
Unit 3: Helminthes (Trematodes)
48
Lecture 2 - Hepatic Flukes
Fasciola hepatica
Common name: sheep liver fluke.
Disease: fascioliasis hepatica
Biology &Life cycle:
The hermophordite adult fluks is leaf shaped & large 30
mm by 13 mm.
It is flattened, the ant.end forms aconical projection that
broadens at the sholders , than gradually narrowers
towards the post. End.
The intestinal caeca, testes, vitelline follicle are highly
branching.
There is short convoluted uterus.
The habitat of F.hepatica adult worm is the larger bile
ducts & gall bladder of sheep, goats & occasionally man.
Occasionally found ectopically in the peritoneal cavity or
other sites.
Eggs pass from the bile duct into the intestinal tract &
evacuated in the feces .It is large ,thin shell with
operculum.
Pathogenesis & Symptomatology:
Pass of the young worms through the hepatic parenchyma
to the bile ducts cause traumatic damage & intense
eosinophilic inflammation. In the larger bile passages they
produce hyperplasia of the biliary epithelium with
leukocytic infilteration & fibrosis of the ducts.
Early symptoms of human infections are:
Right upper quadrant abdominal pain, fever,
hepatomegaly, biliary colic, coughing, vomiting, Jaundice
also abdominal rigidity, diarrhea, fever, profuse sweating,
urticaria, eosinophilia ,macrocytic anemia ,empyema of
gall bladder, cholecystitis or choleithiasis , obstructive
Jaundice. Ectopic worm found in abscess pockets in
blood vs., lung subcutaneous tissues, brain, eye.
False fascioliasis: can occur when F.hepatica egg found
in feces after ingestion of infected liver of sheep, goat or
cattle, raw or cooked.
Diagnosis:
By recovery of eggs in feces .In case of false fascioliasis ,
egg ceased to appear in feces a few days after placing the
patient on a liver-free diet.
Treatment:
-Bihionol in oral dose is the drug of choise.
-Praziquantel is also effective.
Epidemiology:
Human infection is aquired by ingestion of raw aquatic
vegetation contaminated with metacercaria such as lettuce
& green salad.
Reservoir host is primarily the sheep
Control:
Health education of general public regarding the mode of
transmission of parasite & the danger of eating uncooked
or partially cooked & contaminated vegetables is the most
important measure.
Other measures are treated of sheep & other herbivorous
mammals.
Fasciola gigantica
Common name: giant liver fluke.
Disease: Fascioliasis gigantica.
1) is longer & more attenuated
2) with larger acetabulum
3) More ant. Position of the testes.
4) larger size of the egg 160-190
–
m by 70-9
---
m
5) The natural host is cattle, sheep.
Unit 3: Helminthes (Trematodes)
48
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
Common name: Lancet fluke
Disease: Dicrocoeliasis
Habitat: It inhabits the biliary passage of man, sheep &
herbivorous animals .
Morphology:
Adult worm is lancet –shaped, flat, thin, transparent,
small (5-15) mm by (1.5-2.5) mm with smooth tegument.
There are 2 testes anterior to the ovary in the anterior half
of the body .Uterus coiled in the median field of the
posterior part of the body.
Egg: ovoid operculated, thick shelled, dark brown in
color, measuring (35-45) by (22-30) mm embryonated
when laid
Pathogenesis and symptomatology:
Similar to Fasciola hepatica but less marked
Symptoms: biliary colic, hepatitis, abdominal distress,
diarrhea, vomiting, chronic constipation.
Diagnosis: Examination of stool
Treatment: Praziquantel.
Life cycle:
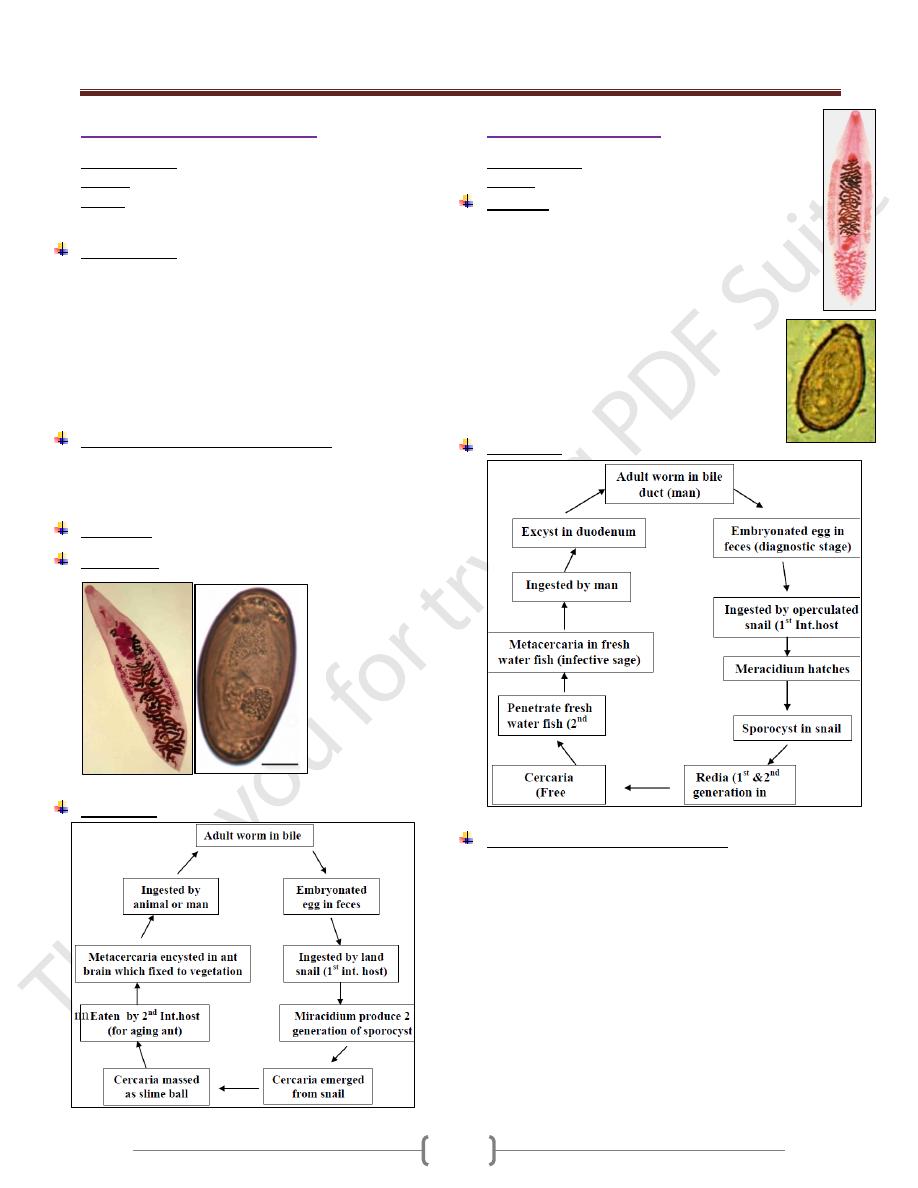
Clonorchis sinensis
Common name: Chinese liver fluke.
Disease: clonorchiasis
Biology:
It lives in bile passage
Lanceolate, flate, transparent, pink in color (10-
25)mm long by (3-5) mm
Broad, smooth tegument, globose oral sucker, small
acetabulum.
Egg: Broadly, ovoid with thick, light,
yellowish, brown shell with distinct operculum
opposite a small knob, measure (27-35) µm in
length by (12-20) µm---- in diameter. fully
embryonated when discharge in faeces.
Life cycle:
Pathogenesis & Symptomatology:
Hyperplasia of biliary epithelium with dense fibrous
envelopment of the duct.
In heavy infection, there is fibrous thickening of the wall
with pressure necrosis of adjacent hepatic parenchyma.
The clinical onset was gradual or sudden with chills &
fever up to 40c˚
Liver is large & tender ,sometime there is congestive
spleenomegaly, eosinophilia counts ranged from 10 to 40%
Some weeks later the picture was one of cholecystitis
& hepatitis.

Unit 3: Helminthes (Trematodes)
48
Diagnosis:
Detection of eggs in direct fecal smear
by
concentration technique.
Duodenal or biliary drainage.
Treatment:
praziquantel is effective.
Epidemiology:
Infection is acquired by eating fresh water fish that is raw
,pickled in brine or rice wine ,
smoked or dried fish containing the encysted metacercaria
Control:
Cooking all fish that intended to be eaten.
Protection of fish ponds from contamination with night
soil.
