Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
2
Z
Z
-
-
t
t
r
r
a
a
n
n
s
s
f
f
o
o
r
r
m
m
Definitions
Z-transform converts a discrete-time signal into a complex frequency-domain
representation. It is similar to the Laplace transform for continuous signals.
The difference between the DTFT and the z-transform lies in the choice of the
independent
variable
used
in
the
transformed
domain.
The
DTFT
of
a
DT
sequence
x[k]
uses
the
complex
exponentials
as
its
basis
function
and
maps
x[k]
in
terms
of
. The z-transform X(z) expresses x[k] in terms of
, where the independent
variable z is given by
. The z-transform is, therefore, a generalization of
the DTFT, just as the Laplace transform is a generalization of the CTFT.
using the z-transform simplifies the algebraic manipulations and leads to flow
diagram representations of the DT systems.
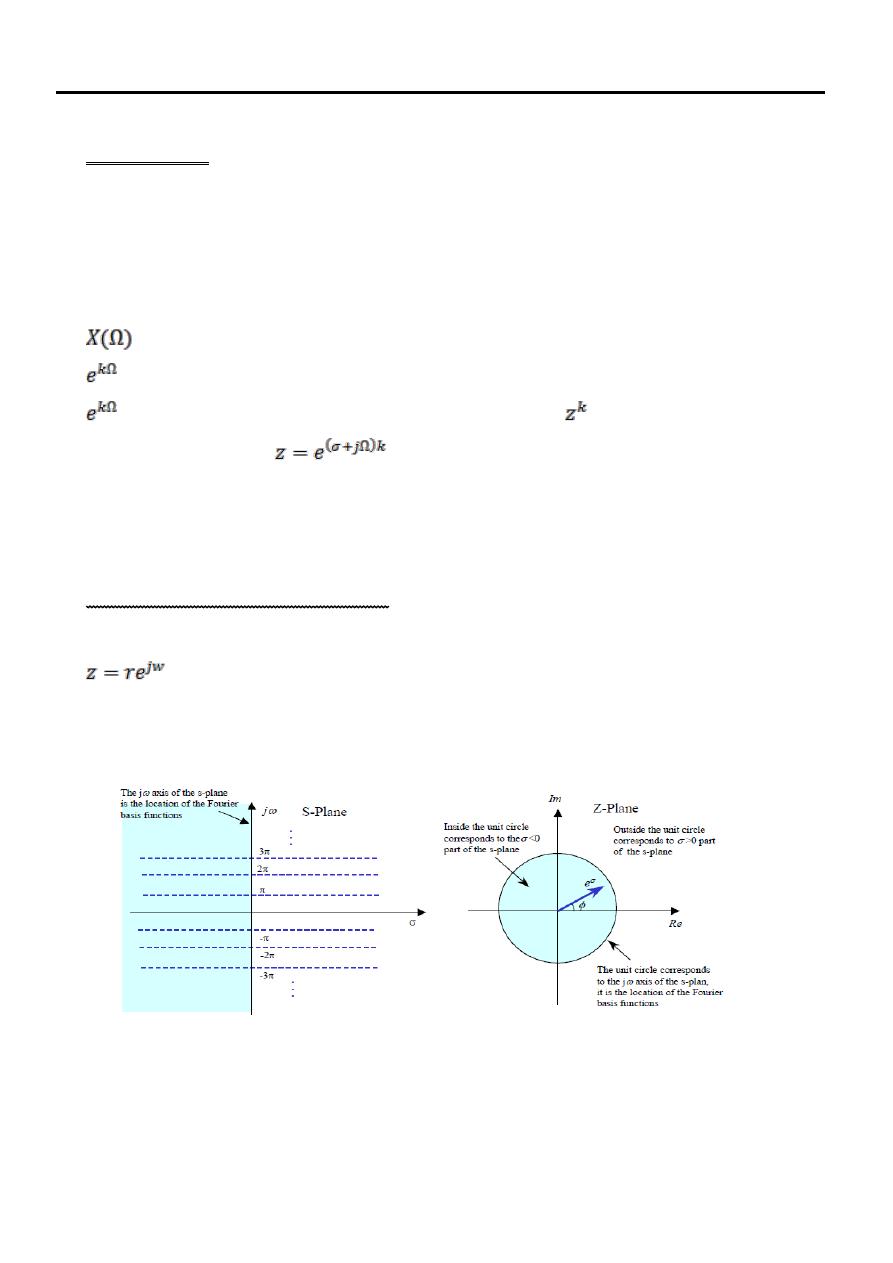
The z-Plane and The Unit Circle
The frequency variables of the Laplace transform s=σ +jω, and the z-tranform
are complex variables with real and imaginary parts and can be visualised
in a two dimensional plane. Figs. 1a and 1.b shows the s-plane of the Laplace
transform and the z-plane of z-transform.
Figure 1 (a) (b)

Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
3
Derive Z-Transform from the Laplace Transform of Discrete-Time Signal
The relationship between x[n] and its z-transform is indicated as
Two-Sided
or
Bilateral z-transform
One-Sided
or
Unilateral z-transform
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
4
:
(1)
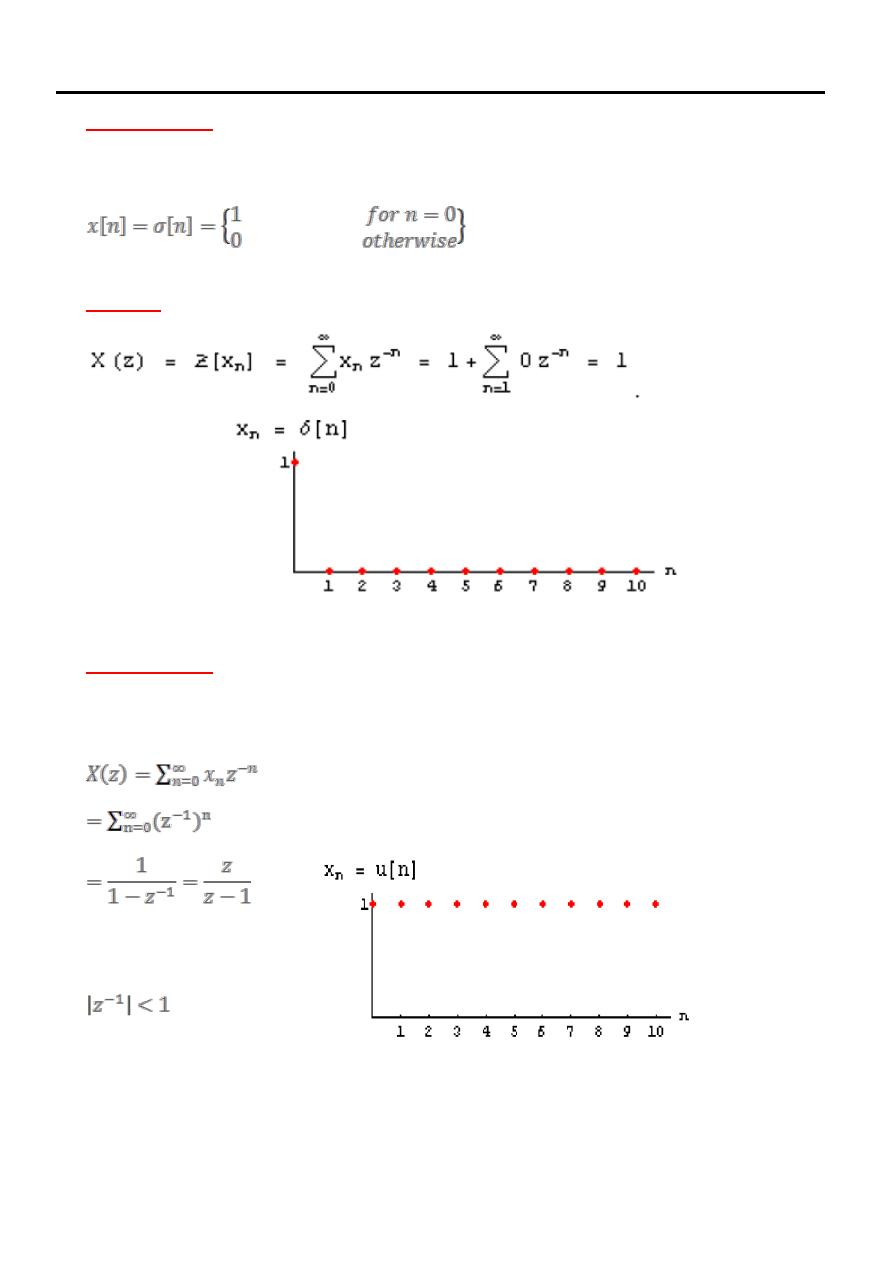
Example
Find the z-
transform of the unit pulse or impulse sequence
Solution
:
(2)
Example
Find the z-
transform of the unit step sequence
condition
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
5
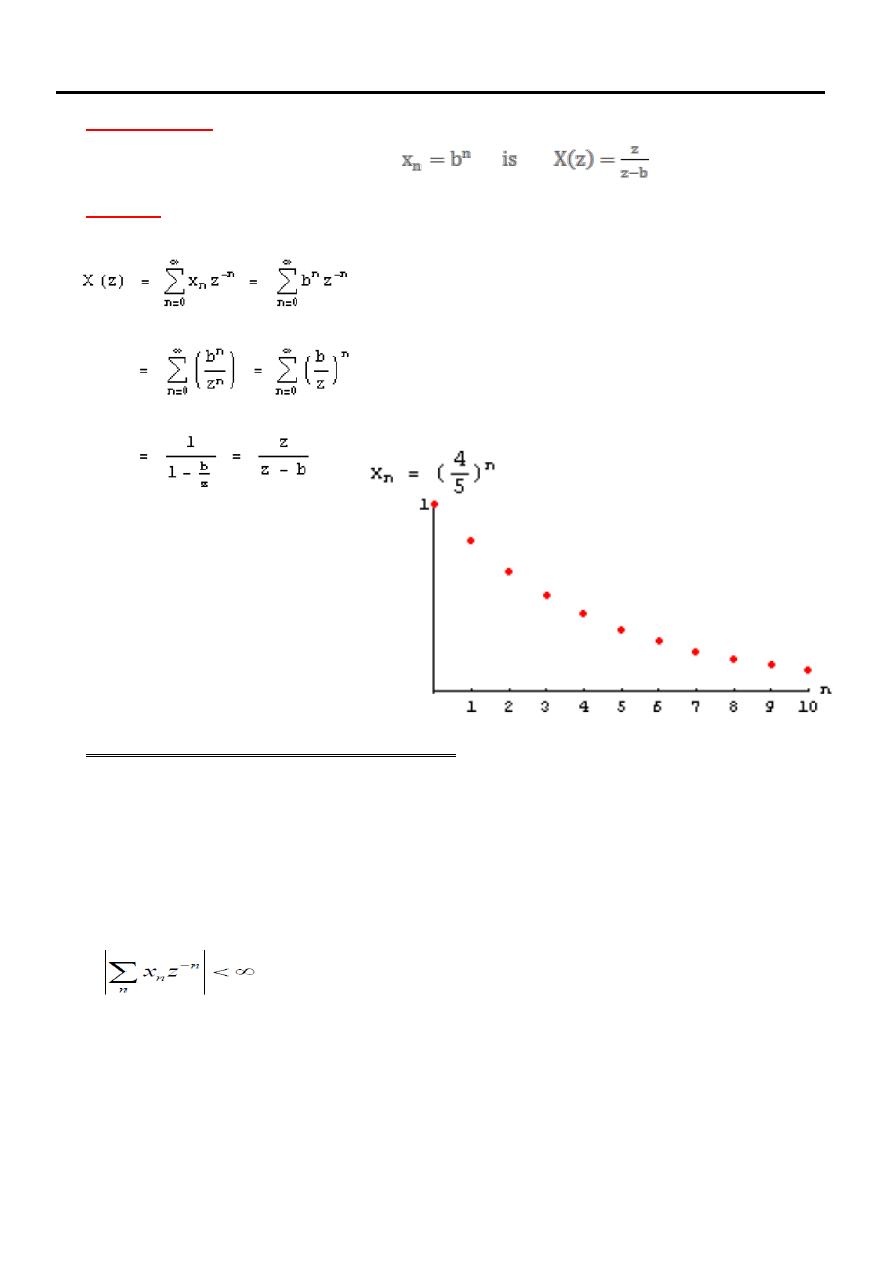
:
(3)
Example
transform of the sequence
-
The z
Solution
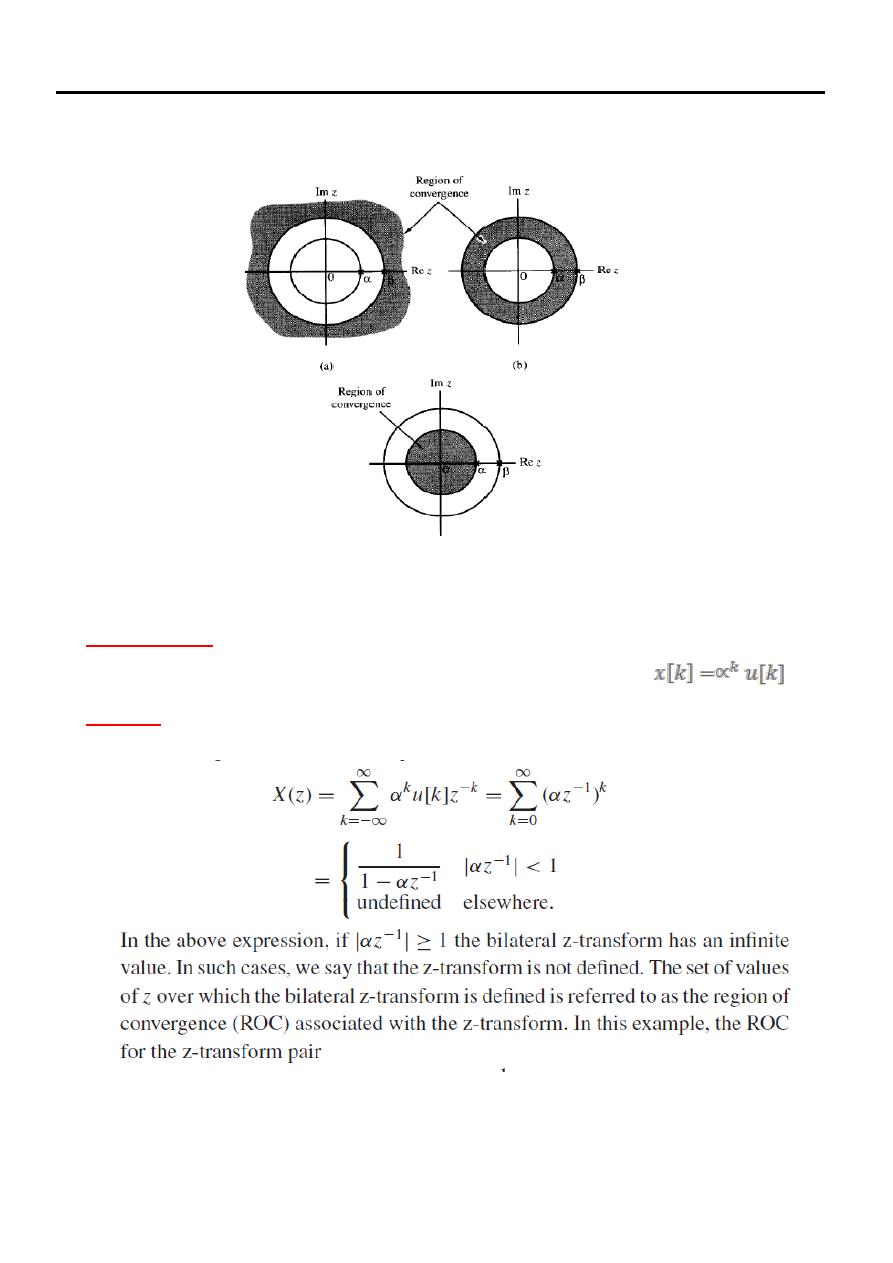
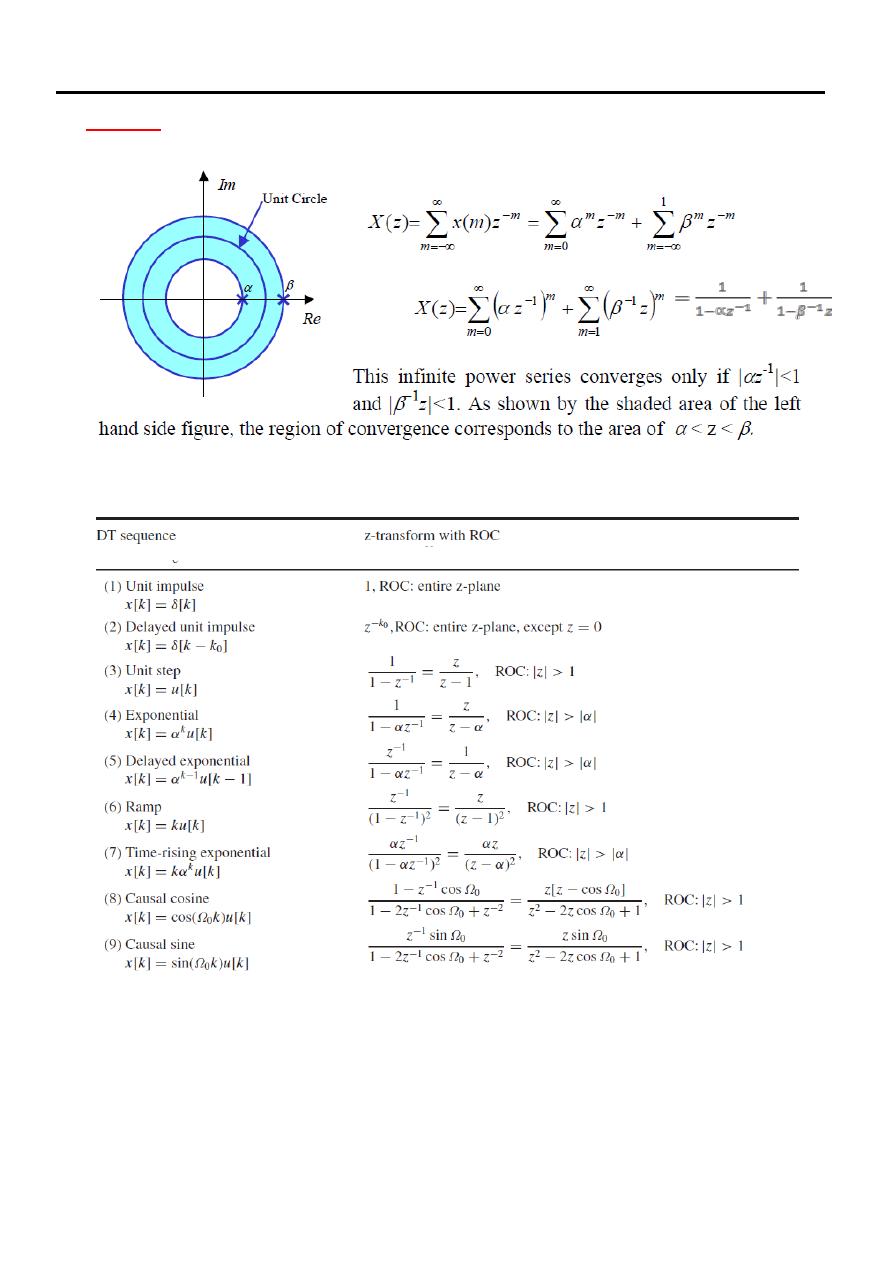
The Region of Convergence (ROC)
Since the z-transform is an infinite power series, it exists only for those values of the
variable z for which the series converges to a finite sum. The Region of convergence
(ROC) is the set of points z in the complex plane, for which the summation is
bounded (converges).
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
6
Examples of ROCs shown in Figure (2)
Figure (2): Examples of Region of Convergence
:
(4)
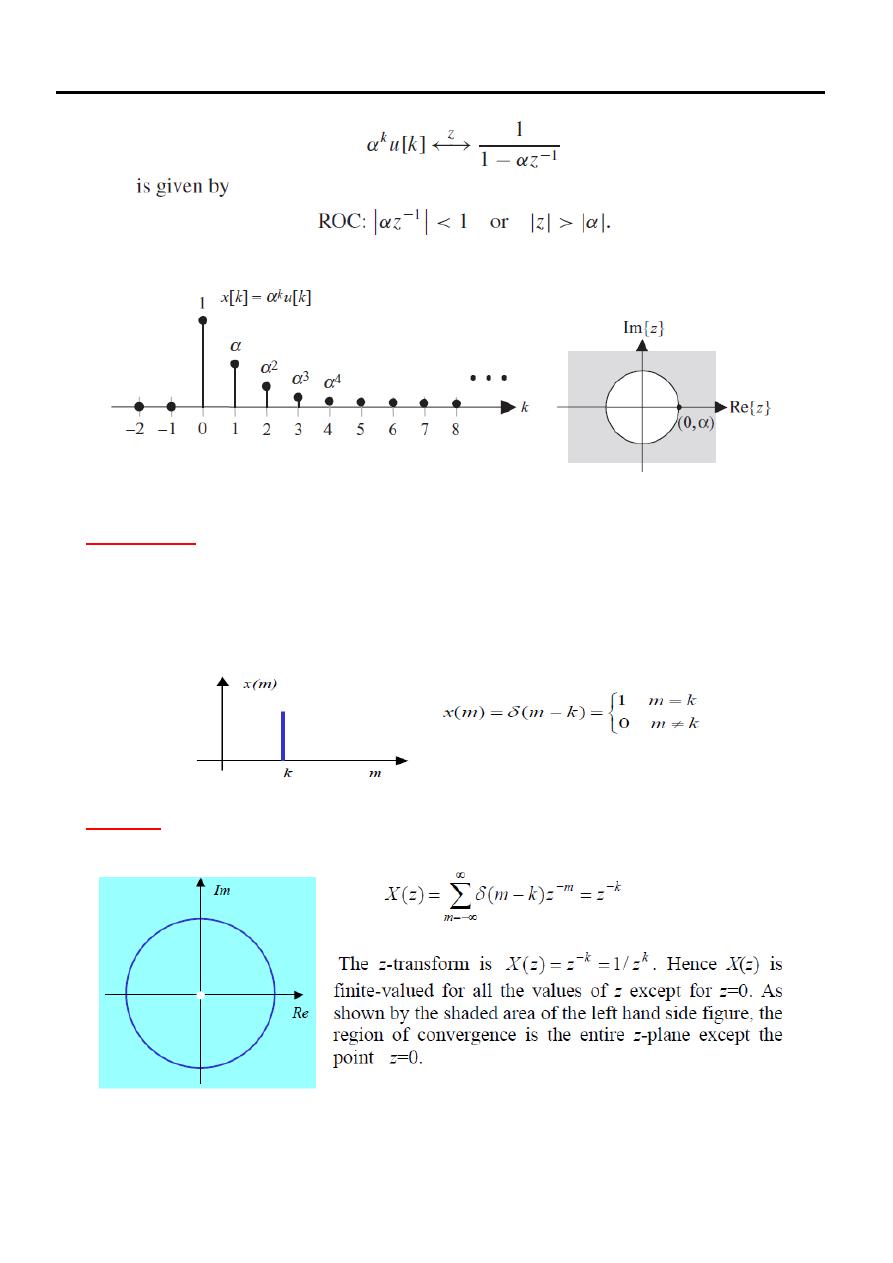
Example
Calculate the bilateral z-transform of the exponential sequence
Solution
(3)
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
7
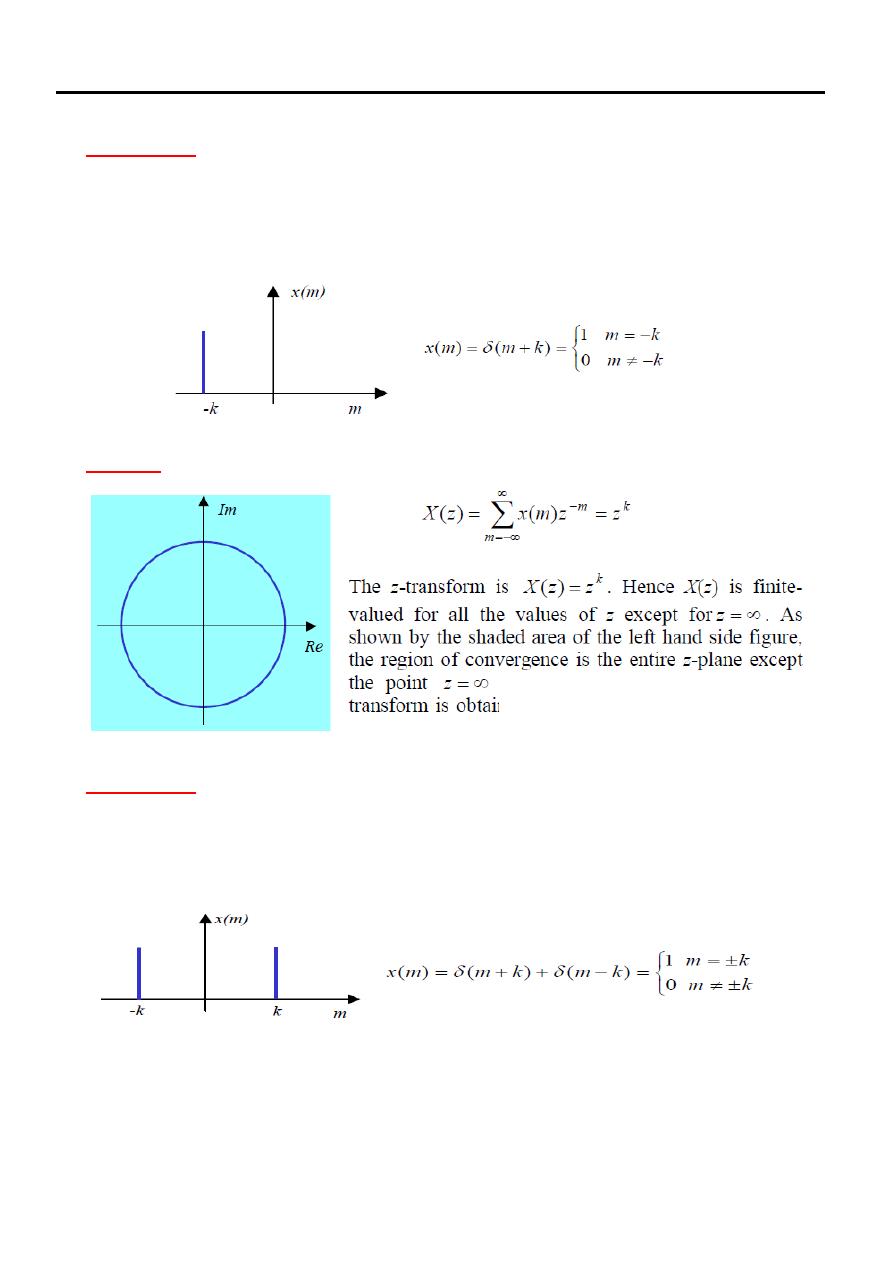
Example (5)
Determine the z-transform and the region of convergence of the following
signal
Solution
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
8
Example (6)
Determine the z-transform and the region of convergence of the following
signal
Solution
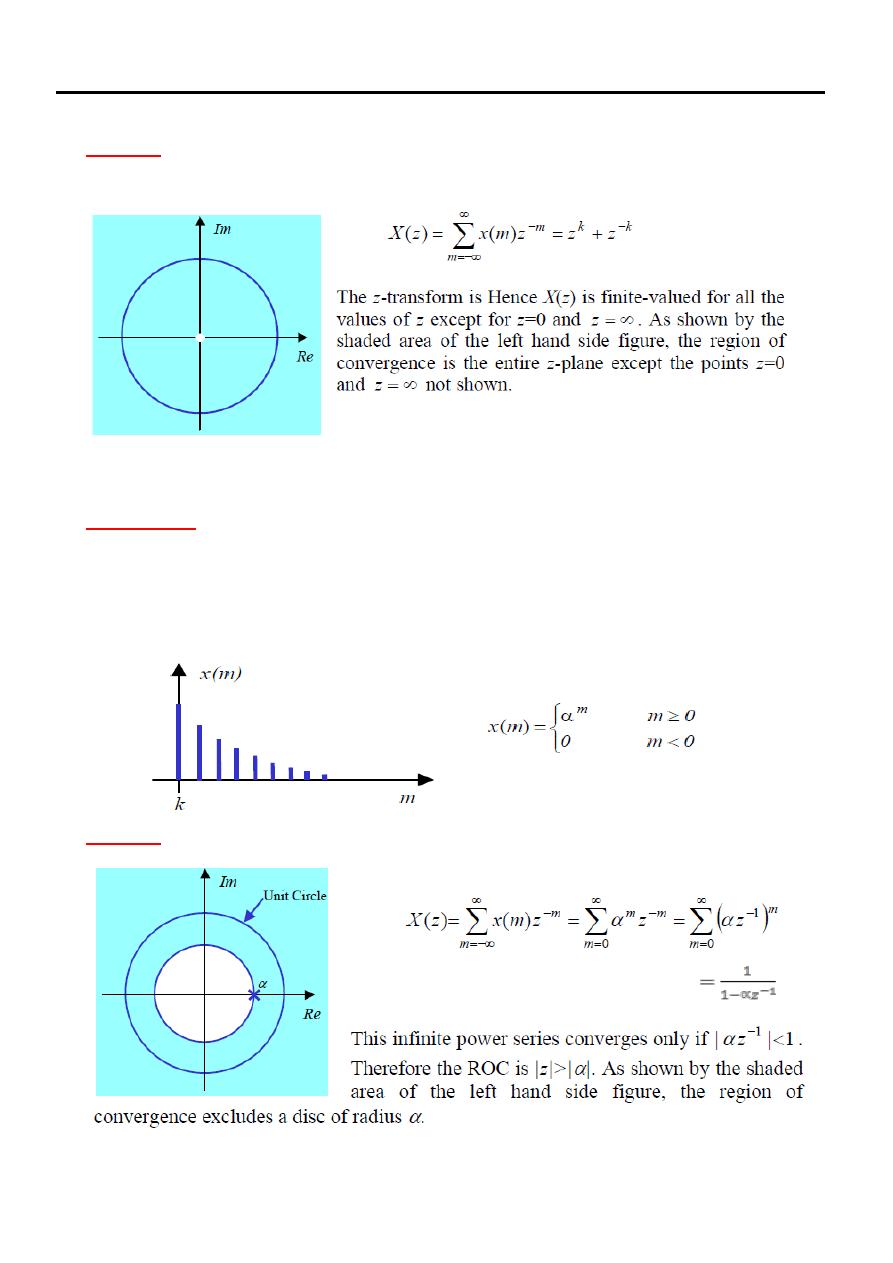
Example (7)
Determine the z-transform and the region of convergence of the following
signal
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
9
Solution
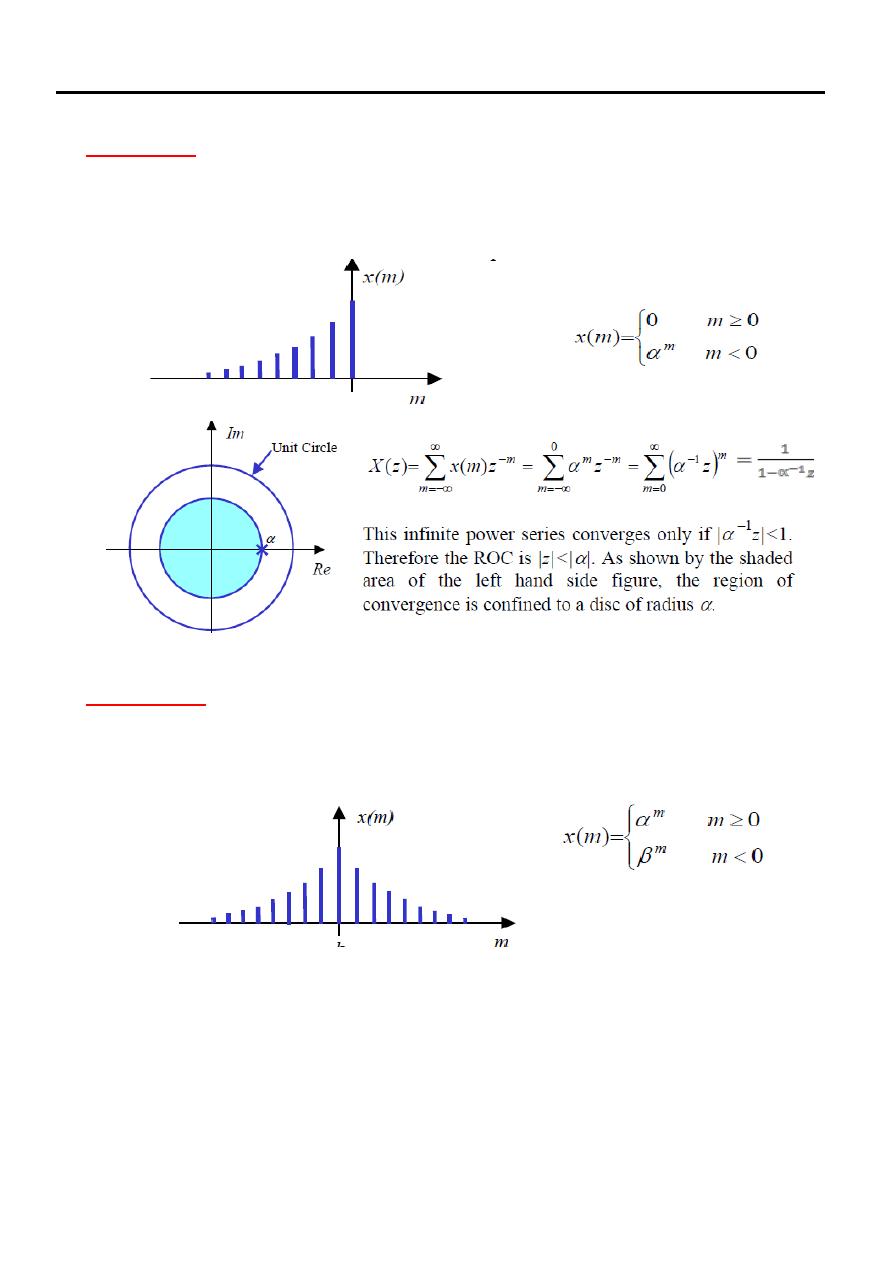
Example (8)
Determine the z-transform and the region of convergence of the following
signal
Solution
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
01
Example (9)
Determine the z-transform and region of convergence of the left-sided sequence
Example (10)
Determine the z-transform and the region of convergence
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
00
Solution
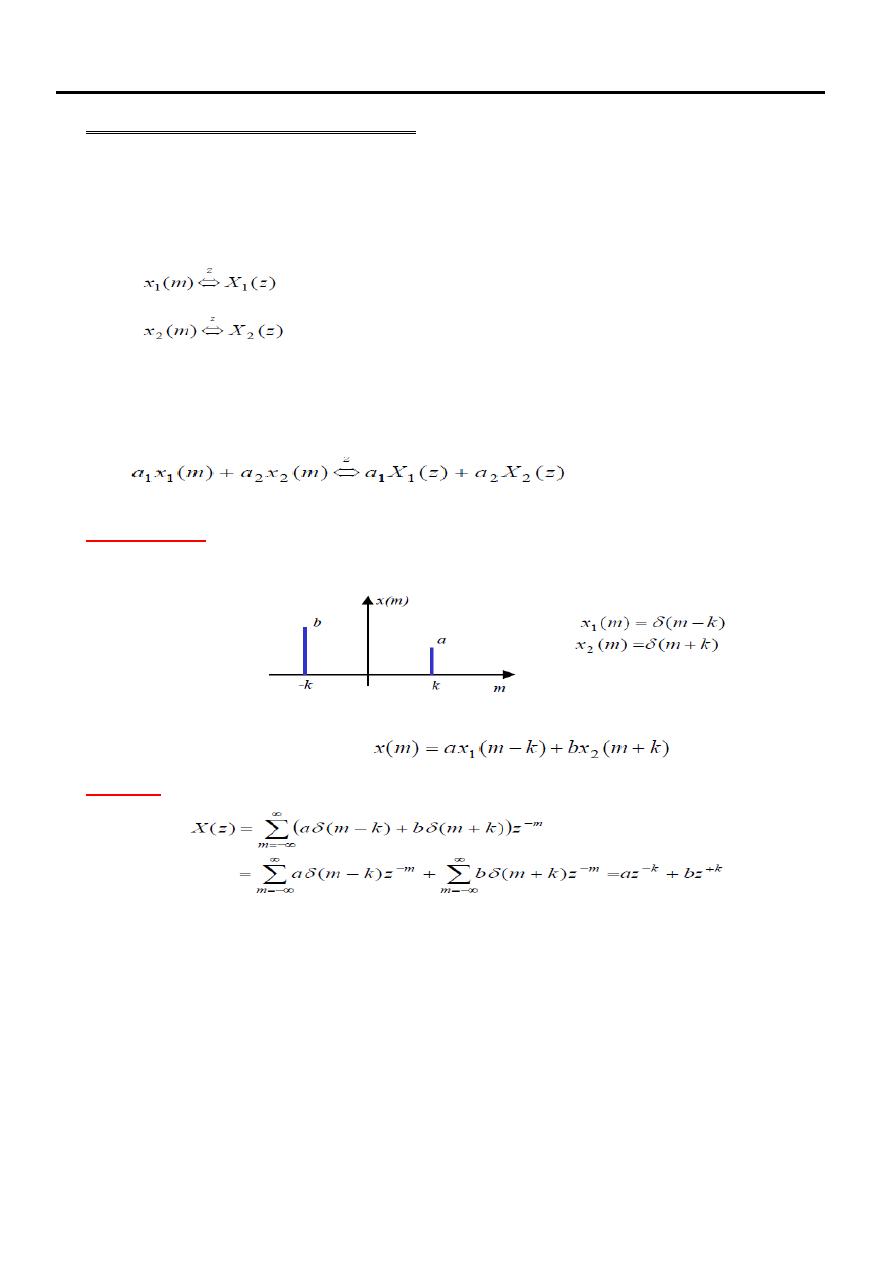
Table (1). Unilateral z-transform pairs for several causal DT sequences
Table (1):z-transform for transform pairs x[k]←→X(z)
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
02
Properties of the z-Transform
As z-transform is a generalisation of the Fourier transform of a sampled signal it has
similar properties to the Fourier Transform as described in the following.
Linearity Given two signals
then the linearity implies that for any linear combination of x1(m) and x2(m) we
have
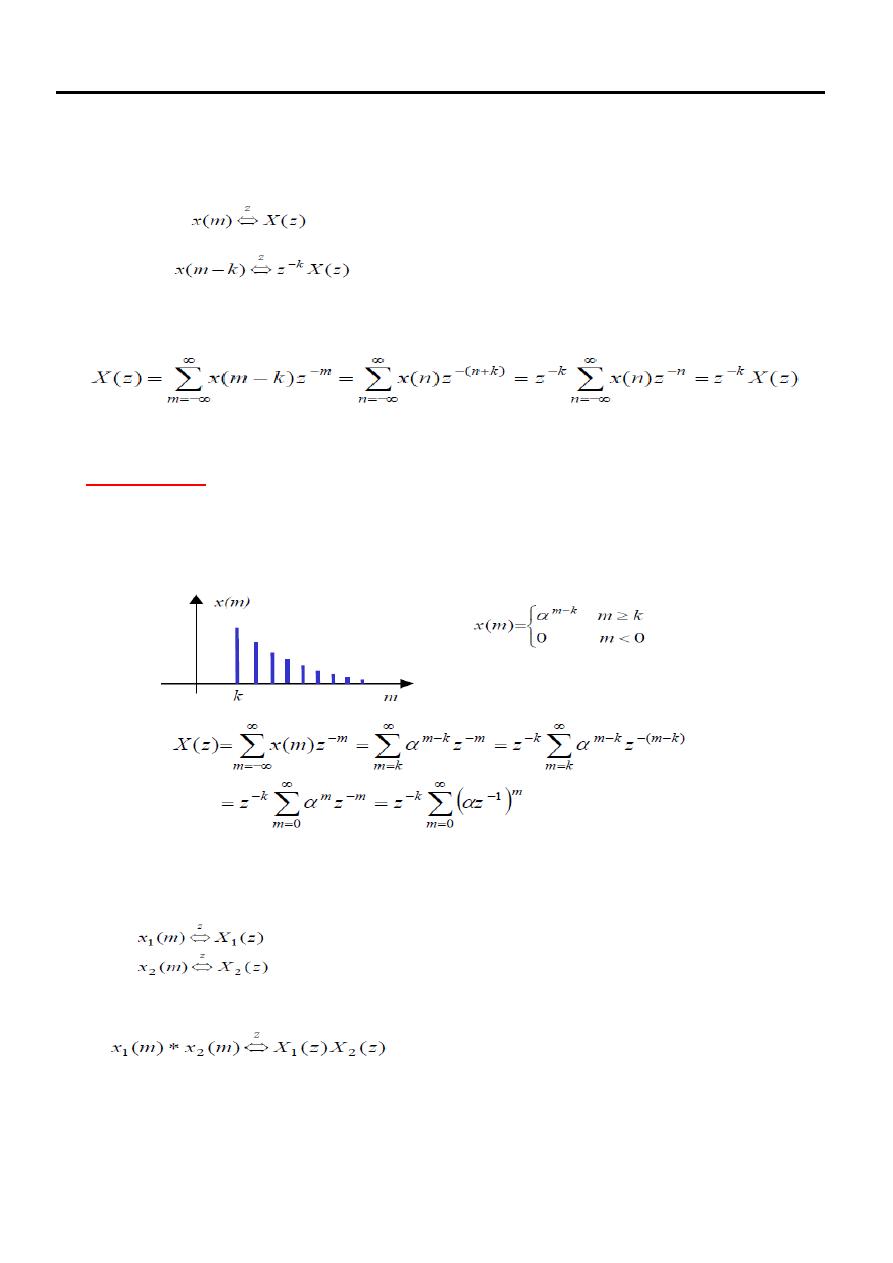
Example (11)
Given the following two signals determine the z transform
Determine the z-transform of
Solution
It is clear in the second line of the above solution that the z-transform of the
combination of two time domain signals x(m)=x1(m)+x2(m) can be written as the
sum of the z-transforms of the individual signals x1(m) and x2(m). (multiply z-
transform results of Ex (7) by a ,b respectively).
Signals & Systems Lecture Ten
Lecturer: Dr.Manal Khadhim.
03
Time Shifting
The variable z has a useful interpretation in terms of time delay. If
then
This property can be proved by taking the z-transform of x(m−k)
Example (12)
Determine the z-transform and region of convergence of a time-delayed version
of example (8) given as
Convolution
For two signals x1(m) and x2(m)
the convolutional property states that
