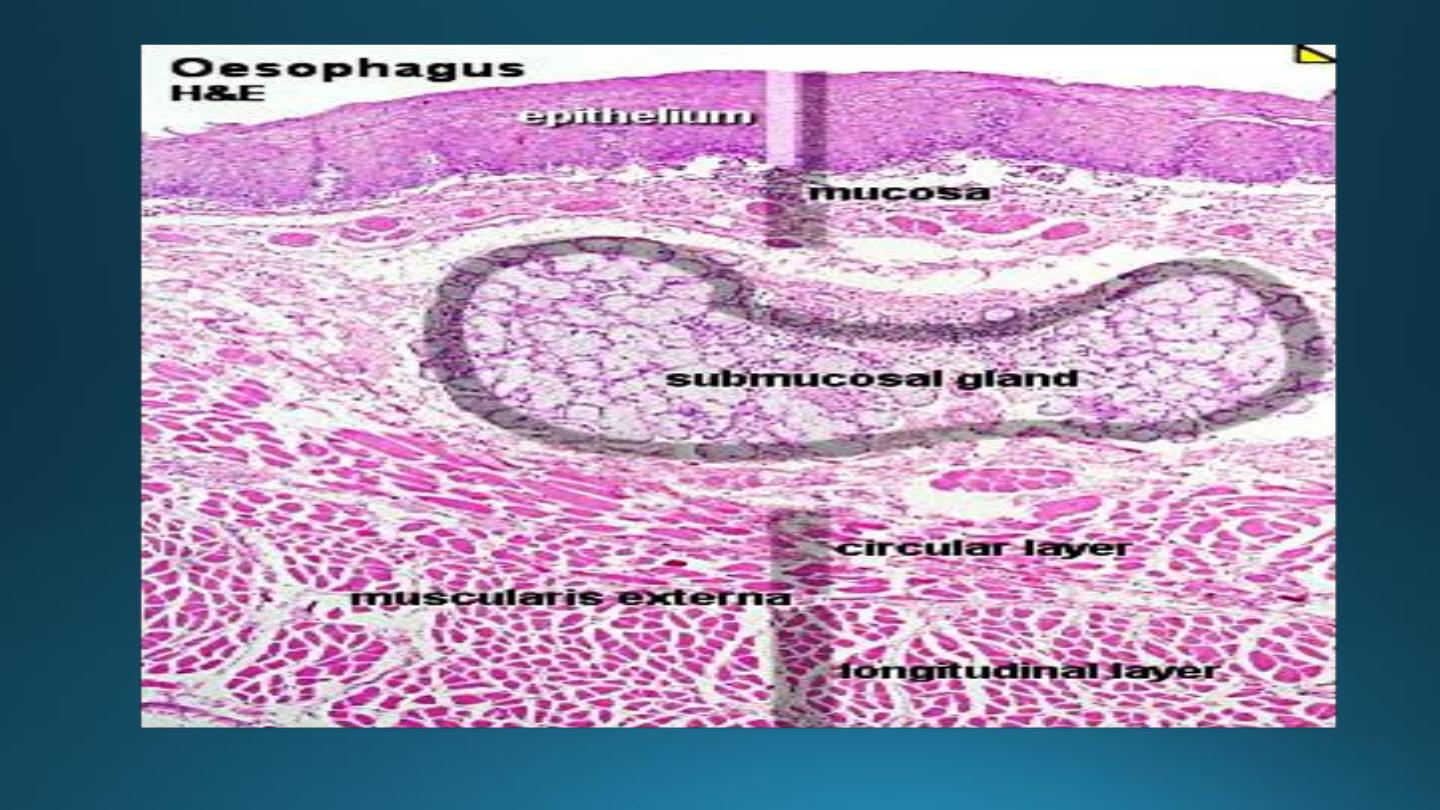
1. The mucosa:-

2. The submucosa:-

3. The muscularis externa:-
4. The adventitial-

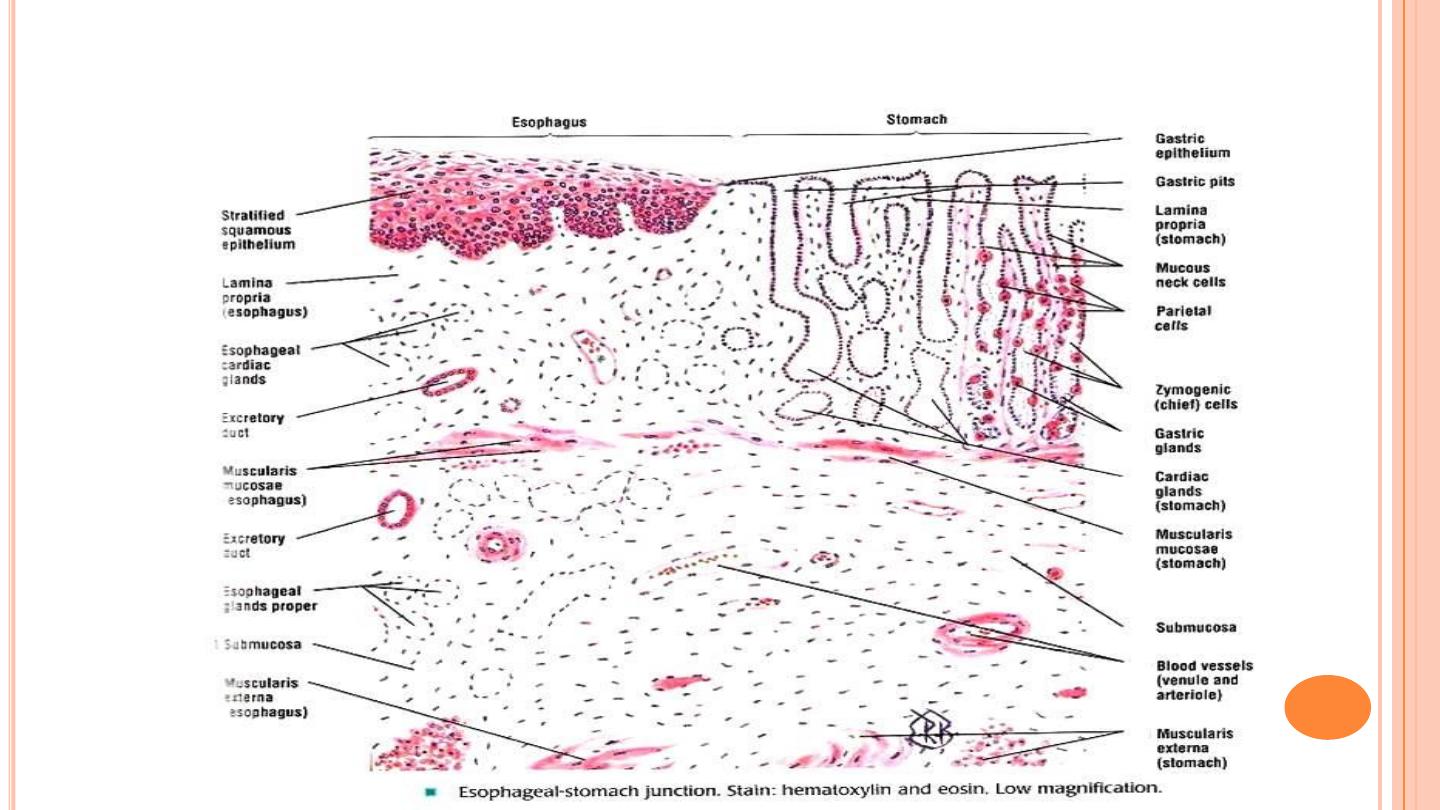
CARDIO-OESOPHAGEAL JUNCTION






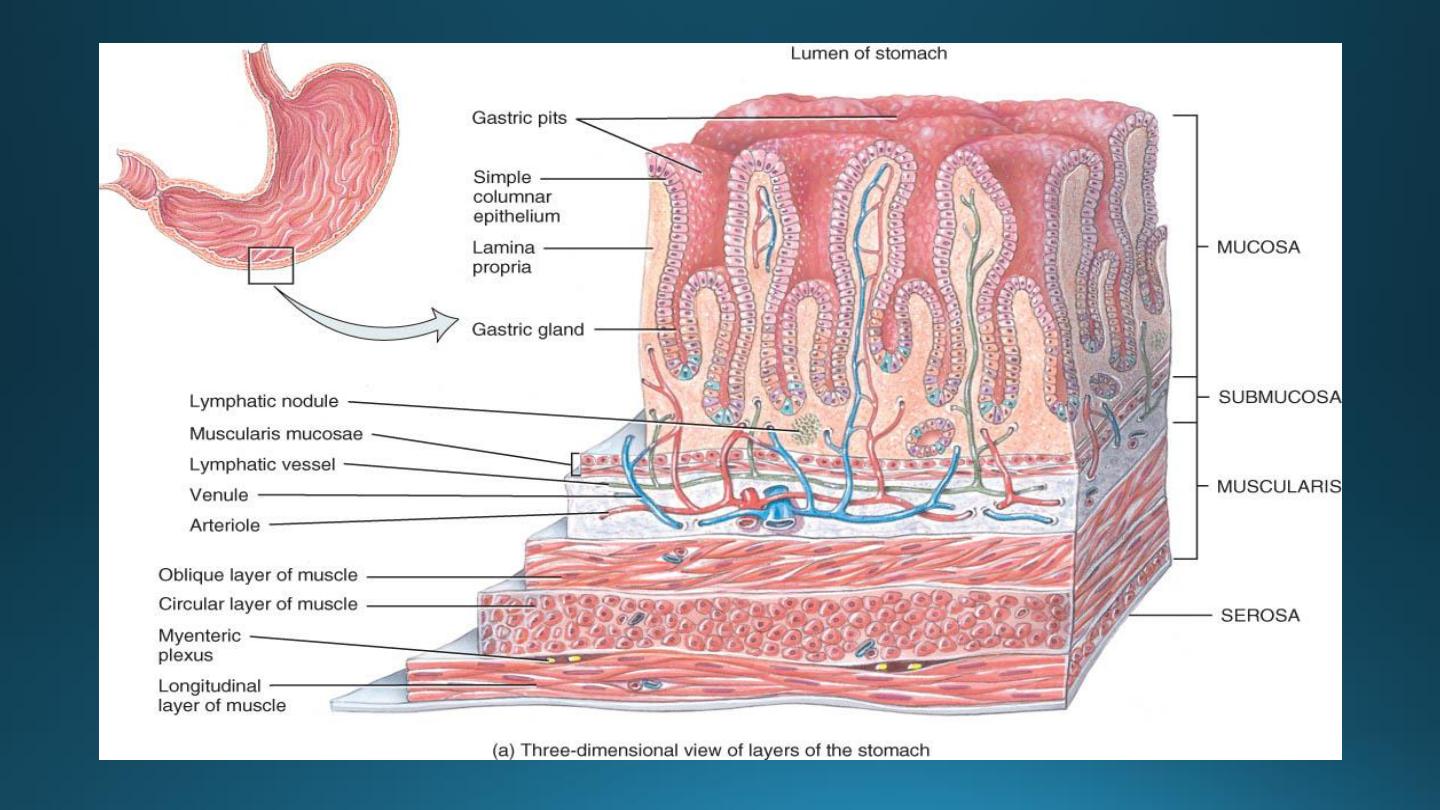
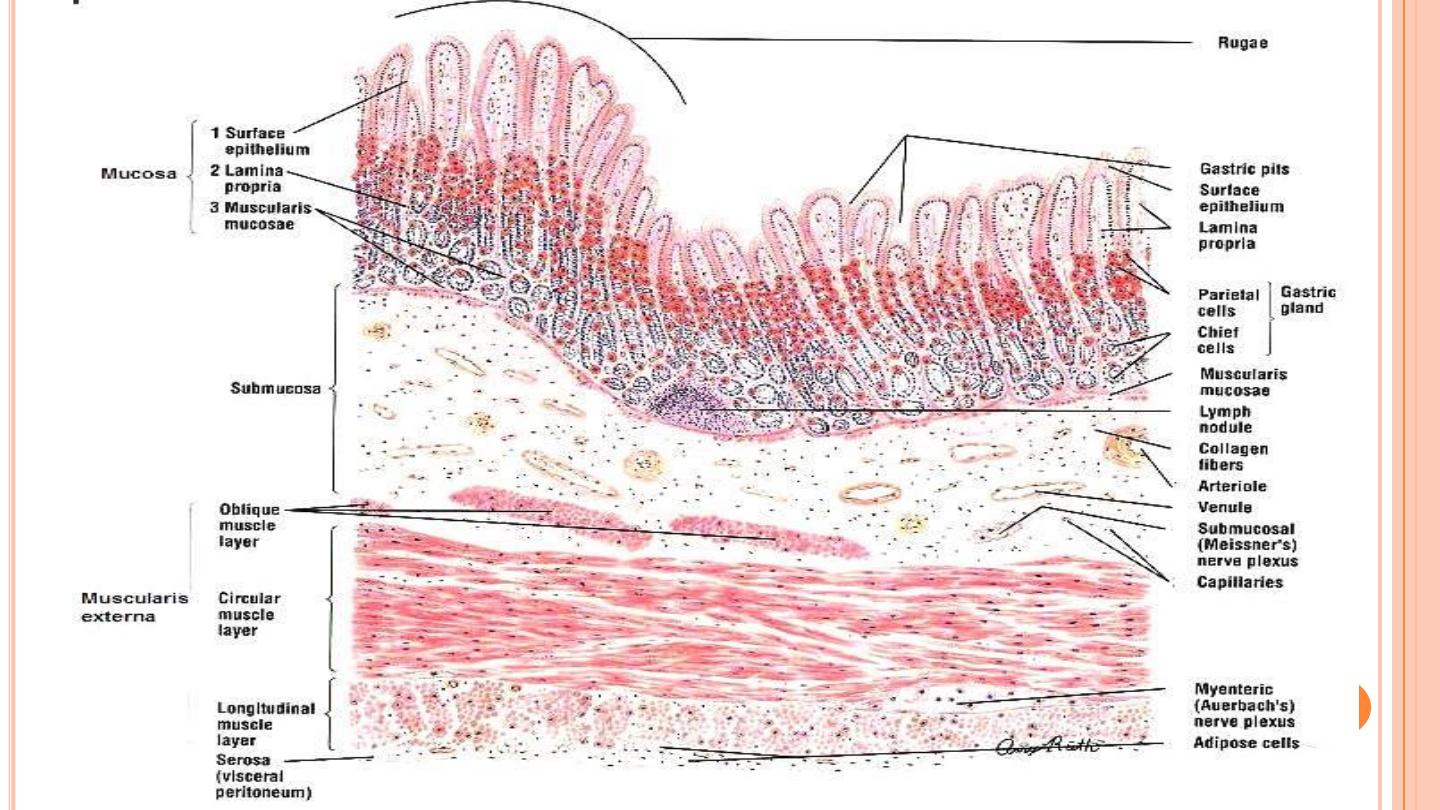

1. The mucosa:-
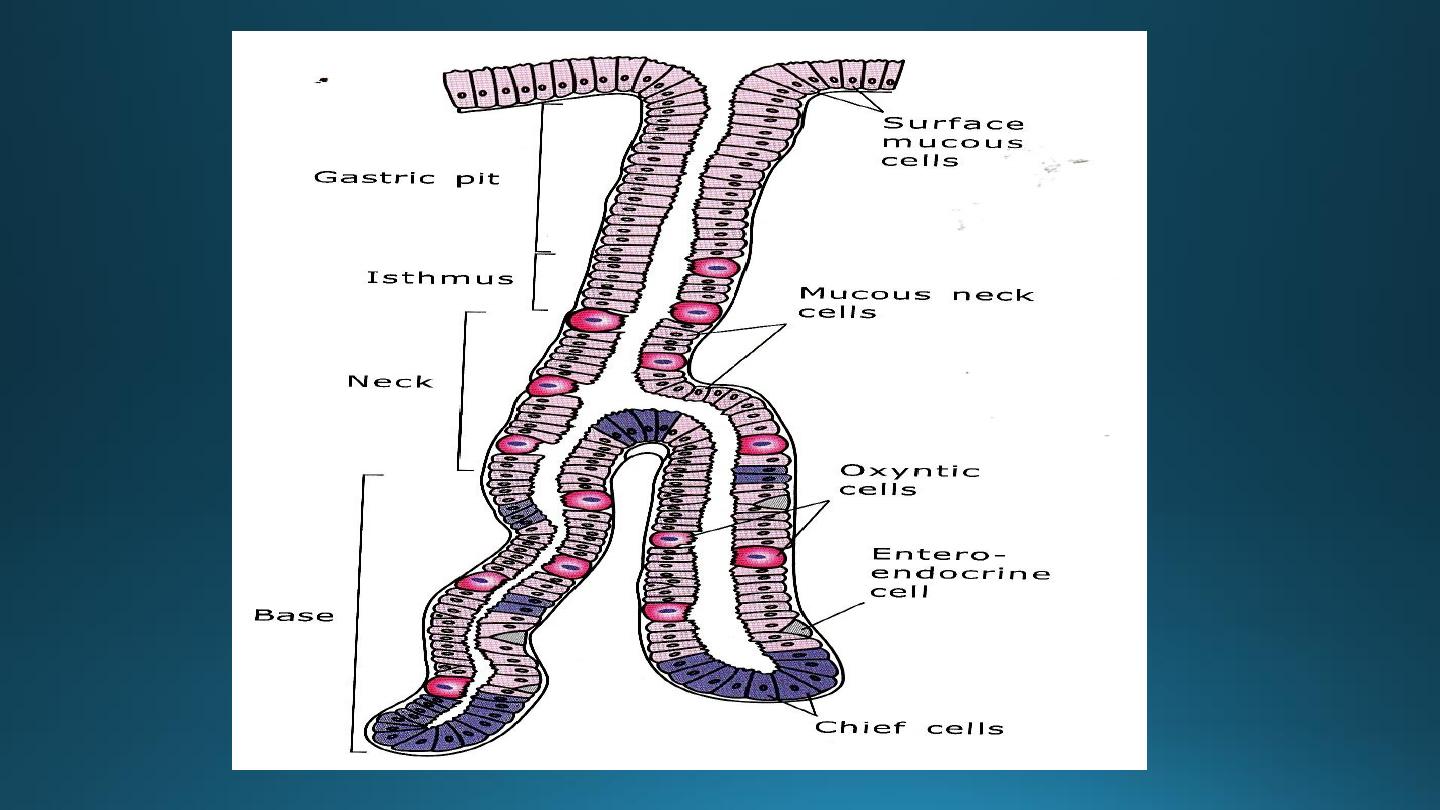
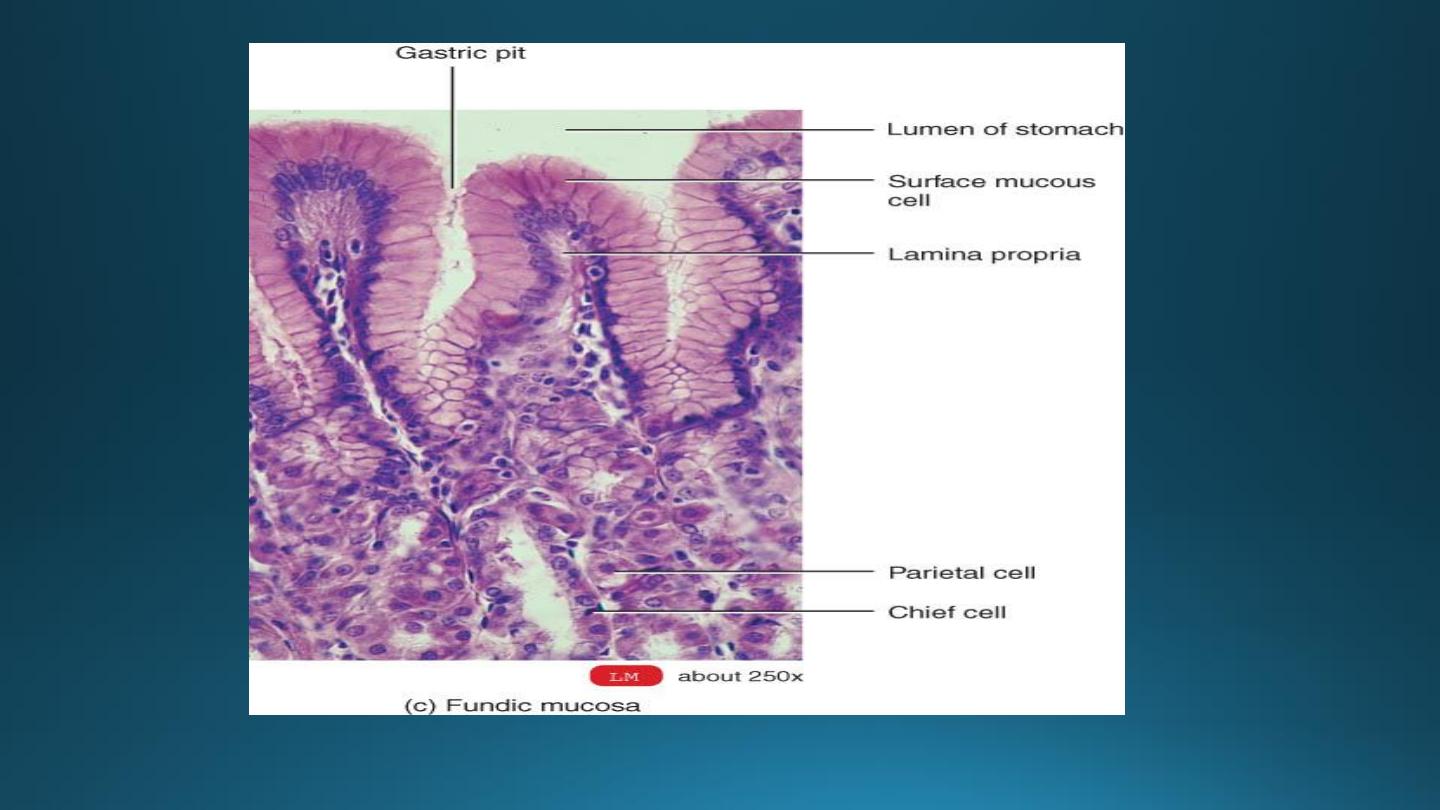
A) Surface epithelium

B) The lamina propria:-

1) The cardiac glands:-
2) Fundic glands (gastric gland proper):-

a) Mucous neck cells:-
b) Peptic (chief or zymogenic)cells:-


c) Parietal(oxyntic) cells:-
d) Enteroendocrine cells(argentaffin & enterochromaffin
cells):-

d) Stem cells (undifferentiated cells):-

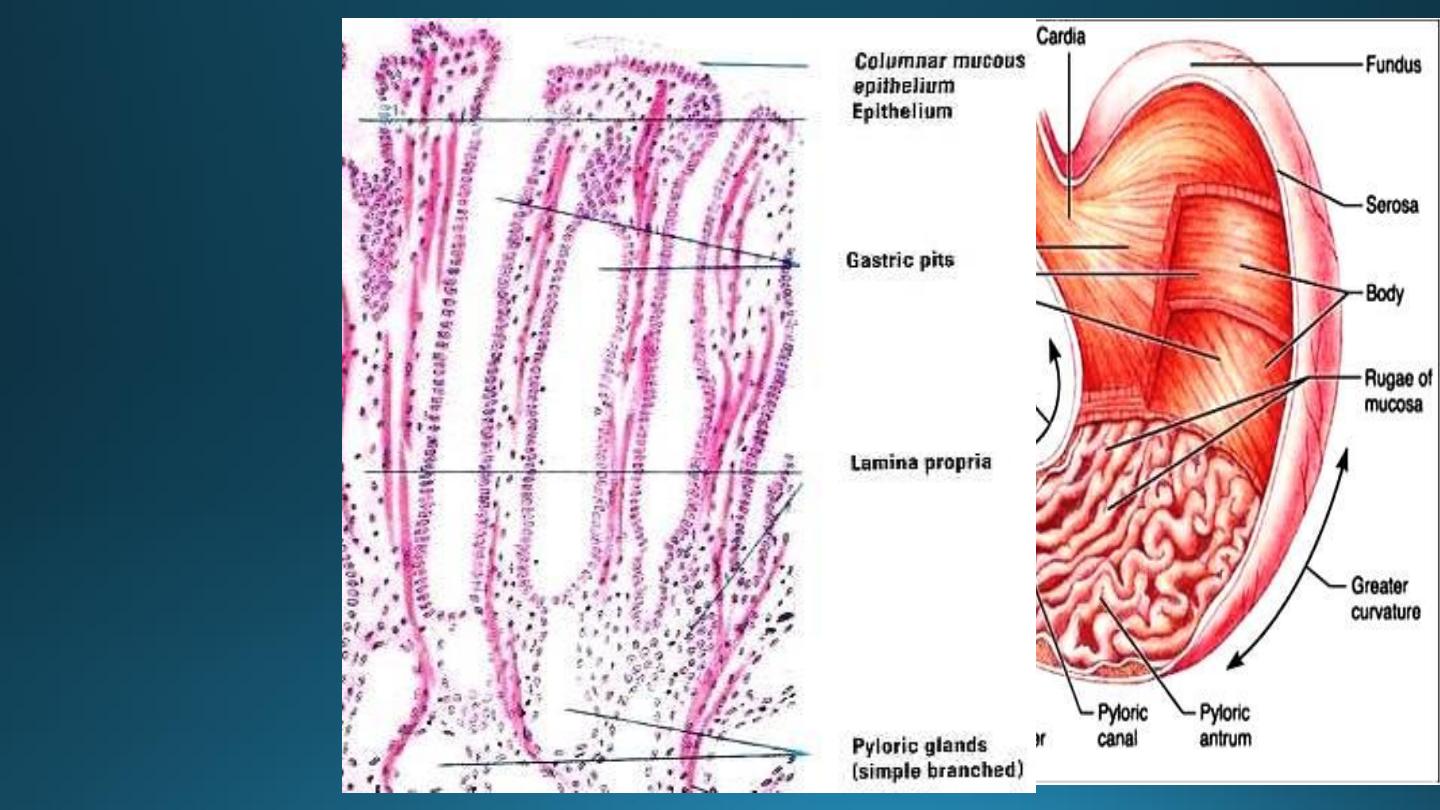
3) Pyloric glands:-
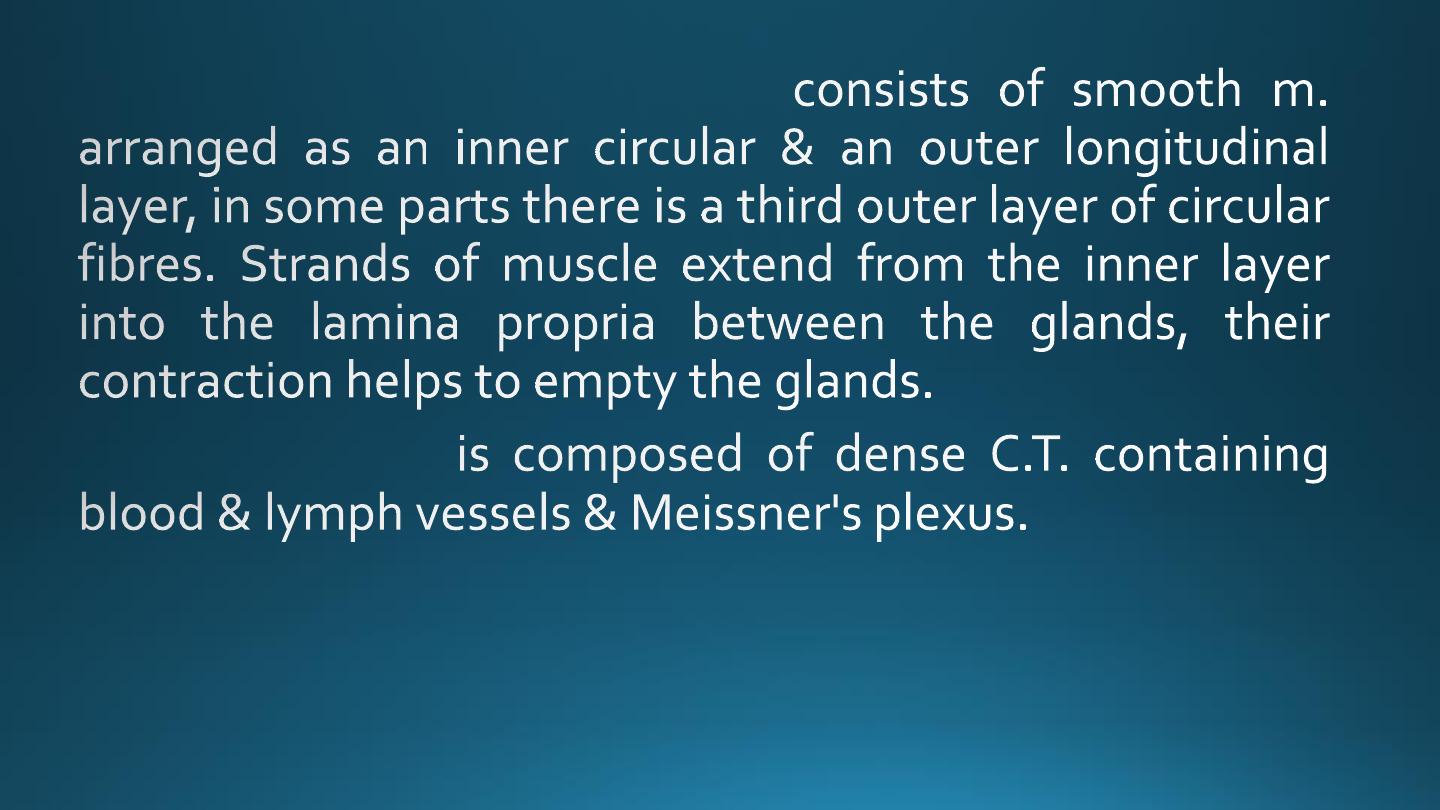
C) The muscularis mucosae:-
2. Submucosa:-

3. Muscularis externa:-
4. Serosa:-




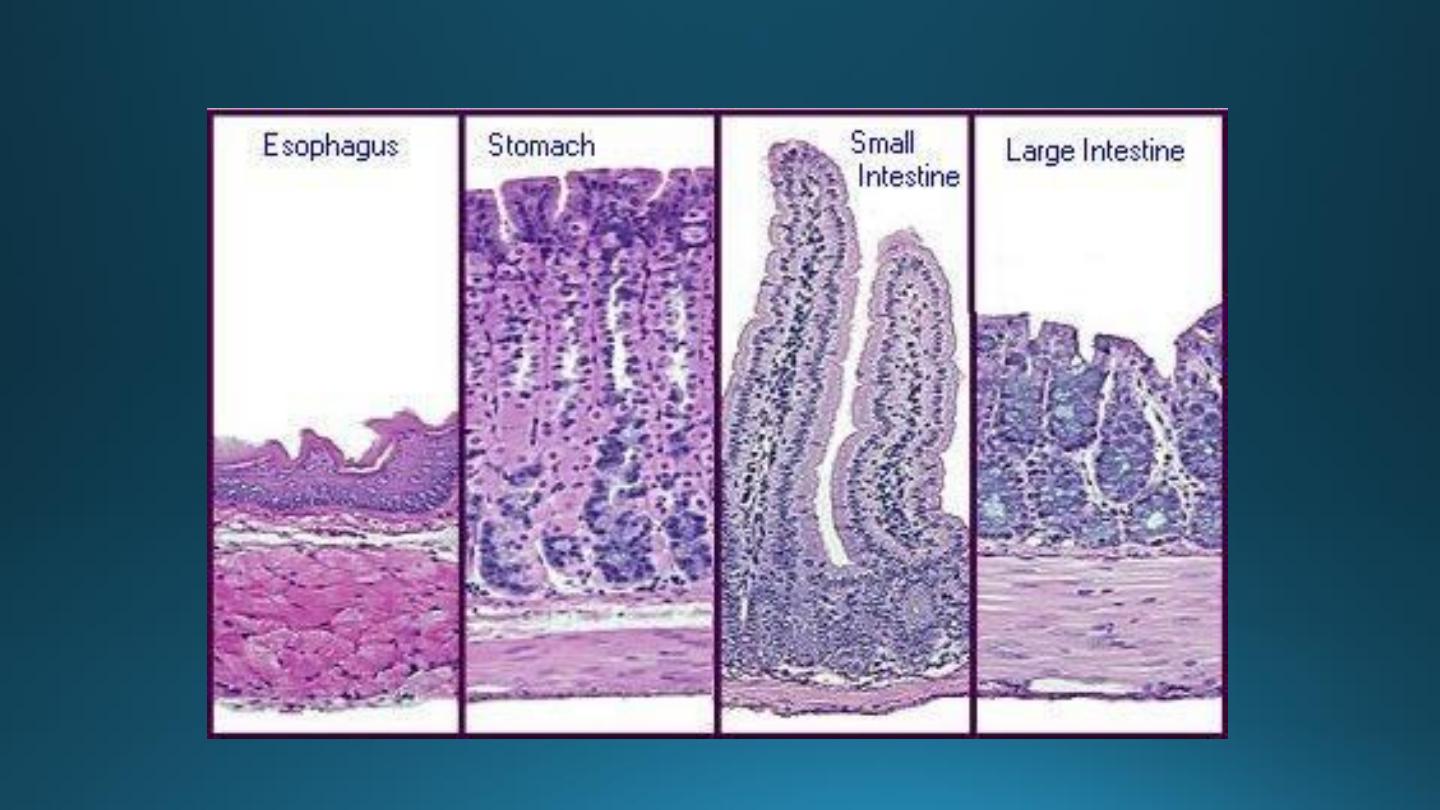
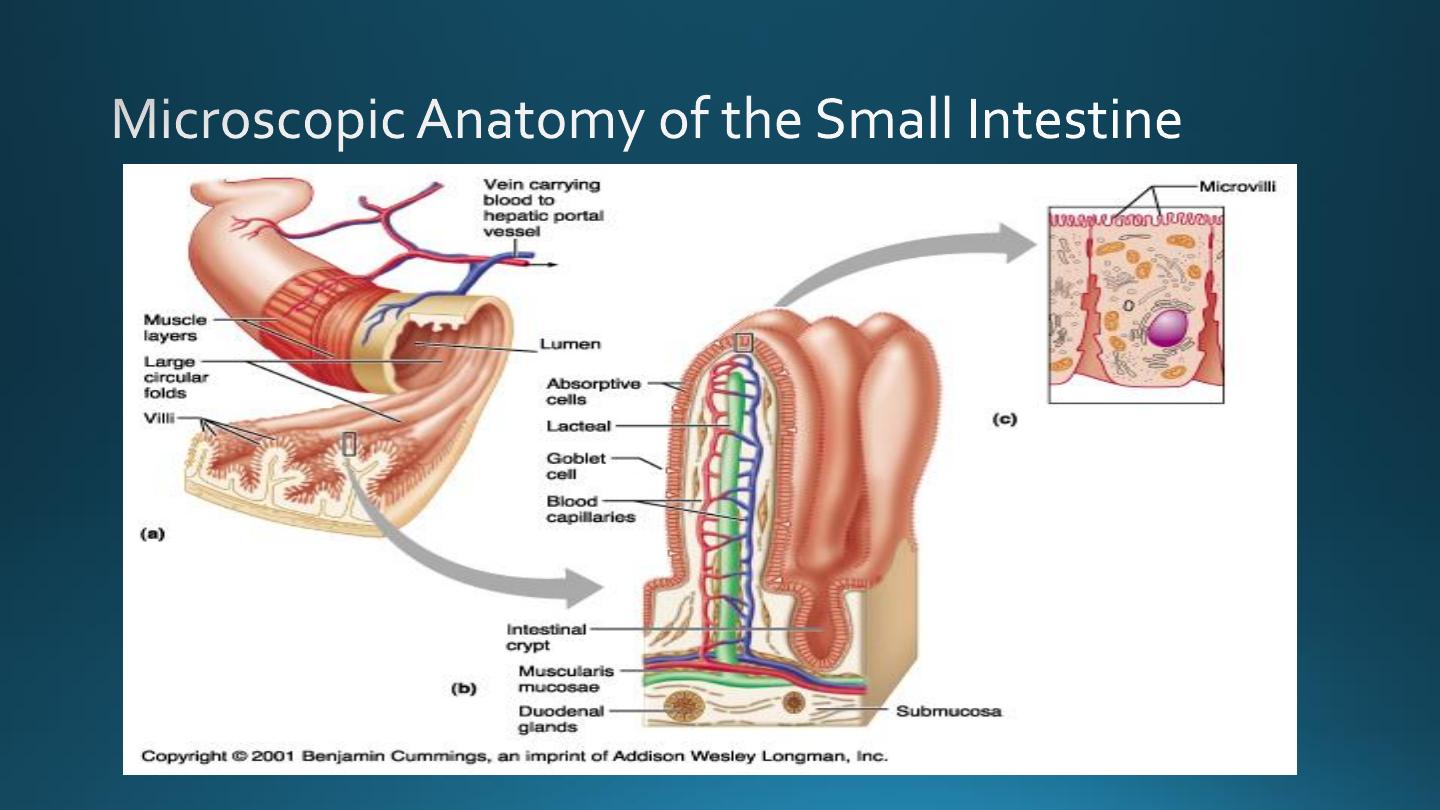
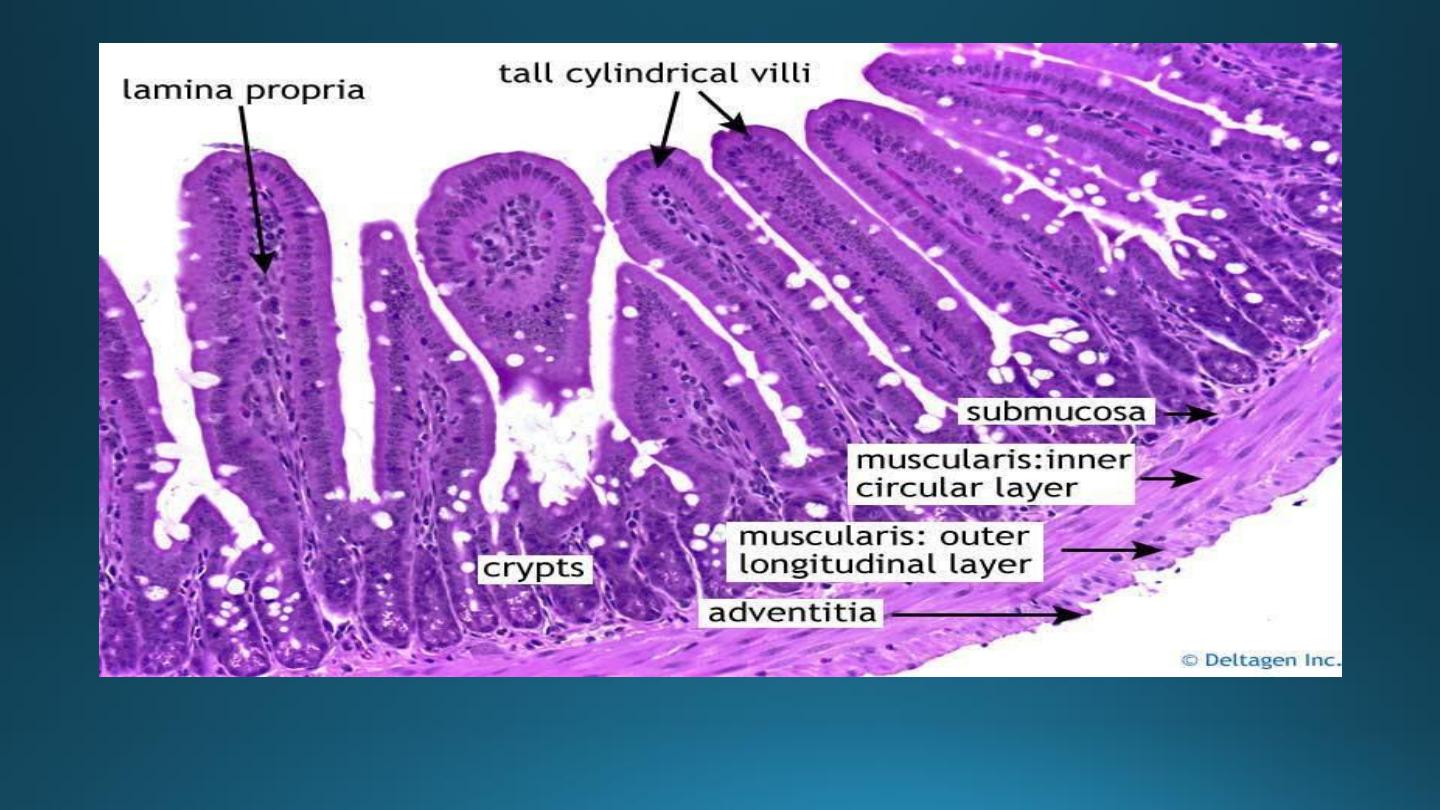
Microscopic Anatomy of Small Intestine
•
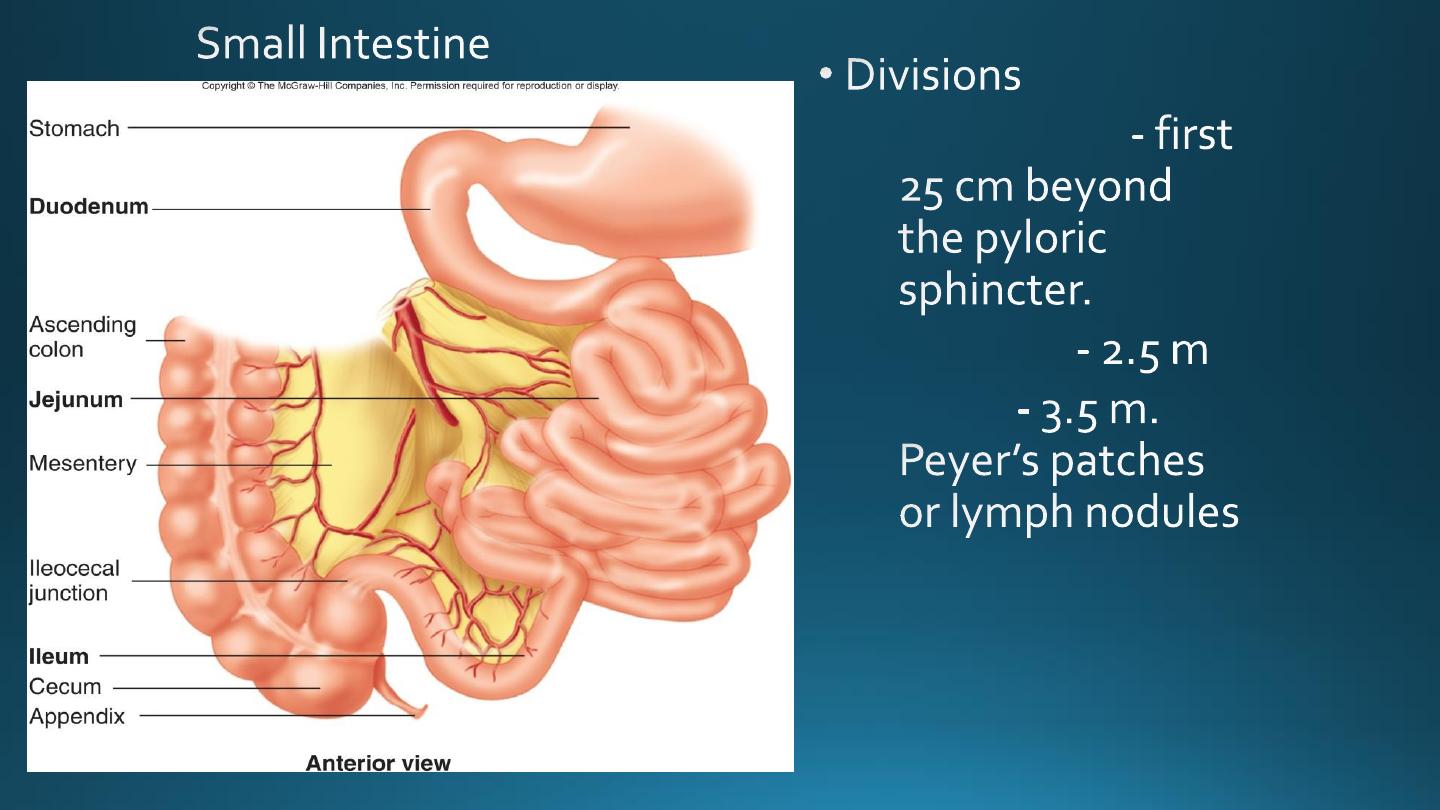
Duodenum
•
Jejunum
•
Ileum
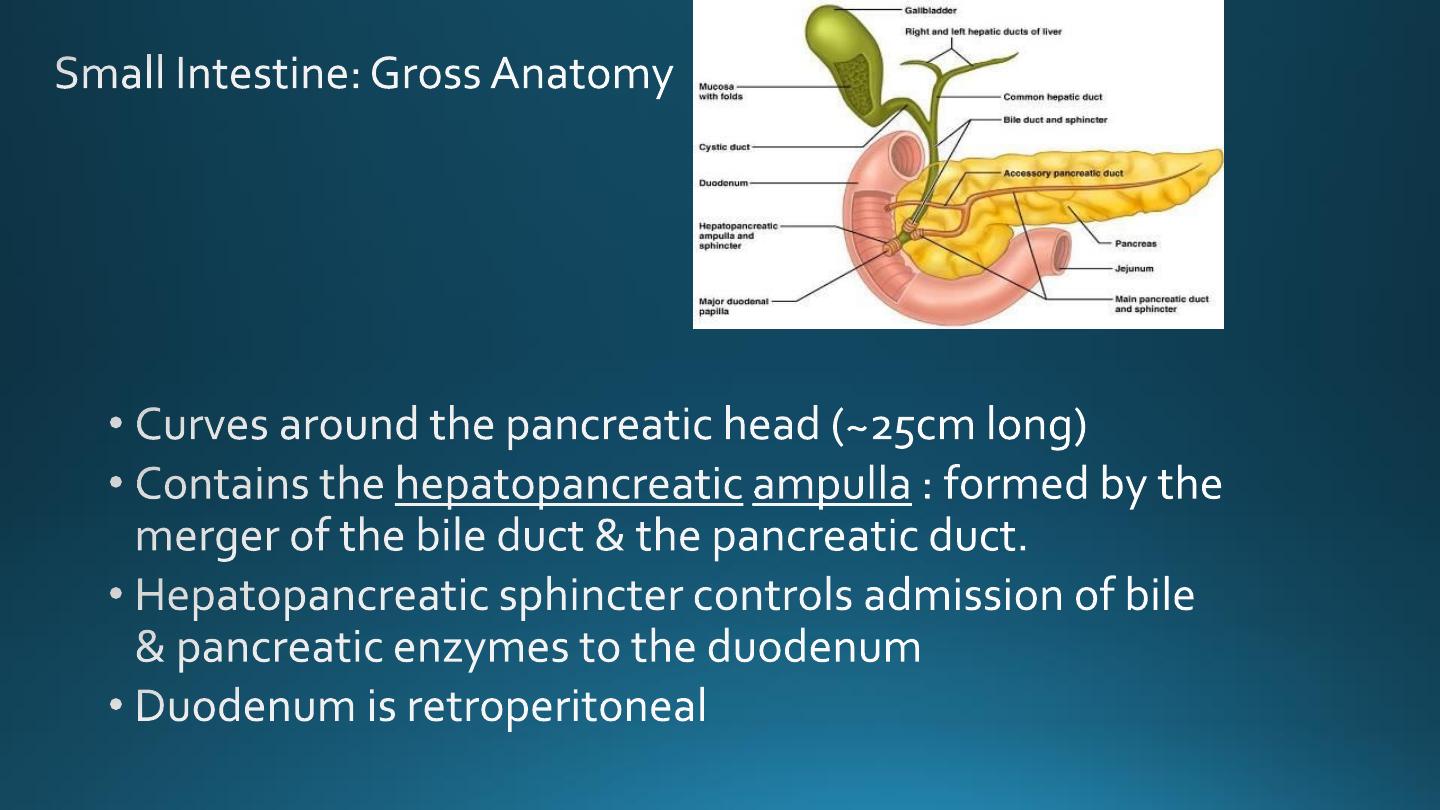
• Duodenum :
Fig 23.20
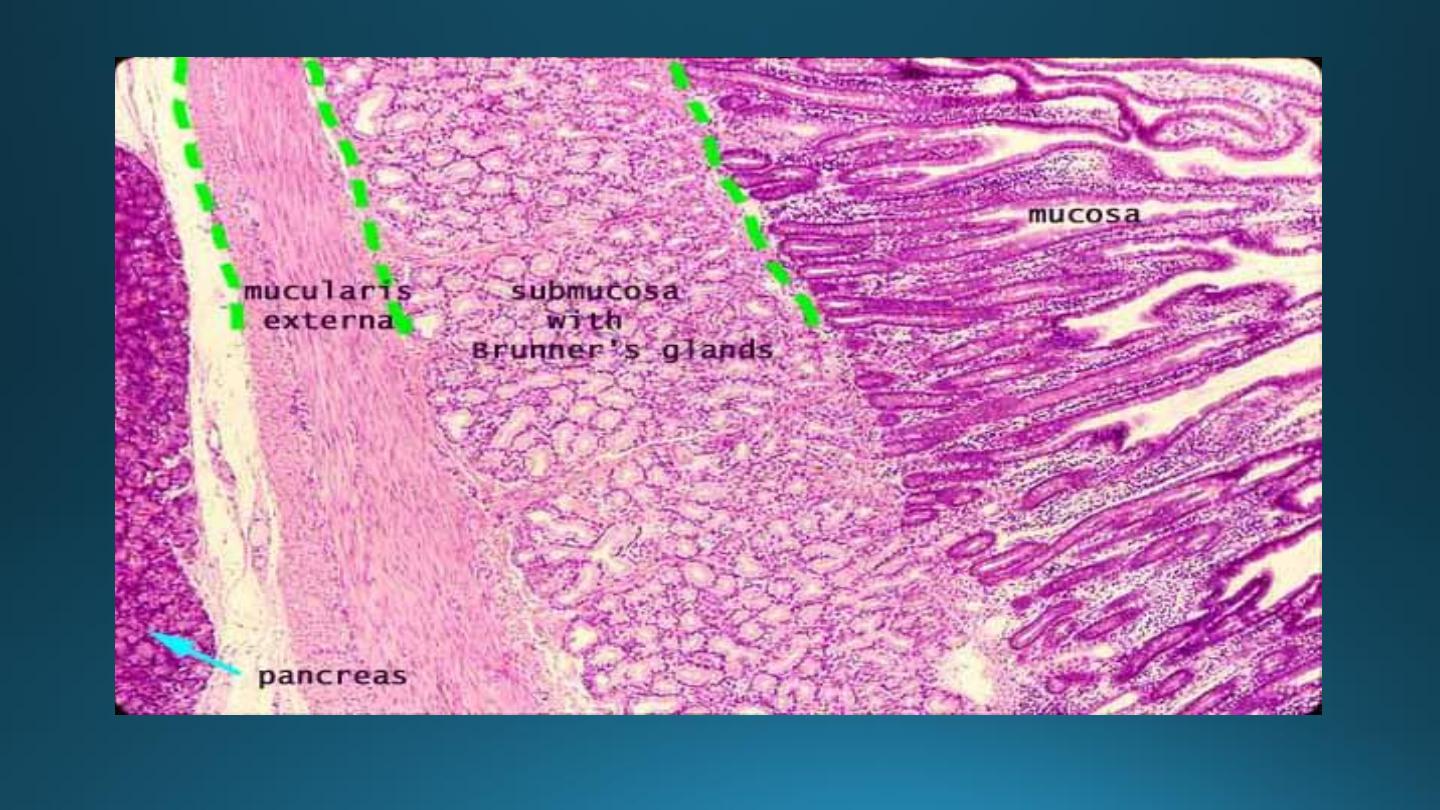
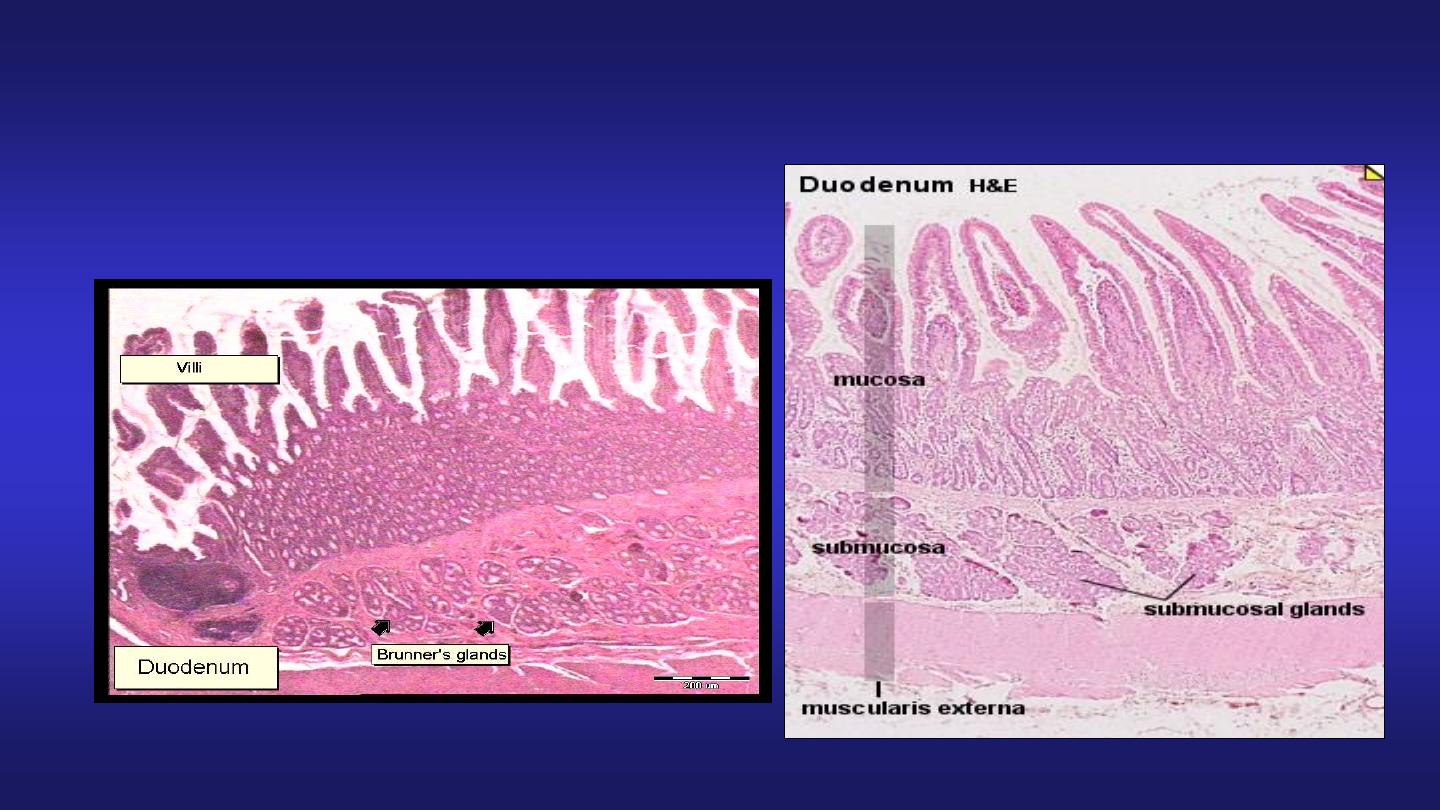
Duodenum
Presence of Brunner’s glands
in submucosa
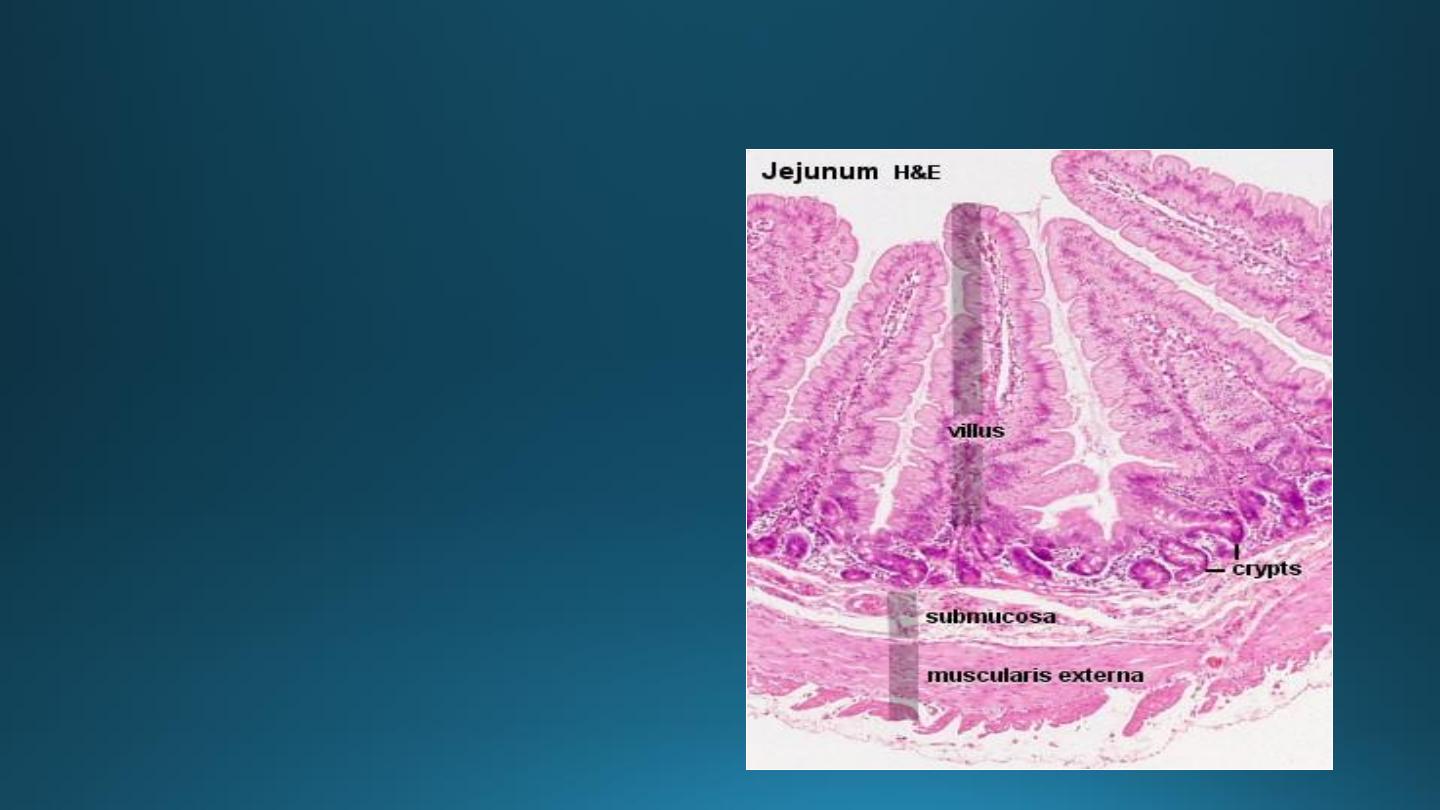
Jejunum
• Villi are tongue shaped.
• Absence of Brunner’s
glands.
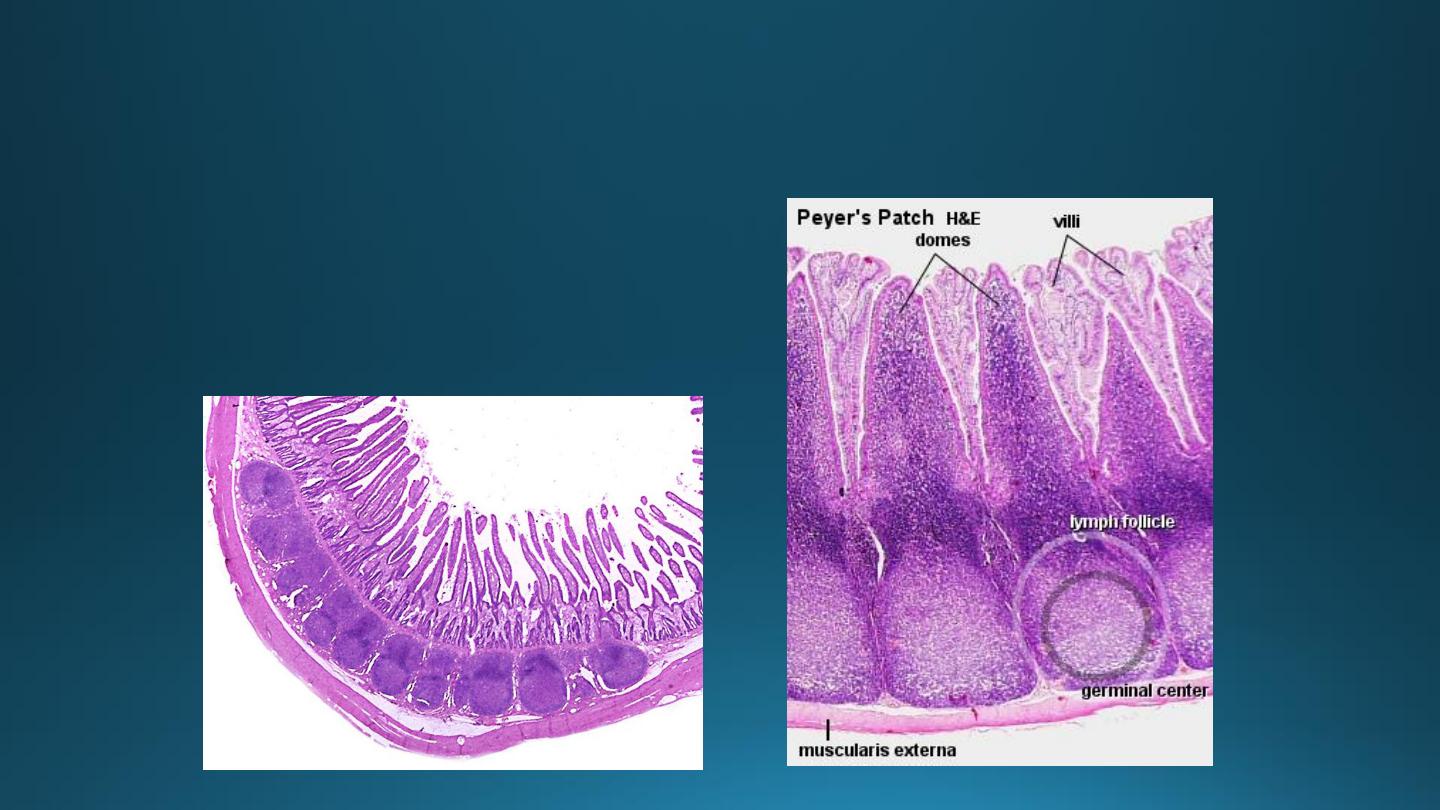
Ileum
• Presence of lymphoid
aggregations in lamina propria
known as Peyer’s patches.
• Villi are short & finger like.


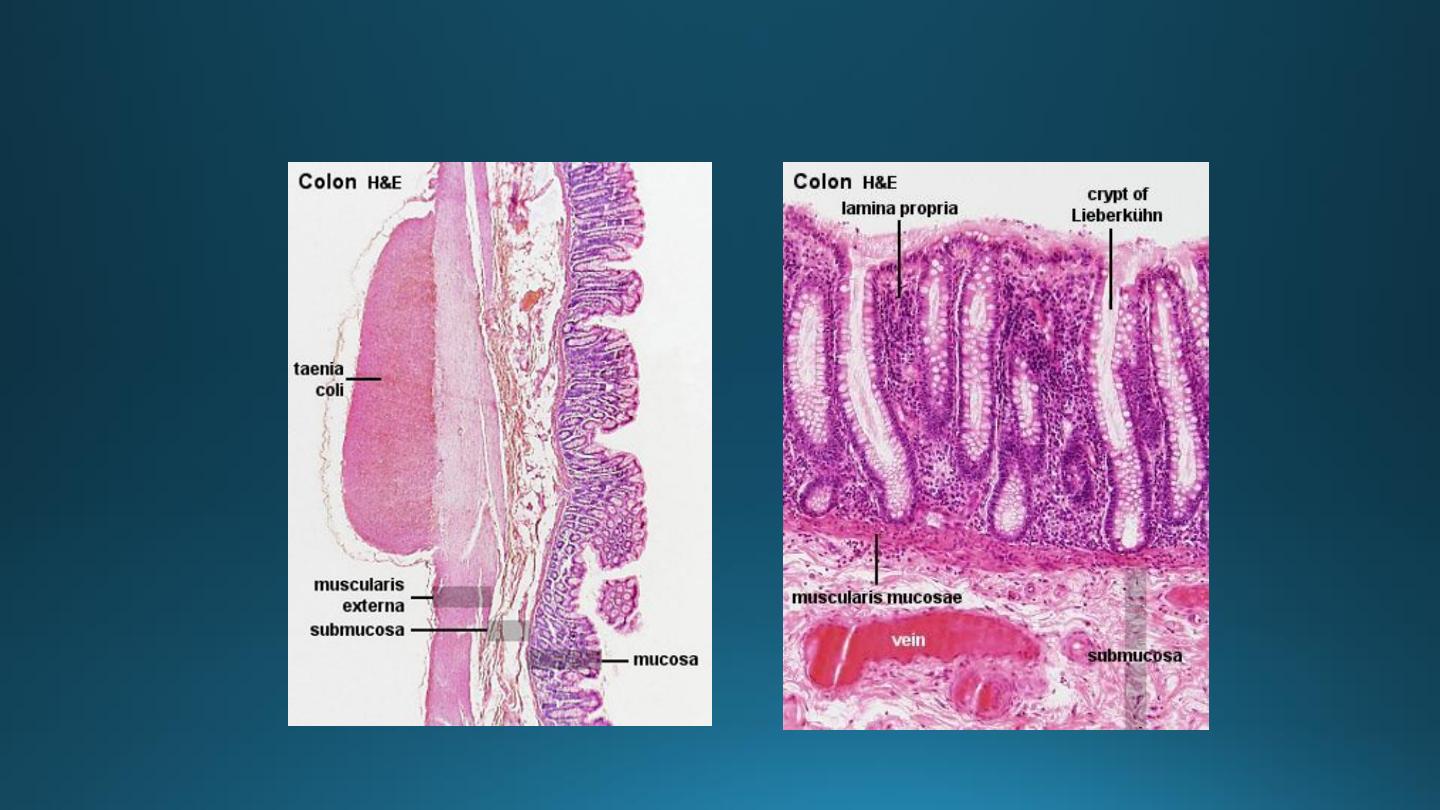
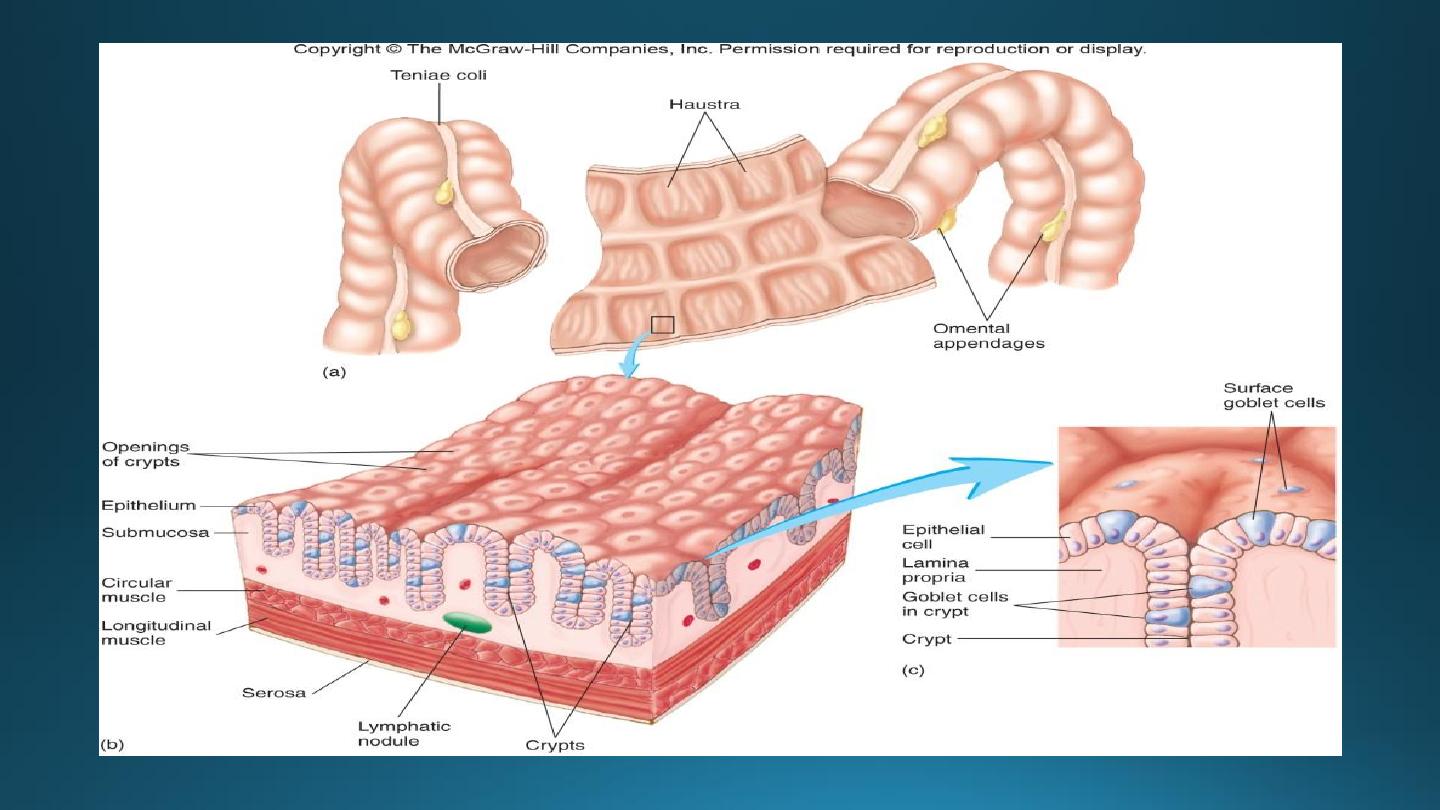
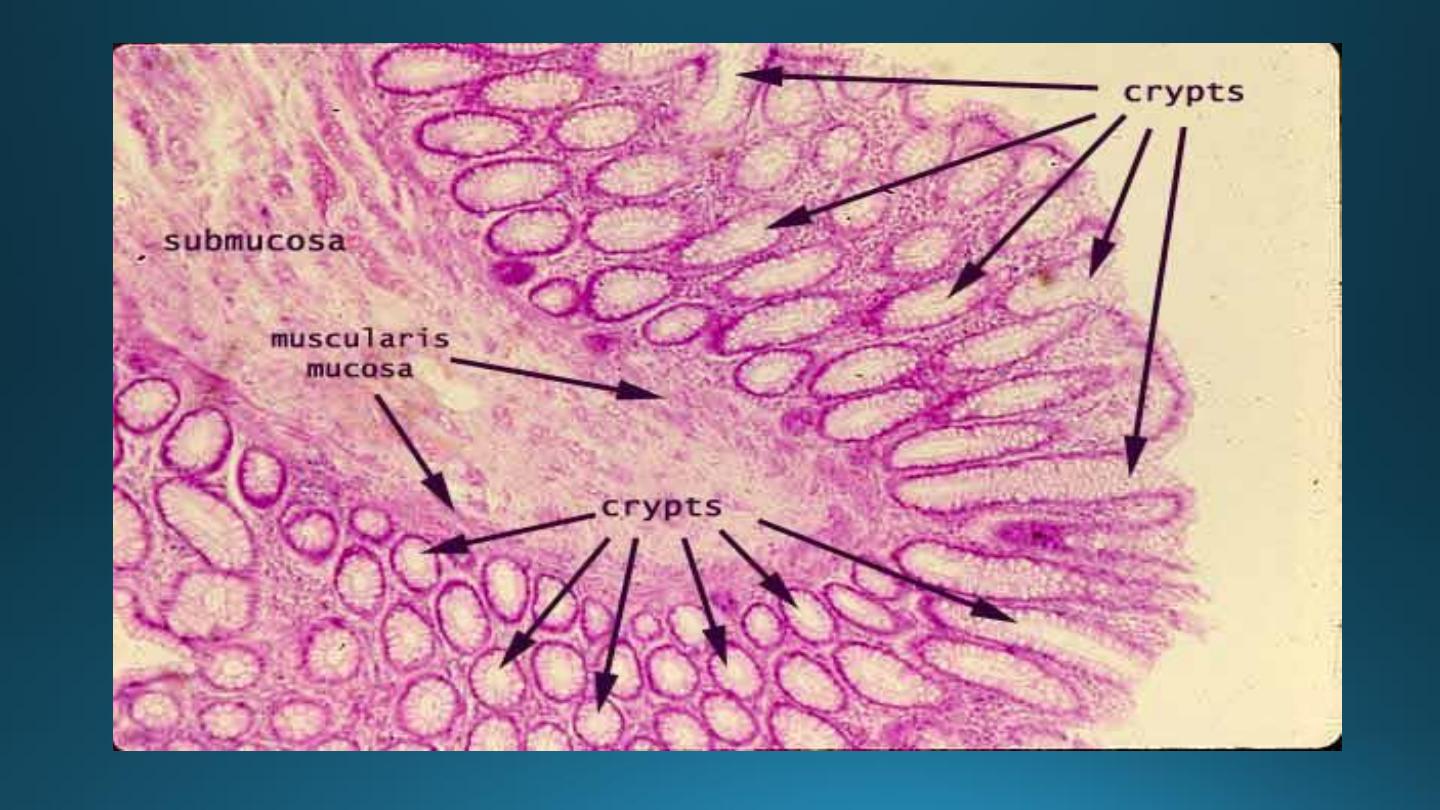
Large Intestine
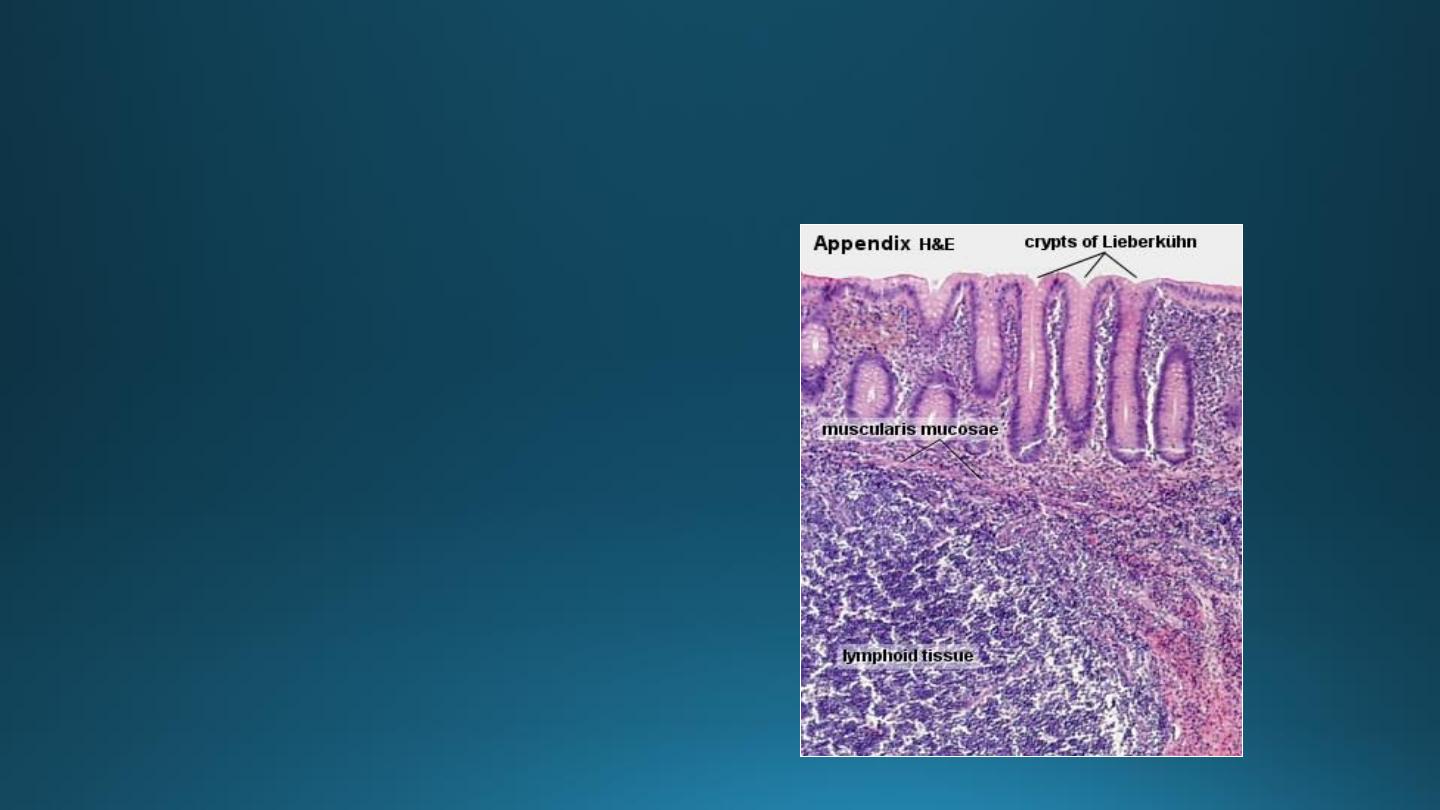
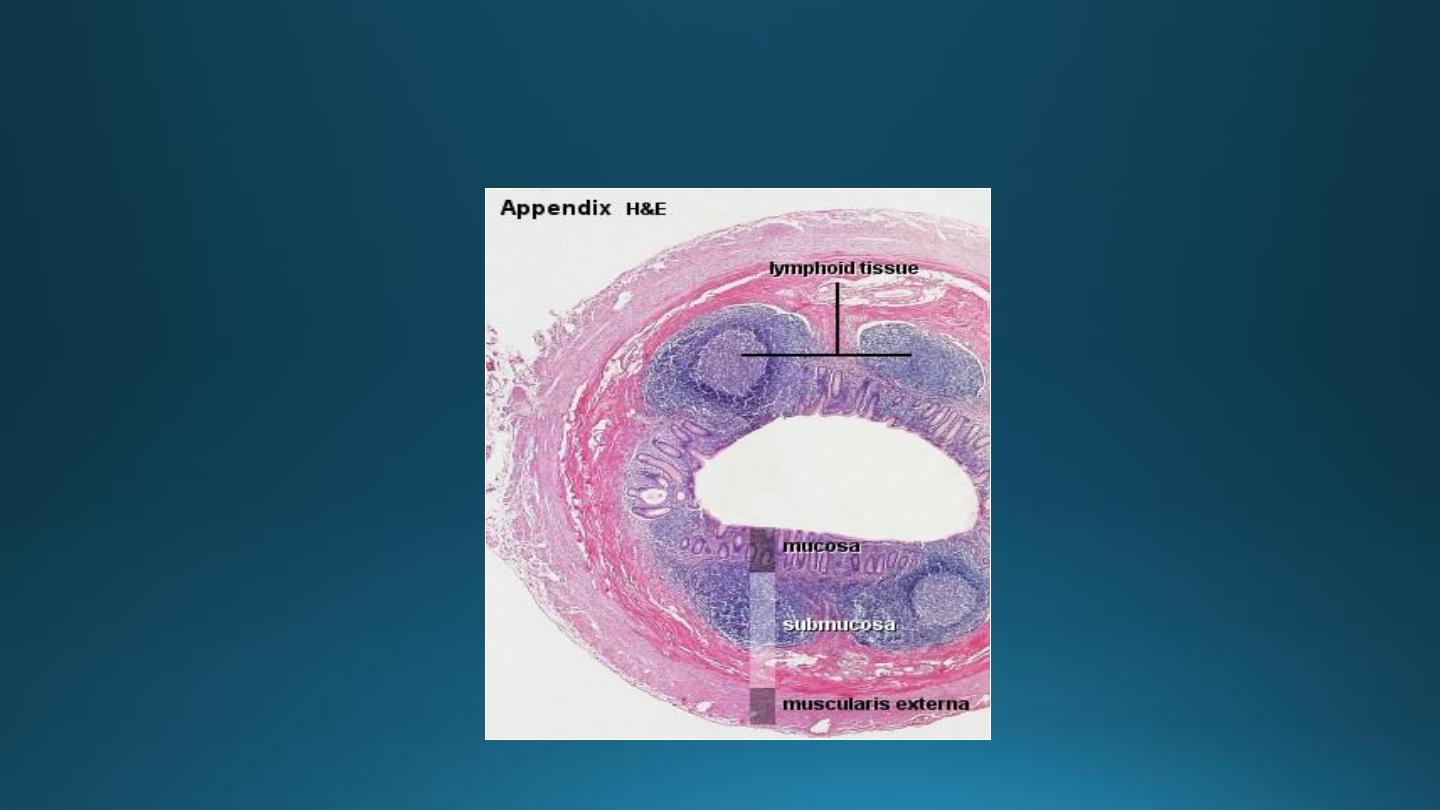
Vermiform Appendix
• A small blind-ending
diverticulum.
• Large accumulations of
lymphoid tissue in lamina
propria which may extend into
submucosa.
• Intestinal villi are usually
absent.
• Crypts are poorly formed.
• Muscularis externa is thin.
• Absence of taenia coli.
Vermiform Appendix
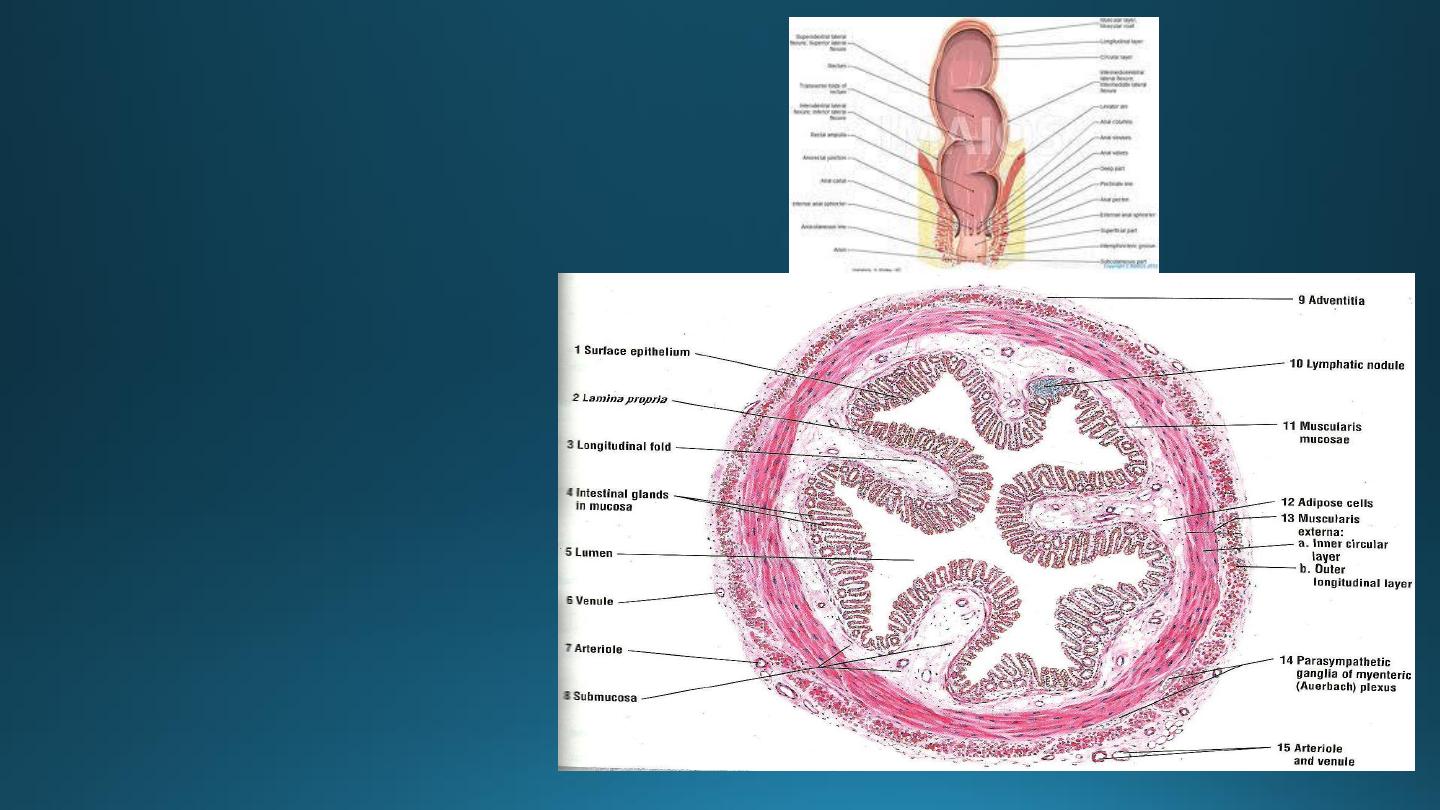
Rectum
• Intestinal glands are straight,
like test tubes.
• A continuous coat of
longitudinal muscle is
present.
• Absence of taenia.
• Absence of appendices
epiploicae
.
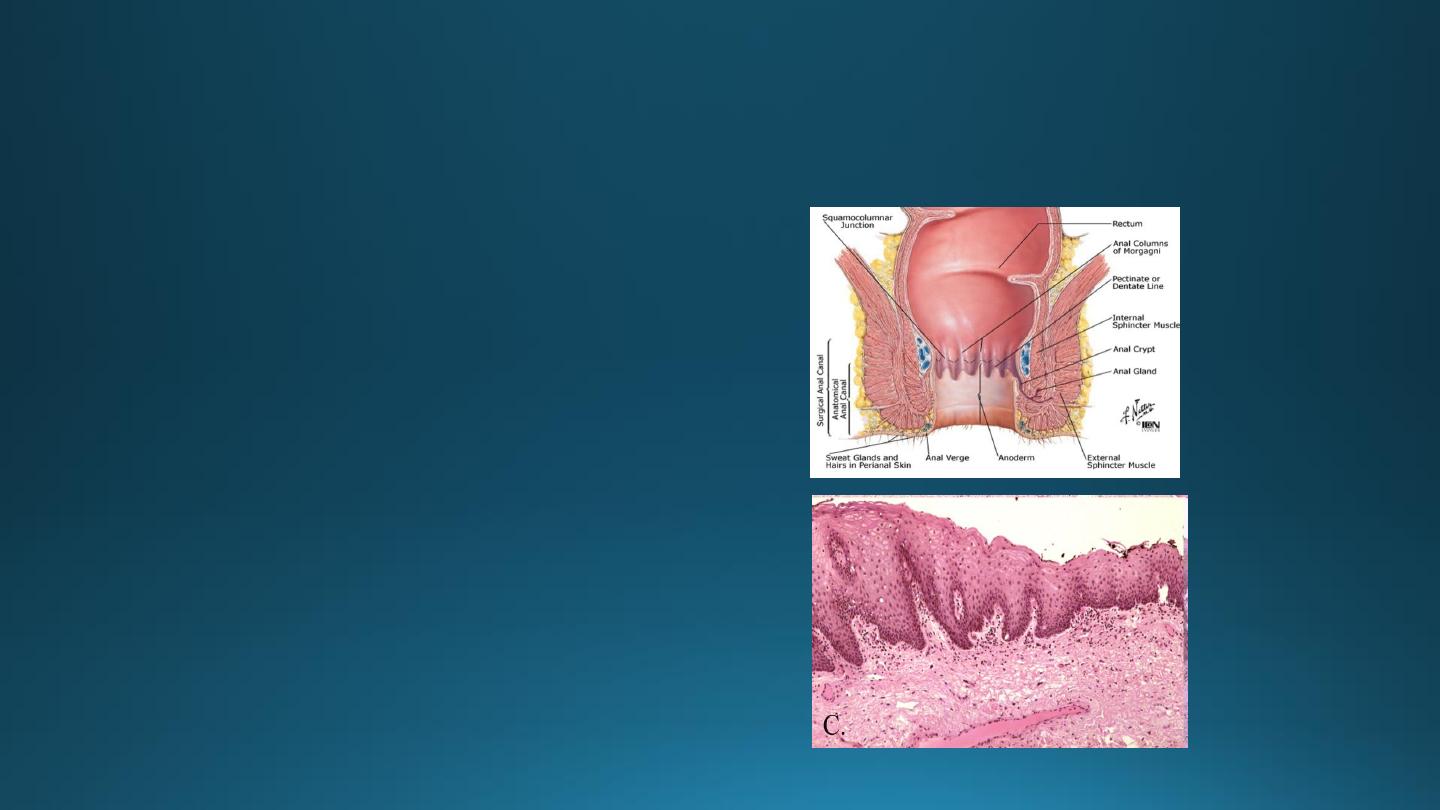
Anal Canal
• Epithelium: upper part-simple columnar,
middle part-stratified squamous non-
keratinized, lower part-covered by true
skin.
• Mucosa has characteristic longitudinal
folds-Anal columns.
• Small mucosal folds between the anal
columns -Pectinate line.
• Crypts disappear below this line.
• Muscularis externa-circular muscle forms
involuntary internal anal sphincter.
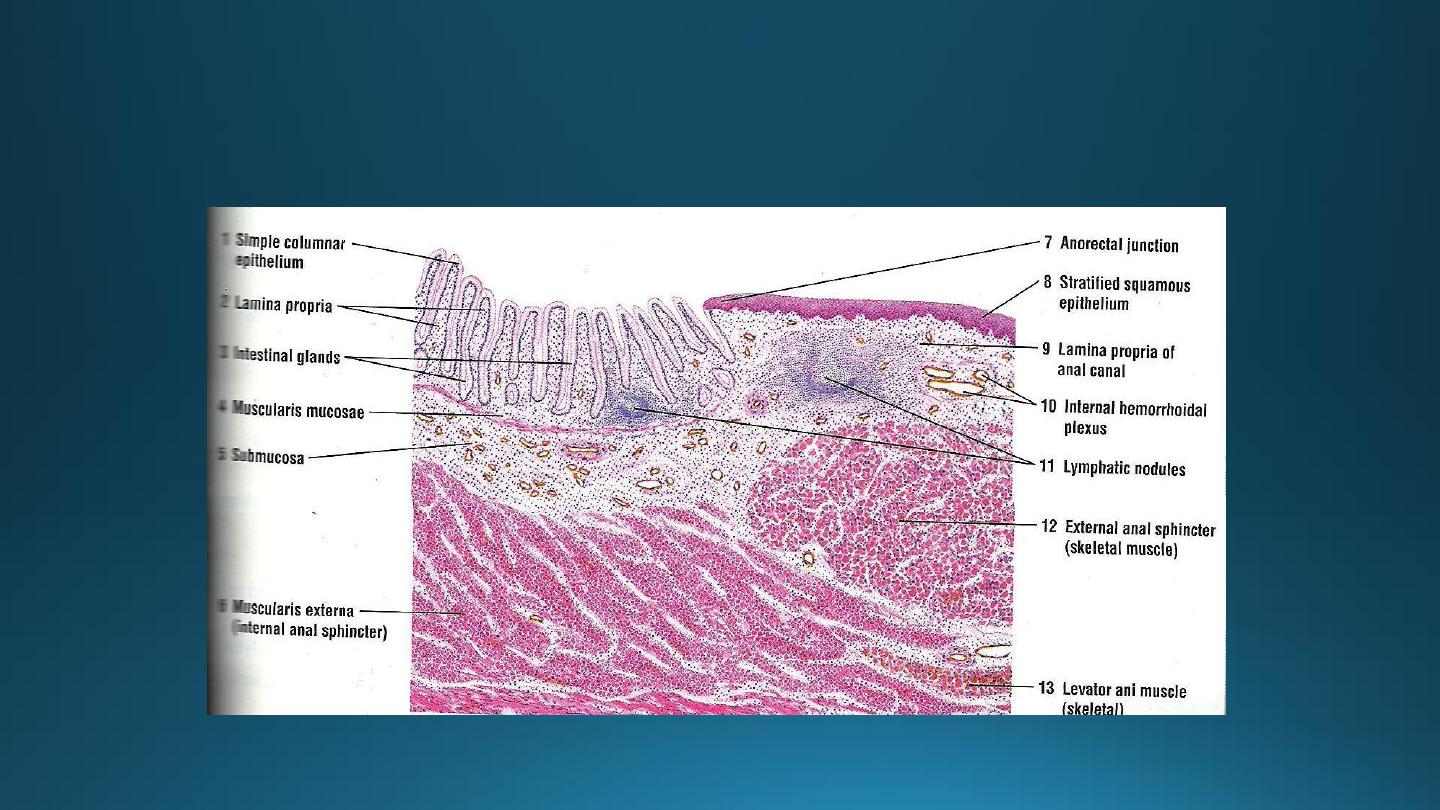
Ano-rectal Junction

Peritoneum
Peritoneum is the largest serous membrane in the body lining the
abdominopelvic cavity
Visceral peritoneum covers the external surfaces of most digestive
organs and is continuous with the parietal peritoneum that lines
the body wall
Between the two peritoneums is the peritoneal cavity
Mesentery is a double layer peritoneum; provides routes for BV,
lymphatics, nerves
Alimentary canal organs are classified as
Retroperitoneal - no mesentery and organs lies posterior to the
peritoneum Intraperitoneal - mesentery and organs lies within the
peritoneal cavity