
322
CHAPTER 8
The Perineum
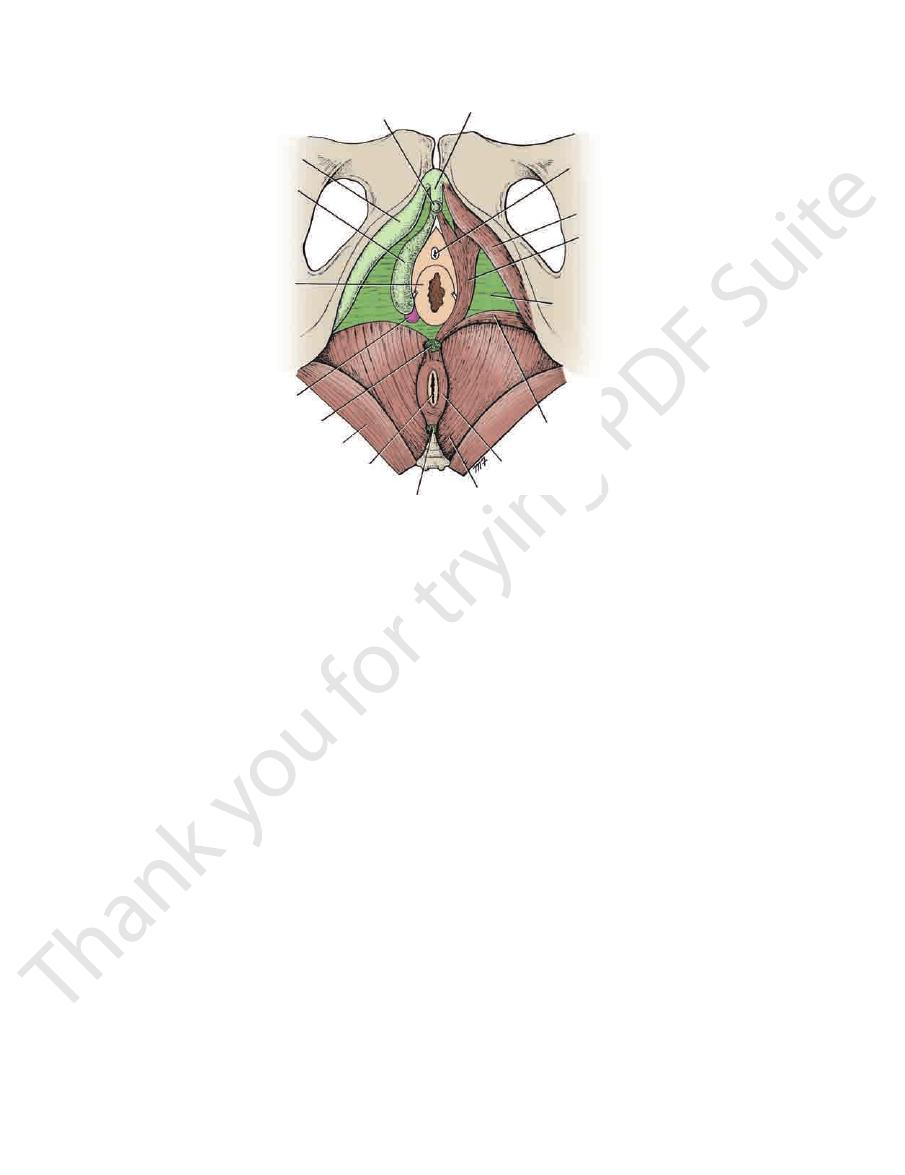
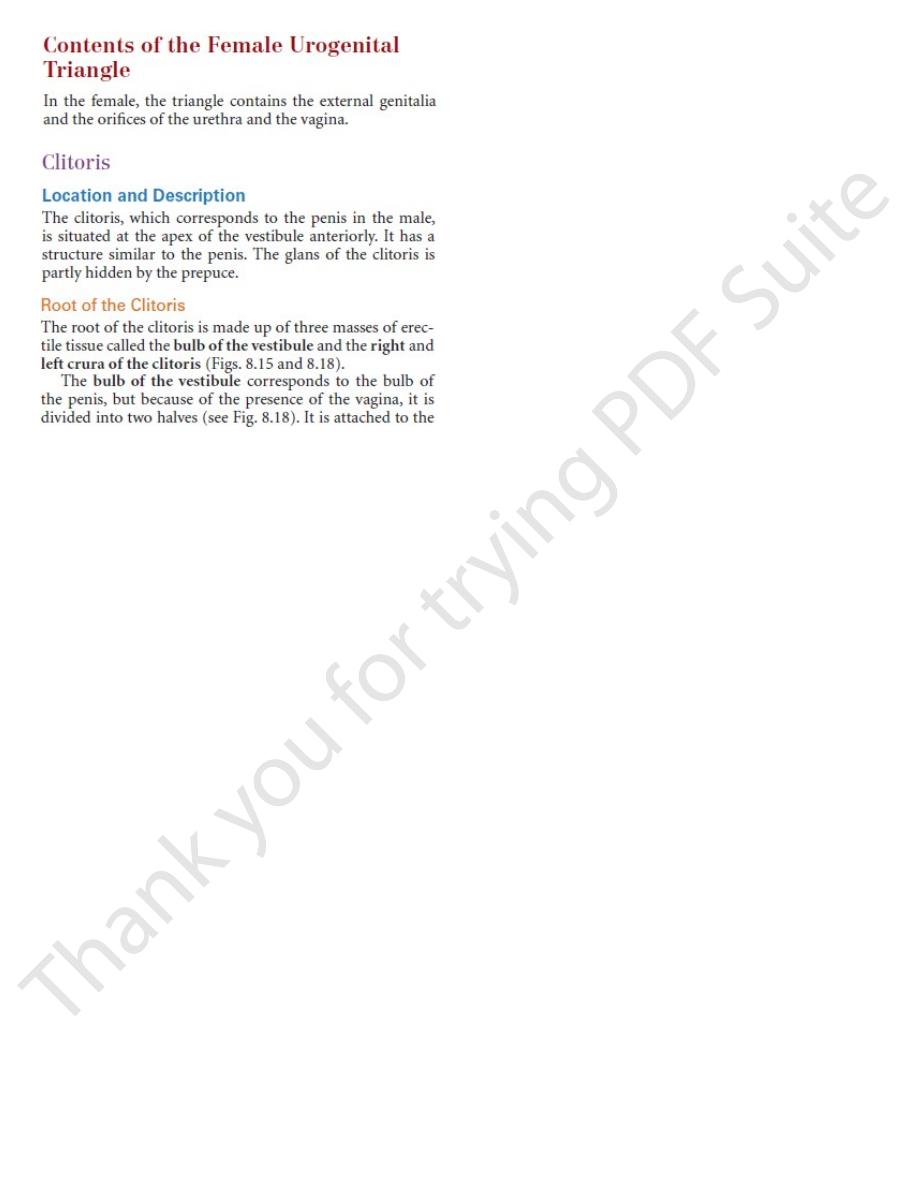
glans of clitoris
hymen
greater vestibular
gland
perineal body
gluteus maximus
anus
anococcygeal body
levator ani
external anal sphincter
superficial transverse
perineal muscle
inferior fascial layer
of urogenital diaphragm
(perineal membrane)
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
urethral orifice
body of clitoris
crus of clitoris
bulb of vestibule
FIGURE 8.18
Root and body of the clitoris and the perineal muscles.
in supporting the posterior wall of the vagina.
the levatores ani muscles; the latter assist the perineal body
ment of many perineal muscles (as in the male), including
anal canal (see Figs. 8.4 and 8.18). It is the point of attach
tissue situated between the lower end of the vagina and the
clinically important. It is a wedge-shaped mass of fibrous
The perineal body is larger than that of the male and is
Perineal Body
plied by the perineal branch of the pudendal nerve.
All the muscles of the superficial perineal pouch are sup
Nerve Supply
structure and function to those of the male.
The superficial transverse perineal muscles are identical in
Superficial Transverse Perineal Muscles
the erection of the clitoris.
of the clitoris. Contraction of this muscle assists in causing
The ischiocavernosus muscle on each side covers the crus
Ischiocavernosus Muscle
the clitoris.
clitoris, thereby assisting in the mechanism of erection in
vaginal orifice and compresses the deep dorsal vein of the
clitoris. The bulbospongiosus muscle reduces the size of the
ward to gain attachment to the corpora cavernosa of the
vagina and covers the vestibular bulbs. Its fibers extend for
The bulbospongiosus muscle surrounds the orifice of the
nosus muscles (see Figs. 8.15 and 8.18).
namely, the bulbospongiosus muscles and the ischiocaver
the root of the clitoris and the muscles that cover them,
The superficial perineal pouch contains structures forming
similar to those of the penis.
The blood supply, lymph drainage, and nerve supply are
and Nerve Supply
Blood Supply, Lymph Drainage,
prepuce.
sensory endings. The glans is partly hidden by the
caps the body of the clitoris. It is provided with numerous
The glans of the clitoris is a small mass of erectile tissue that
to the glans.
amount of erectile tissue leading from the vestibular bulbs
corpus spongiosum of the male is represented by a small
The
ischiocavernosus muscles.
covered by their
ernosa
corpora cav
The body of the clitoris consists of the two
(see Fig. 8.18).
muscle
ischiocavernosus
remains separate and is covered by an
penis and become the corpora cavernosa anteriorly. Each
correspond to the crura of the
crura of the clitoris
The
bulbospongiosus muscles.
by the
undersurface of the urogenital diaphragm and is covered
Body of the Clitoris
-
Glans of the Clitoris
Contents of the Superficial Perineal
Pouch in the Female
-
Bulbospongiosus Muscle
-
-
-

Basic Anatomy
within the clitoris in exactly the same manner as in the male.
Sexual excitement produces engorgement of the erectile tissue
supply, and their action is given in Table 8.1.
A summary of the muscles of the perineum, their nerve
structures found in the male.
have an arrangement similar to the corresponding
clitoris
dorsal nerves of the
internal pudendal vessels
are described on page 319 and 320. The
ineal muscles
deep transverse per
sphincter urethrae
The
The urethra and the vagina are described on pages 324
branches; and the dorsal nerves of the clitoris.
perineal muscles; the internal pudendal vessels and their
pierced by the urethra and the vagina; the deep transverse
urethra; part of the vagina; the sphincter urethrae, which is
The deep perineal pouch (see Fig. 8.15) contains part of the
the muscles and skin (see Fig. 8.8).
terminates in the superficial perineal pouch by supplying
The perineal branch of the pudendal nerve on each side
Perineal Branch of Pudendal Nerve
323
Contents of the Deep Perineal Pouch
in the Female
and 325.
and the
-
and the
Erection of the Clitoris
Muscles of Perineum
T A B L E 8 . 1
Voluntary sphincter of
Together with external
Together with puborec
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Action
External Anal Sphincter Muscles
Subcutaneous part
Encircles anal canal, no
bony attachments
Inferior rectal nerve and
perineal branch of
fourth sacral nerve
-
talis muscle forms
voluntary sphincter of
anal canal
Superficial part
Perineal body
Coccyx
Deep part
Encircles anal canal, no
bony attachments
Puborectalis (part of
levator ani)
Pubic bones
Sling around junction
of rectum and anal
canal
Perineal branch of
fourth sacral nerve
and from perineal
branch of pudendal
nerve
anal sphincter forms
voluntary sphincter
for anal canal
Male Urogenital Muscles
Bulbospongiosus
Perineal body
Fascia of bulb of penis
and corpus spongio-
sum and cavernosum
Perineal branch of
pudendal nerve
Compresses urethra
and assists in erec-
tion of penis
Ischiocavernosus
Ischial tuberosity
Fascia covering corpus
cavernosum
Perineal branch of
pudendal nerve
Assists in erection of
penis
Sphincter urethrae
Pubic arch
Surrounds urethra
Perineal branch of
pudendal nerve
urethra
Superficial transverse
perineal muscle
Ischial tuberosity
Perineal body
Perineal branch of
pudendal nerve
Fixes perineal body
Deep transverse per-
ineal muscle
Ischial ramus
Perineal body
Perineal branch of
pudendal nerve
Fixes perineal body
Female Urogenital Muscles
Bulbospongiosus
Perineal body
Fascia of corpus caver-
nosum
Perineal branch of
pudendal nerve
Sphincter of vagina and
assists in erection of
clitoris
Ischiocavernosus
Ischial tuberosity
Fascia covering corpus
cavernosum
Perineal branch of
pudendal nerve
Causes erection of
clitoris
Sphincter urethrae
Same as in male
Superficial transverse
perineal muscle
Same as in male
Deep transverse per-
ineal muscle
Same as in male
324
CHAPTER 8
brings about sexual contentment, but other women require
rhythmic contraction. In many women, a single orgasm
giosus and ischiocavernosus muscles, which also undergo
the pudendal nerve (S2, 3, and 4) to reach the bulbospon
cally contracts. In addition, nervous impulses travel in
the smooth muscle of the vaginal wall, which rhythmi
trunks. The postganglionic fibers are then distributed to
glia in the lower lumbar or pelvic parts of the sympathetic
and 2nd lumbar ganglia; other fibers may synapse in gan
these fibers synapse with postganglionic neurons in the 1st
segments in preganglionic sympathetic fibers. Many of
thought to leave the cord at the first and second lumbar
The nervous impulses that pass to the genital organs are
the spinal cord to the sympathetic outflow (T1 to L2).
reaching the central nervous system. Impulses then pass down
regions, results in a climax of pleasurable sensory impulses
forced by afferent nervous impulses from the breasts and other
Appropriate sexual stimulation of these sensitive areas, rein
dorsal nerves of the clitoris.
touch and are supplied by the ilioinguinal nerves and the
the labia minora, and the clitoris are extremely sensitive to
sensitive only to stretch. The region of the vaginal orifice,
vic cavity, is supplied by the hypogastric plexuses and is
The upper part of the vagina, which resides in the pel
mucus.
tibular glands at the vaginal orifice secrete a lubricating
gested mucous membrane. In addition, the greater ves
moist because of transudation of fluid through the con
excitement. During this process, the vaginal walls become
psychic stimuli gradually build up the intensity of sexual
As in the male, vision, hearing, smell, touch, and other
The Perineum
Orgasm in the Female
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
a series of orgasms to feel replete.
side of the urethral orifice (Fig. 8.19).
in the male, open into the vestibule by small ducts on either
The paraurethral glands, which correspond to the prostate
Paraurethral Glands
dilated relatively easily.
of the ducts of the paraurethral glands. The urethra can be
sides of the external urethral meatus are the small openings
urethrae and lies immediately in front of the vagina. At the
clitoris (see Figs. 8.4 and 8.18). It traverses the sphincter
it opens into the vestibule about 1 in. (2.5 cm) below the
where
external meatus,
from the neck of the bladder to the
The female urethra is about 1.5 in. (3.8 cm) long. It extends
Female Urethra
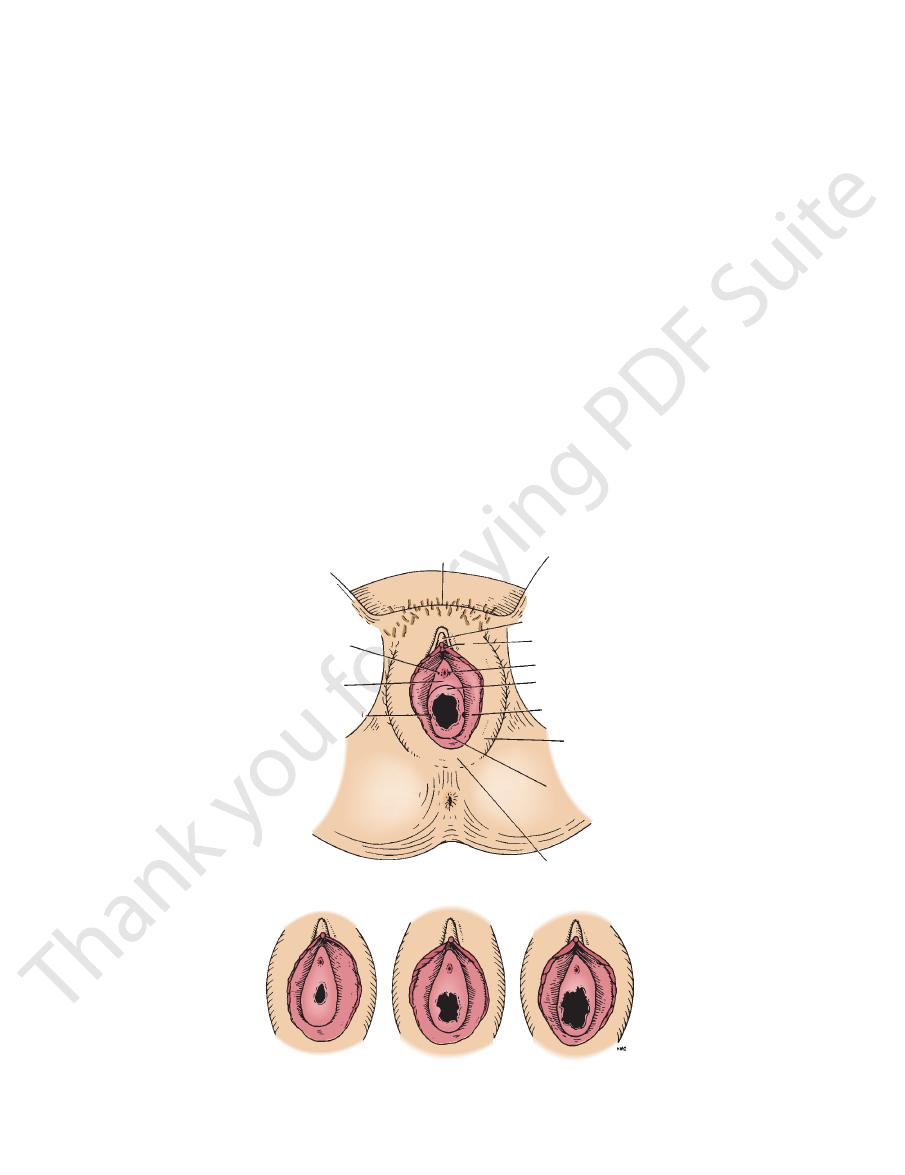
mons pubis
prepuce of clitoris
frenulum of clitoris
urethral orifice
hymen
labium minus
labium majus
fourchette
union of labia majora
duct of paraurethral
gland
vestibule
duct of greater
vestibular
gland
B
C
D
A
FIGURE 8.19
Vulva (
), and a multiparous woman (
), a woman who has had sexual intercourse
). Note the different appearances of the hymen in a virgin (
A
B
(C
D).
