
1
Lec.2
Pediatics
6
th
stage
2016/8/29
Session notes
د.فارس الصواف
convulsion Hx
ebrile
F
1.generalized or focal
2.duration
3.vomiting
4.fever
5.LOC
6.deep sleep *post ictal*
7.Hx of trauma
8.cyanosis
9.drooling saliva
10.staring of the eyes upward.
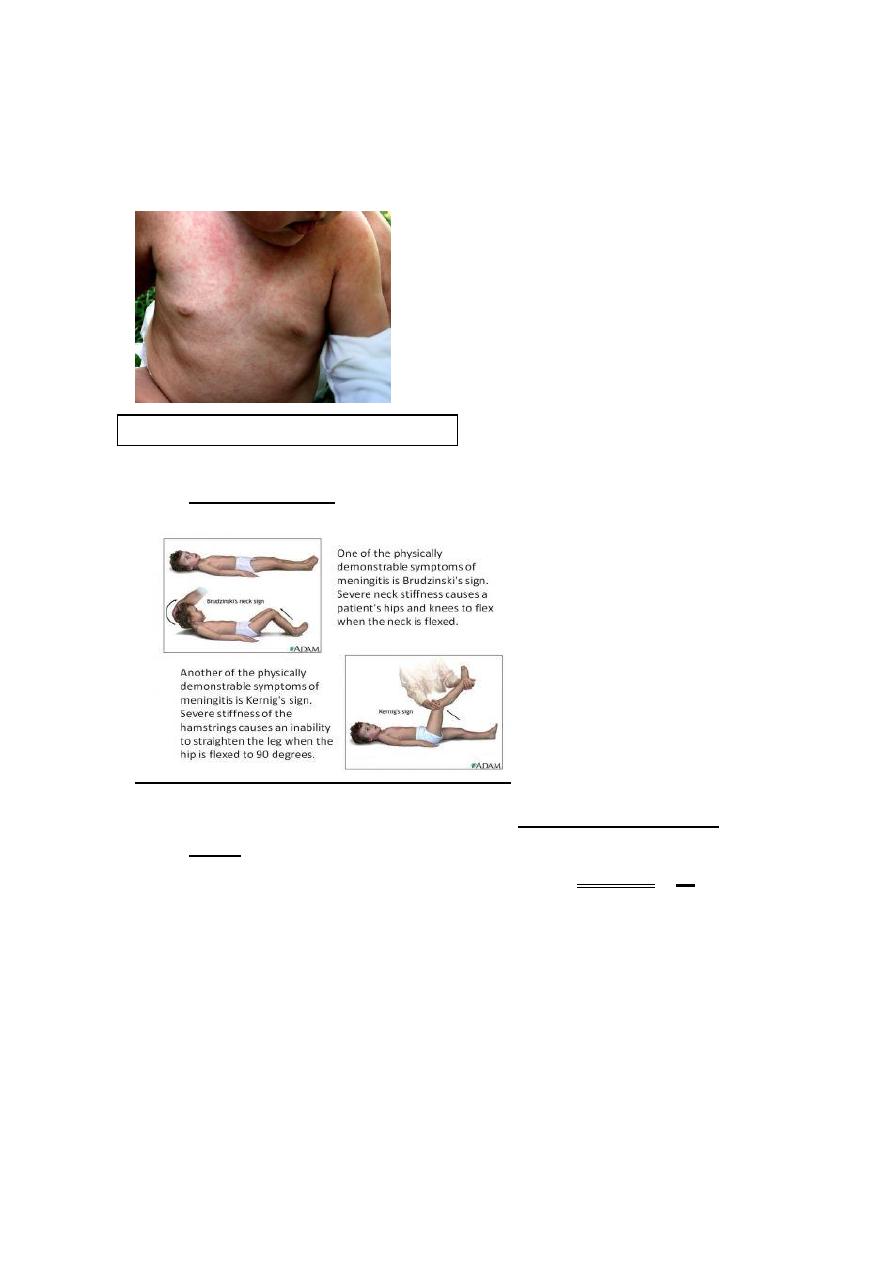
In physical exam ,try first to exclude meningitis ,
2
then labile it "febrile convulsion",may be due to:otitis
media,tonsillitis,UTI,roseola infantum(Human herpes virus-6:febrile
convulsion,high grade fever &morbilliform rash),pneumonia.
Signs of meningeal irritation neck stiffness,kernig sign
,brudizinski sign. All are done & confirmatively in >1yr old infant.
The most reliable sign in meningitis is :deterioration of mental
status(drowsiness).
Fever & convulsion in a child (<18mo)for the 1
st
attackLP is
mandatory.
We exclude raised ICP by fundoscopy(Atropine is given as dilator).
If parents refuse to do LP let them to sign on their
responsibility.
Try to explain the procedure to parents before doing it.
(30%)recurrence of febrile convulsion
Educate the parents
o put the head in lateral position(to avoid URT obstruction).
o wait (1-2)min .
Morbiliform rash in pt with roseola infantum
3
o try to reserve suppositories of anti-pyretics in the home
o always.
Investigations
1.RBS
2.S.electrolytes.
3.CBC
4.blood culture
5.CRP
6.LP
7.CXR
9.GUE
10.CT scan
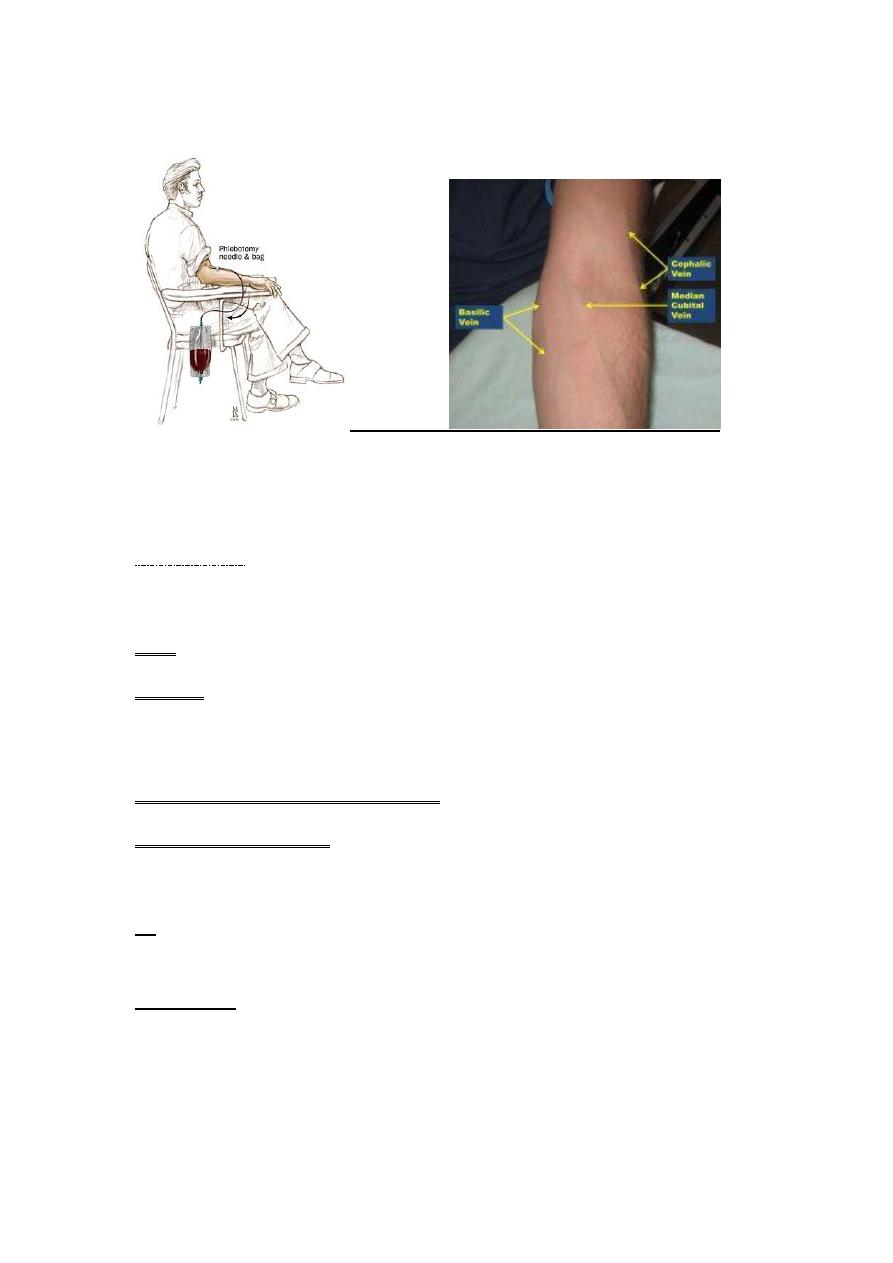
Procedure
1)pt in sitting position & lean forward or laterally directed.
2)sterilization of the area in circular pattern ,beginning from
centre &directed to periphery.
3.transverse line from iliac crest , space above,space below.
4.(2cc)is to be drawnif cloudy.

4
Most common organism is strep.pneumoniae
Try to calm the parents, say its benign problem.
If no meningitis ,put in your mind : viral infection :no need for Rx
only anti-pyretic.
Rx:-
Airway ,O2,suctioning,Iv cannula.
1/2 mg rectally diazepam.
0.25 mg/ kg IV diazepam.
*Next time if fever start:prophylactic diazepam is indicated .
**proper position of bottle feeding ( to avoid air )
POLYCYTHEMIA
Emergency in diabetic mother infant.
Send for PCV,if >65venesection.
5
Heart failure
*admission to ICU.
1.O2
2.IV line ((only give maintainence:150<6mo,125>6mo,after
1yr:100):chart input /output/weighing the child every day is v.imp(to see
if the edema resolved or NOT).
3.head up ,tube feeding "very imp".
4.diuretics.(1-2mg/kg).
5.digoxin
**don't diagnose H.F without cardiomegaly(is a must),tender
hepatomegaly,tachycardia/tachypnea,Galop rhythm.
Signs of H.F
1.dyspnea on exertion.
2.pulmonary rales.
3.tender hepatomegaly.

6
4.tachycardia.
Acute chest syndrome
Severe and may be fatal due to vasooclusive crises leading to
hypoxia and needs urgent exchange blood transfusion and
ventilation.
Rx
regular monthly blood transfusion to dilute the
sickling cells and prevent recurrence. Also give hydroxurea to
increase HBF
Pneumococcal vaccine should be given and also routine
vaccination for H.influenza .
Exclusive curative treatment is by BMT.
Renal failure "anuria"
Chart for input /output,Iv fluid/protein restriction/weighing every
day/if hyperkalemia correct/diuretics(1mg/kg/dose).
**then look for the cause.
Hypoglycemia

7
Presentation :-Hypotonia, lethargy,apathy,poor
feeding,jitteriness,and seizure are common.
Congestive heart failure,tachycardia,cyanosis,pallor,
diaphoresis,apnea,and hypothermia.
Rx:- Requires IV fluid ,hypertonic glucose as initial intravenous
bolus infusion of 200mg/kg [2ml/kg] 10%glucose, this should be
followed immediately by continuous infusion of 6-8mg/kg/min of
glucose.
Note :-aminophylline dose :250mg =250cc/ 375 mg.
Don't use salbutamol in child (<15-12mo)age.
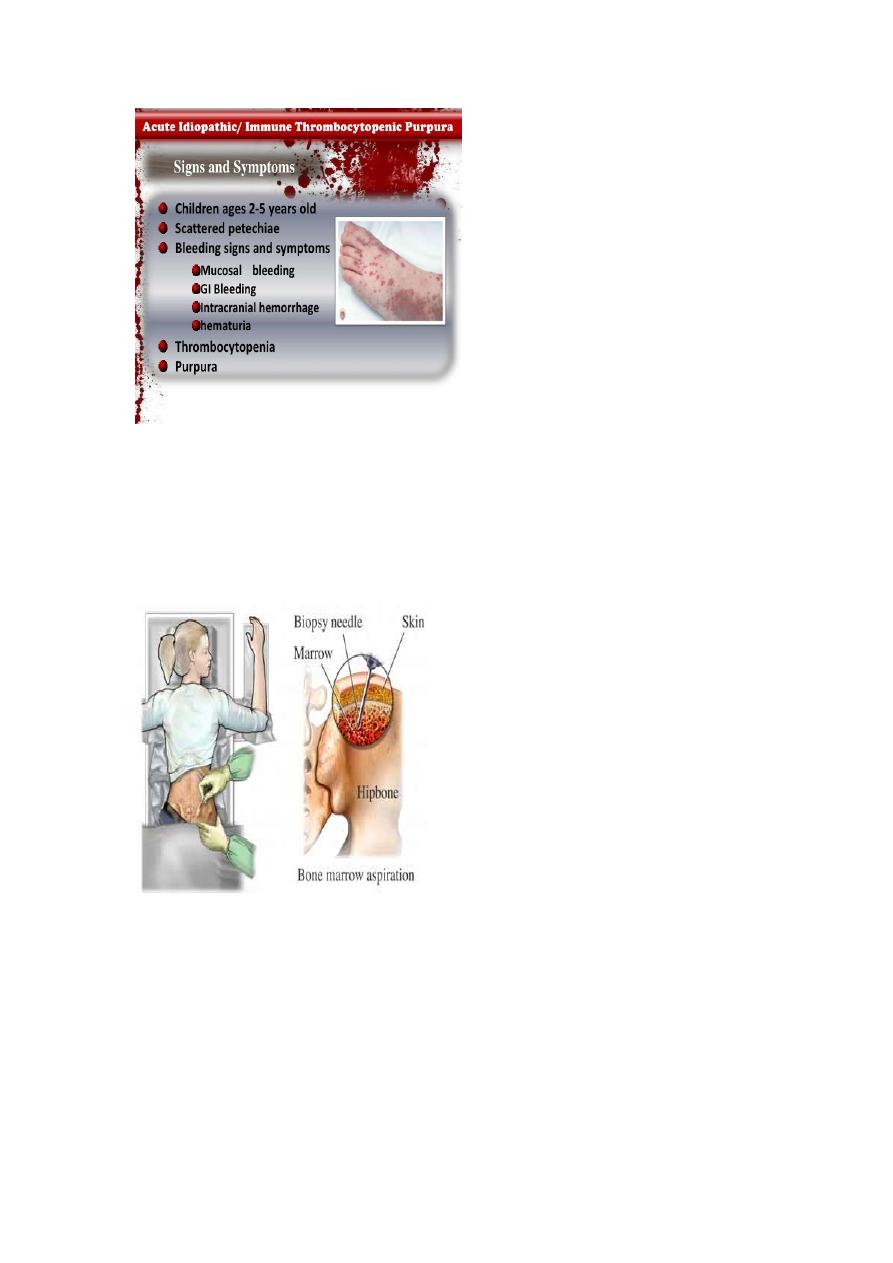
ITP
Hx of previous viral infection (2-3)wks.
Presentation:- in otherwise healthy infant in the absence of
Hepatosplenomegaly/bone pain/anemia/lymphadenopathy.
8
Investigations:-CBC ,blood filmreduction in platelets
count+absent of immature leucocytes.
Do n't do bleeding time test as this leads to severe bleeding
sometimes.
If leukemia is suspected Bone marrow exam is mandatory.
