Lec.1
Pediatrics
6
th
stage
2016/9/6
Session notes
د.مصطفى
Stagnation of development or frank loss of
-
Neurodegenerative diseases:
previously acquired skills.
Types :-
1.gray matter (neuronal degenerative disorders)
2.white matter (leukodystrophies)
disease.
disorder of movement & posture, static non progressive
-
:
CP
Hx of respiratory tract :-
Ask about cough,dyspnea,SOB,fever,sweating,malaise,relieving
&exacerbating factors of the cough&SOB,sleeping & feeding disturbance
,UOP,did you give any drug to relieve the condition?response?.
n,tone,power"
ITP"inspectio
-
:
CNS exam
Inspection
-posture
-conscious level
-dysmorphic features
-abnormal movements
-deformity
-muscle hypertrophy,atrophy"wasting"
-Gait
ممكن نضعها ضمن
cerebellar exam"coordination"
-
:
Tone
Passive movement.
احنة نسويها للمريض
-
Power:
Active movement
:"3" in the upper limbs.
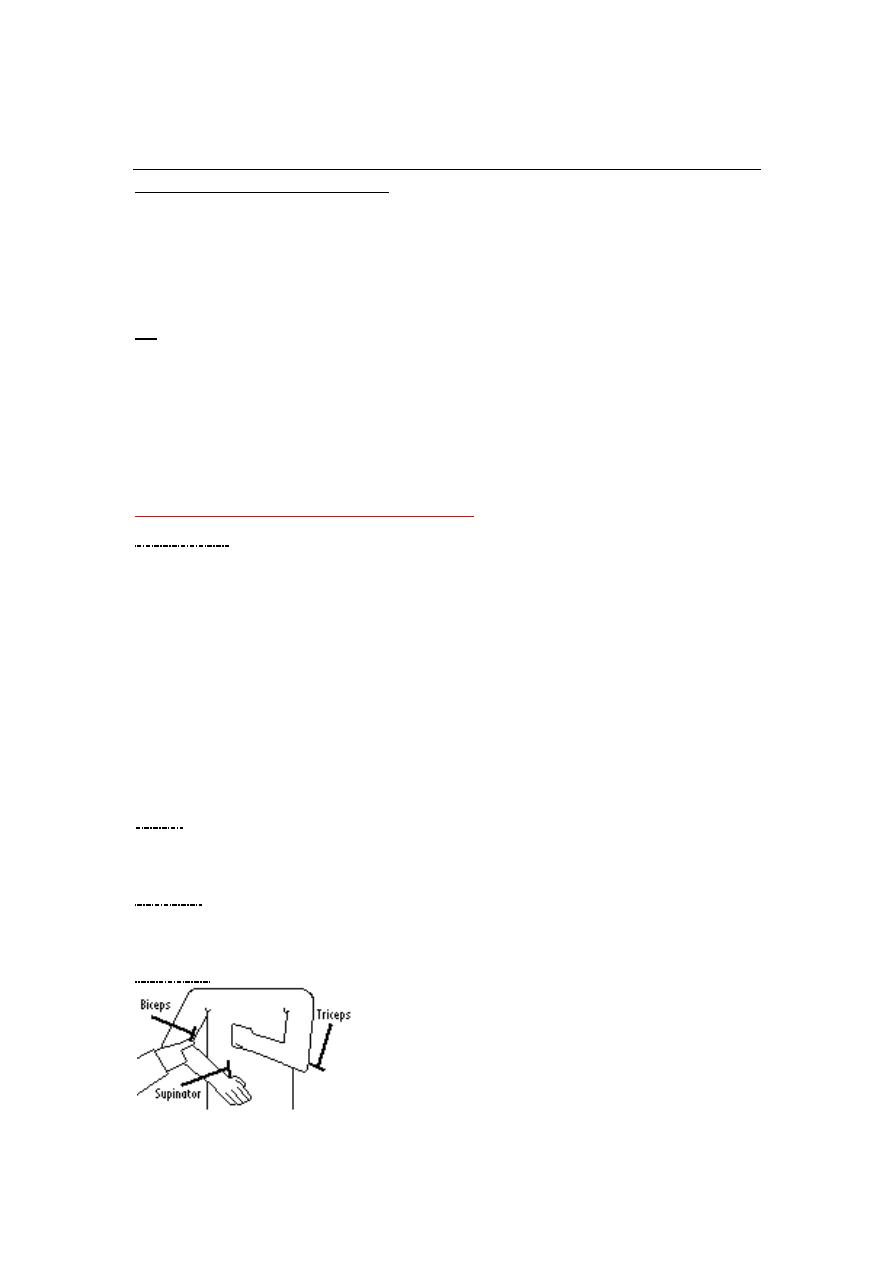
Reflexes

Biceps segment :- C5,C6.
Triceps segment :- C6,C7.
Supinator segment :- C5,C6.
Babiniski response :-
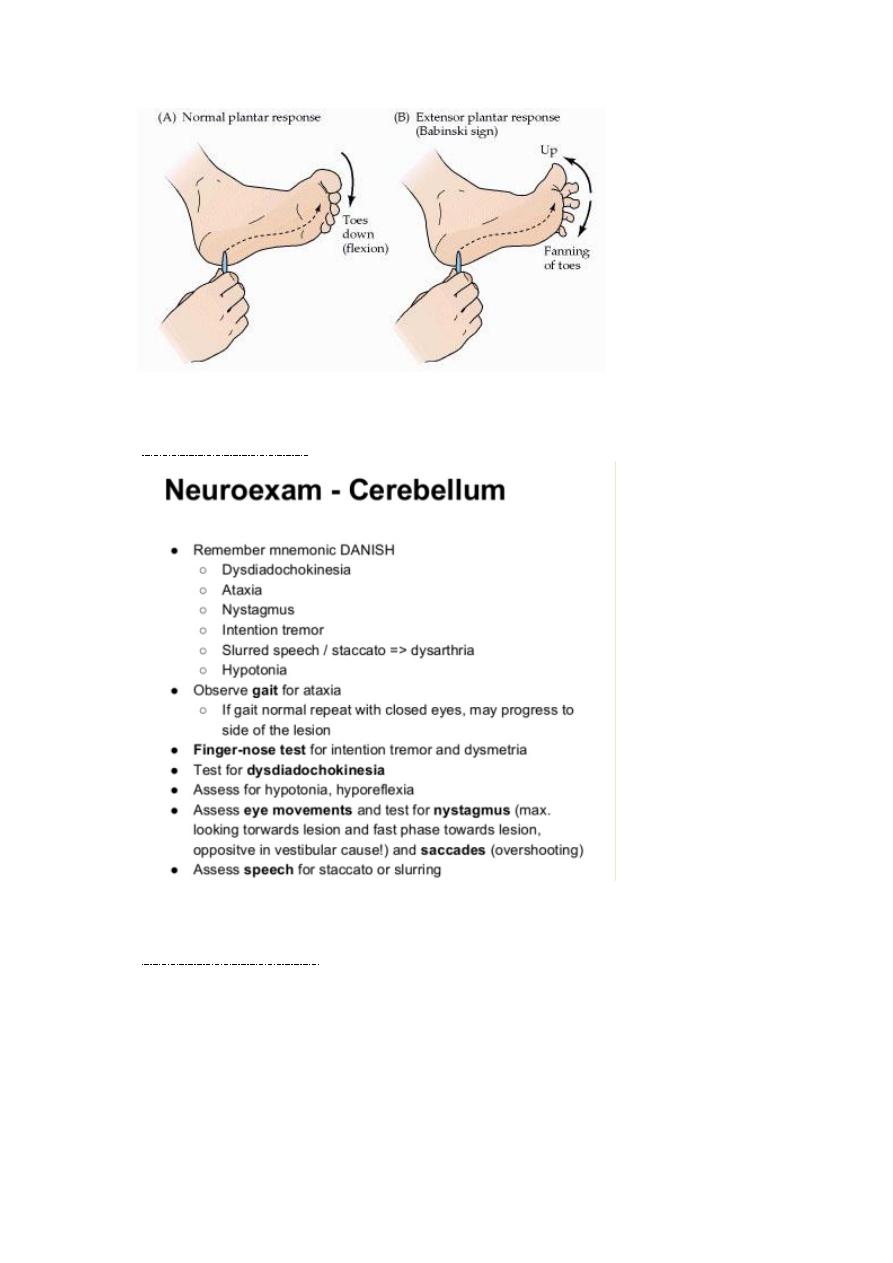
-
coordination tests:
-
Cranial nerves exam
-
Most important "7thCN"
**all of them previously explained in Dr.Aws'session.
Note:-mobius syndrome:-bilateral facial nerve palsy.

important
-
Examination of a child with acites:
1-expose the abdomen from the nipple to mid thigh.
2-inspection:-
Scars(surgical,traumatic),distension(try to kneel down to the level of the
abdomen to check for distension),from end of bed examine for
symmetry,movement with respiration,shape of abdomen(scaphoid or
flat)?state of umbilicus,any bruising,ecchymoses.
3-palpation(from Dr.Roua'session)
4-percussion"most imp.step)
Shifting dullness
Transmitting thrill
DDx of distended abdomen
o Flatus
o Fat
o Fluid
o Feces

o Fetus
Investigations :-
Paracentesis :-
Choose a point between ASIS + umbilicus "Mc burney's point of
appendicitis".
Draw fluid for analysis & therapeutic.
Color "if bloody:-malignancy & T.b//if grey,turbid=infection"
Send for Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level & Cytology"tumour
cells,lymphocytes".
Sometimes we use Ultrasound guidance if small to moderate
amount of ascetic fluid is present.
Distinguish wether this fluid exudate or transudate?
Causes of transudative ascites include the following:
1. Hepatic cirrhosis
2. Alcoholic hepatitis
3. Heart failure
4. Portal vein thrombosis
Causes of exudative ascites include the following:
1. Peritoneal carcinomatosis
2. Inflammation of the pancreas or biliary system
3. Nephrotic syndrome
4. Peritonitis
**replace the pt with fluid or intravenous serum albumin (IV) because
this fluid is third space fluid loss(preventing hypotension).
Respiratory tract examination steps
General exam
1.consciousness
2.cyanosis

3.flaring alae nasi
4.head nodding with the use of accessory muscle.
5.wheeze,stridor:audible noisy breathing.
6.count the RR "over one minute".
7.pale ?
8.dysmorphic features.
9.tracheal tug
examination of the chest
1) exposure:from neck to umbilicus.
2) inspection
1. signs of respiratory distress
2. shape of the chest:pectus excavatum ,pectus carinatum,Barrel chest
:in emphysema& asthma.
3. any scar
4. movement with respiration
5. mode of respiration
3)Palpation : Tracheal deviation , apex beat ,chest expansion(4cm is
norml:decreased in restrictive airway diseases),vocal fremitus, palpate
the liver (palpable in bronchiolitis).
4)Percussion:-on the clavicle (by middle finger)
From axillae
o From anterior compare side to side
o From mid axillary line
o From back
tactile fremitus "44"2yrs&above.
o On percussion if stony dullPleural effusion.
o If Dullconsolidation
o If hyperresonantpneumothorax
o If resonantnormal lung.
5)auscultation :- comment on air entry , type of breathing , added
sounds(rhonchi,crepitation"fine or coarse",pleural rub).
Types of breathing

RR "normal values"
(0-2) mo >60 (tachypnic).
(2mo-12)mo >50 (tachypnic).
(12mo-5yrs)>40 (tachypnic).
HR (normal values)
Newborn 90-180 BPM
Infant 90-160 BPM
2yrs-6yrs (80-140)BPM
6yrs (100-110) BPM
Signs of meningitis :-done previously in Dr.Aws'session.
