
15
Lecture
Limbic System

LIMBIC SYSTEM
the limbic system
is involved with many other structures beyond the border zone
in the control of emotion, behavior, and drive; it also appears to be important
to memory
Anatomically
, the limbic structures include
1 - the subcallosal,
2 - the cingulate,
3 - the hippocampal formation (a- hippocampus , b- the dentate gyrus and c-
parahippocampal gyrus)
4 - the amygdaloid nucleus,
5 - the mammillary bodies
6 - the anterior thalamic nucleus
The alveus, the fimbria, the fornix, the mammillothalamic tract, and the stria
terminalis constitute the
connecting pathways of this system

The hippocampus
is a curved elevation of gray matter that extends throughout
the entire length of the floor of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
Its anterior end is expanded to form
the pes hippocampus
The convex ventricular surface is covered with ependyma, beneath which lies a
thin layer of white matter called
the alveus
The alveus consists of nerve fibers that have originated in the hippocampus,
and these converge medially to form a bundle called
the fimbria
The fimbria, in turn, becomes continuous with the
crus of the fornix
The hippocampus terminates posteriorly beneath the
splenium of the corpus
callosum
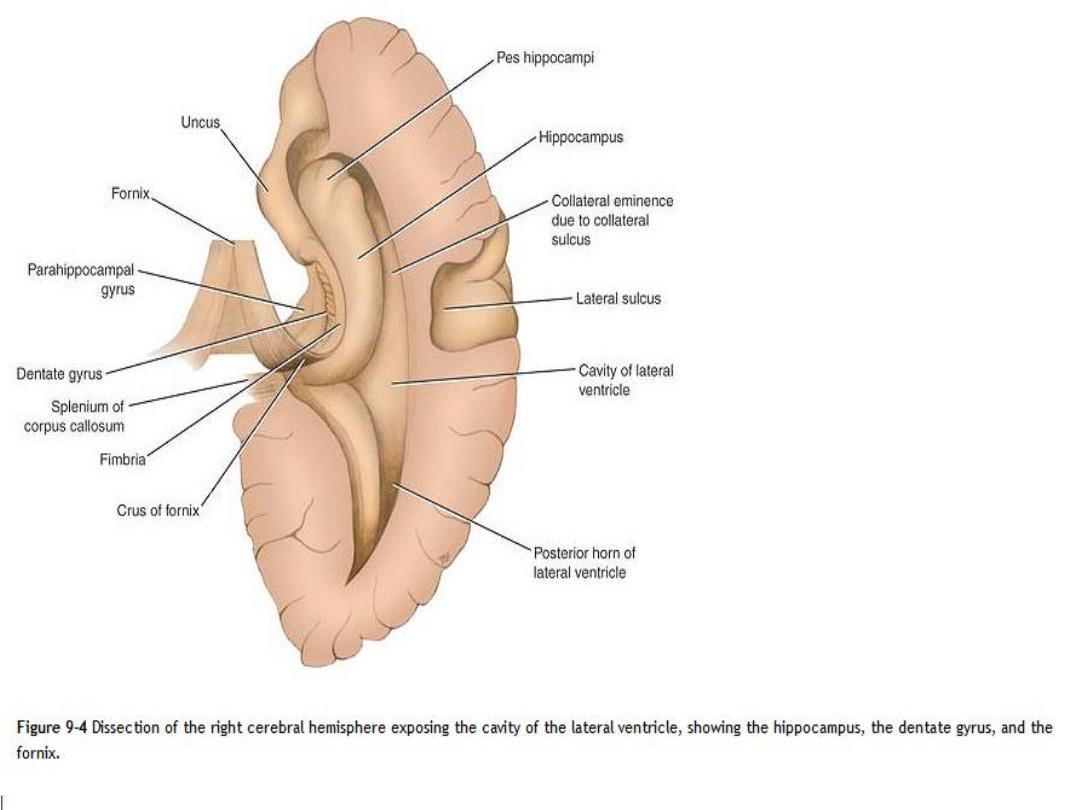

The dentate gyrus
is a narrow, notched band of gray matter that lies between
the fimbria of the hippocampus and the parahippocampal gyrus
Posteriorly,
the gyrus accompanies the fimbria almost to the splenium of the
corpus callosum and becomes continuous with
the indusium griseum
The indusium griseum
is a thin, vestigial layer of gray matter that covers the
superior surface of the corpus callosum
Embedded in the superior surface of the indusium griseum are two slender
bundles of white fibers on each side called
the medial and lateral
longitudinal striae
. The striae are the remains of the white matter of the
vestigial indusium griseum.
Anteriorly
, the dentate gyrus is continued into the uncus
parahippocampal gyrus
lies between the hippocampal fissure and the collateral
sulcus and is continuous with the hippocampus along the medial edge of
the temporal lobe
Amygdaloid Nucleus
It is situated partly anterior and partly superior to the tip of the inferior horn of
the lateral ventricle
The amygdaloid nucleus consists of a complex of nuclei that can be grouped
into a larger basolateral group and smaller corticomedial group
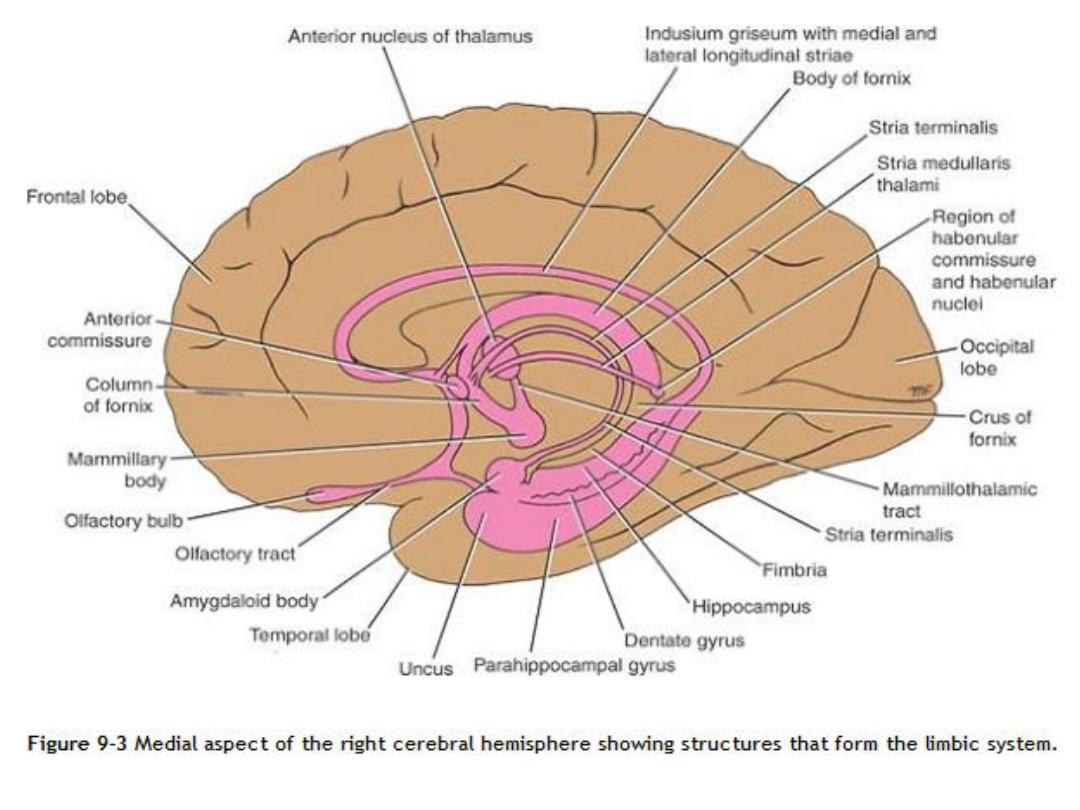

Connecting Pathways of the Limbic System
The connecting pathways of the limbic system are the alveus, the fimbria, the
fornix, the mammillothalamic tract, and the stria terminalis
Afferent Connections of the Hippocampus
Afferent connections of the hippocampus may be divided into six groups
1.
Fibers arising in the cingulate gyrus pass to the hippocampus.
2.
Fibers arising from the septal nuclei pass posterior in the fornix to the
hippocampus.
3.
Fibers arising from one hippocampus pass across the midline to the
opposite hippocampus in the commissure of the fornix.
4.
Fibers from the indusium griseum to the hippocampus.
5.
Fibers from the entorhinal area or olfactory-associated cortex pass to the
hippocampus.
6.
Fibers arising from the dentate and parahippocampal gyri travel to the
hippocampus.

Efferent Connections of the Hippocampus
- Axons of the large pyramidal cells of the hippocampus emerge to form the
alveus and the fimbria.
- The fimbria continues as the crus of the fornix.
- The two crura converge to form the body of the fornix.
- The body of the fornix splits into the two columns of the fornix,
- the two columns of the fornix curve downward and forward in front of the
interventricular foramina

The fibers within the fornix are distributed to the following regions:
1.
Fibers pass to enter the mammillary body, where they end in the medial
nucleus.
2.
Fibers pass to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus.
3.
Fibers to enter the tegmentum of the midbrain.
4.
Fibers pass to the hypothalamus.
5.
Fibers to the habenular nuclei
Functions of the Limbic System
1.
is able to influence many aspects of emotional behavior. These include
particularly the reactions of fear and anger and the emotions associated
with sexual behavior and hunger instict.
2.
converting recent memory to long-term memory
3.
effect homeostatic responses to a wide variety of environmental stimuli
