ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
١
1. Fundamental to Digital Computer
1.1 Introduction to Digital computer
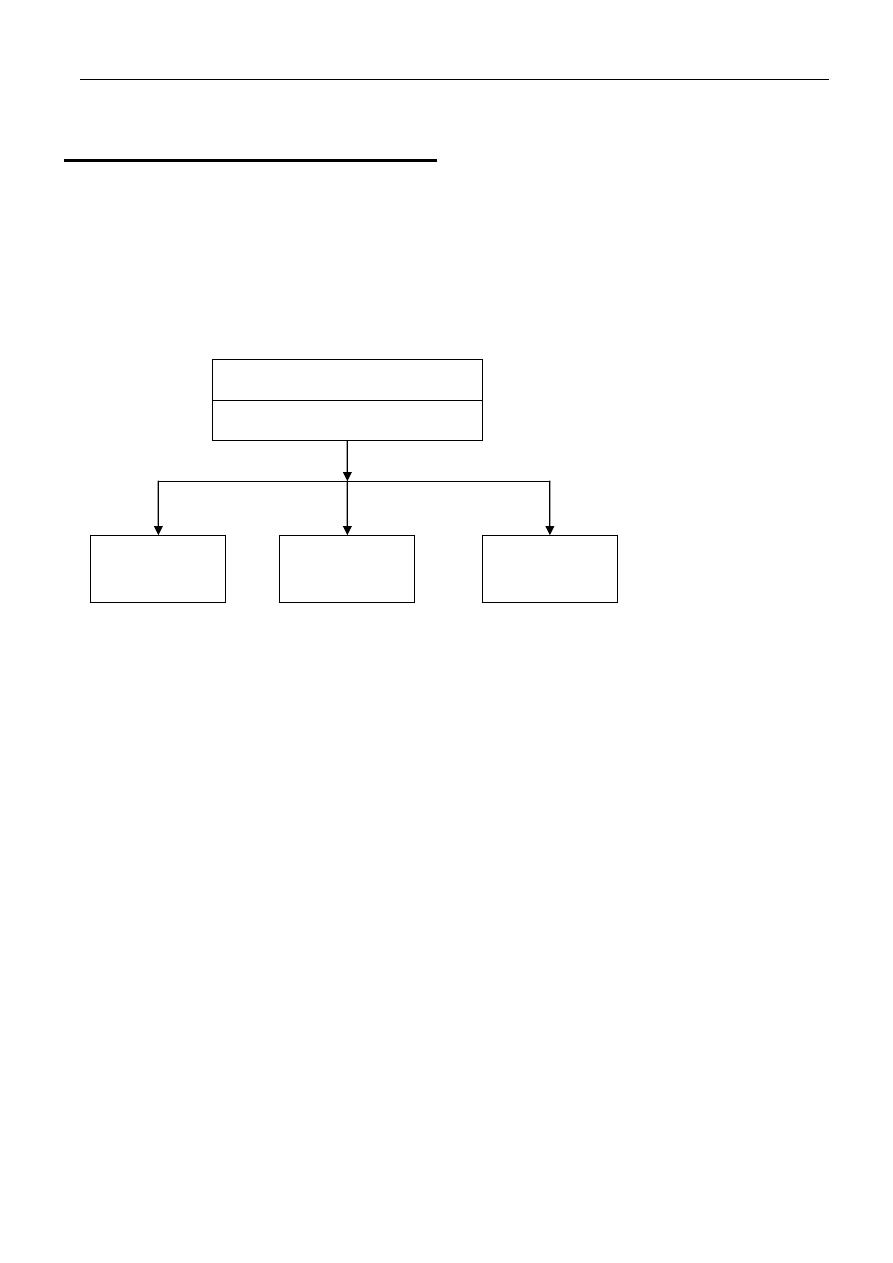
The simple diagram in fig 1 give a good starting point for discussion of computer
organization .
ﺍﻟﻤﺨﻁﻁ ﺭﻗﻡ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ ﻴﻤﺜل ﻨﻘﻁﺔ ﺒﺩﺍﻴﺔ ﺠﻴﺩﺓ ﻟﻤﻨﺎﻗﺸﺔ ﺘﺼﻤﻴﻡ ﺤﺎﺴﻴﺔ ﺭﻗﻤﻴﺔ
Fig -1-
Simplified Block Diagram a Digital Computer
As indicate by fig -1-, the four fundamental components of a computer are its memory ,
central processing Unit (CPU) , Mass storage subsystems, and input / output (I/O)
subsystem.
ﻜﻤﺎ ﻫﻭ ﻤﺅﺸﺭ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﻁﻁ ﺭﻗﻡ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ
ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﺼﺭ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻴﺔ ﻟﺤﺎﺴﺒﺔ ﻫﻭ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴ
ﺔﻴ
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﻜﺯﻴﺔ،
ﻤﻨﻅﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻨﻭﻴﺔ ﻭ ﻤﻨﻅﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ،
.
The purpose of the memory is to save both the instruction that indicate the operation of the
computer and the data being operated on .
ﺍﻥ ﻭﻅﻴﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻴﺔ
ﻫﻭ ﺨﺯﻥ ﻜل ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺤﺩﺩ ﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺍﺩ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﻡ ﺒﻬﺎ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺠﺭﻯ
ﻋﻠﻴﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ
.
Arithmetic / Logic unit
(ALU)
Control Unit
Memory
I /O
Subsystem
Mass storage
Subsystem

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٢
The CPU Controls the decoding and execution of the instructions.
ﺘﻘﻭﻡ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﻜﺯﻴﺔ ﺒﺎﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻏﻠﻰ ﺘﻔﺴﻴﺭ ﻭﺘﻨﻔﻴﺫ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ
.
The Mass storage subsystems store large quantities of all types of information over
extended periods.
ﺘﺨﺯﻥ ﻤﻨﻅﻤﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻨﻭﻱ ﻜﻤﻴﺎﺕ ﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ ﻤﻥ ﻜل ﺍﻨﻭﺍﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ ﻭﻟﻤﺩﺩ ﺯﻤﻨﻴﺔ ﻤﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ
.
The Input / Output subsystems gives the external world a means of communicating with
the digital computer.
ﺘﻭﻓﺭ ﻤﻨﻅﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ ﺍﻟﻴﺔ ﺍﻻﺘﺼﺎل ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﺴﺒﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺭﺠﻲ
.
The diagram shows all of the components connected to a common line that represent a set
of conductors referred to as the system bus.
ﻴﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﻁﻁ
ﺍﻥ ﻜل ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﺼﺭ ﻤﺭﻴﻭﻁﺔ ﺒﻤﺴﺎﺭ ﻤﺸﺘﺭﻙ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﻴﻤﺜل ﺒﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺼﻼﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﻌﺭﻑ ﺒﺎﻟﻨﺎﻗل
ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻲ ﻟﻠﻨﻅﺎﻡ
.
The CPU is divided into major parts, one part being responsible for the overall control of
the system and for retrieving and decoding the instructions and the other part, called the
arithmetic logic unit (ALU) being responsible for the arithmetic and logic operation. The
CPU in a microcomputer system is called the microprocessor unit (MPU).
ﺘﻘﺴﻡ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﻜﺯﻴﺔ
CPU
ﺍﻟﺠﺯﺀ ﺍﻻﻭل ﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﻤ، ﺔﻴﺴﻴﺌﺭ ﺀﺍﺯﺠﺍ ﻰﻟﺍ
ﺴﻭﺅل ﻋﻥ ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻨﻅﺎﻡ
ﺒﻴﻨﻤﺎ ﻴﻜﻭﻥ ﺍﻟﺠﺯﺀ ﺍﻻﺨﺭ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺴﻤﻰ ﺒﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺏ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻨﻁﻕ، ﺎﻫﺭﻴﺴﻔﺘﻭ ﺓﺭﻜﺍﺫﻟﺍ ﻥﻤ ﺕﺍﺯﺎﻌﻴﻻﺍ ﺏﺤﺴﻭ
ALU
ﻤﺴﻭﺅﻻ ﻋﻥ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﻡ ﺒﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺏ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻨﻁﻕ
.
ﻭﺘﻌﺘﺒﺭ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﻜﺯﻴﺔ ﻨﻅﺎﻡ ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺔ ﻤﺎﻴﻜﺭﻭﻴﺔ ﻭﺘﺴﻤﻰ
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﻴﻜﺭﻭﻴﺔ
.
ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٣
1.2 Microcomputer architecture
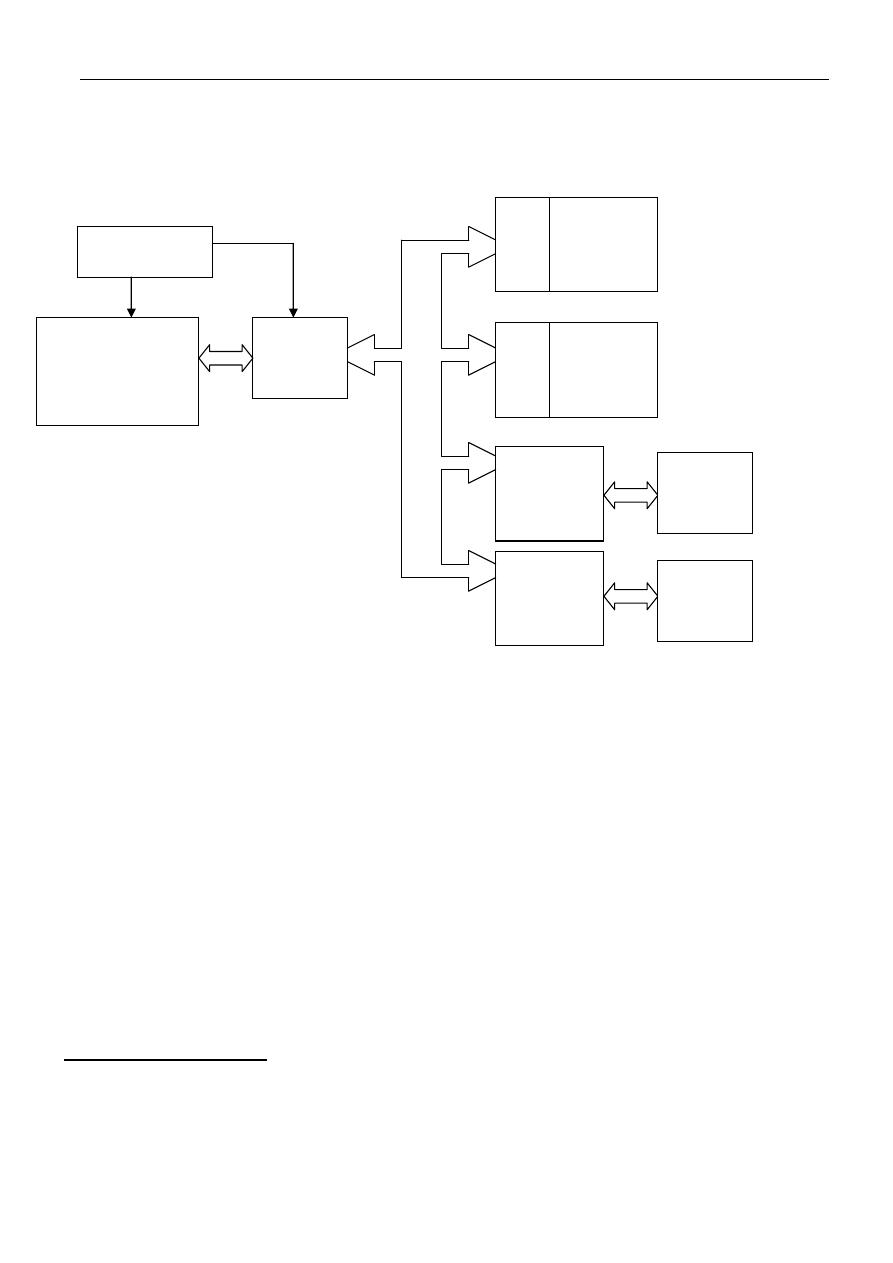
We will now take an architecture of a typical microprocessor which shown in Fig (2).
Fig (2)
Architecture of a typical microprocessor
We see in Fig (2) the overall architecture of a typical microcomputer system and the
components shown in this figure are the central processing unit CPU, timing circuitry
memory, input / output (I/O) subsystem, bus control logic and system bus.
ﻨﻅﺎﻡ، ﺓﺭﻜﺍﺫﻟﺍ ﻊﻤ ﺕﻴﻗﻭﺘﻟﺍ ﺓﺭﺌﺍﺩ ، ﺔﻴﺯﻜﺭﻤﻟﺍ ﺔﺠﻟﺎﻌﻤﻟﺍ ﺓﺩﺤﻭ ﻥﻤ ﻥﻭﻜﻤﻭ ﺔﻴﻭﺭﻜﻴﺎﻤﻟﺍ ﺔﺒﺴﺎﺤﻟﺍ ﻨﻅﺎﻡﺔﻴﺭﺎﻤﻌﻤ ﻯﺭﻨ ﻥﺤﻨ
ـ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻁﻘﻴﺔ ﻟﻠ، ﺝﺍﺭﺨﻻﺍﻭ لﺎﺨﺩﻼﻟ ﻲﻋﺭﻔﻟﺍ
BUS
ﻭﻨﻅﺎﻡ
BUS
.
Microprocessor (CPU): Its purpose is to decode the instructions and use then to control
the activity with in the system. It also performs all arithmetic and logic computations.
Microprocessor
Timing
Bus
Control
Logic
Memory
Module
Memory
Module
Interface
Interface
In
terfa
ce
In
terfa
ce
Mass
Storage
Device
I/O
Device
Memory
I/O subsystem
System Bus

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٤
ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
)
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﻜﺯﻴﺔ
: (
ﺍﻟﻐﺭﺽ ﻤﻥ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﻫﻭ ﺘﻔﺴﻴﺭ ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻤﻬﺎ ﻟﻠﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻓﻌﺎﻟﻴﺎﺕ
ﺍﻟﻨﻅﺎﻡ ﻭﺘﻘﻭﻡ ﺒﻜل ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺭﻴﺎﻀﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻨﻁﻘﻴﺔ
.
Timing Circuity (Clock): It is needed to synchronize the activity within the
microprocessor and the bus control logic and may the timing circuity and microprocessor
is included in the same integrated circuit.
ﺩﺍﺌﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻭﻗﻴﺕ
:
ﻭﻫﻲ ﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻟﻌﻤل ﺘﺯﺍﻤﻥ ﻟﻔﻌﺎﻟﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﺍﻟﻤ
ـﺭﻜﺯﻱ ﻤﻊ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻁﻘﻴﺔ ﻟﻠ
Bus
ﻭﺘﻜﻭﻥ
ﺍﻟﺩﺍﺌﺭﺘﻴﻥ ﻤﺒﻨﻴﺔ ﻀﻤﻥ ﻨﻔﺱ ﺍﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻭ ﺍﻟﺩﺍﺌﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻜﺎﻤﻠﺔ
.
Main Memory ( Simple Memory ): is used to store both the data and instructions that are
currently being used . It is normally broken into several modules, with each module
containing several thousand locations . Each location may contain part or all of instruction
and is associated with an identifier called a memory address (or address), the Memory
modules used in Multiprogramming.
The CPU does its work by successively inputting or fetching instructions from memory
and carrying out the tasks dictated by them.
ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻴﺔ
)
ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺒﺴﻴﻁﺔ
(
ﻭﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﻜل ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻴﺠﺭﻯ
ﺍﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻤﻬﺎ ﺤﺎﻟﻴﺎ
.
ﻭﻜل ﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﻗﺩ ﻴﺤﻨﻭﻱ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺠﺯﺀ، ﻊﻗﺍﻭﻤﻟﺍ ﻑﻻﺍ ﻱﻭﺤﻴ ﻊﻁﻘﻤ لﻜﻭ ، ﻊﻁﺎﻘﻤ ﺓﺩﻋ ﻰﻟﺍ ﻡﺴﻘﺘ ﻲﻫﻭ
ﺍﻭ ﻜل ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﻭﺘﺭﺘﺒﻁ ﻤﻊ ﻤﻌﺭﻑ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﺍﻭ ﻤﺎﻴﺴﻤﻰ ﺒﻌﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﻗﻊ
)
ﻋﻨﻭﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ
(
ﻭﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻤﻘﺎﻁﻊ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻓﻲ،
ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﻤﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻌﺩﺩﺓ
.
ﻭﻴﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼل ﺍﺩﺨﺎل ﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ ﺍﻭ ﺍﺨﺭﺍﺝ ﺍﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ
ﻭﻤﻥ ﺜﻡ ﺘﻨﻔﻴﻴﺫ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺩﺩﺓ ﺒﺘﻠﻙ
ﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯﺍﺕ
.
I/O Subsystem: It 's may consists of a variety of devices for communicating with the
external world and dealing with large quantities of information.
ﻤﻨﻅﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ ﺍﻟﻔﺭﻋﻴﺔ
:
ﻭﻫﻲ ﺘﺘﻜﻭﻥ ﻤﻥ ﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﻤﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻻﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﻓﻲ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ
ﺍﻻﺘﺼﺎل ﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺭﺠﻲ
ﺒﺤﻴﺙ ﺘﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻊ ﻜﻤﻴﺎﺕ ﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ
.
ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٥
Keyboards, light pens, and analog to digital (A/D) converts are examples of input
equipment, CRT monitors, line printers, plotters and digital to analog (D/A) converts are
output devices. Some devices, such as terminals, provide both input and output
capabilities.
ﺘﻌﺘﺒﺭ
ﻟﻭﺤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﺘﻴﺢ ﻭﺍﻻﻗﻼﻡ ﺍﻟﻀﻭﺌﻴﺔ ﻭﻤﺤﻭﻻﺕ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻤﺎﺜﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺭﻗﻤﻴﺔ ﺍﻤﺜﻠﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﺍﺩﺨﺎل
ﺍﻤﺎ،
ﺍﻟﺸﺎﺸﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﻁﺎﺒﻌﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺴﻁﺭﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺭﺍﺴﻤﺎﺕ ﻭﻤﺤﻭﻻﺕ ﺍﻻﺸﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺭﻗﻤﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻤﺎﺜﻠﻴﺔ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻤﺜﻠﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ
ﻭﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺍﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﻤﺜل ﺍﻟﻤﺤﻁﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻁﺭﻓﻴﺔ ﻓﻠﻬﺎ ﻗﺎﺒﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﺨﺭﺍﺝ
ﻓﻲ ﺍﻥ ﻭﺍﺤﺩ
.
Mass storage units: It 's the components that permanently storing programs and data. The
more popular types of mass storage equipment are magnetic tape and disk units but recent
technology has made available magnetic memories (MBMs).
ﻭﺤﺩﺍﺕ ﺍ
ﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ
:
ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﻭﺤﺩﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺤﺯﻥ ﺒﺸﻜل ﺜﺎﺒﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﺍﻤﺞ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ
.
ﻭﻤﻥ ﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﺍﻻﻨﻭﺍﻉ ﺸﻴﻭﻋﺎ ﻟﻬﺫﻩ
ﺍﻻﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻻﺸﺭﻁﺔ ﻭﺍﻻﻗﺭﺍﺹ ﺍﻟﻤﻐﻨﺎﻁﻴﺴﻴﺔ ﻭﻟﻜﻥ ﻤﻭﺨﺭﺍ ﺘﻡ ﺘﻭﻓﻴﺭﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻐﻨﺎﻁﻴﺴﻴﺔ
.
Although a mass storage unit may be used to store both programs and data, programs
must be transferred to memory they are executed, and data must be in memory before they
can be operated on by a programs.
ﺤﻴﺙ ﺍﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﺍﻤﺞ ﻴﺠﺏ ﺍﻥ ﺘﻨﻘل ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺤﺘﻰ، ﺕﺎﻨﺎﻴﺒﻟﺍﻭ ﺞﻤﺍﺭﺒﻟﺍ ﻥﺯﺨ ﺔﻴﻠﻤﻋ ﻲﻓ ﺓﺭﻴﺒﻜﻟﺍ ﻥﺯﺨﻟﺍ ﺓﺩﺤﻭ ﻡﺩﺨﺘﺴﺘﻭ
ﻭﻴﺠﺏ ﺍﻥ ﺘﺘﻭﻓﺭ، ﺎﻫﺫﻴﻔﻨﺘ ﻡﺘﻴ
ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻗﺒل ﺫﻟﻙ ﺤﺘﻰ ﺘﺘﻤﻜﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺭﺍﻤﺞ ﻤﻥ ﺍﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻤﻬﺎ ﺍﺜﻨﺎﺀ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻘﻴﺫ
.
System Bus: is a set of conductors that connects the CPU to its memory and I/O devices.
It is over these conductors, which may be wires in a cable or lines on a printed circuit (PC)
board that all information must travel. Exactly how information is transmitted over the bus
is determined by the bus specifications.
ـﻴﻌﺭﻑ ﺍﻟ
system bus
ﺒﺎﻨﻪ ﻤﺠﻤﻭﻋﺔ ﻤﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺼﻼﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺭﺒﻁ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻭ ﺍﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل
ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ ﻭﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺼﻼﺕ
ﺘﻤﺜل ﺒﻭﺍﻴﺭﺍﺕ ﺩﺨﺎل ﻜﻴﺒل ﺍﻭ ﺨﻁﻭﻁ ﻤﻁﺒﻭﻋﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺒﻭﺭﺩ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻴﺠﺏ ﺍﻥ ﺘﻨﺘﻘل ﺨﻼﻟﻬﺎ
ـ ﻭﺒﺎﻟﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﻜﻴﻑ ﻴﺘﻡ ﺘﺭﺍﺴل ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ ﺨﻼل ﺍﻟ، ﺕﺎﻤﻭﻠﻌﻤﻟﺍ
bus
ـﻓﻬﺫﺍ ﻴﺤﺩﺩ ﺤﺴﺏ ﻤﻭﺍﺼﻔﺎﺕ ﺍﻟ
bus
.
Normally, the bus conductors are separated into three groups:

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٦
ـ ﻓﺎﻥ ﻤﻭﺼﻼﺕ ﺍﻟ، ﺎﻴﻌﻗﺍﻭ
bus
ﺘﺼﻨﻑ
ﺍﻟﻰ ﺜﻼﺜﺔ ﻤﺠﺎﻤﻴﻊ
:
1. The data lines for the transmitting the information.
ﺨﻁﻭﻁ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﻨﻘل ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ
.
2. The address lines, which indicate where the information is to come from or is to be
placed.
ﺨﻁﻭﻁ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻭﺍﻨﻴﻥ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﺤﺩﺩ ﺍﻴﻥ ﺘﺫﻫﺏ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ ﺍﻭ ﻤﻥ
ﺍﻴﻥ ﺘﺎﺘﻲ
.
3. The control lines, which regulate the whole system.
ﺨﻁﻭﻁ ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻁﺭﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺘﻨﻅﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻅﻭﻤﺔ ﺒﻜﺎﻤﻠﻬﺎ
.
Interfaces:
It is the device that manages the connection between two devices in the digital computer
system. And it's way of management is differ and depend on which devices is connected
.Therefore we can simply classified it into:
ﻭﻫﻭ ﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﻴﻨﻅﻡ ﻜﻴﻔﻴﺔ ﺭﺒﻁ ﺠﻬﺎﺯﻴﻥ ﻨﻅﺎﻡ ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺔ ﺭﻗﻤﻲ
.
ﻭﻁﺭﻴﻘﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻅﻴﻡ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺘﺨﺘﻠﻑ ﺒﺎﺨﺘﻼﻑ ﺍﻻﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺒﻭﻁﺔ
ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼﻟﻪ ﻭﺒﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﻴﻤﻜﻥ ﺘﺼﻨﻴﻑ ﺍﻨﻭﺍﻋﻪ ﺍﻟﻰ
:
1. Interface between CPU and Main Memory
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﺨﺎﻁﺏ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻴﺔ
In this case the interface is a simple device offers these jobs:
ﻓﻲ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻓﺎﻥ
interface
ﻫﻭ ﺠﻬﺎﺯﺒﺴﻴﻁ ﻭﻟﻪ ﺍﻟﻭﻅﺎﺌﻑ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ
:
a. specified the type of operation with Main Memory if it Read or write.
ﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ
ﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﻴﺔ ﺍﻥ ﻜﺎﻨﺕ ﻗﺭﺍﺀﺓ ﺍﻭ ﻜﺘﺎﺒﺔ
b. specified the location which will consider to execute the operation.
ﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺍﺩ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻌﻪ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺫﺍﻜﺭﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﺴﺘﺠﺭﻯ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼﻟﻪ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٧
2. Interface between CPU and Mass Storage Memory
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﺨﺎﻁﺏ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻭﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ
In this case the interface is a more complicated device offers these jobs:
ﻓﻲ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻓﺎﻥ
interface
ﻫﻭ ﺠﻬﺎﺯﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﺘﻌﻘﻴﺩﺍ ﻭﻟﻪ ﺍﻟﻭﻅﺎﺌﻑ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ
:
a. Specified the type of operation with Mass Storage Memory if it Read or write.
ﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻭﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ ﺍﻥ ﻜﺎﻨﺕ ﻗﺭﺍﺀﺓ ﺍﻭ ﻜﺘﺎﺒﺔ
b. Specified the location which will consider to execute the operation.
ﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﻗﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺍﺩ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻌﻪ ﻓﻲ
ﻭﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ
ﻭﺍﻟﺫﻱ ﺴﺘﺠﺭﻯ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼﻟﻪ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ
c. Synchronize the CPU with Mass storage device
ﻋﻤل ﻤﺯﺍﻤﻨﺔ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻭﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺨﺯﻥ ﺍﻟﻜﺒﻴﺭﺓ
d. Present a temporally storage for transferred information.
ﺨﺯﻥ ﻤﺅﻗﺕ ﻟﻠﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻨﺎﻗﻠﺔ
3. Interface between CPU and I/O Sub System
ﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﺨﺎﻁﺏ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ
ﻭﺍﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ
In this case the interface is a very complicated device offers these jobs:
ﻓﻲ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻓﺎﻥ
interface
ﻫﻭ ﺠﻬﺎﺯﻤﻌﻘﺩ ﺠﺩﺍ ﻭﻟﻪ ﺍﻟﻭﻅﺎﺌﻑ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ
:
a. Specified the type of operation with I/O sub system if it Read or write.
ﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﻨﻭﻉ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠ
ﻴﺔ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻭﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ ﺍﻥ ﻜﺎﻨﺕ ﻗﺭﺍﺀﺓ ﺍﻭ ﻜﺘﺎﺒﺔ
b. Specified the device which will consider to execute the operation.
ﺘﺤﺩﻴﺩ ﺍﻟﺠﻬﺎﺯﺍﻟﻤﺭﺍﺩ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻤل ﻤﻌﻪ ﻀﻤﻥ ﻤﻨﻅﻭﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﻭﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ
c. Synchronize the CPU with I/O sub system
ﻋﻤل ﻤﺯﺍﻤﻨﺔ ﺒﻴﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎ
ﻟﺞ ﻭﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﺍﻻﺩﺨﺎل ﺍﻭ ﺍﻻﺨﺭﺍﺝ
d. Present a Temporally storage for transferred information

ﺤﺎﺴﺒﺎﺕ ﻤﺘﻘﺩﻤﺔ
ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺤﻠﺔ
ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
ﻫﻨﺩﺴﺔ
ﻜﻬﺭﻭ ﻤﻴﻜﺎﻨﻴﻙ
ﺍﻟﻤﺩﺭﺱ ﻤﺴﺎﻋﺩ
ﺍﻨﻤﺎﺭ
ﺨﻠﻴل ﺍﺒﺭﺍﻫﻴﻡ
٨
ﺨﺯﻥ ﻤﺅﻗﺕ ﻟﻠﻤﻌﻠﻭﻤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻨﺎﻗﻠﺔ
e. convert the information in suitable form that match the required task.
ﺘﺤﻭﻴل ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻨﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺸﻜل ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻁﻠﻭﺒﺔ
.
Bus Control Logic
This unit control the bus system and have these jobs:
ﺘﺴﻴﻁﺭ ﻫﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻭﺤﺩﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ
Bus
ﻭﻟﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻭﻅﺎﺌﻑ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ
1. synchronize devices connected to the CPU from reading it's specifications and tell the
timing circuit to generate the suitable pulse for the device.
ﻋﻤل ﺘﺯﺍ
ﻤﻥ ﻟﻼﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺒﻭﻁﺔ ﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﻤﻥ ﺨﻼل
ﻗﺭﺍﺀﺓ ﻤﻭﺍﺼﻔﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺒﻭﻁﺔ
ﻭﺍﻻﻴﻌﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺩﺍﺌﺭﺓ
ﺍﻟﺘﻭﻗﻴﺕ ﺒﺘﻭﻟﻴﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺎﺴﺒﺔ ﻟﻌﻤل ﺍﻟﺠﻬﺎﺯ
.
2. choose the device that connect to the CPU First if more than one device is requst an
service in the same time with respect to priority specified from the designer or the user.
ﺍﺨﺘﻴﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﻤﺭﺒﻭﻁ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺞ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻥ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺍﻜﺜﺭ ﻤﻥ ﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﻴﻁﻠﺏ ﺨﺩﻤﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻨﻔﺱ ﺍﻟﻭﻗﺕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﺴﺎﺱ ﺍﺴﺒﻘﻴﺎﺕ
ﻴﺤﺩﺩﻫﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﺼﻤﻡ ﺍﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ
.
The priority specified by three ways:
ﺘﺤﺩﺩ ﺍﻟﺼﻼﺤﻴﺎﺕ ﺒﺜﻼﺜﺔ ﻁﺭﻕ
1. By the designer if the computer is general purpose .
ﻤﻥ ﻗﺒل ﺍﻟﻤﺼﻤﻡ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻨﺕ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﺴﺒﺔ ﻤﺨﺼﺼﺔ ﻟﻼﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻡ
.
2. By the user if the computer is special purpose .
ﻤﻥ ﻗﺒل ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺩﻡ ﺍﺫﺍ ﻜﺎﻨﺕ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﺴﺒﺔ ﻤﺨﺼﺼﺔ ﻟﻼﺴﺘﺨﺩﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺹ
.
3. Some special situation that manage the priority in special way for some devices in the
configuration and the others have the default priority.
ﻭﻓﻲ ﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺨﺎﺼﺔ ﺘﻌﻁﻰ ﺍﺴﺒﻘﻴﺎﺕ ﻟﺒﻌﺽ ﺍﺠﻬﺯﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻘﻴﺔ ﺘﺒﻘﻰ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺼﻼﺤﻴﺎﺘﻬﺎ ﺍﻻﺴﺎﺴﻴﺔ
.
