Parasitology
Lab-21 (Sarcoptes scabiei + lice + Ticks)
1- Sarcoptes scabiei :
1- morphology:
Tow separated sex.
Oval in shape
Has mouth part
Gray-yellow color
Have dorsal bristles.
Four pairs of leg (tow anterior pair and tow posterior pair).
Larval stage (nymphs) has same morphology of adult except it has one posterior
pair of leg, in case of nymph develop to male only one stage will occur, but if
nymph develop to femal two stage will occur.
2- habitat : live in stratum corneum ( feed on keratinized cells – make tunnels in skin )
3- Life cycle :
Start
adult parasite make tunnels in the epidermis and eat the dead cells
mating of adult male and female
give 50 eggs daily
eggs develop to larva
nymph
adult
repeat the cycle
female :: adult
egg
nymph 1
nymph 2
adult
male :: adult
egg
nymph
adult
4- diagnosis :
Clinically.
Scarping test. (( invasive scraping of the skin until bleeding ))
Ink test (easy & non invasive).
Laboratory test (very rare & invasive).
serology test are not found.
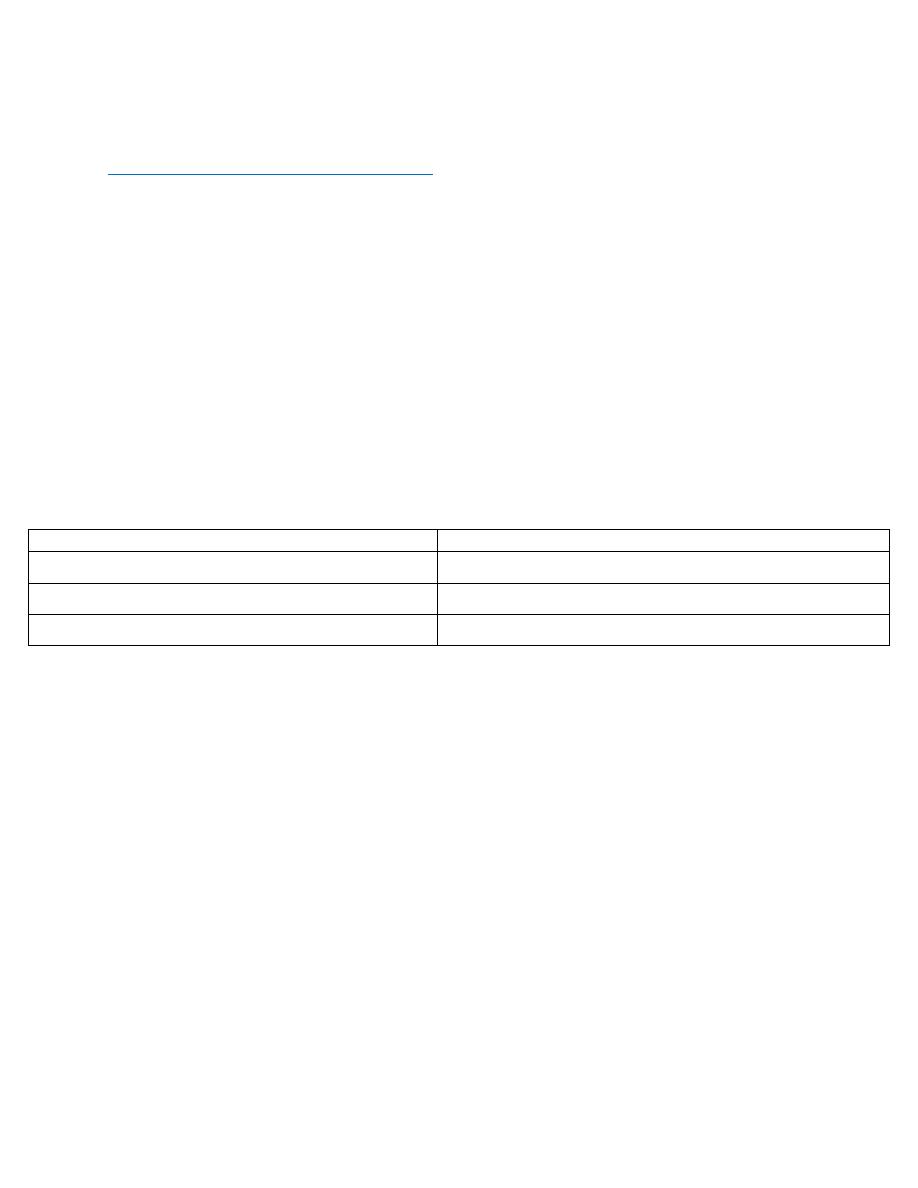
Female
Male
0.4 mm
0.25 mm
Have long bristles
Have short bristles
Have cup like sucker in the anterior pair of leg
Have cup like sucker in anterior & posterior pair of leg

2- Lice :
Head louse : peniculus humans capitus
body louse : peniculus humans corporis
pubic louse : phthrius pubis
1- morphology :
small
ectoparasite
wingless
dorsoventrally flattened ( compressed dorsoventrally )
claw at the end of each leg ( 3 pairs of legs )
composed of head , thorax and abdomen
have mouth part ( adapted for piercing and sucking the blood from the host )
pubic louse compact body (abdomen plus thorax) + small size(0.25 mm) +
large claw on the legs so it called crab louse ( crab = ) سلطعون the claw help
the lice to catch the hair
2- area of isolation :
Head louse : found on scalp ( feed on human blood when need )
body louse : found on clothing ( feed on human blood when need )
pubic louse : found on pubic hair ( it is one of the major STDs )
lice present in crowded area and low hygiene ( handy cape -metal retarted
patient )
3- clinical importance :
lead to bleeding
STD (pubic louse)
Body louse is vector for : Epidemic typhus – Relapsing fever – Trench fever
Head and pubic louse not vectors

3- Ticks :
1- Hard ticks ( Ixodide spp. )
Hard skeleton of keratinized material cover the body (in female 1/3 of the body
is covered - in male whole body is covered) this hard skeleton called scutum
Oval in shape
4 Pairs of legs
We can see mouth part from both dorsal and ventral surface
See it brown in color
2- soft ticks ( orinithodourus spp. )
Leather texture ( lack of scutum )
rounded in shape
4 Pairs of legs
Not see mouth part from dorsal surface
It is the biggest insect in low-power
3- ticks feed on blood ( it not need human blood but human affect accidentally )
4- clinical importance :
Neurotoxin : it is anesthetic material ( to prevent human from sense the bite )
More than 5 adult ticks produce neurotoxin will reach the C.N.S ( may lead to
death ) ……. Sometimes lead to paralysis
Vector for :
1. Tularemia ( bacterial )
2. Hemorrhagic fever ( viral )
3. Babesia ( parasitic ) …… malaria like parasite that destroy the R.B.Cs
