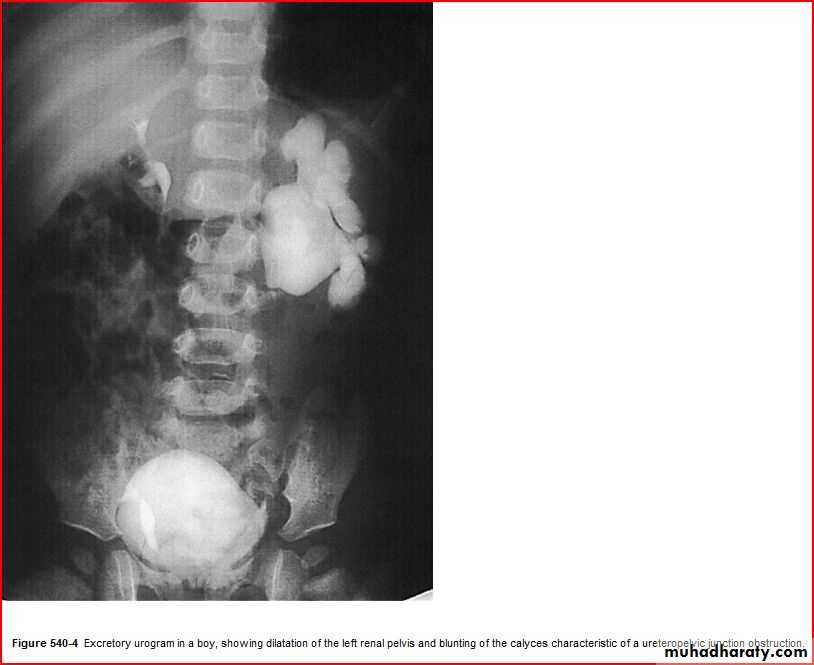
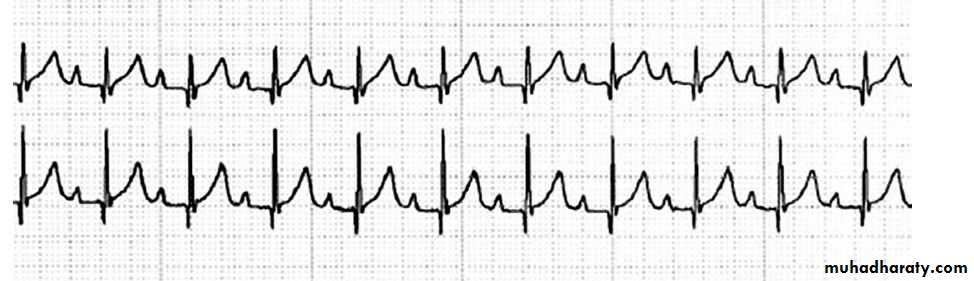
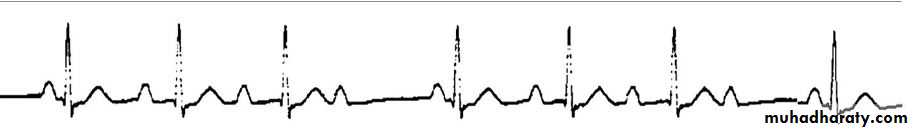
Pediatric E.C.G
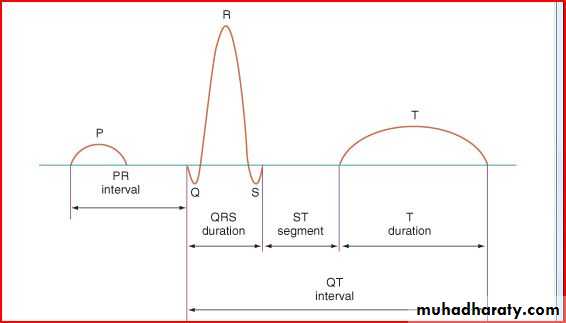
The electrocardiogram should be read systematicallyHeart rate (300/no.of large squares between R-R)OR(1500/NO.of small squares between R-R)
P wave axis (the P wave should be upright in leads I and aVF and inverted in lead Avr)-Normally less than 2-3 small squares (0.08-0.12 sec) wide and tall
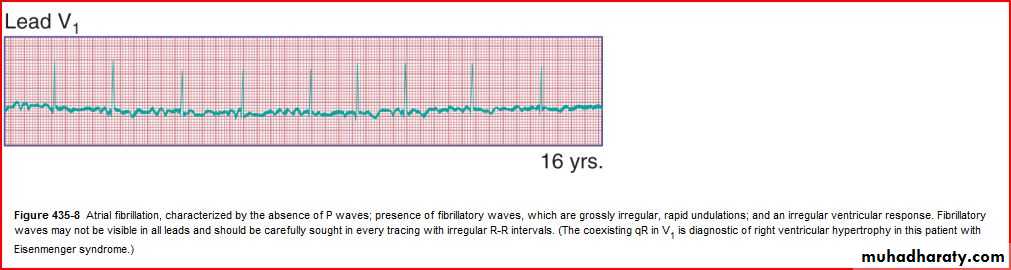
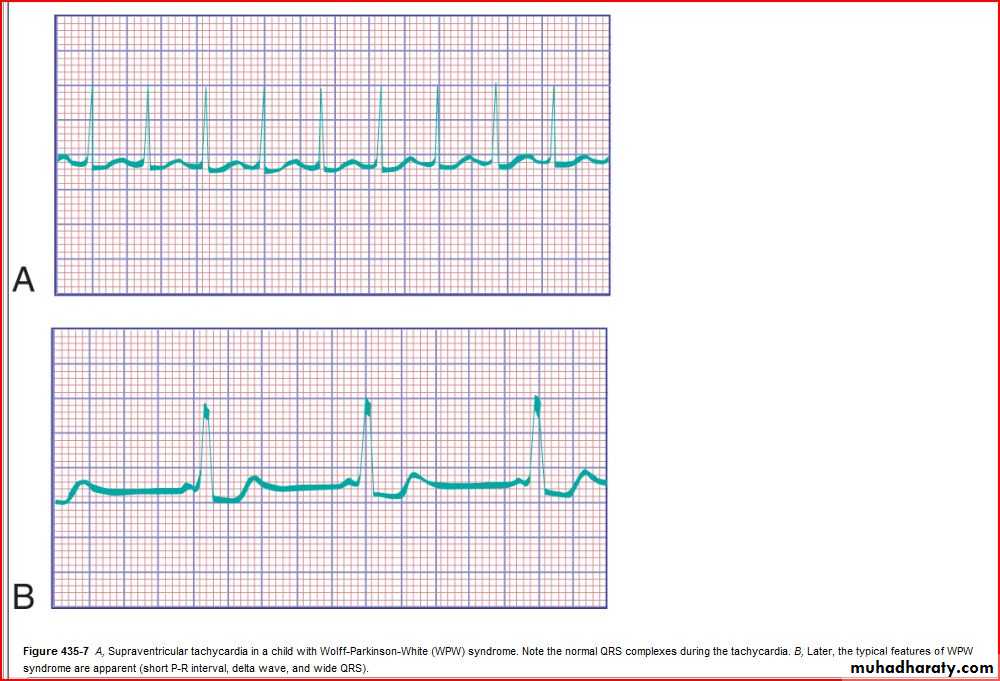
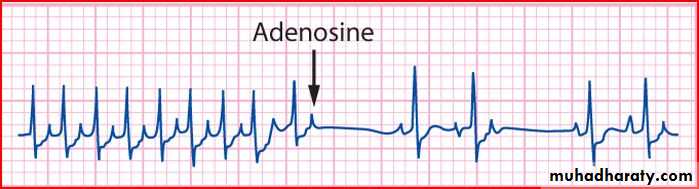
Rhythm
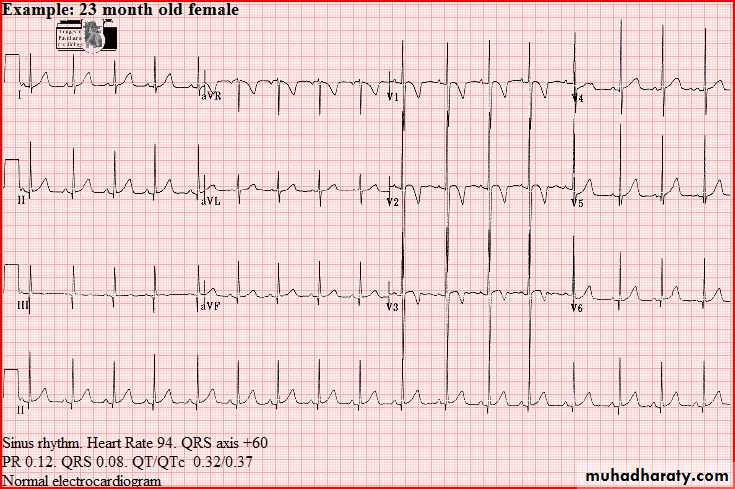
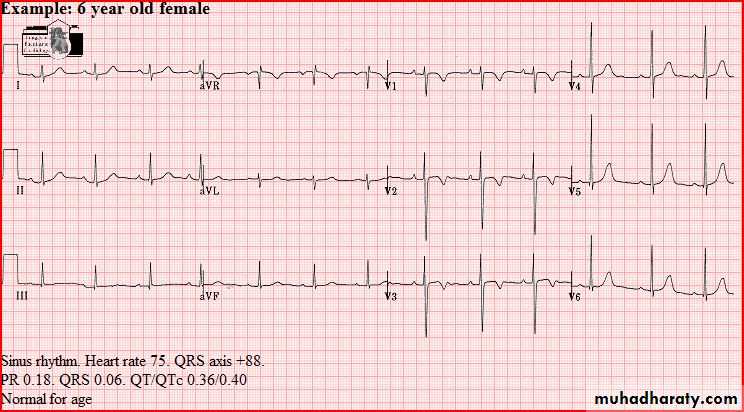
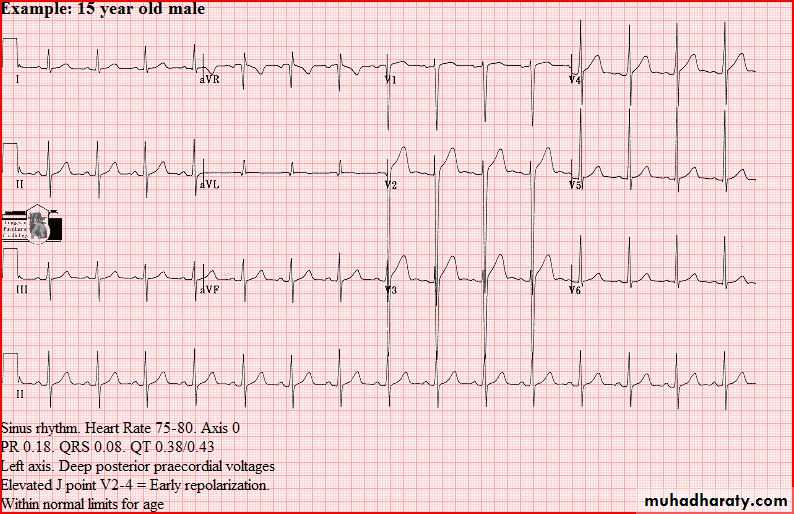
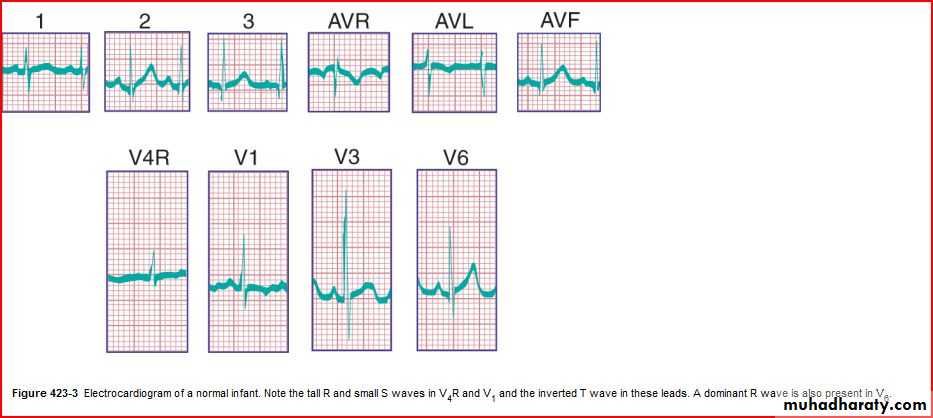
QRS axis (In a newborn, the mean QRS frontal-plane axis normally lies in the range of +110 to +180 degrees. The right-sided chest leads reveal a larger positive (R) than negative (S) wave and may do so for months or years because the right ventricle remains relatively thick throughout infancy-Over the years, the QRS axis gradually shifts leftward, and the right ventricular forces slowly regress. Leads V1, V3R, and V4R display a prominent R wave until 6 mo to 8 yr of age)
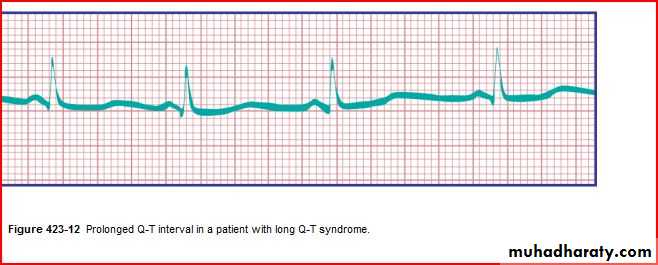
Intervals PR, QRS, QT/QTc (PR 3-5 SMALL SEQUARES)(QRS If longer than 2-3 square (0.08-0.12 sec), that's bundle branch block (BBB).
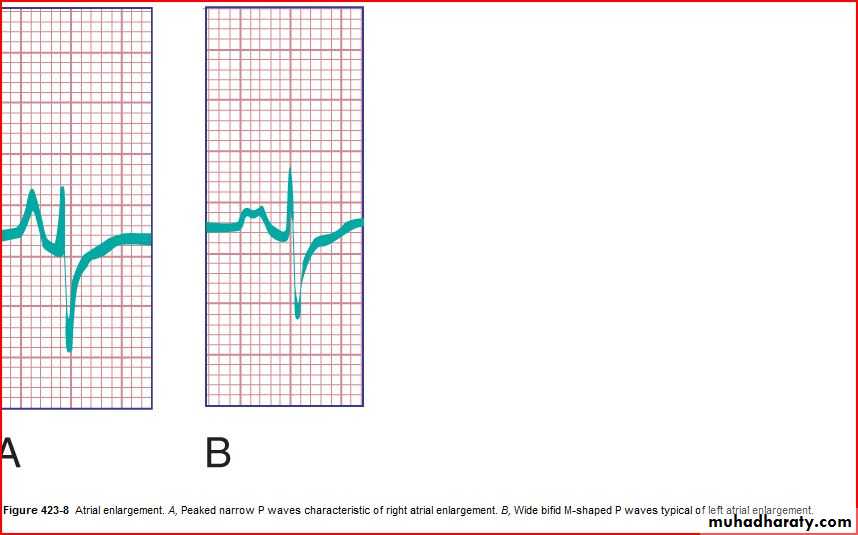
P wave amplitude and duration (RA and LA enlargement)
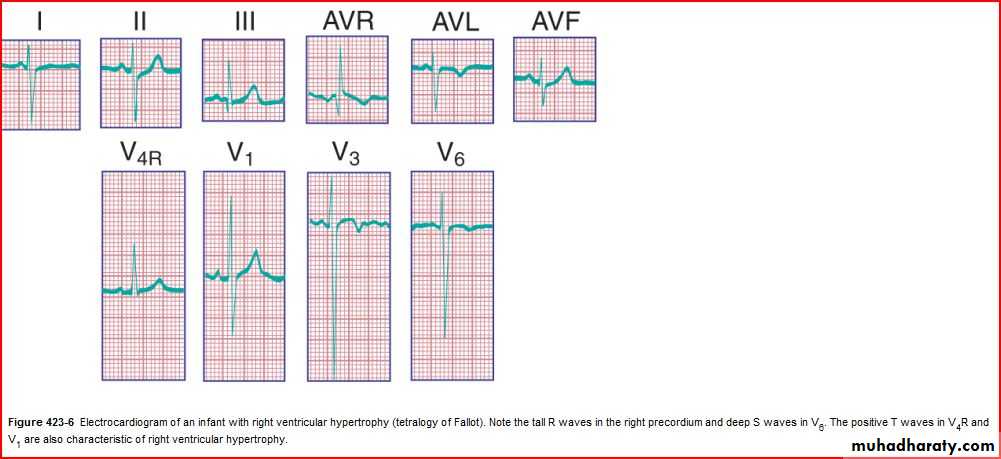
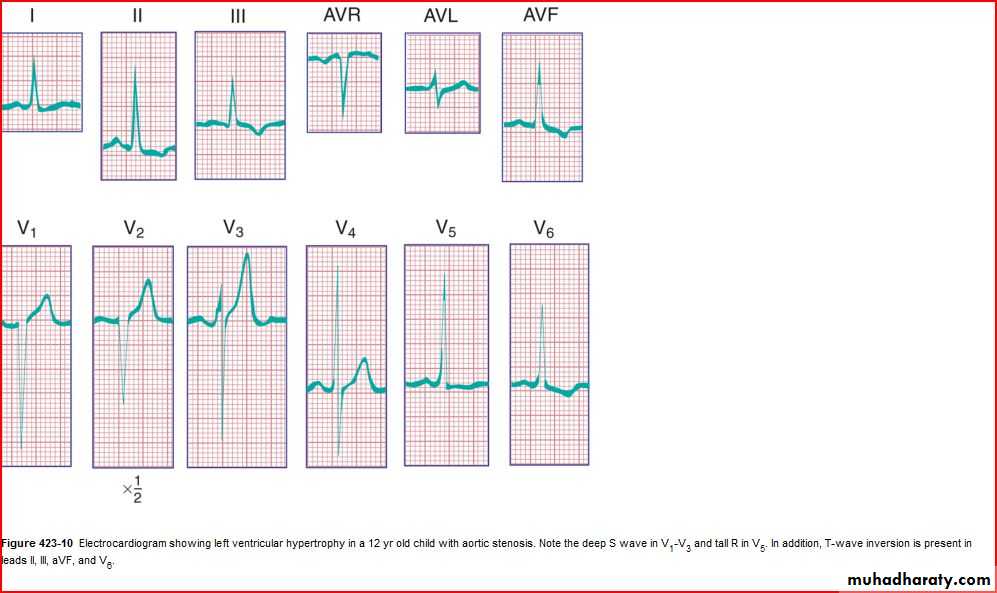
QRS amplitude, R/S ratio, Q waves (RVH – LVH)
ST segments and T wave
T wave inversion: Infants older than 48 hours of age should have inverted T waves in the right praecordial leads. These findings persist throughout childhood with inversion to V4 being accepted as normal. There is a progressive change to an upright T wave across the praecordial leads from left to right as the child grows older. Until 8 years of age an upright T wave in V1 is considered a sign of right ventricular hypertrophy. Many children will show persistence of an inverted T wave in V1 until their late teens
PR interval if > 5 small sequares is prolonged
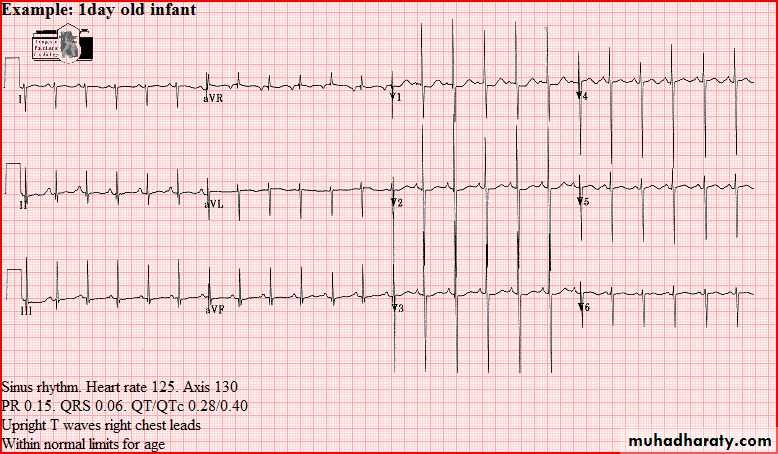
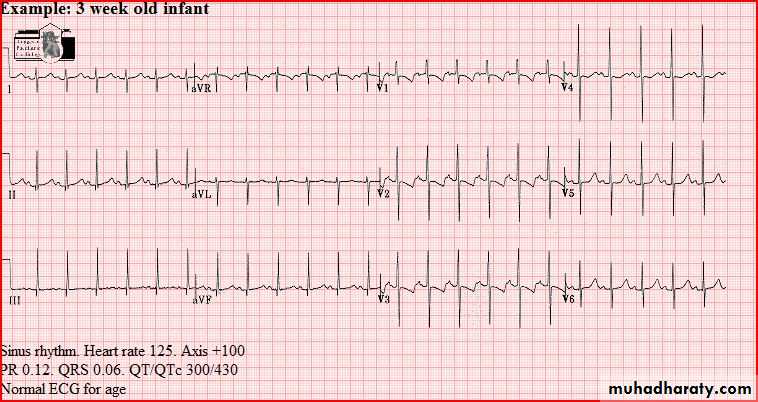
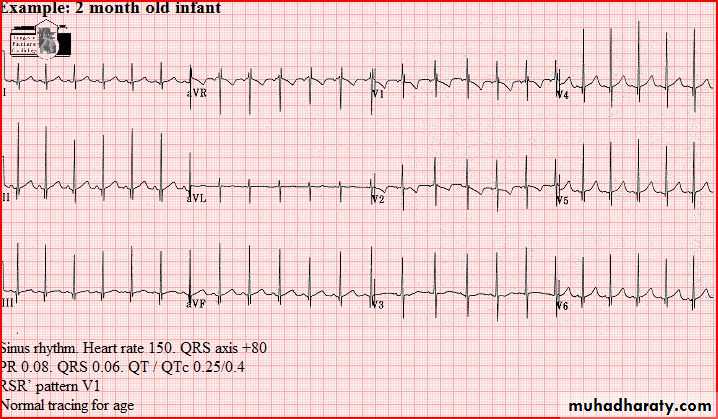
Normal tracings Examples of normal tracings for the different age groups follow, preceded by a general description of the characteristics of that age group.