
PEDIATRICS OSCE
Stagiaire
NMC-MCM
2016-2017

Part A

OSCE 1 Match the following
A. PROTECTIVE FACTORS IN BREAST MILK
1.
Bile salt stimulated Lipase A. Inhibits E.coli
2.
Par amino Benzoic acid B. CNS growth factor
3.
Bifidus Factor C. Kills amoeba & giardia
4.
Lactoferrin D. Protects against
malaria
5.
Human Beta Casomorphin E. Promotes Lactobacilli
B. TRACE ELEMENT DEFICIENCY
1. Copper A. Hyperglycemia
2. Selenium B. Central Scotoma
3. Chromium C. Cardiomyopathy
4. Molybdenum D. Reddening of Hair
5. Manganese E. Refractory Anemia

OSCE 2
6 Hours after ingesting 10 tablets from his grandfather’s
medicine box, a 4yr old child is brought to ER with nausea
vomiting and restlessness. O/E, His vitals; RR-50/min ,HR-
60/min ,BP-70/40mmhg. Auscultation reveals Bilateral
wheeze. ECG shows Sinus Bradycardia. CBG done at ER is
40 mg/dl .
1. What is the likely poison?
2. Mechanism of toxicity?
3. Steps in managment?
4. Drug of choice?
5. Indication for ECMO?

OSCE-3 TRUE OR FALSE
Regarding Rett disorder,
1. X linked recessive disorder - True or False
2. Affects predominantly girls - True or False
3. Microcephaly noted at birth - True or false
4. EEG normal in most children - True or false
5. Hand wringing movements are typical-True
or false.

OSCE-4
Match the Organism with the condition associated:
1. Meliodosis A. HHV-8
2. Pontiac fever B. Coxsackie virus
3. Oroya fever C. Corona virus
4. Swimming pool granuloma D. Bartonella bacillifomis
5. Bornholm disease E. Treponema pallidum
6. Ecthyma gangrenosum F. Aspergillus fumigatus
7. Condyloma lata G. Mycobacterium marinum
8. Malt workers lung H. Psudomonas aeruginosa
9. SARS I. Burkholderia pseudomallei
10. Kaposi sarcoma J. Legionella micdadei

OSCE-5
Meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MCV)
1. Dosage and administration
2. Composition of vaccine
3. Contra indication for vaccine
4. IAP Recommendations for use: (any 2)
5. Which vaccine cannot be co-administered
with MCV?

OSCE-6
MATCH THE FOLLOWING:
1. Ujjawala A. Safe Motherhood
services
2. The Sharda act B. NRHM
3. Kishori Shakthi Yojana C. Child trafficking
4. ASHA D. Child marriage
prevention
5. Vandemataram Scheme E. Adolescent girl health.

OSCE 7
MYCOPHENOLATE MOFETIL
1. Mechanism of Action
2. Indications (ANY 4)
3. Dose
4. Serious Adverse Effects
5. Drug Interactions (ANY 2)

OSCE 8
Identify the colour coding & Type of container used for
disposing these Health Care Wastes:
1. Disinfectants
2. IV sets
3. Syringes
4. Soiled Linen
5. Discarded Medicine
6. Biopsy Specimen
7. Used Gloves
8. Packaging Material
9. Placenta
10. Broken Glass

OSCE 9
Obtain history from a mother who has brought
her 6 yrs old child with history of unprovoked
seizures.
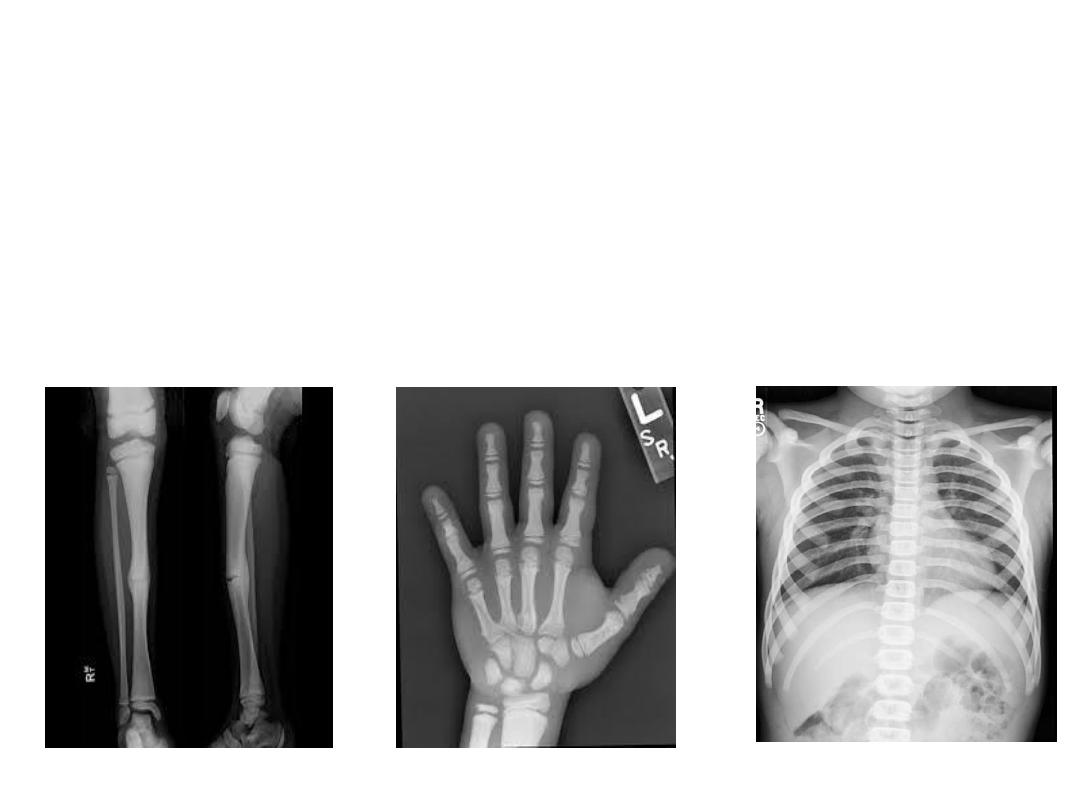
OSCE 10
X ray pictures of a 11 year old boy presenting
with recurrent long bone fractures

OSCE 10
1. Identify the condition?
2. Mode of inheritance ?
3. Underlying pathology?
4. Mention 1 differential diagnosis:
5. Other clinical Features in this condition? (Any 4)
OSCE 11

OSCE 11
1. What is the diagnosis?
(2)
2. What is the mode of inheritance?
(2)
3. What are the 4 stages?
(4)
4. Name 2 associated defects.
(2)

OSCE 12
• A 7 month old boy presents with
pallor , tri-phalangeal thumbs and
mild hepato-splenomegaly.
• Hb- 7g%, MCV- 100 fl, Reti.count-
< 1%, P.smear- normocytic to
macrocytic RBCS, normal WBCs
and platelets.
• Vitamin B12 and folate levels are
normal.
• Hb electrophoresis- raised HbF.

OSCE 12
1. What is the diagnosis?
2. What is the underlying defect?
3. What is the closest Differential diagnosis ?
4. Give two points to differentiate them .
5. Name at least one malignancy it can
predispose to.

OSCE 13
Regarding Hyponatremia,
1. What is the dreaded complication of overzealous
correction of hyponatremia?
2. This complication is more common during correction
of chronic hyponatremia - True/ False.
3. What is the advisable rate of correction of
hyponatremia to prevent this complication?
4. When do the clinical features develop?
5. What are the neurological features seen?
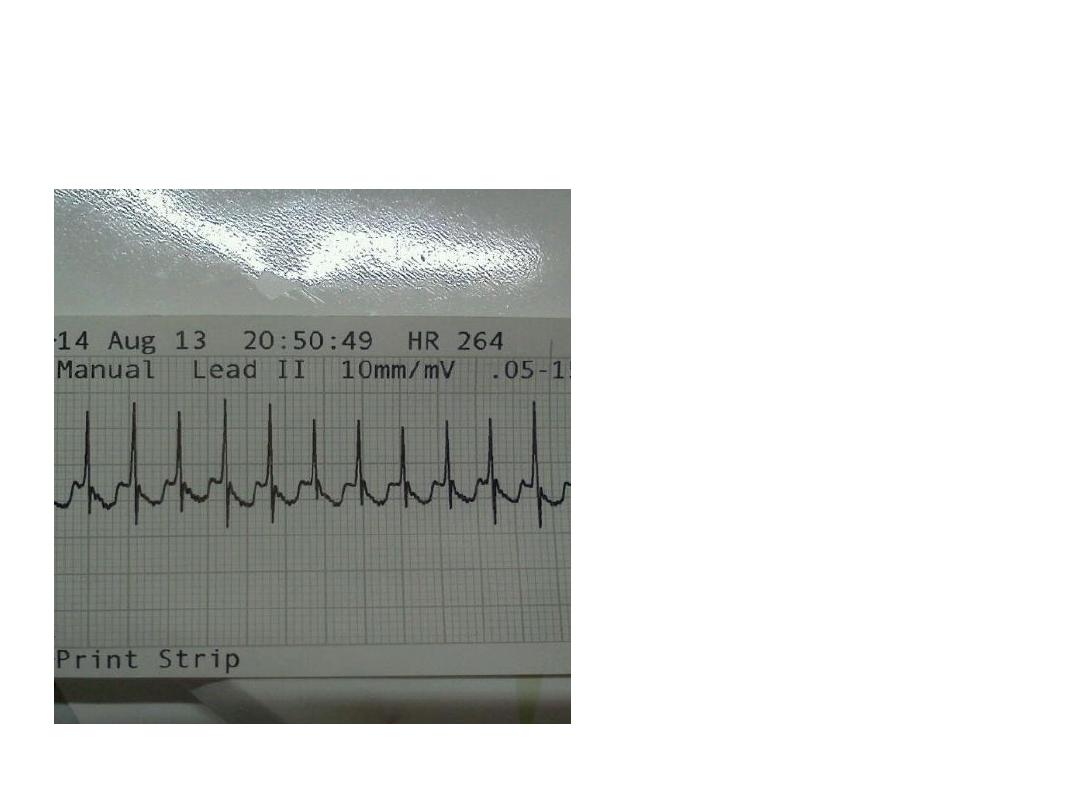
OSCE 14
1. What are the findings in
the E.C.G?
2. What is the diagnosis?
3. When should the E.C.G
be done to identify
these findings?
4. Which is the drug of
choice for this
condition?
5. Which drugs are contra-
indicated?

OSCE 15
• A new rapid test was compared with the gold standard of
blood culture for diagnosing enteric fever. Of total 500 fever
cases, Culture was positive in 400 children. Rapid test was
positive in 300 children and both culture and rapid test
were positive in 260 children.
• Calculate the following for the rapid test:
a)Sensitivity
(1)
b) Specificity
(1)
c) Positive predictive value
(2)
d) Negative predictive value (2)
e) Likelihood ratio positive
(2)
f) Likelihood ratio negative
(2)

OSCE 16
What is the developmental age at which the following
milestones are achieved?
1) Can tie shoelaces
Differentiate between morning and afternoon
2) Can button up clothes
Say which line is longer of two lines
3) Build tower of nine
Unbutton shirt
4) Picks up ball without falling
Uses ‘I’, ‘Me’ and ‘You’.
5) Kneels without support
Likes to take off shoes
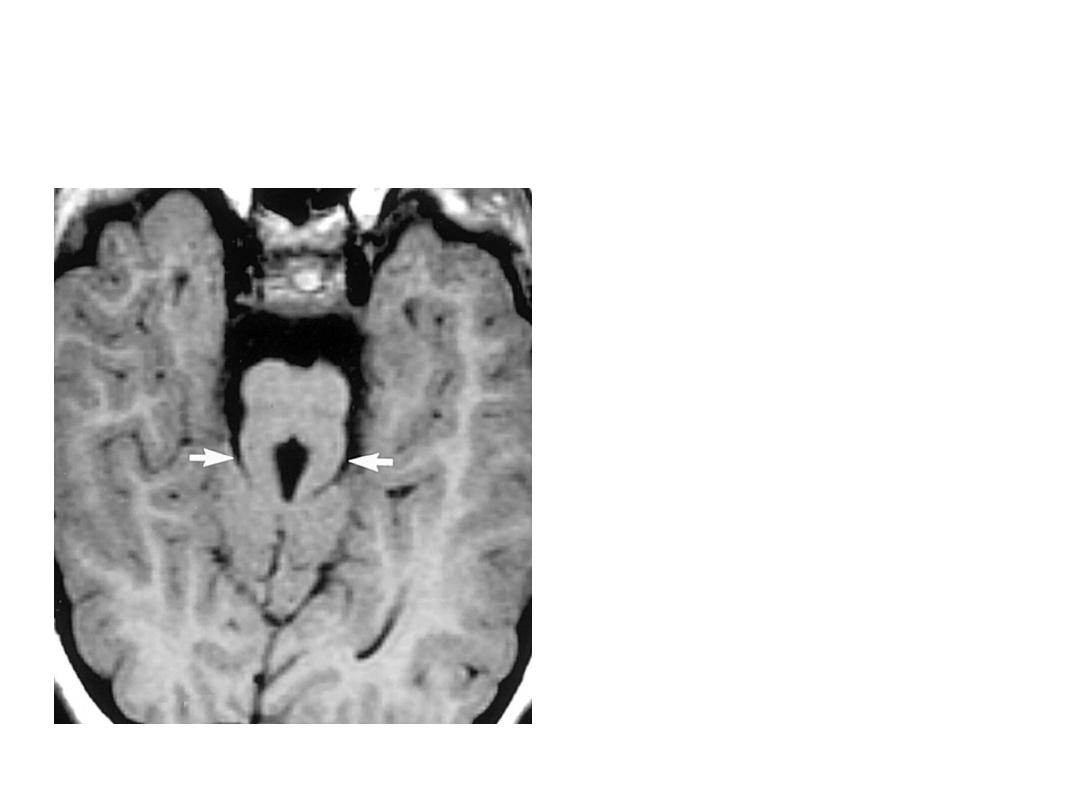
OSCE 17
1. What is the finding?
2. What is the diagnosis?
3. What causes this
finding on the MRI?
4. What is the mode of
inheritance?
5. Give two clinical
features of this
condition.

OSCE 18
A 11 year old child meets with a
RTA and has injury to the cervical
region. Vitals are as follows:
Airway partially obstructed
with snoring noises, RR-
20/min, paradoxical breathing,
mild retractions, SpO2- 94%
HR- 80/min, Peripheral pulses
are feeble, cold extremities,
BP- 86/34, cold perpheries
GCS- 13/15
PERL
1. What is the
physiological
status?(1)
2. What is the probable
cause of shock?(2)
3. What are the points
in favor of the
diagnosis?(2)
4. Initial steps in
management?(5)

OSCE 19
14 years old girl, history of recurrent muscle
cramps,
ABG- PH 7.6, PO2 99,HCO3 36,PCO2 47,SaO2 98.
1. Interpret the ABG
2. Is it compensated? What is the formula for
compensation?
3. What is the probable diagnosis?
4. What is the basic defect?
5. Mention 3 associated metabolic
abnormalities in this condition?

OSCE 20
HIV INFECTION IN NEW BORN
1. Mother has HIV infection and if baby is PCR positive
within 48 hrs. What does it imply?
2. Another baby born of HIV +ve mother tests negative
for PCR at 48 hrs but PCR turned positive within 7 –
90 days. What does it imply?
3. How early can P24 antigen test be done?
4. When do you label a newborn as HIV infected?
5. After what age is HIV ELISA considered the best test
for diagnosis and what is its sensitivity and specificity.

OSCE ANSWERS

OSCE 1 – Matched Answers
A. PROTECTIVE FACTORS IN BREAST MILK
1. Bile salt stimulated Lipase C. Kills amoeba & giardia
2. Par amino Benzoic acid D. Protects against malaria
3. Bifidus Factor E. Promotes Lactobacilli
4. Lactoferrin A. Inhibits E.coli
5. Human Beta Casomorphin B. CNS growth factor
B. TRACE ELEMENT DEFICIENCY
1. Copper E. Refractory Anemia
2. Selenium C. Cardiomyopathy
3. Chromium A. Hyperglycemia
4. Molybdenum B. Central Scotoma
5. Manganese D. Reddening of Hair

OSCE 2 ANSWER
1. Beta Blocker poisoining.
2. Decreased chronotropy, Decreased Inotropy
3. Orogastric lavage within 1hr of injection
Activated charcoal &
Whole bowel irrigation
4. Glucagon. (Other useful agents include Atropine,
high dose insulin & vasopressors)
5. Refractory Hypotension.

OSCE 3 ANSWER
Regarding Rett disorder,
1. X linked recessive disorder - False
2. Affects predominantly girls - True
3. Microcephaly noted at birth - False
4. EEG normal in most children - False
5. Hand wringing movements are typical -True

OSCE 4 ANSWER
Match the Organism with the condition associated:
1. Meliodosis I. Burkholderia pseudomallei
2. Pontiac fever J. Legionella micdadei
3. Oroya fever D. Bartonella bacilliformis
4. Swimming pool granuloma G. Mycobacterium marinum
5. Bornholm disease B. Coxsackie virus
6. Ecthyma gangrenosum H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
7. Condyloma lata E. Treponema pallidum
8. Malt workers lung F. Aspergillus Fumigatus
9. SARS C. Corona virus
10. Kaposi sarcoma A. HHV - 8

OSCE-5 ANSWER
1. 0.5ml, Intramuscular
Individuals 2yr-55yrs of age - Single dose
2. Quadrivalent A,C,Y and W-135 polysaccharide 4mcg
each conjugated to 48 mcg of diphtheria toxoid
3. Anphylaxis after previous dose of MCV
Guillian Barre Syndrome
4. Disease outbreaks , Immuno compromised children,
Lab/Health care workers, Saudi pilgrims, Students
5. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (Prevenaar)

OSCE 6 ANSWER
MATCH THE FOLLOWING:
1. Ujjawala C. Child Trafficking
2. The Sharda act D. Child Marriage Prevention
3. Kishori Shakthi Yojana E. Adolescent Girl Health
4. ASHA B. NRHM
5. Vandemataram Scheme A. Safe Motherhood Services

OSCE 7 ANSWER
1. Mechanism of Action – It inhibits inosine monophosphate
dehydrogenase, that is important for DNA formation
2. Indications: Nephrotic Syndrome, SLE, Rheumatoid Arthritis,
Inflammatory Bowel disease – Crohns Disease, ITP, Myasthenia
grevis, Polymyositis, Atopic dermatitis, Dermatomyositis, Auto
immune Hepatitis, Prophylaxis for Renal / Liver transplant Graft
rejection
3. Dose : 40 to50 mg/kg/day or 400 mg/m
2
twice daily
4.Serious Adverse Effects :
a) Blood Dyscrasias – Leukopenia / Pure Redcell Aplasia
b) GI Bleed / Perforation / Ulcers
5. Drug Interactions : Azathioprine, Cholestyramine, Norfloxacin,
Metronidazole, Rifampicin, Cyclosporin, Hormonal Contraceptives,
Antacids, Cotrimoxazole, Acyclovir/Gancyclovir/Valacyclovir

OSCE 8 ANSWER
Identify the colour coding & Type of container used for
disposing these Health Care Wastes:
1. Disinfectants – Black plastic bag
2. IV sets – Red plastic bag
3. Syringes – Blue Puncture proof container
4. Soiled Linen – Red Plastic Bag
5. Discarded Medicine – Black plastic bag
6. Biopsy Specimen – Yellow plastic Bag
7. Used Gloves – Red plastic bag
8. Packaging Material – Black plastic bag
9. Placenta – Yellow plastic bag
10. Broken Glass- Blue puncture proof container

OSCE 9 ANSWER
Checklist:
1) Introduces and establishes rapport.
2) Asks her to act out or re-create a seizure
3) Asks for Aura and automatism
4) Asks about headache and vomiting
5) Elicits h/o failure to thrive
6) Asks for details of medications used that may
precipitate seizure
7) Asks for details of anticonvulsant therapy

OSCE 9 ANSWER
8) Asks for compliance
9) Asks for family history
10)Asks for developmental history
11)Asks for birth and neonatal problem
12)Asks for the time of occurrence of seizures
13)Asks for frequency
14)Asks for precipitating factor like from fever.
15)Asks for personality change / school problem /
Intellectual deterioration.

OSCE 10 ANSWER
1. Pyknodysostosis
2. Autosomal recessive
3. Lysosomal disorder due to genetic deficiency of
Cathepsin K, which is important for normal
osteoclast function
4. Osteopetrosis
5. Short stature, Delayed closure of cranial sutures,
fronto-parietal bossing, short broad hands with
hypoplasia of nails, nasal beaking, proptosis,
obtuse mandibular gonial angle.

OSCE 11 ANSWER
1. Incontinentia pigmenti/ Bloch- Sulzberger disease.
2. X-Linked dominant
3. A) Vesicular streaks B) Hypekeratotic plaques
C) Pigmentary stage D) Hypopigmentation
4. Associated Defects:
i.
Dental: Delayed dentition, conical teeth, impaction
ii.
Skin: Alopecia, Nail dystrophy,
iii.
CNS: Dev.delay, microcephaly, spasticity, seizures
iv.
Ocular: Microphthalmos, optic atrophy, strabismus, cataracts,
retrolenticular masses, neo-vascularisation
v.
Skeletal defects.

OSCE 12 ANSWER
1. Diamond Blackfan syndrome.
2. Decrease in number and function of erythroid
precursors with probable insensitivity to EPO
3. TEC (Transient Erythroblastopenia of childhood)
4. Age of onset(TEC usually beyond 6 months),
MCV(normocytic in TEC), h/o preceding viral
infection( present in TEC), HbF& ADA( Both
increased in DBA)
5. AML, MDS, Osteosarcomas

OSCE 13 ANSWER
• Central Pontine Myelinolysis / Osmotic
demyelination syndrome.
• True
• Not > 12 meq/L/day.
• At least 2- 6 days after the rapid correction of
hyponatremia
• Spastic quadri/ paraparesis, Locked –in
syndrome, obtundation, seizures, dysarthria.

OSCE 14 ANSWER
1. Short PR interval, presence of Delta wave.
2. Wolf- Parkinson White syndrome
3. During resting stage when there is no
tachycardia.
4. Propanolol
5. Digoxin, CCBs.
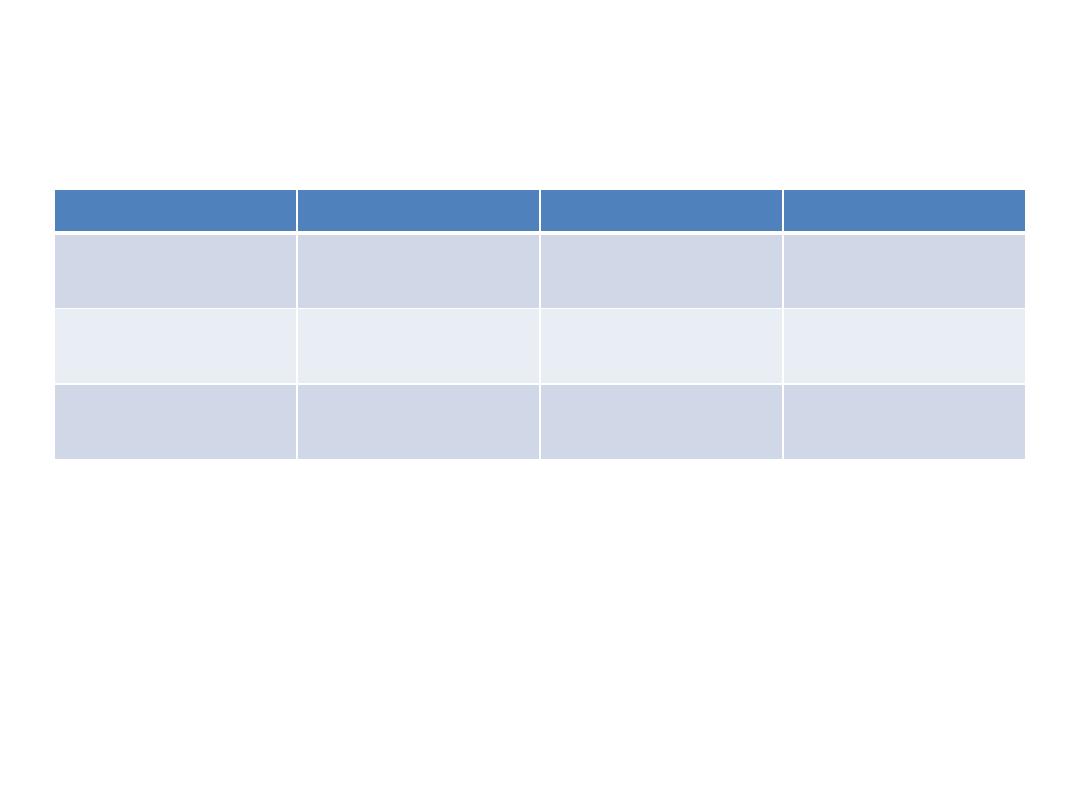
OSCE 15 ANSWER
Culture positive
Culture negative
Rapid test Positive
260
(a)
40
(b)
300
(a+b)- TEST positive
Rapid test negative
140
(c)
60
(d)
200
(c+d)- TEST negative
Total
400- DISEASE
positive
100- DISEASE
negative
500- TOTAL
SENSITIVITY- a/ a+c = 260/ 400 = 65%
SPECIFICITY – d/ b+d = 60/ 100 = 60%
POSITIVE PREDICTIVE VALUE- a/ a+b = 260/300= 87%
NEGATIVE PREDICTIVE VALUE – d/ c+d = 60/200 = 30%
LIKELIHOOD RATIO POSITIVE = Sensitivity/ 1- Specificity =0.65/ 0.4 = 1.625
LIKELIHOOD RATIO NEGATIVE = 1- Sensitivity/ Specificity = 0.35/ 0.6 = 0.58
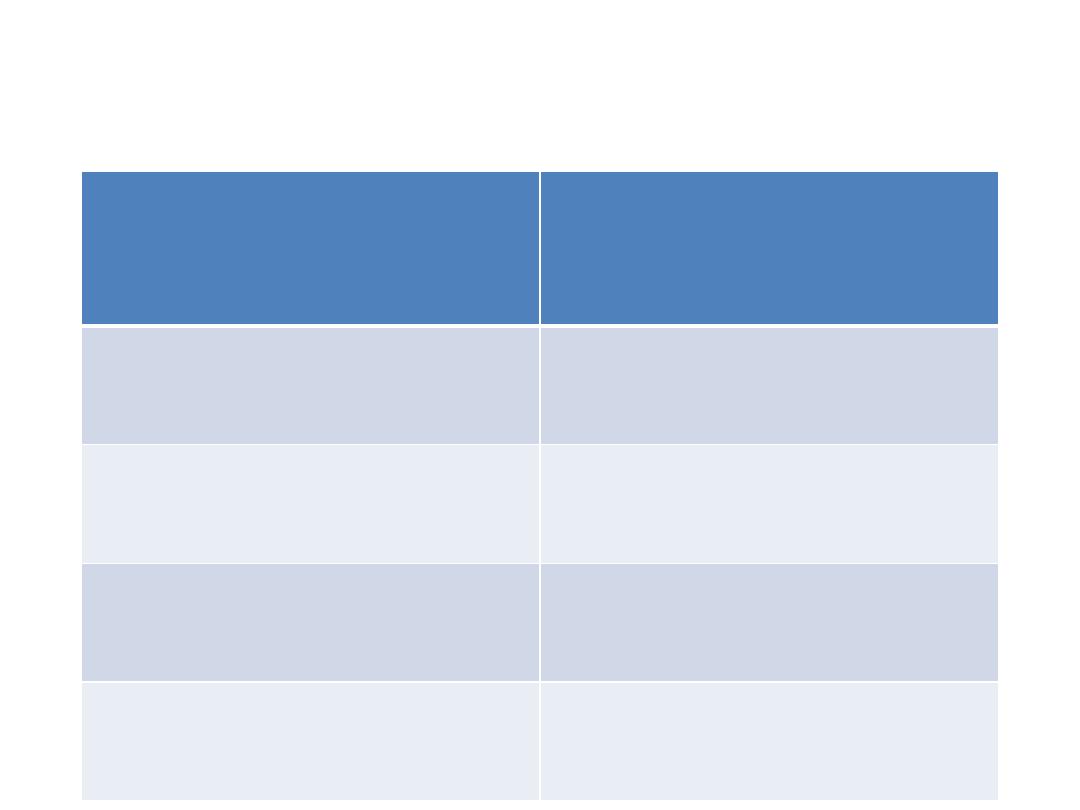
OSCE 16 ANSWER
Can tie shoelaces
Differentiate between morning &
afternoon
5 years
Can button up clothes
Say which line is longer of two lines
4 years
Build tower of nine
Unbutton shirt
3 years
Picks up ball without falling
Uses ‘I’, ‘Me’ and ‘You’.
2 years
Kneels without support
Likes to take off shoes
15 months
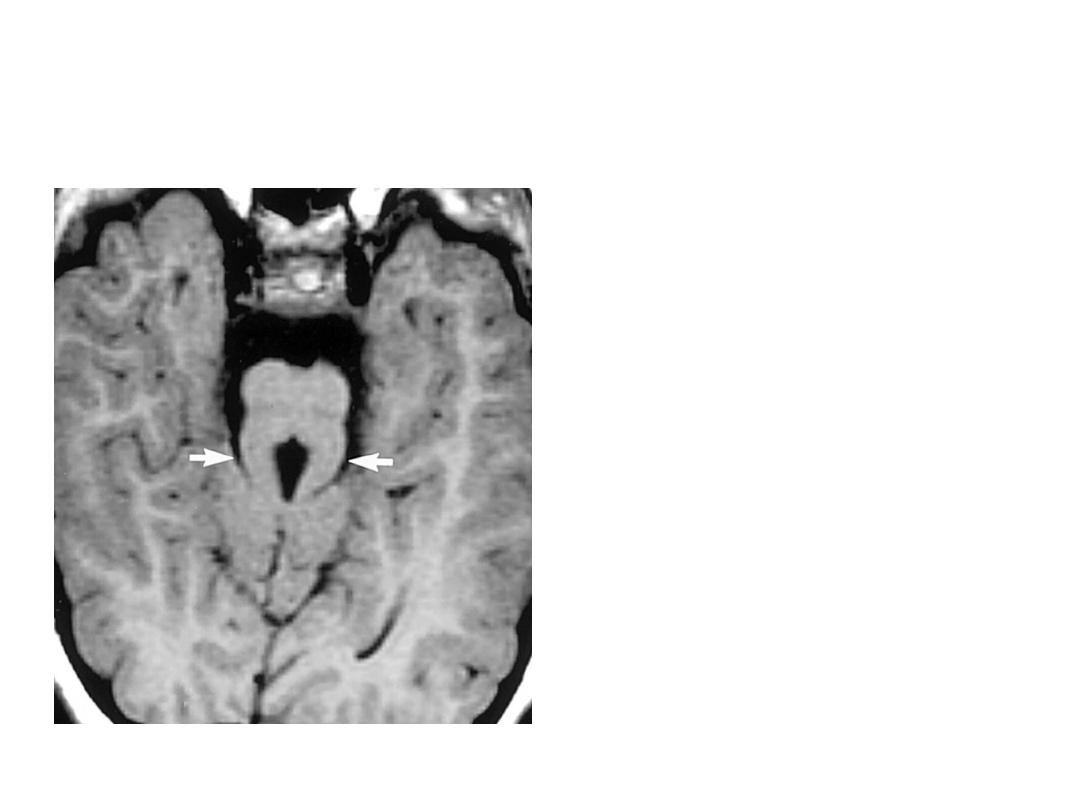
OSCE 17 ANSWER
1.
Molar tooth sign
2.
Joubert’s syndrome
3.
Absence of decussation of
superior cerebellar
peduncles
4.
Autosomal recessive
5.
Ataxia, irregular respirations,
hypotonia, abnormal eye
movements ,retinitis
pigmentosa, polydactyly,
nephronopthisis.
CLASSIFIED UNDER CILIOPATHIES
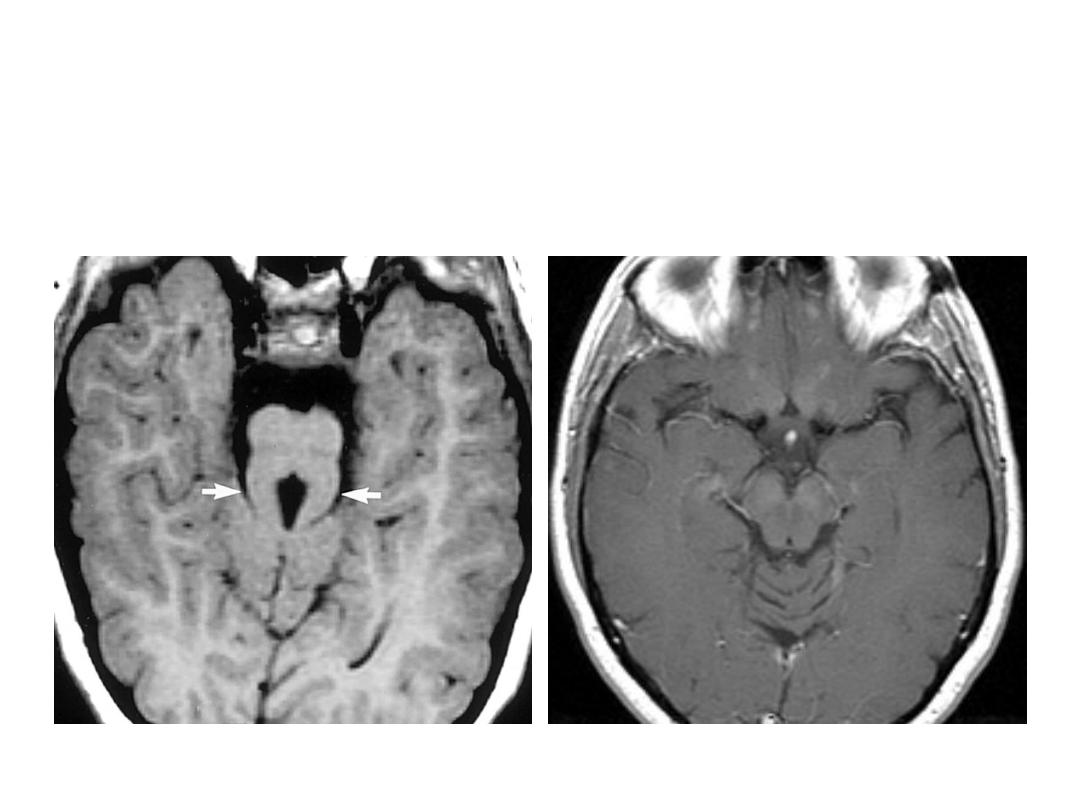
OSCE 17 ANSWER
Joubert’s syndrome
Normal Brain at Midbrain level

OSCE 18 ANSWER
1) Airway Obstructed/ Respiratory distress/ Hypotensive Shock/ ALOC
2) Neurogenic shock
3) Normal heart rate , paradoxical breathing( diaphragmatic
breathing),hypotensive shock and wide pulse pressure.
4) Initial steps in management:
a) Stabilise airway by jaw- thrust manouvre, C-spine immobilisation.
b) High flow O2 by NRBM
c) Trendelenberg position
d) Isotonic fluid NS 20ml/kg boluses as rapidly as you can upto 3
boluses /till perfusion improves & Ionotropes if fluid refractory.
e) Look for and evaluate other life-thtreatening conditions like
systemic bleeding, pneumothorax.

OSCE 19 ANSWER
1. Metabolic Alkalosis.
2. Compensated. PCo
2
increases by 7 for every
10mm increase in Hco3.
3. Gitelman syndrome
4. Defect in sodium chloride co transporter in
DCT.
5. Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia &
hypocalciuria.

OSCE 20 ANSWER
1. It implies in utero infection and rapidly
progressive disease
2. It implies postnatal transmission and slowly
progressive disease
3. After 1 month of age (as false positive rates are
higher if done before)
4. If two positive virologic tests (PCR / culture P24
antigen) are obtained from different blood
samples.
5. > 18 months of age – it is almost 100 % specificity
sensitive.

Part B

• A 2 yr old child presents to emergency
department with severe pallor. Take the
history of the child from mother.

• Introduces himself and tries to make the mother comfortable 0.5 marks
• Asks onset sudden or gradual 1 mark
• history of bleeding or bluish spots 1 mark
• History of associated symptoms : fever, failure to thrive 1 mark
• Recurrent blood transfusions 1 mark
• History of associated jaundice 1 mark
• History of worm infestation 0.5 mark
• Birth history 0.5 mark
• Community and religion and history of consanguinity 1 mark
• Dietary history 0.5 mark
• Family history 0.5 mark
• Drug history 1 mark
• Thanks 0.5 mark

• EXAMINATION OF B.P IN A 10 YEAR OLD ?
• Rapport with patient and Bystander
• Choice of cuff size
• Positioning of the patient
• Site of tubing in relation to artery is correct
• Initial palpation, then auscultation method
• Rate of deflation is correct
• Reconfirm reading/ ask for BP chart
• To say if reading is normal or otherwise
• Thanking patient and bystander

• Administer MMR Vaccine to this 17 month old
child who is otherwise normal?

• 18 month old boy presented with fever with
rash 8days
• Take the appropriate history

• Introduction and rapport with parents 1
• Onset –sudden/ insidious 0.5
• Timing and pattern of fever ,pattern and distribution of
rash 2
• h/o associated symptoms-joint pain swelling, conjunctivitis
1
• h/o of travel, mosquito bite, animal exposure, season of the
year 2
• h/o medications, lab testing1
• Family history1
• Immunization-measles, MMR 1
• thanking parents 0.5

• Do the musculoskeletal examination of this 8 year old boy
Introduction rapport, permission for examination
INSPECTION-observe child sit, stand, walk looks and
reports obvious abnormalities in gait, muscle
PALPATION-swelling tenderness deformities ,abn
curvatures in spine
RANGE OF MOVTS-IN major joints of UL AND LL
SPINE- INSP,PALP of spine, forward bending(touching toes
without bending knees)assess flexion extension ,lateral
flexion,rotation
Reporting impression to examine
Thanking child and parents

29weeks male 1.1kg delivered just now,
developed grunting
Counsel about the immediate treatment
plan hospital stay and future prognosis

• Introduces, asks language, establishes rapport with parents
• Importance of early CPAP, and surfactant replacement
therapy, need for mechanical ventilation
• Frequent blood gases ,xrays and relevant blood testing and
cultures
• Monitor for expected complications-air leaks pulmonary
haemorrhage,apnea,septicemia
• Need for long hospital stay till child accepts orally tolerates,
euthermic, weighs at least 1.5kg,discharge check with
screen for cong anomalies, rop, hearing
• Prognosis-prolonged oxygen requirement(BPD),ROP,
neurodevelopmental impairment
• Thanks, asks for doubts

• Check weight length/height head
circumference of the new born
• Discuss cord and eye care with the mother

• Introduction and rapport
• Take permission for examination, washes hands
• Weight-removes cloths adjusts 0,removes parallax,reports wt to
examiner
• Length-head at 0 movable end at feet, reports L to examiner
• HC-uses nonstretchable tape, covers areas of max protuberance of
occiput and point just above glabella, reports to examiner
• Cord care-clean stump with soap and water, allow to dry
• Eye care-wipe eyes with sterile moist cotton, no routine topical
antibiotics
• Thanking mother

• Demonstrate liver biopsy procedure with given material?
• Takes consent
• Asks for pre procedure work up-CBC, coagulation profile,
LFTS
• Position ,painting and draping the area
• Administer local anesthesia
• Checks liver biopsy needle, uses correct technique, checks
movement of needle with respiration after entering in liver
• Sends piece of biopsy in formalin bulb
• Applies benzoin, monitors abdominal girth post procedure
• Dispose in BMW

• Assess the developmental age of the child ?
• Introduction and rapport with child
• DOLL-asks to tell the parts
• Paper-good enough draw a man test, shows number of
body parts drawn by the child
• Crayons, pencils- scribbles, copies circle, rectangle,
triangle, hexagon
• Cubes-makes tower of 6,9,12,makes bridge
• Tells developmental age to examiner and says thanks to
child/parent

• Introduction and rapport with child [1]
• DOLL-asks to tell the parts [1]
• Paper-good enough draw a man test, shows
number of body parts drawn by the child[ 2]
• Crayons, pencils- scribbles, copies circle,
rectangle, triangle, hexagon [2]
• Cubes-makes tower of 6,9,12,makes bridge[ 2]
• Tells developmental age to examiner and says
thanks to child/parent [2]
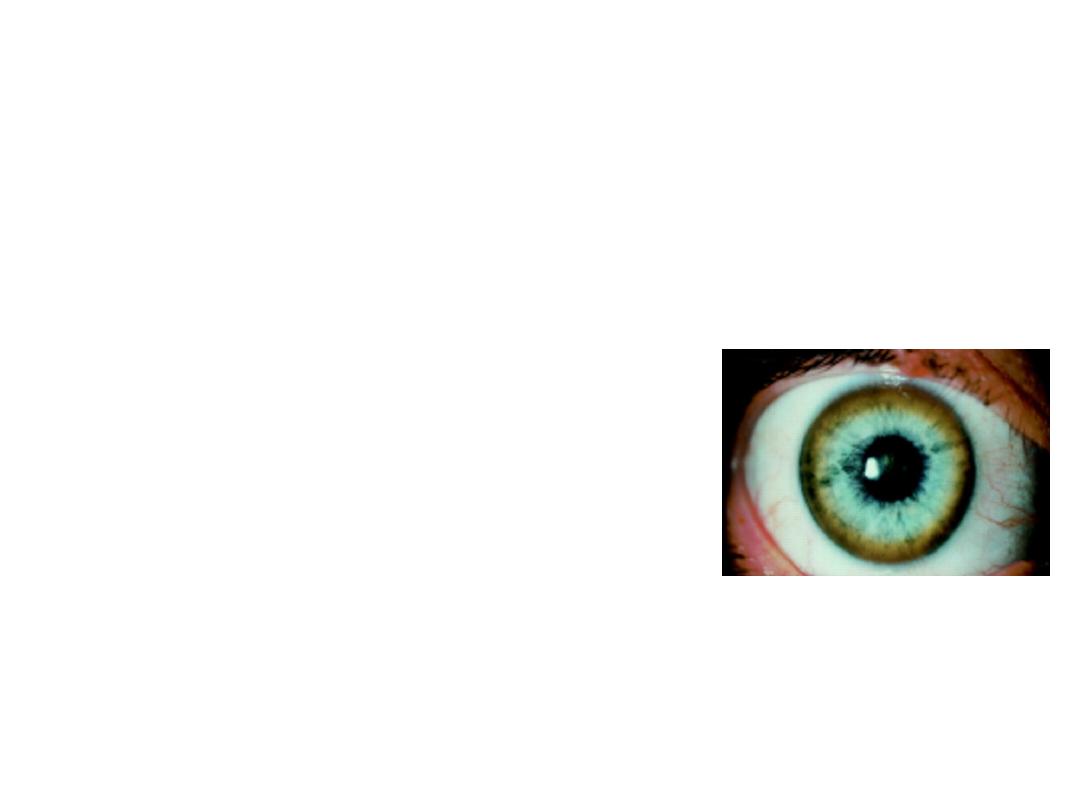
• Station No.1
A 11 yr old male child is admitted with sudden change of
behavior, slurring of speech, ataxia and dystonia. On
investigations, he found to have anemia with renal tubular
acidosis. His ophthalmic examination was done and shown in
fig. (1x5=5)
Describe the findings?
What is the most possible diagnosis
What is the pattern of inheritance for it?
What are the most specific investigations?
What is the complete treatment in this case?

.
Slit lamp examination showing brown discoloration at outer margin
of cornea
• Wilson disease with lenticular degeneration
• Autosomal recessive
• Hepatic copper content (µg/gm dry wt. of liver- it exceeds >250
µg/gm dry wt.)
• D-Penicillamine with Pyridoxine and Zinc and all family members
should be screened with s. ceruloplasmin and urinary excretion of
cu, slit lamp examination

•
Station No 2
: A term newborn who required resuscitation at birth with a 5 minute
APGAR of 5 is admitted in NICU. The neonate had seizures in first 12 hrs of life
•
Identify the findings-
•
What is the significance of this finding-
•
Name of the staging system other than Sarnat and Sarnat and give its component-
•
Station No 2
: A term newborn who required resuscitation at birth with a 5 minute
APGAR of 5 is admitted in NICU. The neonate had seizures in first 12 hrs of life
•
Identify the findings
•
What is the significance of this finding-
•
Name of the staging system other than Sarnat and Sarnat and give its component-
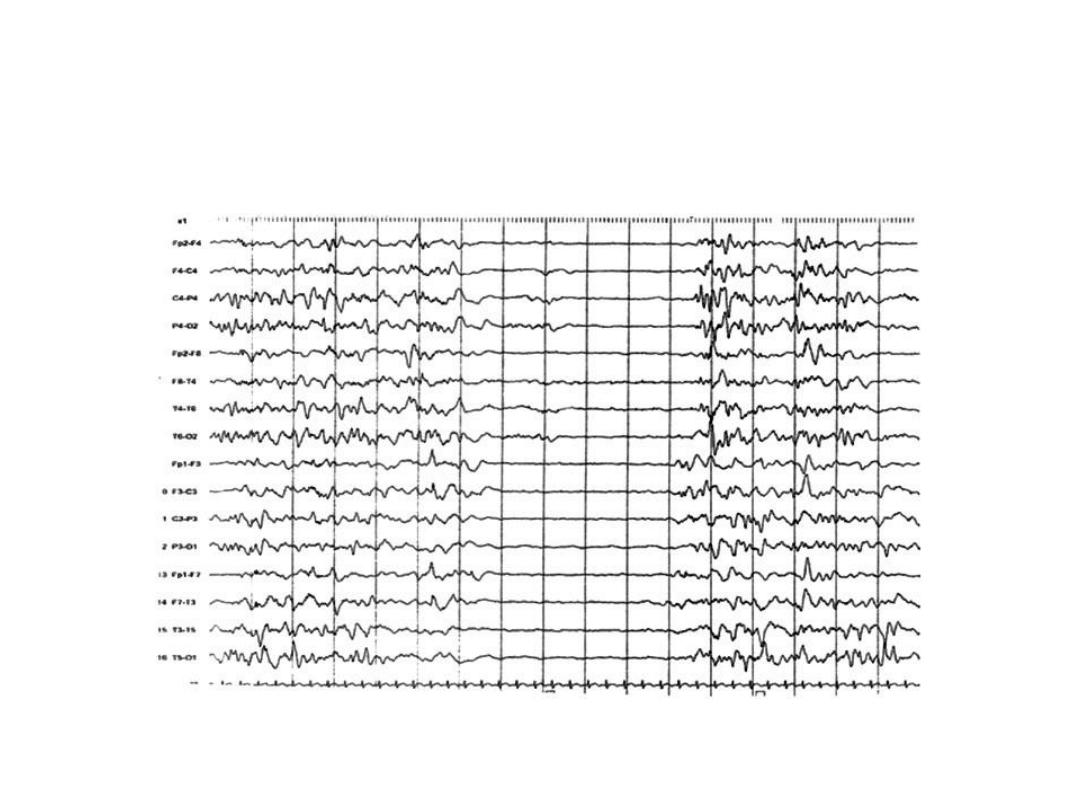

• EEG of neonate showing Burst Suppression pattern
• It indicates serious outcome in HIE patients
• Levene’s staging system (Mild, Moderate and Severe)
– Consciousness
– Tone
– Seizures
– Sucking/Respiration

Station No 3
14 year old boy has sustained injury to the neck due to a Road
Traffic Accident. He is breathing but cannot move or feel his arms
or legs.
1.
What is the recommended maneuver for opening the airway in
neck injuries?
2.
X ray of the Cervical spine shows no bony injury. Is it still possible
for the boy to have a spinal cord injury? Name the condition and
mode of diagnosis?
3.
What is the Emergency drug treatment that can be offered to this
boy?

1. Jaw Thrust without Head tilt.
2. YES. SCIWORA (Spinal Cord Injury Without
Radiographic bone Abnormalities), MRI
Spine.
3. Bolus of High dose Methyl Prednisolone (30
mg/kg) within 8 hrs of injury followed by a
23-hr infusion (5.4mg/kg/hr) -

•
Station No 4:
• A 10 day old newborn was rushed to NICU by a local
doctor as he found different pattern of his cardiac activity.
O/E child had fine rashes over the face specially the
periorbital area . ECG done in ER showed (1x5=5)
• a) What is the ECG diagnosis? b )What is probable
diagnosis?
• c) What is the pathogenesis of this disease?
• d) What is the Rx of this acute stage?
• e) What is the earliest age at which this cardiac defect can
detected antenatally?
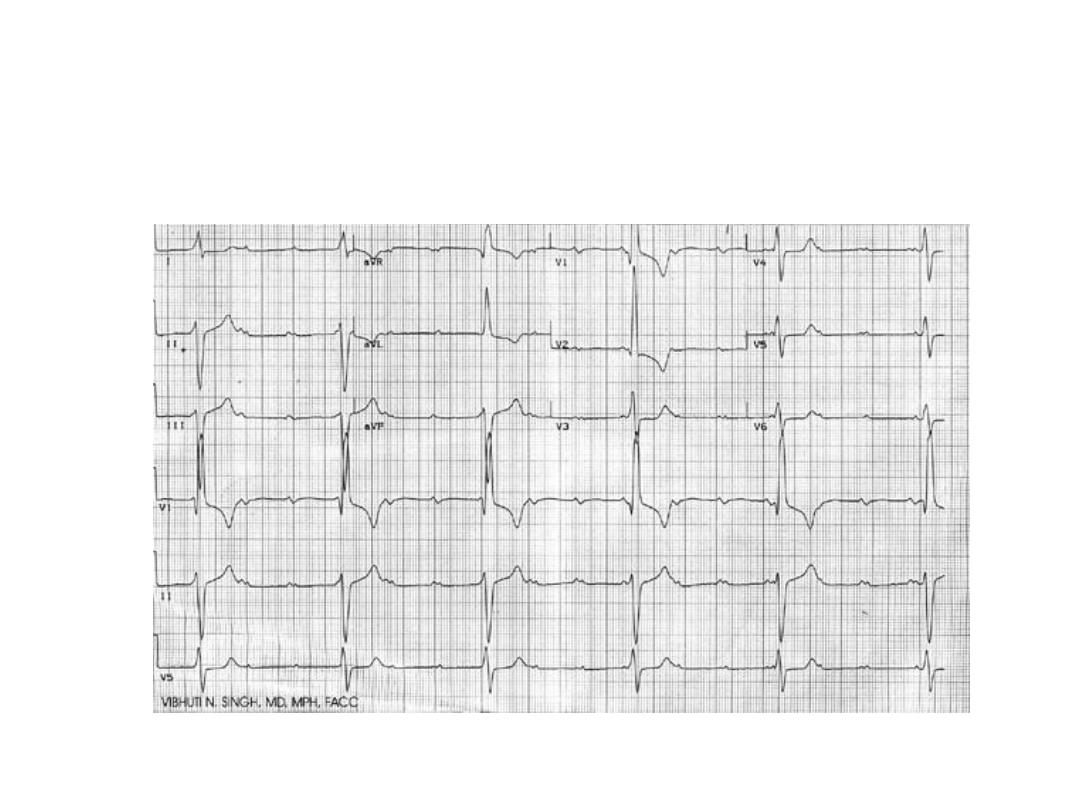

• a) Complete heart block
• b) Neonatal Lupus
• c) Transfer of anti Ro antibodies between 12-
16 wks of gestation
• d) Cardiac pacing
• e) 16 wks of GA
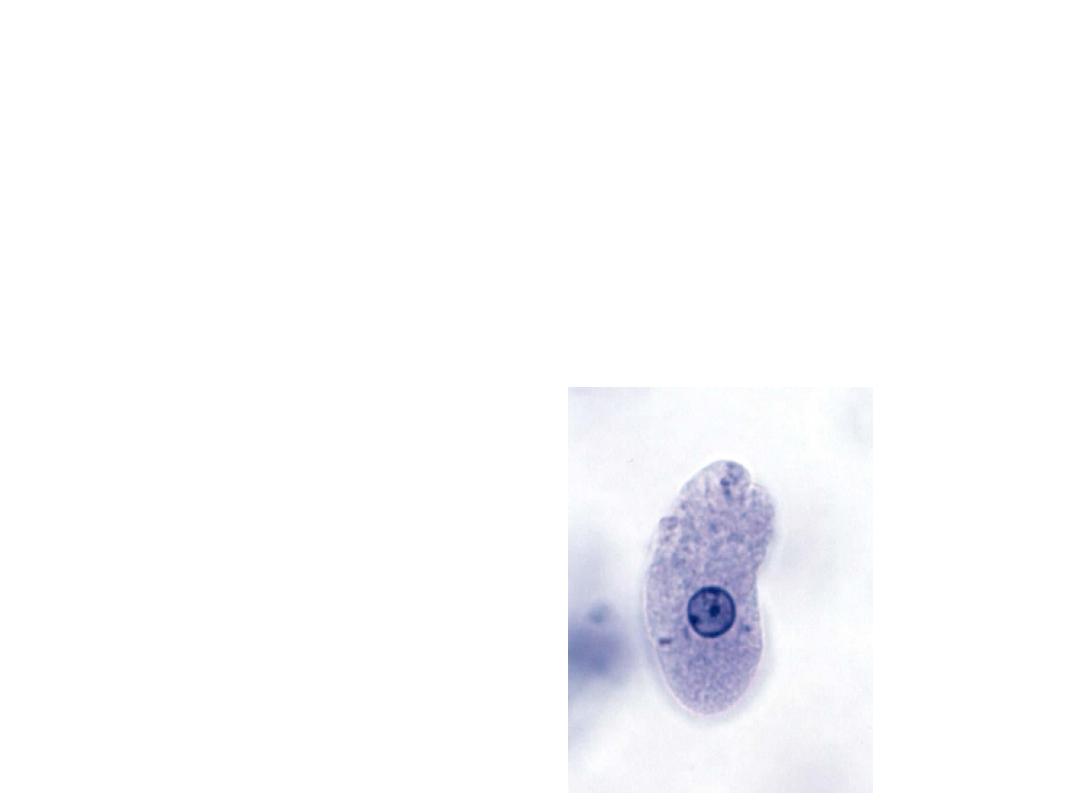
• Station No 5
A
( 1/2x6=3)
Dispose the following biomedical waste in suitable bags
1) blood agar media 2)used injection needle
3) amikacin injection with expiry 4)blood soaked cotton swab
5) i.v set 6) incinerated ash
• B
(1x2=2)
Identify the organism .
• What is treatment?

• 1. yellow/red
• 2. blue/white
• 3. black
• 4. yellow/red
• 5.blue/white/red
• 6. black
• B. E. Histolytica
• nitroimidazole, metronidazole, chloroquine

Station No 6
This 3 yrs old female child
came with neuro regression from early infancy with
abnormal hand movements and autism (1x5=5)
What is the diagnosis ?
What is the hallmark of this disorder?
What is age of onset of neuroregression ?
Which are earliest neurological findings?
Which milestones are delayed?

• Retts syndrome –(1)
• Repetitive hand wringing movement and loss
of purposeful and spontaneous use of hand
(1)
• I year of age (1)
• Ataxic gait and fine tremors of hand (1)
• motor, language(1)
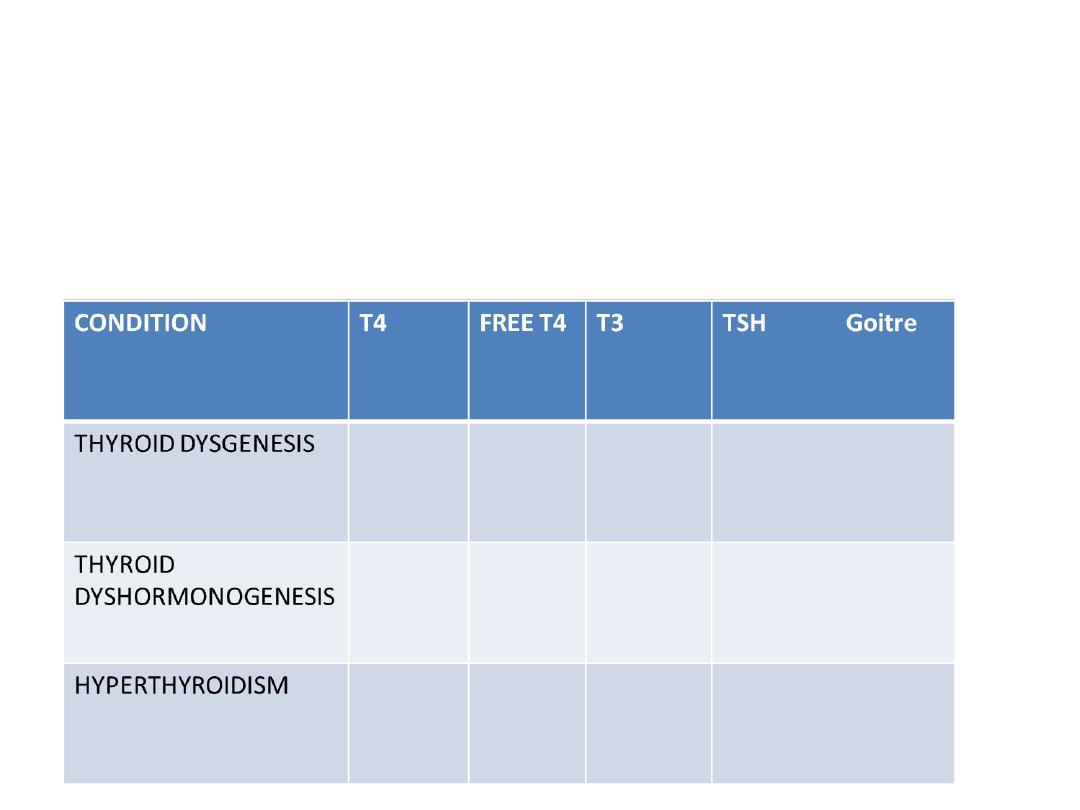
Osce-7
Write the results for each (dec/increase/absent)
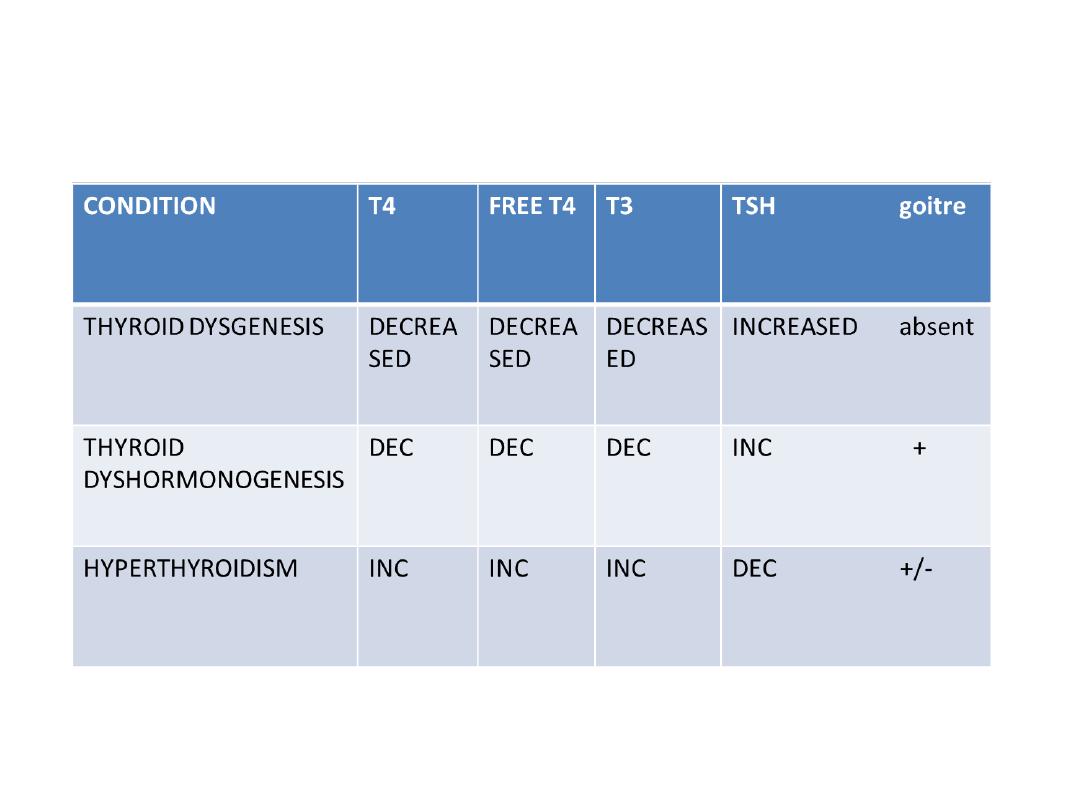
• Osce- 7
TOTAL MARKS-5 (1x 5=5)
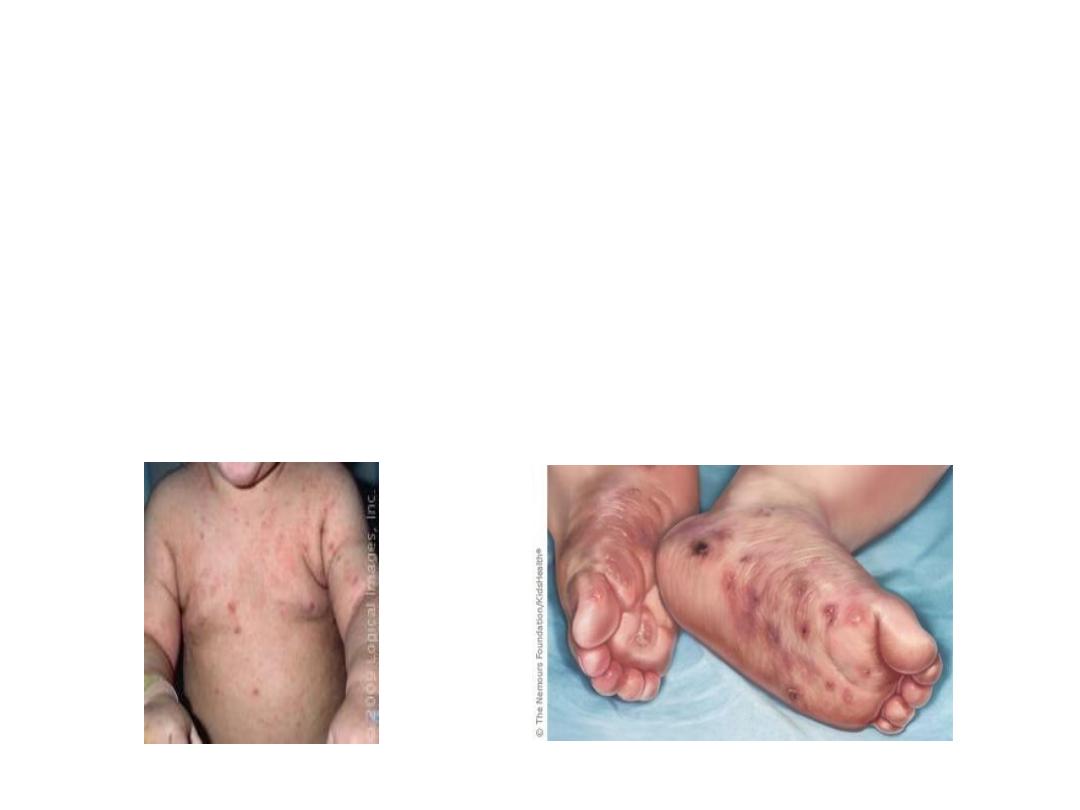
•
Station 8
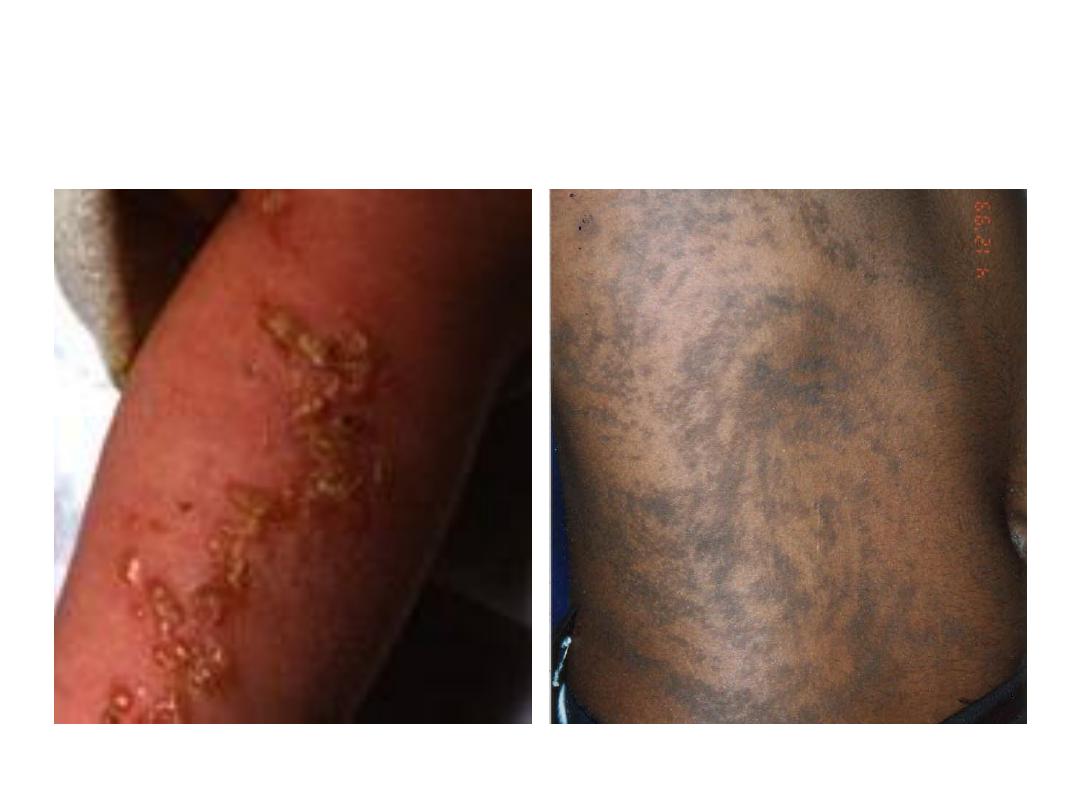
The above pictures are of a 2 yrs old child who presented
with intense pruritis , particularly at night. There are similar complaints
seen in other family members. [1x5=5]
1) What is the diagnosis?
2) What the characteristic finding for same?
3) What are complications seen?
4) What is the causative agent?
5) What is the complete treatment for this case

1) SCABIES-0.5
2) BURROWS -0.5
3) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS AND PYODERMA
(0.5+ 0.5)
4) Sarcoptes scabies
5) PERMETHRIN 5% (0.5+ 0.5)
PRURITIS- TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROIDS (1)
TREAT ENTIRE FAMILY(1)

• Station No.9
RNTCP DOTS-Plus 2010What are five essential
components of RNTCP DOTS-Plus?(2 1/2)
• What is RNTCP Category IV used for and what
it includes? ( 2 ½)

• Sustained political and administrative commitment
• Diagnosis of MDR-TB through quality-assured culture and drug
susceptibility testing
• Appropriate treatment strategies that utilize second-line drugs
under proper management conditions 4.
• Uninterrupted supply of quality assured anti-TB drugs.
• Recording and reporting system designed for DOTS-Plus
programmes that enable performance monitoring and evaluation of
treatment outcome
• RNTCP Category IV is a standardized regimen for treatment of
MDR–TB patients.
• RNTCP CATEGORY IV REGIMEN: 6 (9) Km Ofx
• (Lvx) Eto Cs Z E / 18 Ofx (Lvx) Eto Cs E

Station 10
A :
In population sample of children with mean
Ht66cm and SD 2.7 cm , Can a sample of 100
with mean ht 67cm occur easily? If you find
that probability is low P<o.01 What does it
indicates (2 1/2)
B:
Find the limit within which you would expect
the population proportion to be if you have
examined the records of all 50 children of
school and found 23 had tonsillectomy done
(2 ½)

• A;S X- =s/ ∫n= 2.7/ ∫100=0.27
• 67 is more than 66=3X0.27=66.8 cm this sample
can’t easily occur in this population p is less than
0.01 it indicates 99% children are that sample are
not drawn from same population might be higher
age group. Probability of its being taken from
same universe is less
• B;SEP= ∫pxq/n= ∫46x54/50=7.05
• 95% confidence limit of population proportion of
tonsillectomy done will be 46+/- 2x7=32-60%

Station 11
• A)Arrange following in ascending order of
requirement daily (RDA) [2 1/2 ]
Vit B6, Vit E, Cu, Iron, Calcium
• B) Write age independent anthropometric
parameters for PEM( any 5) [2 ½]

• Vit B6-0.5-1.5 mg/d
• Vit E 5-15 Cu-1-2mg/d
• Iron-10-20mg/d
• Ca-500-1000mg/day
• Age independent anthropometric parameters for PEM( any 5)
• Bangle test
• Shakirs tape
• Modifed quac test
• Kanawati index
• Ponderal index
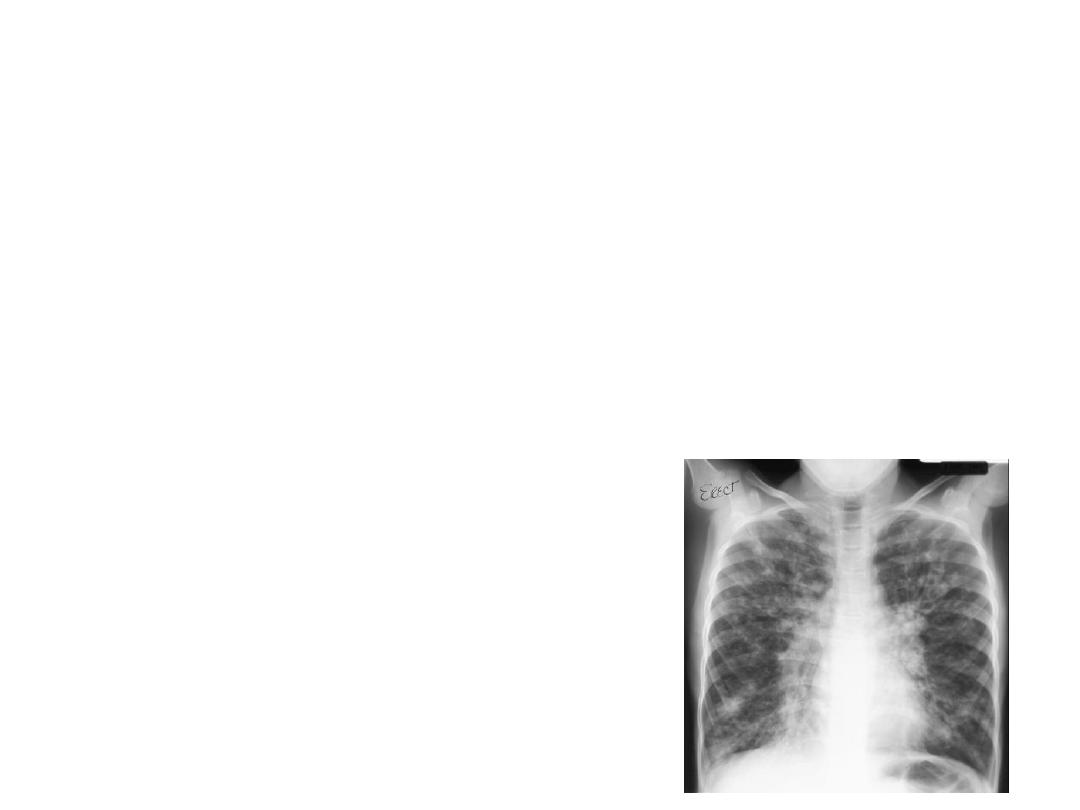
• Station 12
:This the Chest X ray of an 11 year old female
child with h/o recurrent lower respiratory infections. 1x5=5
1) What is the diagnosis?
2) Write the a) clinical features and b) one important
diagnostic clinical sign for the above condition
3) Which syndrome is associated with the above condition?
4) Write the management
5) What is investigation of choice

1) Bronchiectasis
2) a) Productive cough with copious expectoration
Hemoptysis
Growth retardation
Cyanosis
Chest Deformities (Harrison’s sulci)
Crepitations, wheeze, crackles may be heard on auscultation
b) Clubbing
3) Kartagener’s syndrome may be associated.
4) Management-
1. Treatment of underlying disorder
2. Postural drainage
3. Chest Physiotherapy
4. Antibiotics
5. Surgical removal of the affected area
5) HRCT
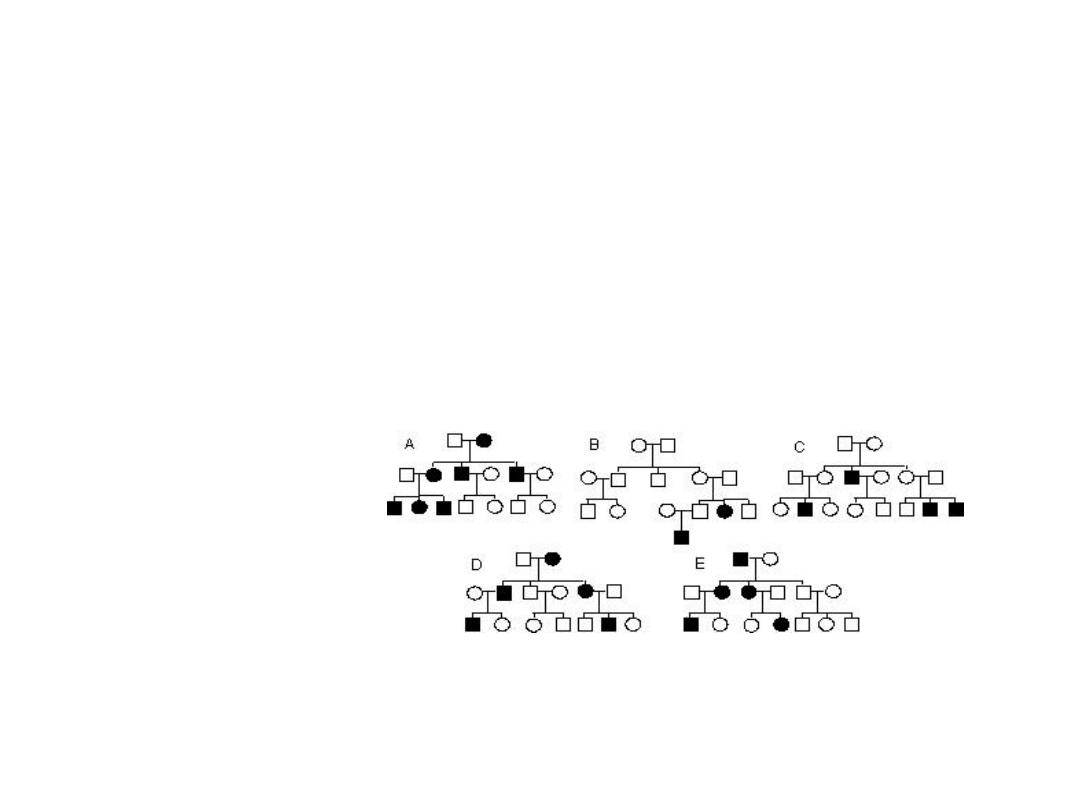
Station 13
Name each inheritance
pattern and one example of
each
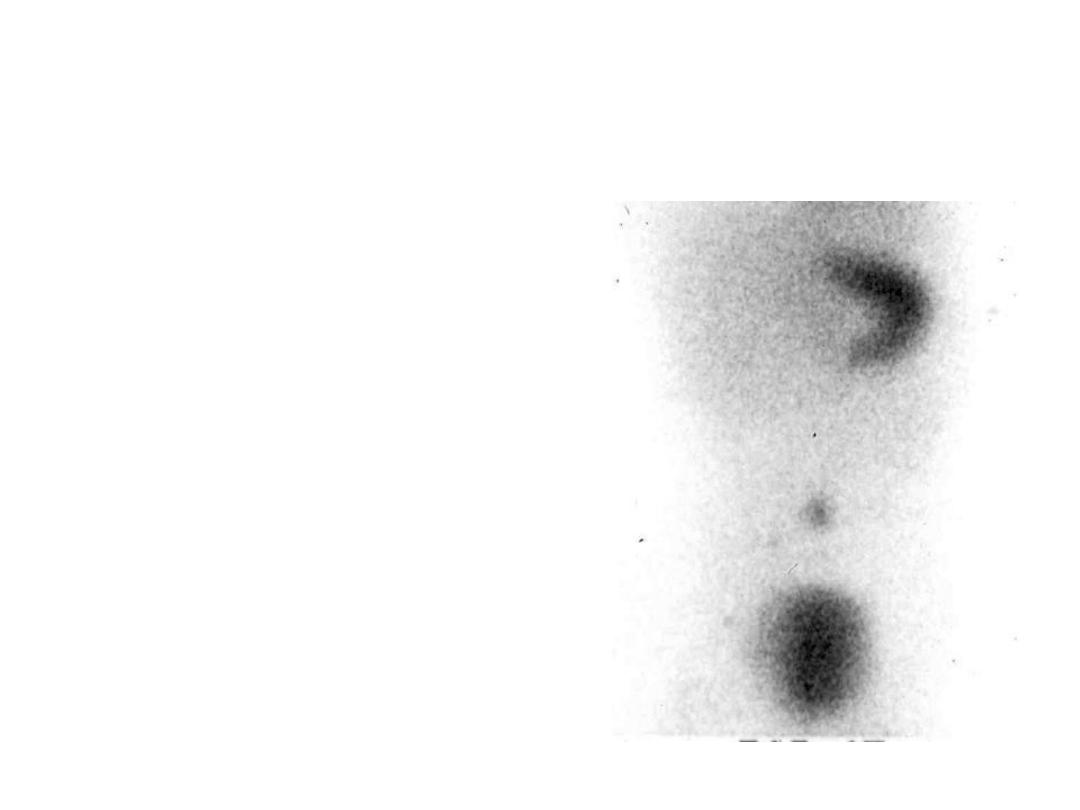
STATION 14
2 yr old boy brought with H/o intermittent painless rectal
bleeding for last few months. The stool is described as
brick colour or currant jelly colour. There is anaemia.
Following study was performed. [1x5=5]
1) What is the test performed?
2) Name the isotope used in the test.
3) Identify the dark areas on the film.
4) How do you enhance the yield of this test?
5) What is the treatment in this case?
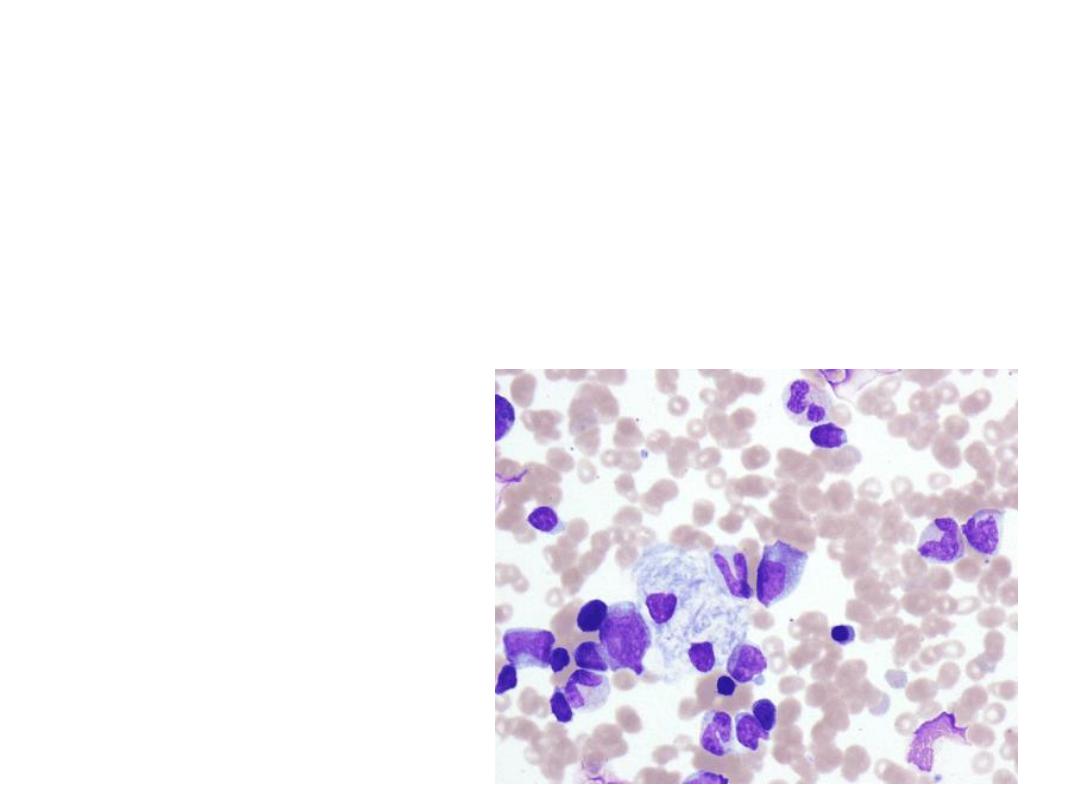
Station 15
This is the bone marrow aspirate of a
15 month old child with a history of hypertonicity,
aspiration pneumonia ,hepatosplenomegaly.
1) What are the findings?
2) What is the diagnosis? What are x ray faetures
3) What is confirmatory test
4) Give 2 differential diagnosis for BM finding
5) What is the Management?

Station 16
A
Match the following MPS

• ANSWER
TOTAL MARKS -2.5 ( 1/2X5)
• 1-c
• 2-a
• 3-d
• 4-e
• 5-b

• Station 16
B
Longitudinal studies are-
a) Either prospective or retrospective- T/F
b) Either experimental or observational- T/F
c) Are particularly suitable for estimating point
prevalence of a condition -T/F
d) Cannot be used to estimate the incidence of a
disease- T/F
e) Can be used for assessing causality- T/F

• Longitudinal studies are-
• a) True
• b) True
• c) False
• d) False
• e) True

• Station 17
A)Write examples of each(2 ½)
• Live attenuated bacteria
• Live attenuated virus
• Inactivated bacteria
• Inactivated virus
• Toxoids
B)Write down the time limits for using the following vaccines after
reconstitution-
• Varicella ,Measles/MMR ,DTaP/Hib Combination
C)Write the schedule of rabies vaccine for a person, who has been bitten by a
dog but has received 5 doses of rabies vaccine earlier.
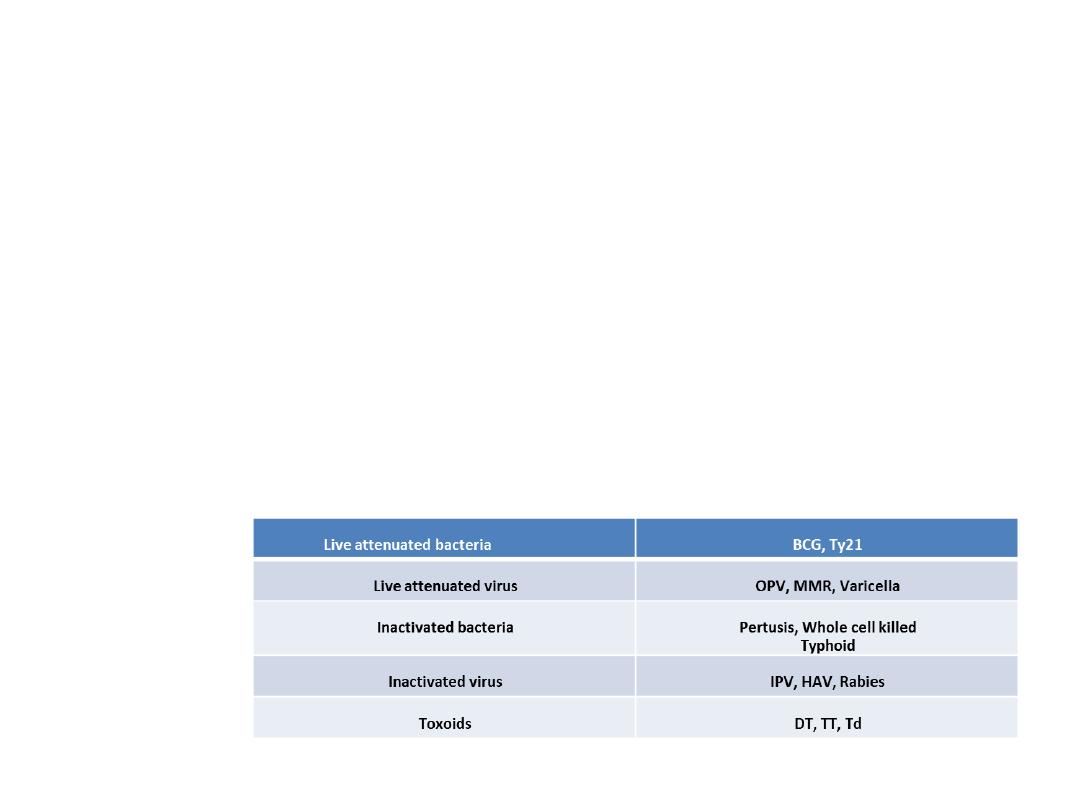
Station 18
Varicella = 30 min (and protect from light)
Measles/MMR = 4 to 6 hours
DTaP/Hib Combination = 30 min
For re exposure at any point of time after completed (and documented) pre or post
exposure prophylaxis, two doses are given on days 0 and 3.

1. 165.25
(Formula)
AaDO
2
= (713 x FiO
2
) – (pCO
2
/ 0.8) – (paO
2
)
2. a)Partial compensation metabolic acidosis with hypoxia
b) IVF/Inotopic support,inc Fio2
3. 11 ml O2 /dl
Arterial Oxygen content = (Hb x 1.36 x SpO2 ) + (
0.0031 x PaO2)
• Station 19
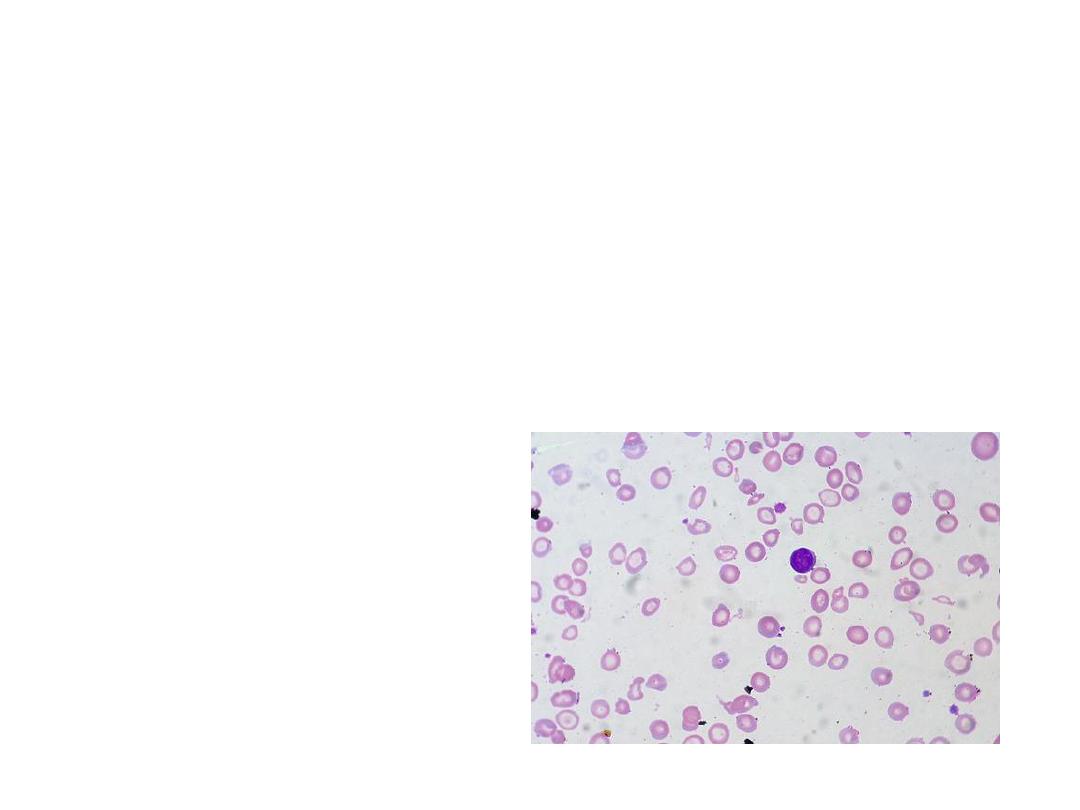
15 months old child admitted with anemia without hepatosplenomegaly for
evaluation, PS shows.
1)
Identify and describe Slide?
2)
What is the diagnosis?
3)
What is the treatment?
4)
What are differential diagnosis?
5) What is the inv of choice

1) MCHC
2) IDA
3) Iron supplement
4) Lead poisoning/ sideroblastic anemia
5) Serum ferritin

STATION - 20
A
Match the following anti-arrhythmics with their classification
• a) 1A- inhibits sodium fast
channel- prolongs RP
• b) 1C- inhibits sodium channel
• c) 111-prolongs repolarization
• d) 1B- inhibits sodium fast
channel-shortens RP
• e) 11- beta blockers

• 1-c)
• 2-e)
• 3-b)
• 4-d)
• 5-a)

Station 20
B
Match the following antiarrhythmics
with their side effects
• 1) amiodarone
• 2) phenytoin
• 3)procainamide
• 4)atenolol
• 5) flecainide
• A) agranulocytosis
• B) thyroid dysfunction
• C) blurred vision
• D) macrocytic anemia
• E) bradycardia

• 1 – b)
• 2- d)
• 3- a)
• 4-e)
• 5-c)

• Station 21
A
• A high risk OPD newborn investigated
1) Identify the figure [½]
2) What do waves I-VII stand for [1]
3) What are the indications for its use [1]

1)BERA
2)
1.Cochlear nerves - waves I and II
2. Cochlear nucleus - wave III
3. Superior olivary complex - wave IV
4. Nulclei of lateral lemniscus - wave V
5. Inferior colliculus - waves VI and VII
•
Criteria for screening newborn babies using BERA for hearing :
•
1. Parental concern about hearing levels in their child
•
2. Family history of hearing loss
•
3. Pre and post natal infections
•
4. Low birth weight babies
•
5. Hyperbilirubinemia
•
6. Cranio facial deformities
•
7. Head injury
•
8. Persistent otitis media

Station 21
B This is an EEG recording of a 5 month old
infant who episodically raises his arms and then flexes
his neck, trunk and hips. The episodes last for a few
seconds and end with a brief cry and return to a
normal posture. What does the EEG show?
1) What syndrome is suggested by the history and EEG?[
½ ]
2) What are the types of the syndrome? [1]
3) Give one condition associated with this syndrome
[1/2]
4) Drug of choice for the above condition and its
principal side effect [1/2]
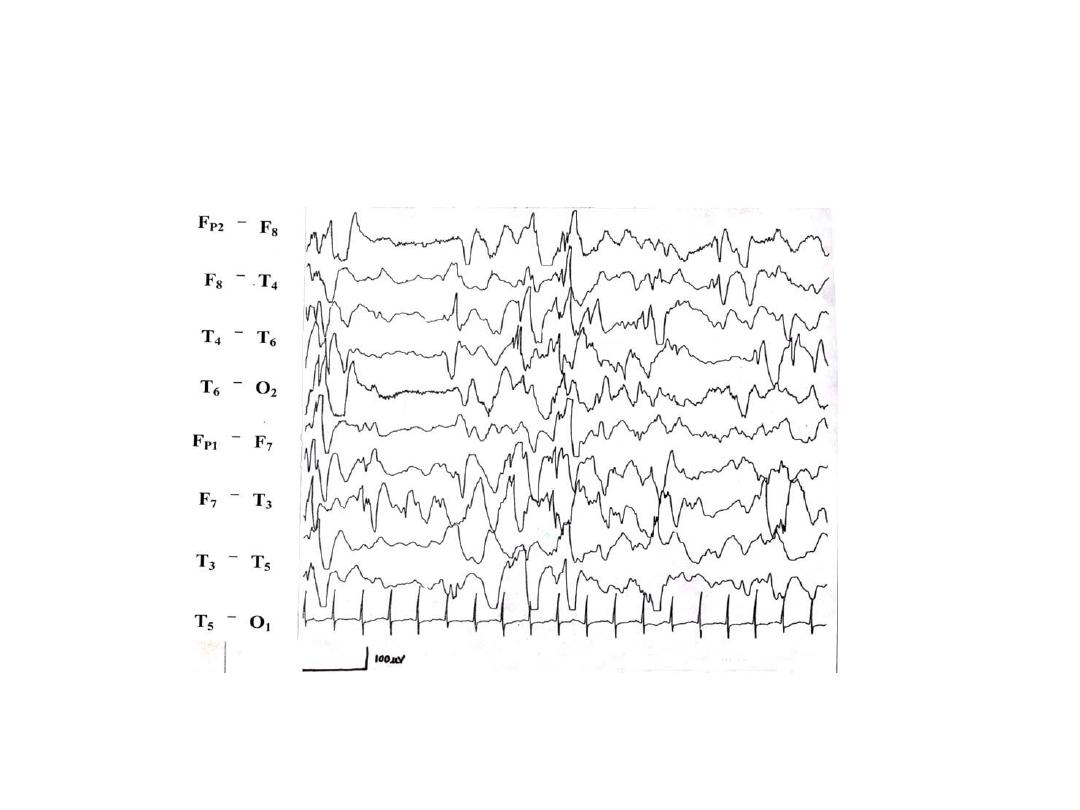

• Hypsarrhythmia –[1]
• Infantile spasms- west syndrome- [1]
• Cryptogenic and symptomatic [0.5 + 0.5]
• Tuberous sclerosis- [1]
• Vigabatrin, retinal toxicity with resultant visual
field defect [0.5+0.5]
