
Lab 2 – Energy
47
Daily requirement according to age ,sex, activity, and
other conditions
Energy”
The ability to:
1- Perform work,
2- Produce change
3- Maintain life
All requires energy.
Energy exists in many forms
; mechanical, chemical,
heat, electrical, light, & nuclear energies
• In the body, chemical energy from food is converted
to mechanical energy & heat.
• The major dietary sources of energy-yielding
substrates are CHO, fats & proteins.
Units of Energy
Calorie:
It is the basic unit of energy.
It is the amount of heat energy required to raise the
temperature of one gram of water by 1°C at the standard
temperature.
But because the calorie is a small unit we usually use;
Kilocalorie (Kcal or Cal) =1000 calorie.
Which is the amount of heat energy required to raise the
temp. of a kilogram of water 1°C
Joule (J):
Is the work done (energy expended) when 1 kg is moved
1 m. by a force of 1 Newton.
The total calorie content of food can be measured by a
device called (Bomb Calorimeter). It is design to burn
food & the amount of energy produced per gram of
protein, fat or CHO by Bomb calorimeter are;
1 gm of: protein = 4 Kcal, fat = 9 Kca, CHO = 4
Kcal, alcohol =7 Kcal (not nutrient)
The nutrients release energy when they are catabolized
forming Co2 &H2O. The released energy becomes caught
within ATP = the fuel for all energy- requiring processes
in the body.
E.g. 2 eggs =100 gm;
13% protein = 13 gm x 4 = 52 kcal
12% fat = 12 gm x 9 = 108 kcal
1% CHO = 1 gm x 4 = 4 kcal
Total = 164 kcal
Bread 100 gm contains;
8% protein = 8 gm x 4 = 32 kcal
2% fat = 2 gm x 9 = 18 kcal
58% CHO = 58 gm x 4 = 232 kcal
Total = 282 kcal
100 cc of milk = ½ cup contain;
3.5% protein = 3.5 gm x 4 = 14 kcal
3.5% fat = 3.5 gm x 9 = 31.5 kcal
5% CHO = 5 gm x 4 = 20 kcal
Total = 65.5 kcal
Cup of milk = 200 cc = 200 gm
One table spoonful = 15 cc = 15 gm
One tea spoonful = 5 cc = 5 gm
One tea spoonful of oil = 5 gm x 9 = 45 kcal
= = = = sugar = 5 gm x 4 = 20
Anaerobic & aerobic pathways:
For the 1
st
or 2
nd
minutes of exercise, oxygen has not
arrived at the muscles & energy must come from
anaerobic sources. After several minutes aerobic pathway
takes over, & as the exercise continues, there is a constant
interchange or use of energy sources, which depends on:
1- The intensity ,2- length of exercise, 3- the
person’s fitness level, 4- the food eaten.
Short term, high intensity activities (e.g. sprinting) rely
mostly on the anaerobic pathway & only CHO (from
muscle glycogen) can be used.
Exercise of low to moderate intensity is supported by
aerobic system & both CHO & fats are utilized. Fats are
an important energy source during exercise, because the
fatty acids are abundant in the body & using them spares
muscle glycogen.
Long term activity, the fat becomes the primary source of
energy.
Sedentary person breaks down glycogen faster (lactic acid
accumulated in the tissues causing muscle fatigue), but
physically fit person has a higher aerobic capacity i.e.
more fat than glycogen is used
Total energy requirement (TER):
This depends on summation of 3 factors;
1 - Basal metabolism.
2- Physical activity.
3- Specific dynamic action of food (S.D.A.) = thermic
effect of food (TEF)
= . التأثير الديناميكي النوعي لألطعمة
4-Other factors like growth, pregnancy, lactation &
temperature regulation.
Energy requirement =BMR+ physical activity +TEF
Lab 2 – Energy
48
1)
Basal Metabolism (BMR) ( معدل االستقالب االساسي=
Basal energy requirement = resting metabolic rate:
Which is the minimum amount of energy needed by the
body at rest in fasting state (post absorptive state) to
sustain life processes, basal energy expenditure is
measured as BMR by direct& indirect calorimeter
Condition to measures BMR: the person should be;
At complete physical& mental rest.
Relaxed but not sleep.
At least 12 h. after last meal.
Several hours after strenuous exercise or activity.
In a comfortable temp. & environment
To calculate the energy requirement for BMR:
BMR for male = I.B.W.(kg) × 1 Kcal/ kg / hr × 24hr
BMR for female= I.B.W.(kg) × 0.95 Kcal /kg/hr × 24hr
I.B.W.= ideal body wt.
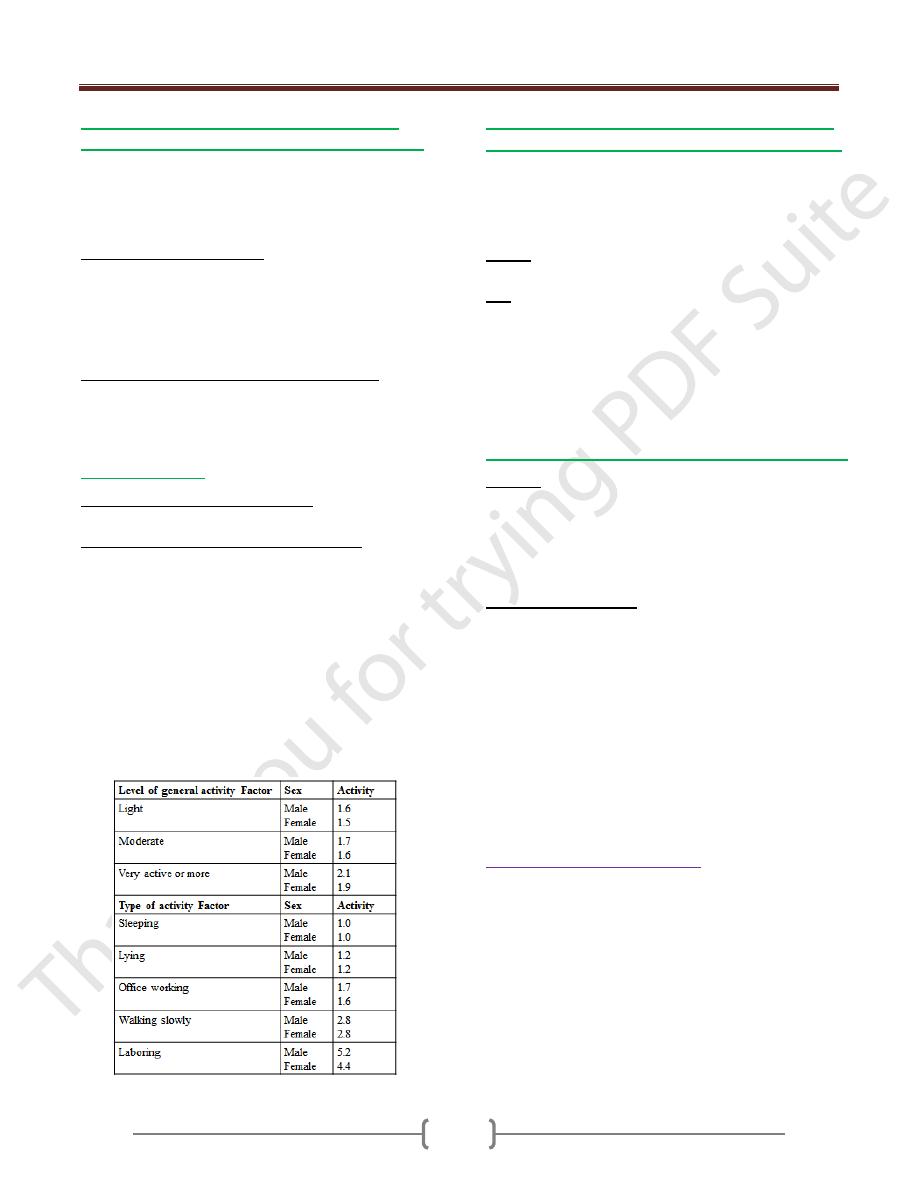
2) Physical Activity:
To calculate physical activity either;
Physical activity=BMR × activity factor
Rough classification of occupation(activity);
Light activity (sedentary)=30% of BMR: office
worker, lawyer, doctor, teacher, shop worker, house
cleaning.
Moderate activity= 50% of BMR: industrial worker,
farmer, student, solder (not in active service),
housewife, carrying a load & cycling.
Heavy activity (75-100% of BMR): agriculture
worker, unskilled laborer, mine worker, solder in
active service, &walking with a load uphill.
NOTE: mental activity dose not appreciably affect the
energy requirement.
3) Specific Dynamic Action of food (SDA)= Thermic
Effect of Food(TEF) = diet induced thermo genesis:
Which is the extra energy released due to digestion,
absorption, &metabolism of food reaches its maximum
level 3-5 hours after ingestion of food.
This effect is not equal for all type of food;
TEF of: protein= 25-30% of BMR, CHO = 6% of BM,
fat = 4% of BMR, for mixed diet= 10% of BMR
E.g. Calculate the total energy requirement (TER) of a 4th
year medical male student whose ideal body wt. is 60kg?
(moderately active male)
BMR = 60kg × 1 Kcal/kg/hr × 24hr =1440 Kcal/day
Physical activity = 1440 Kcal/day × 1.7 = 2448 Kcal/day
TEF = 10% × 1440 Kcal/day = 144 Kcal/day
TER= 2448+ 144 =2392 Kcal/day
4) Other factors; Like growth, pregnancy & lactation:
Growth: additional energy is required to cover the cost of
increasing B.wt.& Ht., a growing infant may store 12-15% of
energy expenditure for growth & formation of new tissues.
When the child gets older , his rate of growth is diminish
&the caloric requirement for growth is reduced but the
TER is increased because of increased body size.
Pregnancy &Lactation:
Additional calories are required to meet the energy cost of
pregnancy &lactation will add to the TER of normal women
In pregnancy 300 Kcal/day (esp. in 3rd trimester)
In lactation 500 Kcal/day will added
E.g. Calculate the TER of 60kg housewife woman?
BMR= 60kg × 0.95Kcal/kg/hr × 24hr =1368Kcal/day
Phys. Act. =1368 Kcal/day × 1.6 = 2188.8 Kcal/day
TEF = 10% × 1368 Kcal/day = 136.8 Kcal/day
2188.8+ 136.8 = 2325.6
If she is pregnant add 300 Kacl/day
If she is lactating add 500 Kcal/day
Adequate diet (Balanced diet):
Is the diet that composed of various nutrients that the body
needs for maintenance, repair & the living process of growth
& development (in children) & to meet all the nutritional &
energy requirement of a person. It should contain; protein,
CHO, fat, vitamins, minerals, fibers& water.
The percentage of various nutrients to the total calories
intake; Protein10-20% , fat 20-30%, CHO 50-60% of total
calories (or according to the food guide pyramid). The
intake more than two third of the R.I. of nutrients are
considered adequate.
