
د
.
لؤي
Overview of Carbohydrate
Metabolism
(
رؤوس نقاط و ليس شرح
)
1.
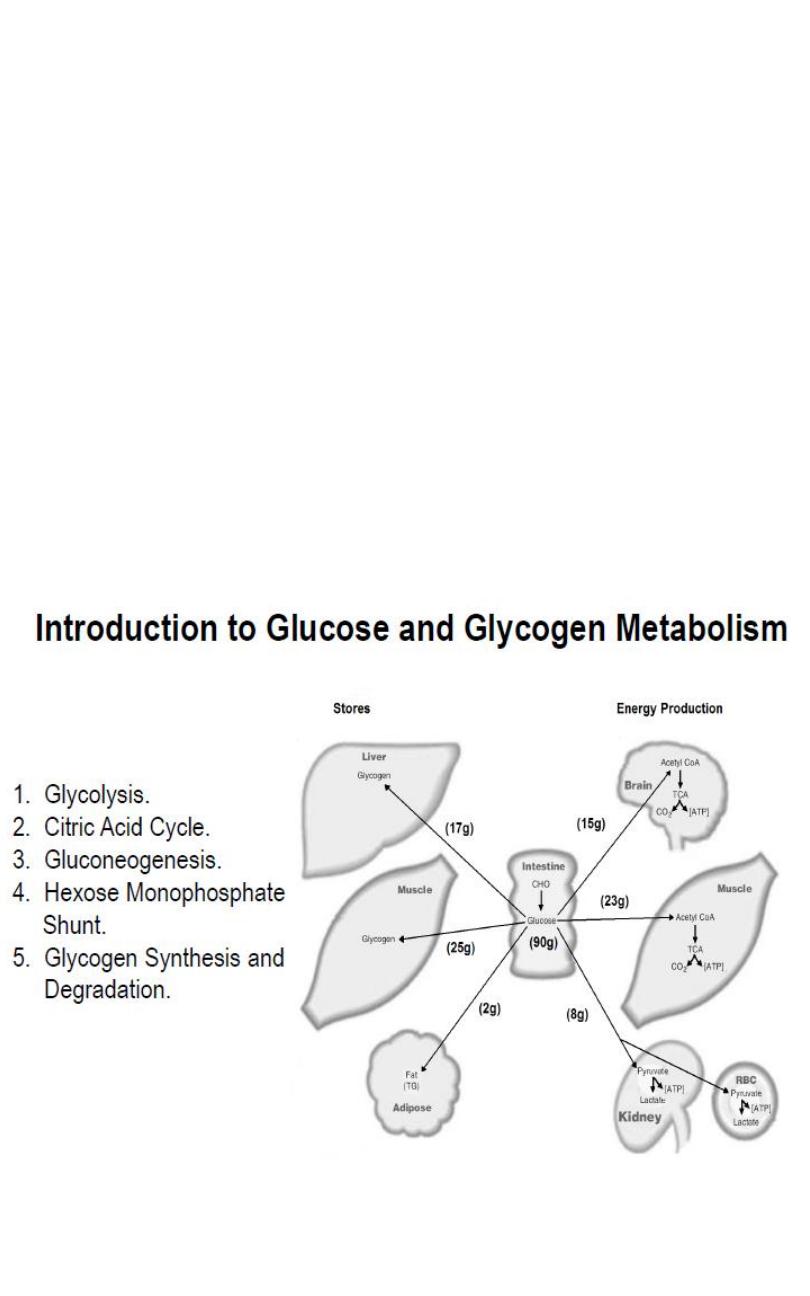
Introduction to Glucose and Glycogen Metabolism.
2.
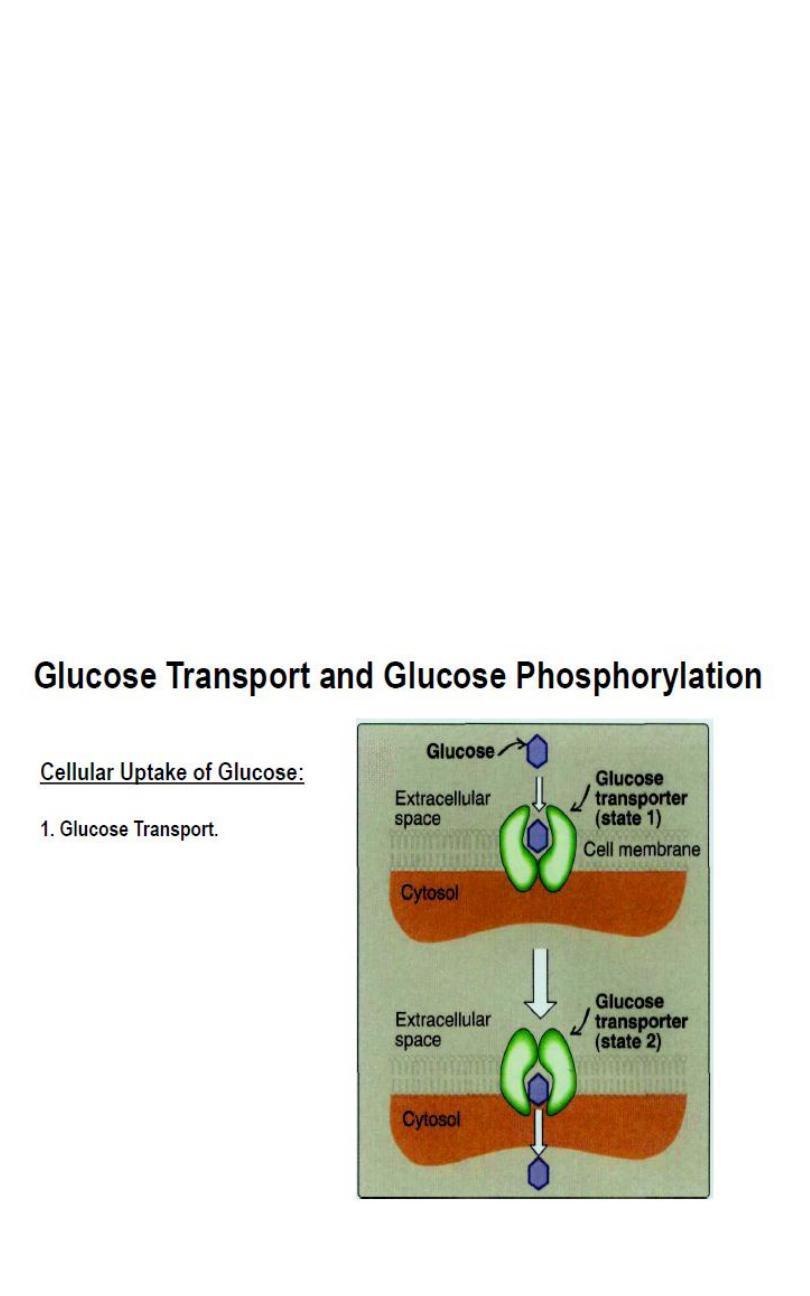
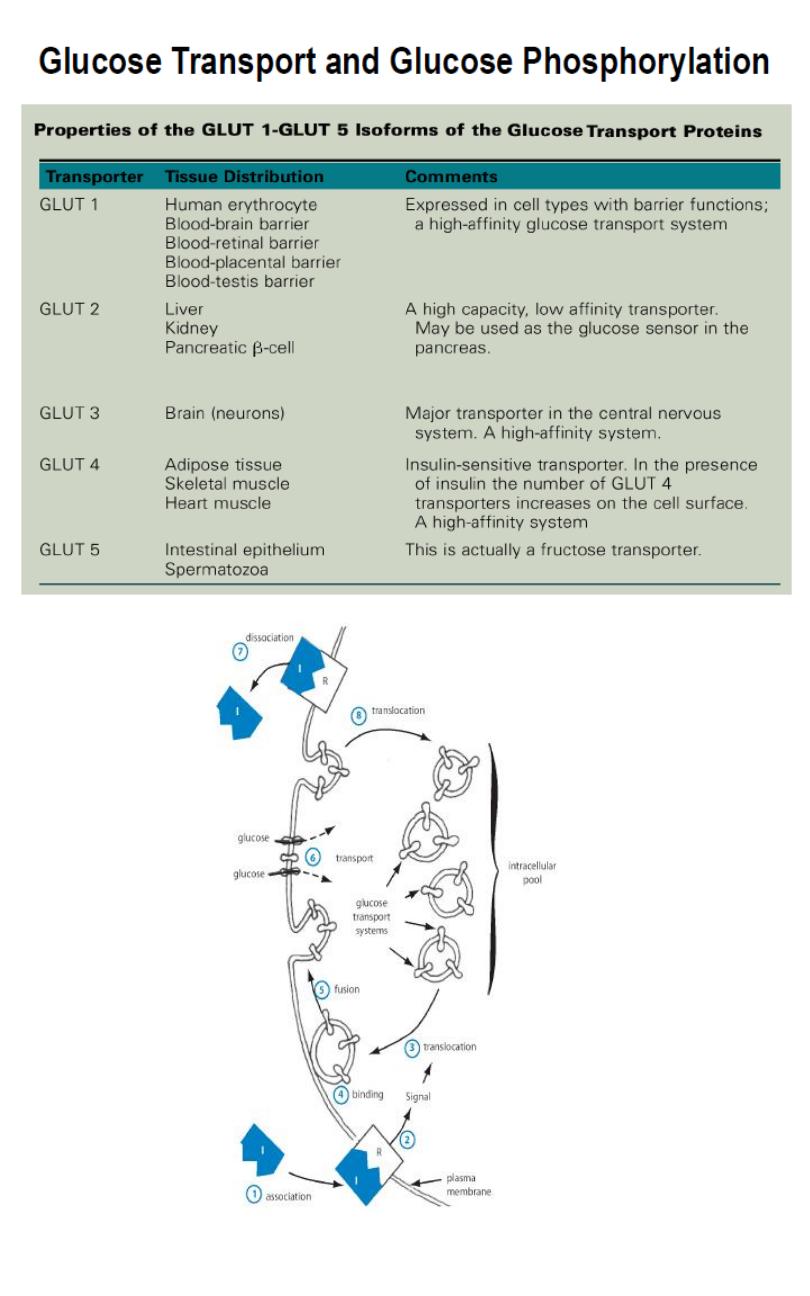
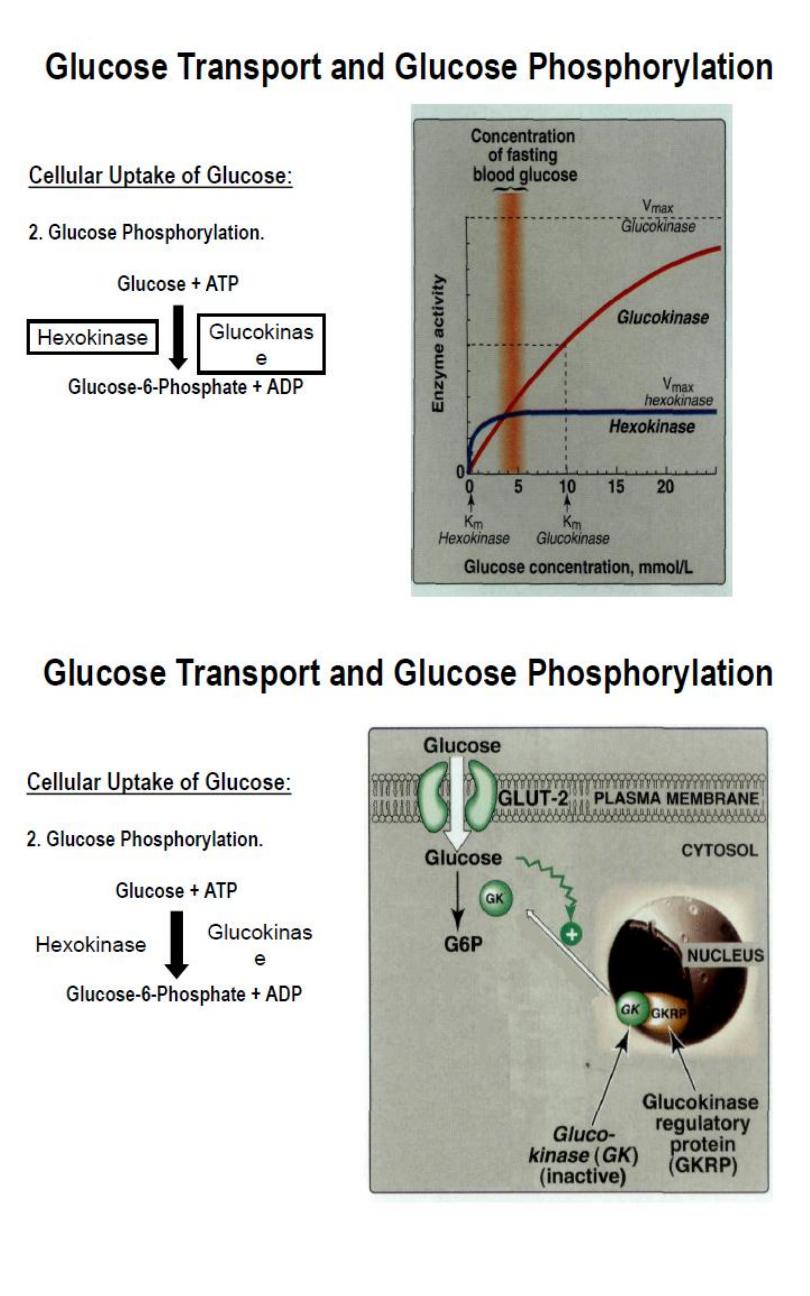
Glucose Transport and Glucose Phosphorylation:
–
a. Cellular Uptake of Glucose.
–
b. Cellular Release of Glucose.
3.
Hormonal Regulation of Glucose and Glycogen Metabolism.
–
a. Insulin. b. Glucagon. c. Catecholamines. d. Glucocorticosteroid.
4.
Regulation of Blood Glucose:
–
a. Fed State and Rate of Glucose Absorption.
–
b. Fasting State and Release of Endogenous Glucose.
–
c. Renal handling of Glucose.
–
5. Dysregulation of Blood Glucose:
–
a. Hyperglycemia. b. Hypoglycemia.
1
Lecture 1
Introduction to Glucose
and
Glycogen Metabolism.
2
Lecture 2
Glucose Transport and Glucose
Phosphorylation:
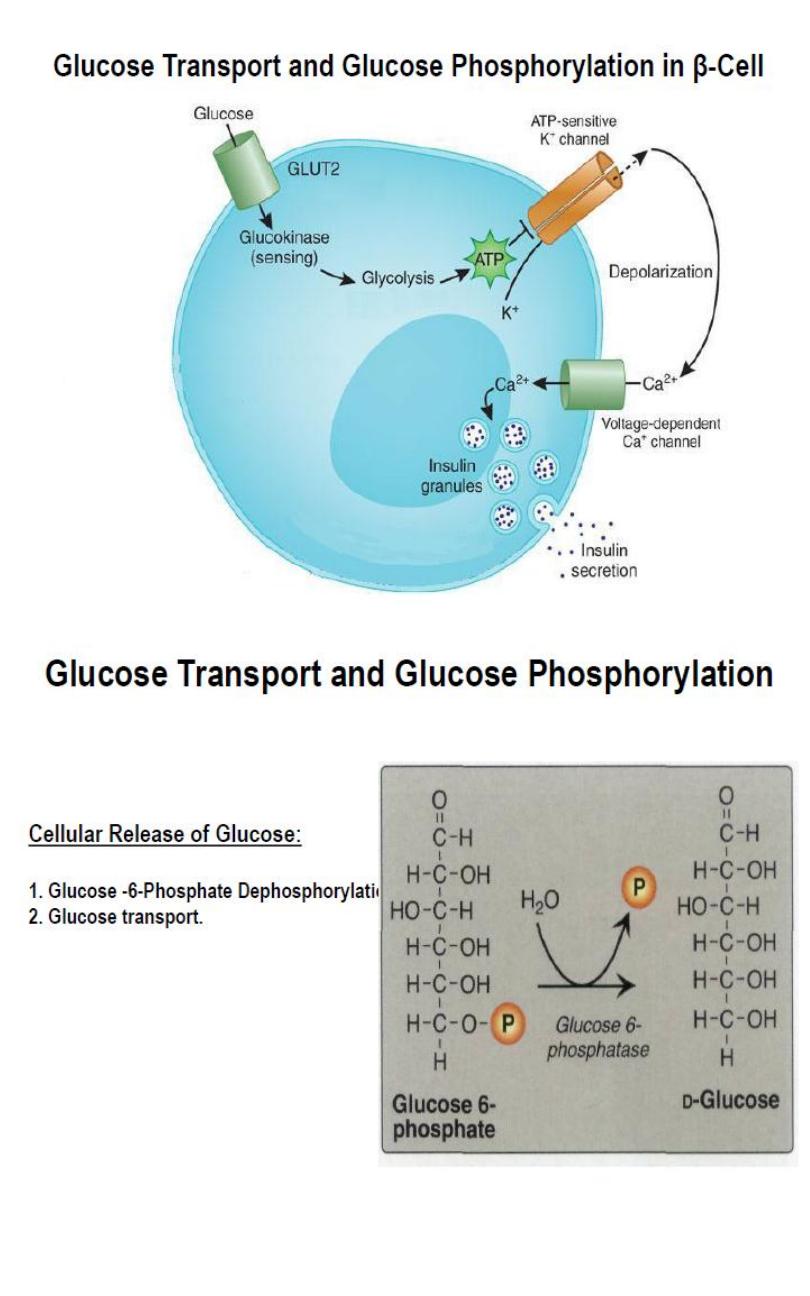
a. Cellular Uptake of Glucose.
b. Cellular Release of Glucose.
3
4
5
6
Lecture 3+4+5
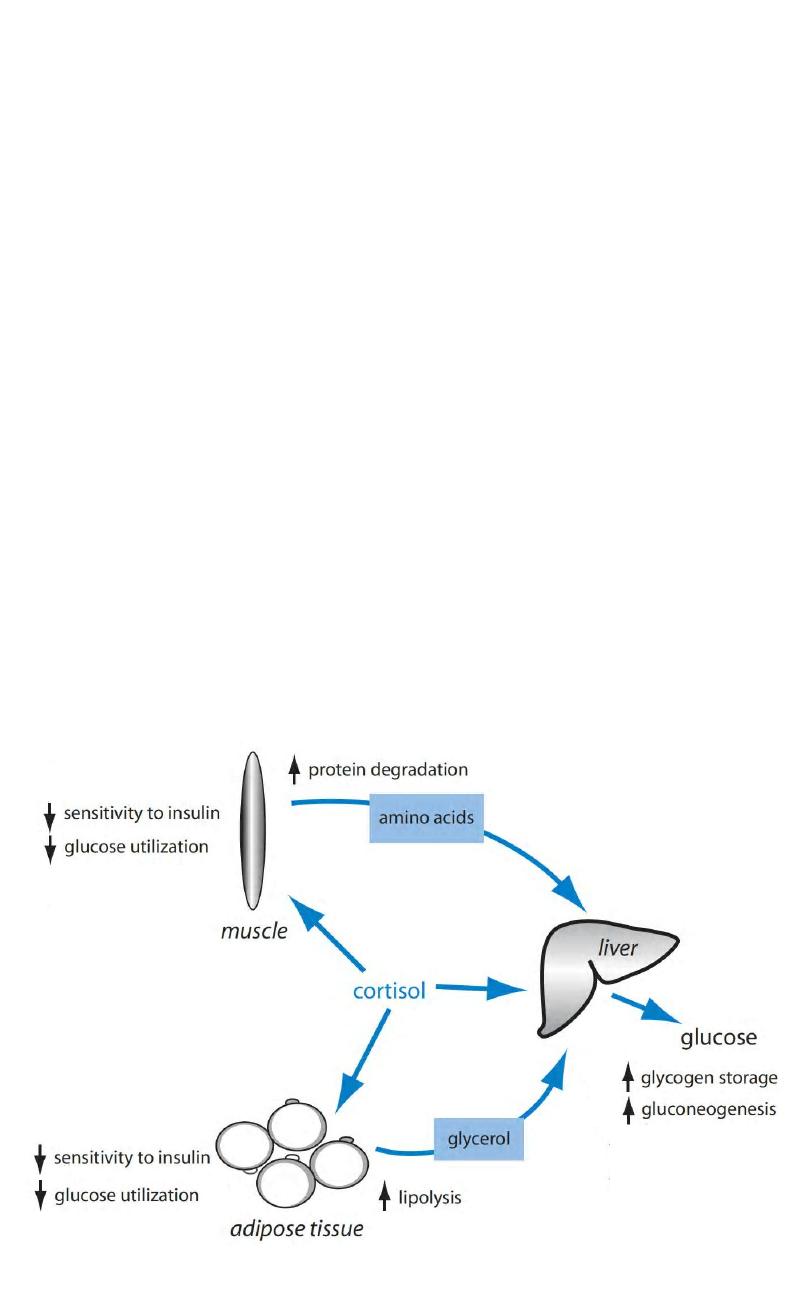
Hormonal Regulation of
Glucose and Glycogen
Metabolism.
a. Insulin.
b. Glucagon.
c. Catecholamines.
d. Glucocorticosteroid
7
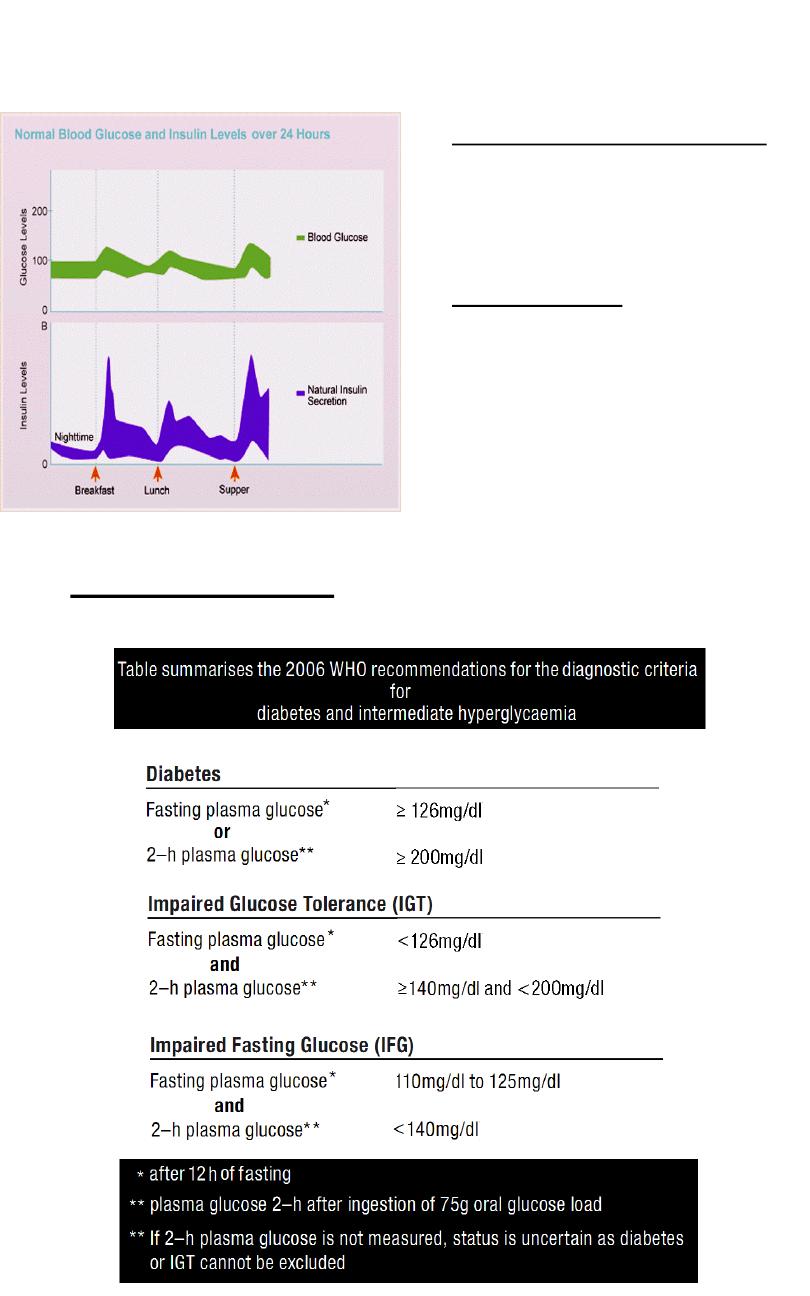
Regulation of Blood Glucose
The Fed State ( Absorptive State);
The period from the start of
absorption until absorption is
completed.
The Fasting State;
Begins approximately 2 to 4 hours
after a meal ( when blood glucose
levels return to basal levels) and
continues until blood glucose levels
begin to rise after the start of the
next meal.
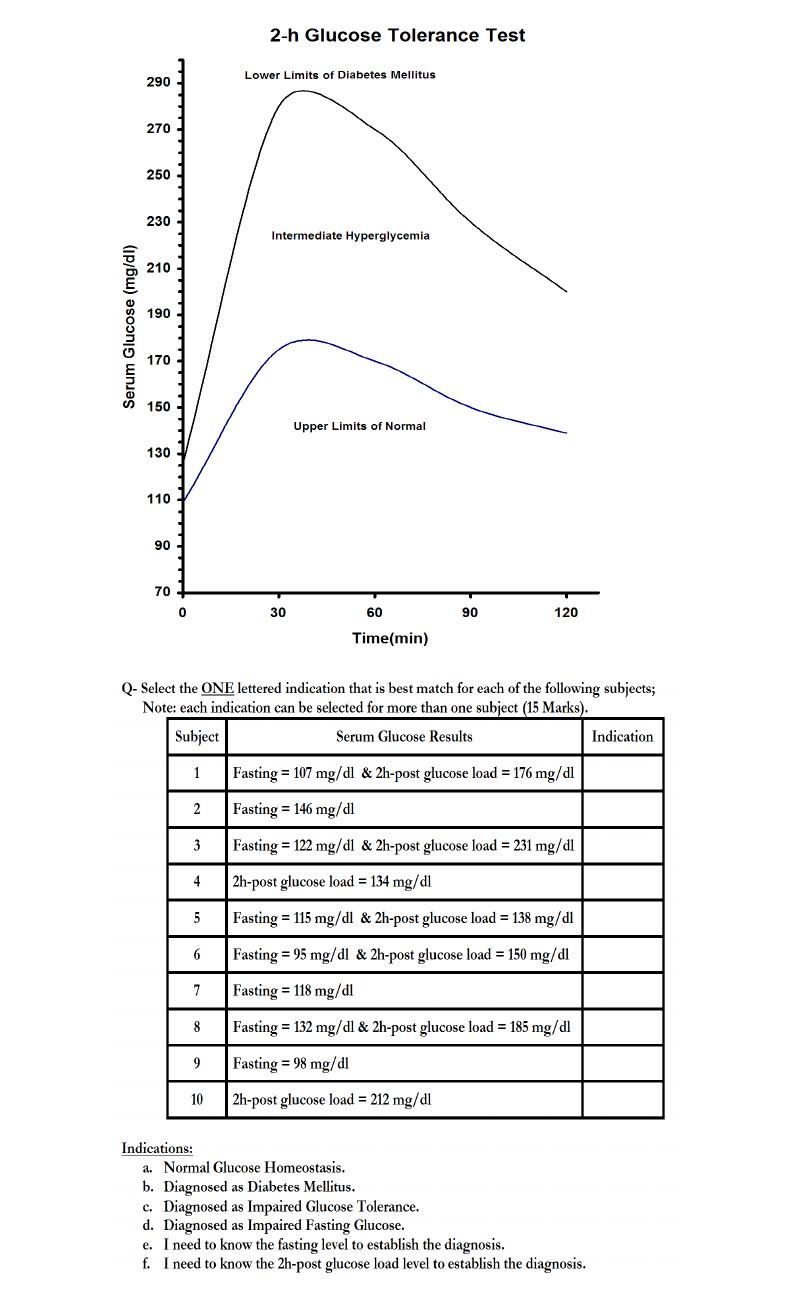
2-h Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
Objectives of the test; Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and
Intermediate Hyperglycemia
8
9
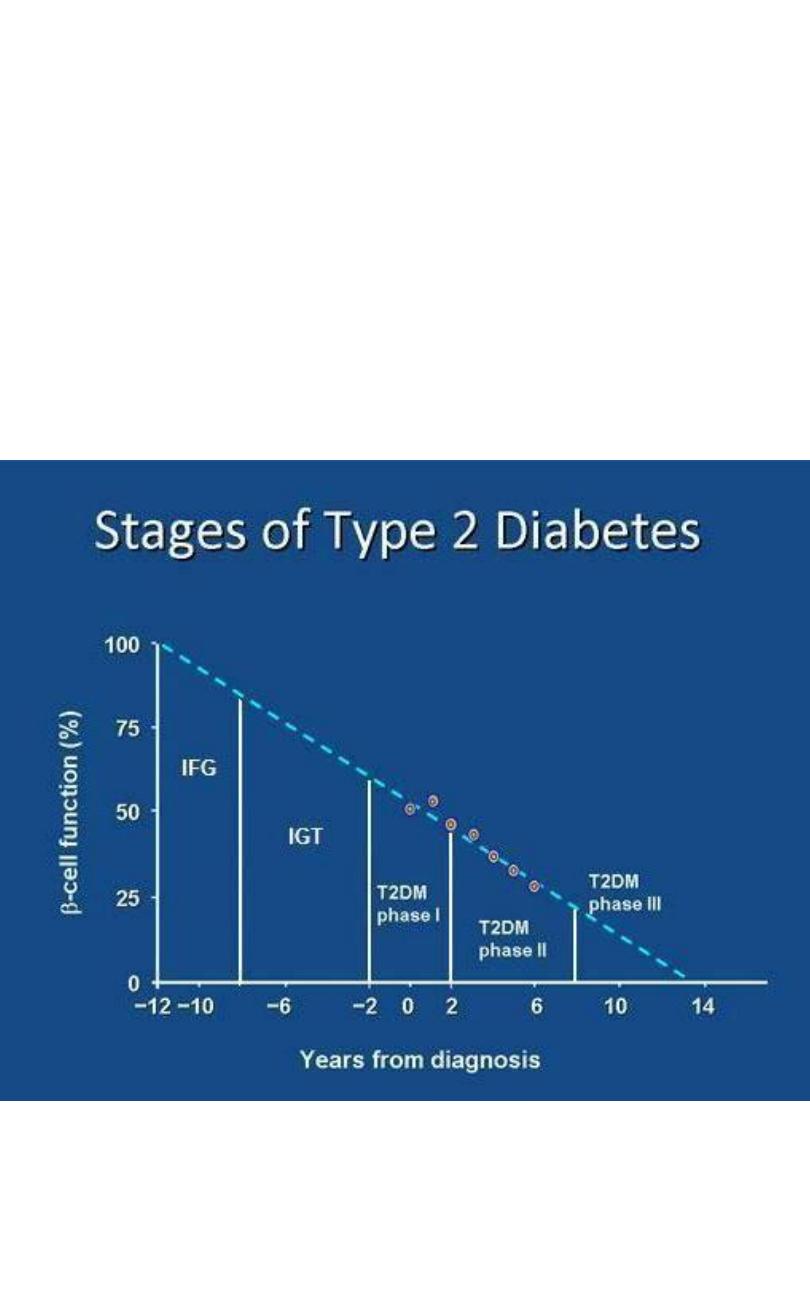
Lecture 6+7
Abnormalities & Disease of
carbohydrate metabolism
(hyperglycemia &
Hypoglycemia)
10
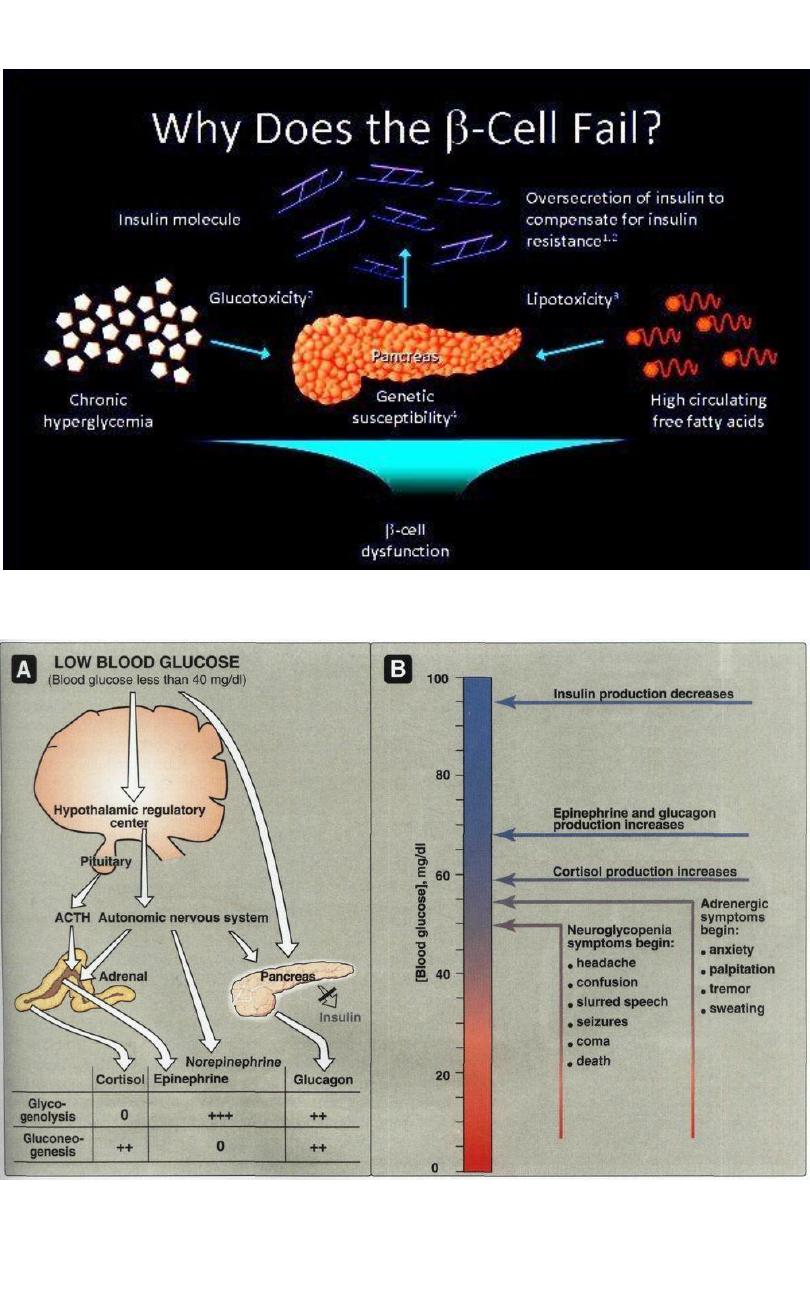
11
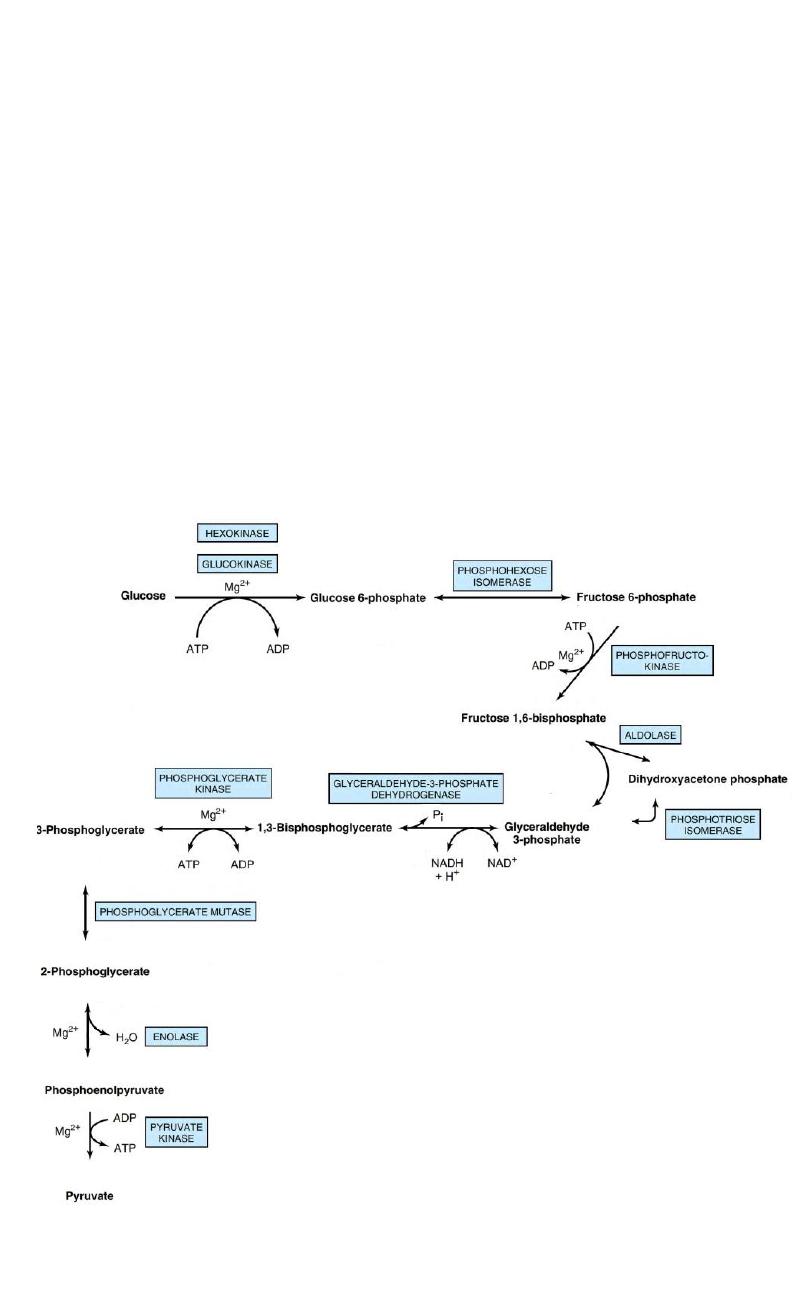
Lecture 8
Carbohydrate abnormalities
(Enzyme Deficiency)
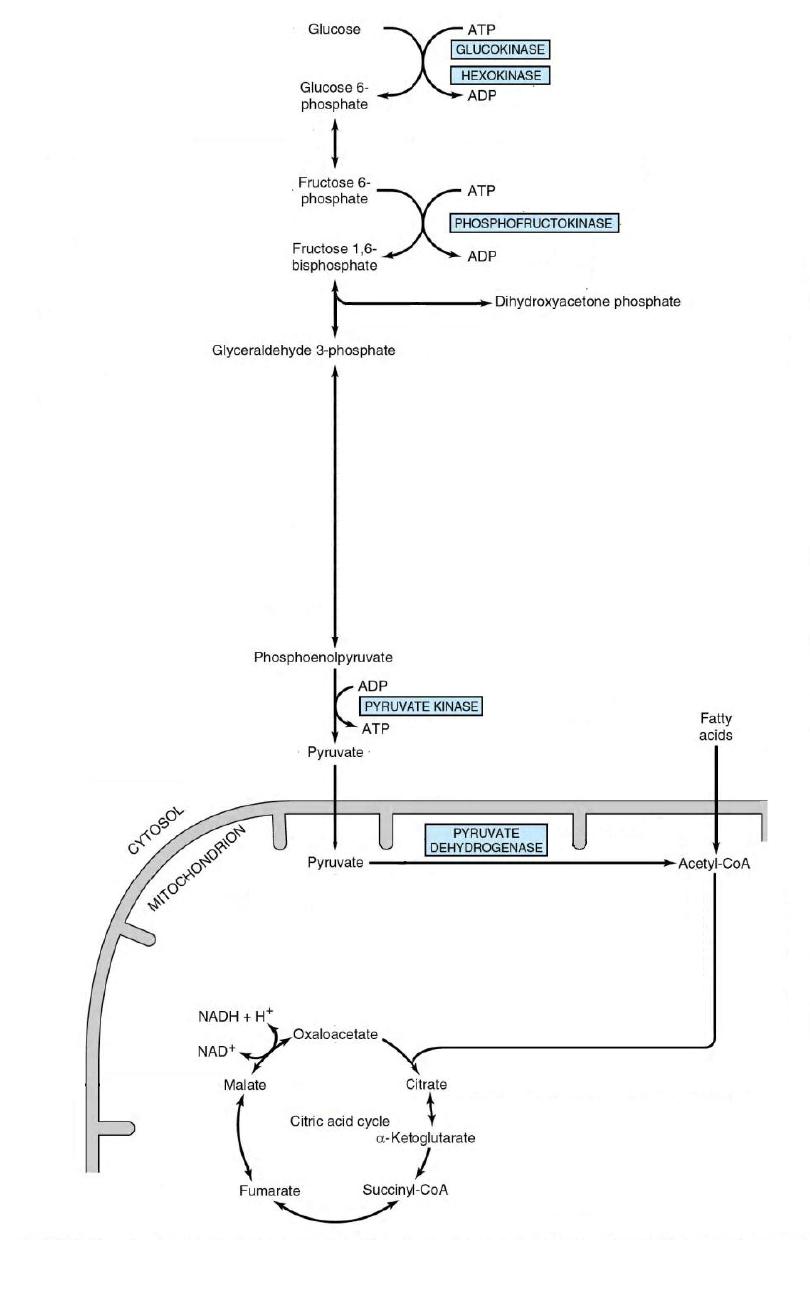
Glucolysis
12
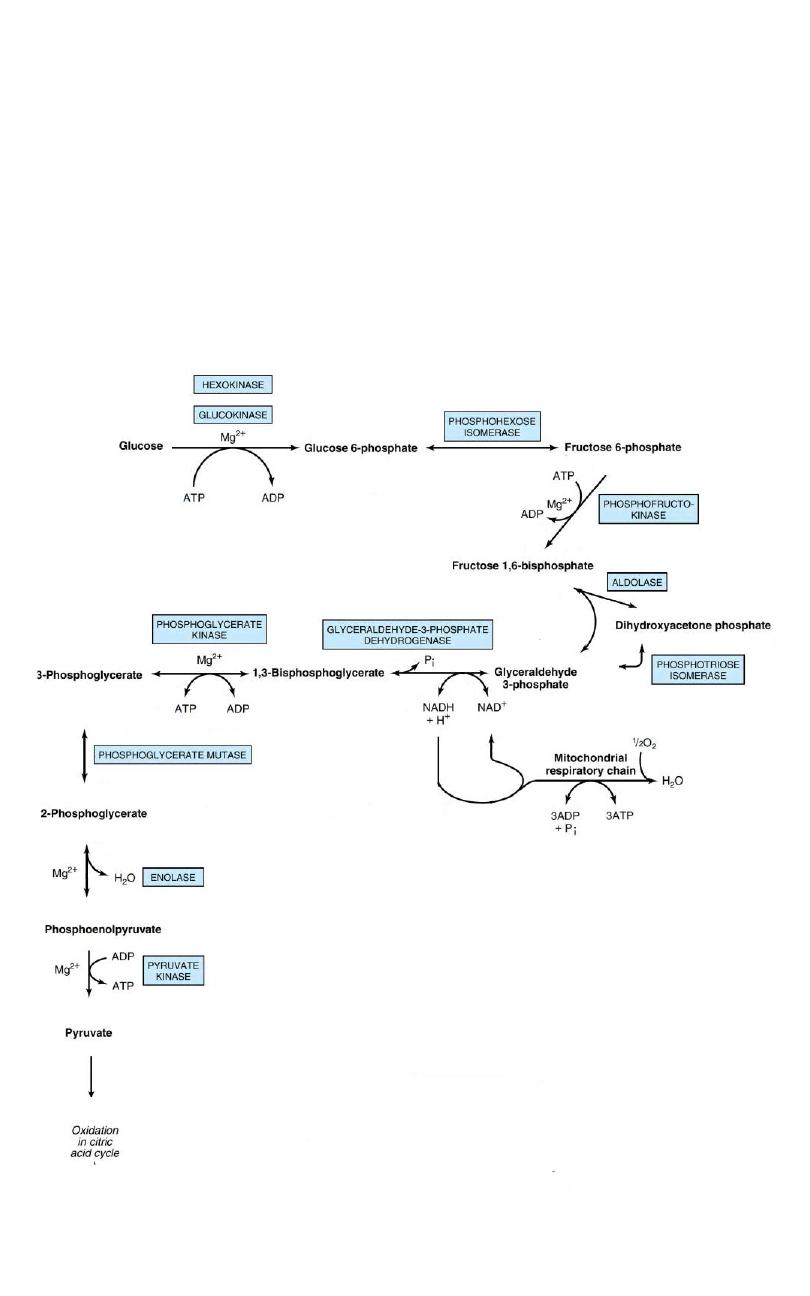
Aerobic Glycolysis
13
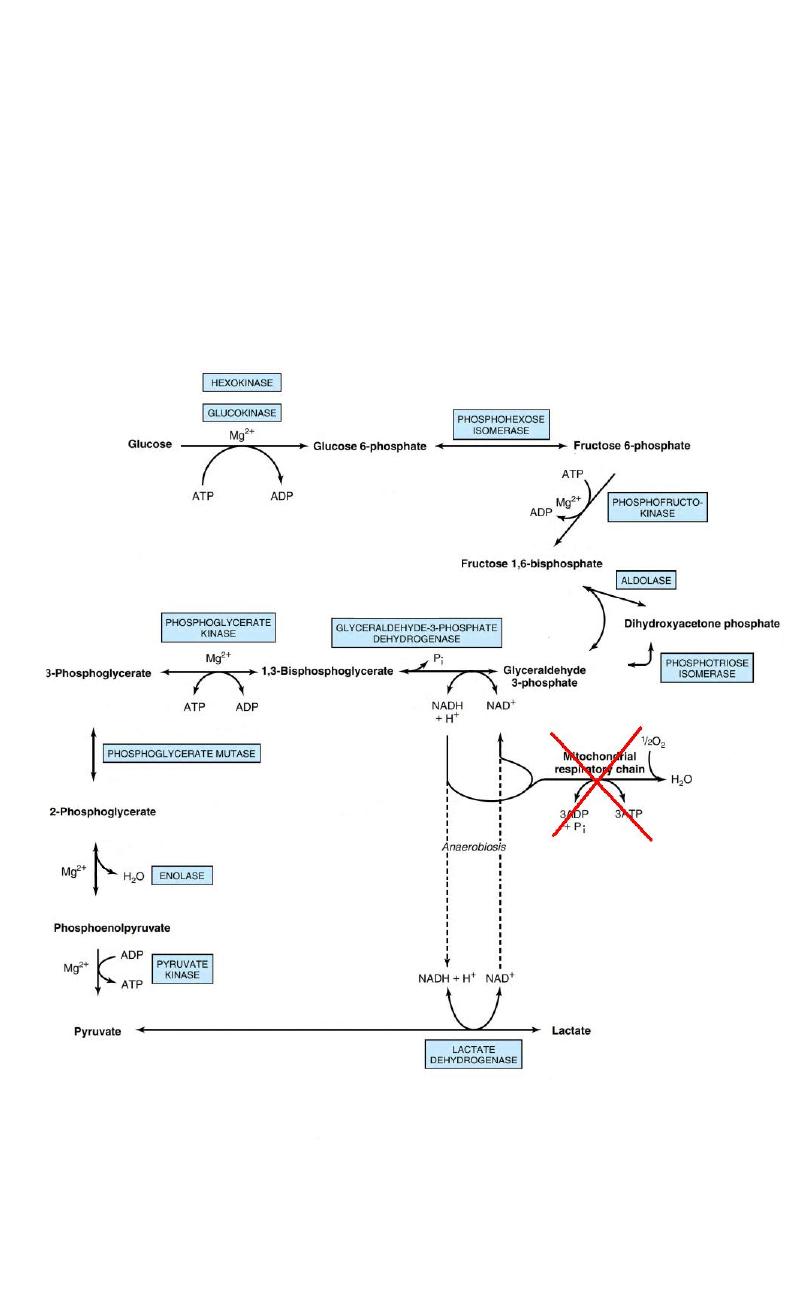
Anaerobic Glycolysis
14
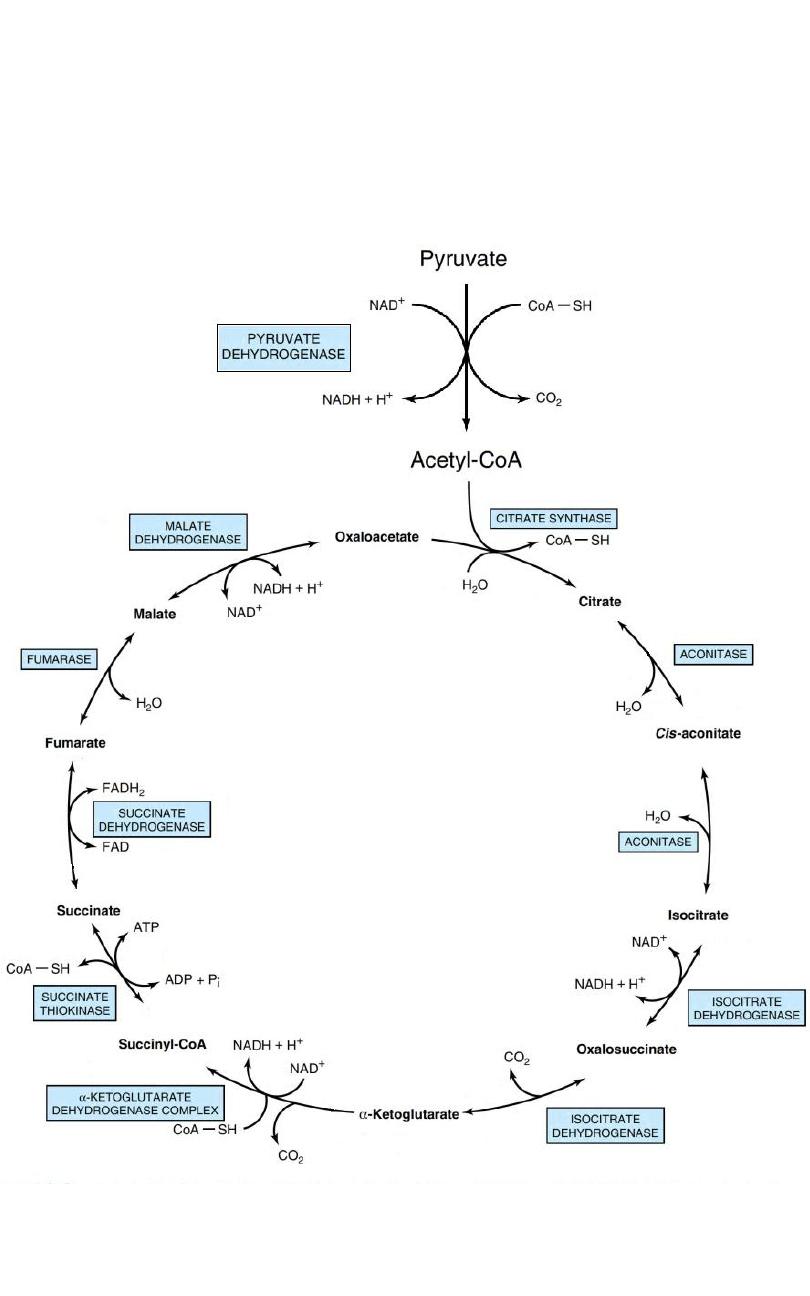
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC)
15

Generation of ATP
16
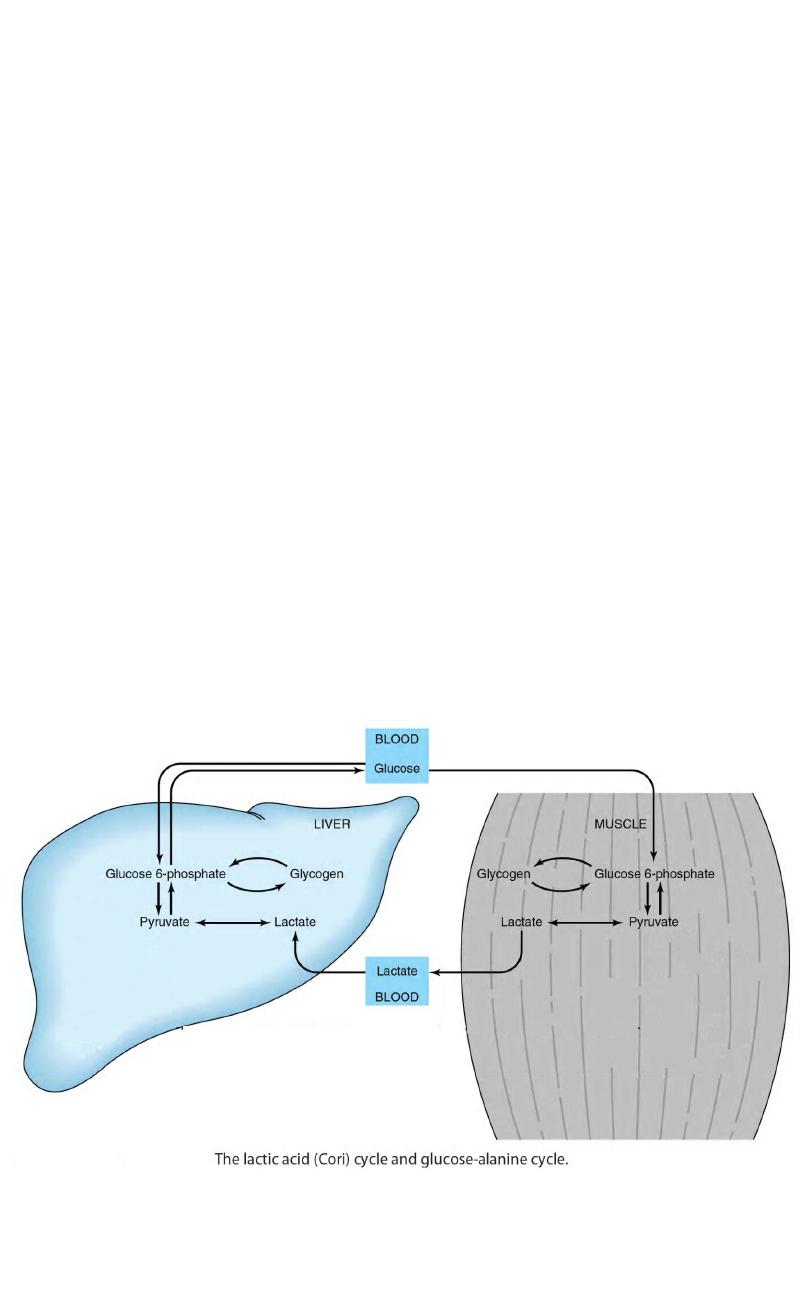
Lecture 9
Gluconeogenesis of
Lactic Acidosis
Cori Cycle
17
18
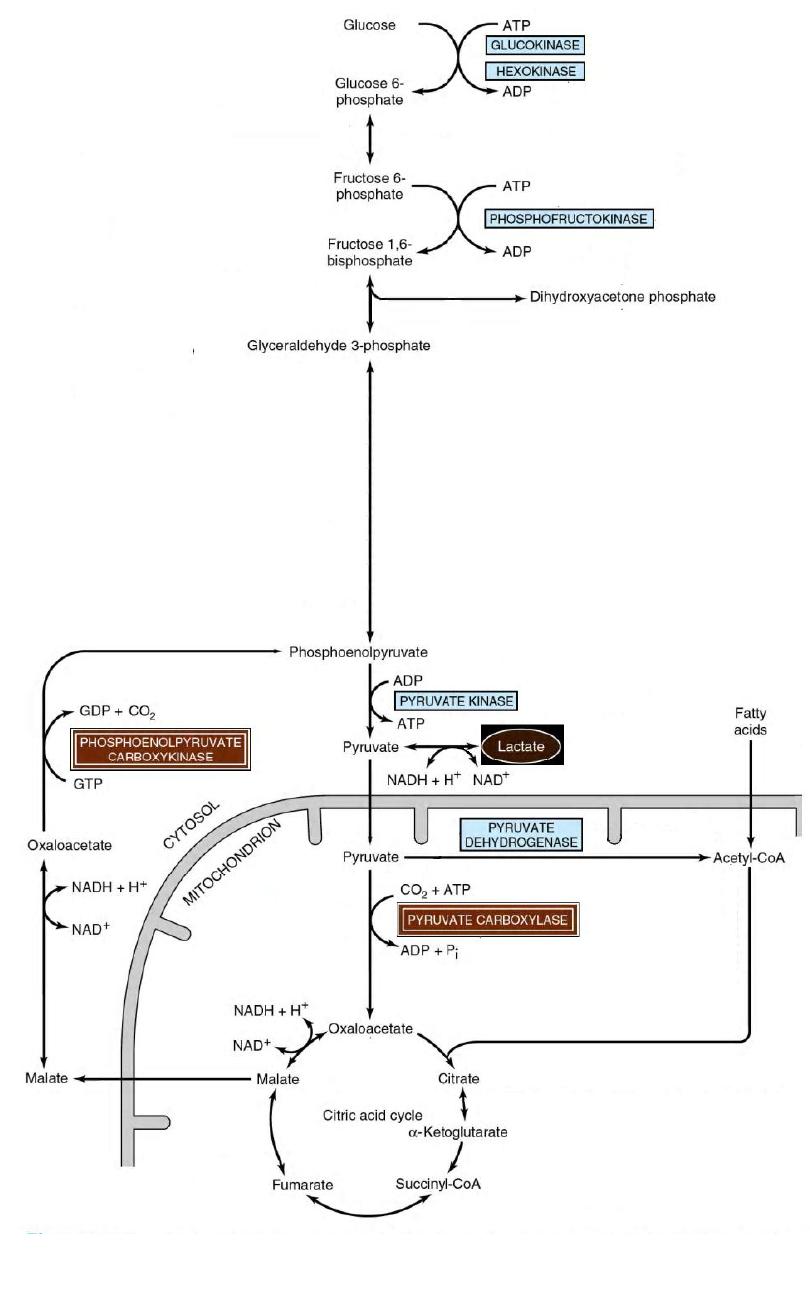
19
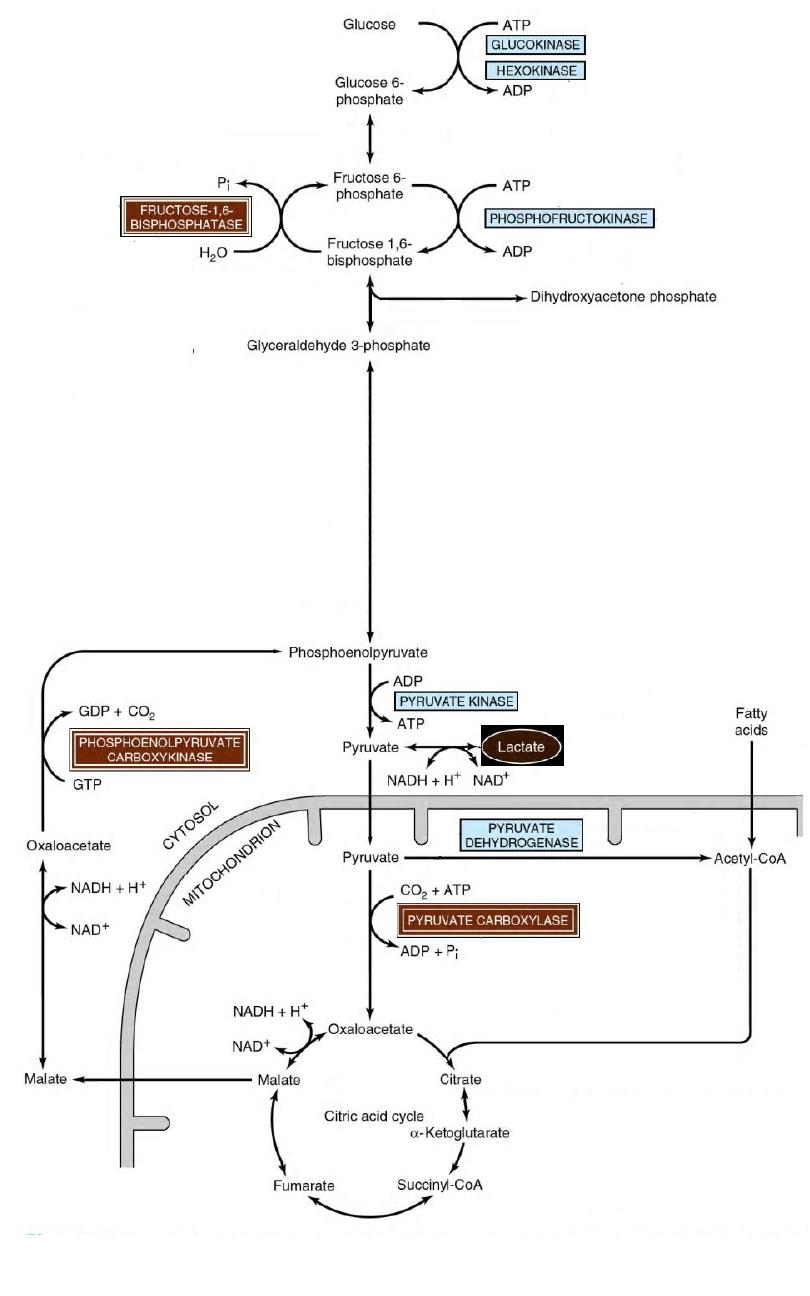
20
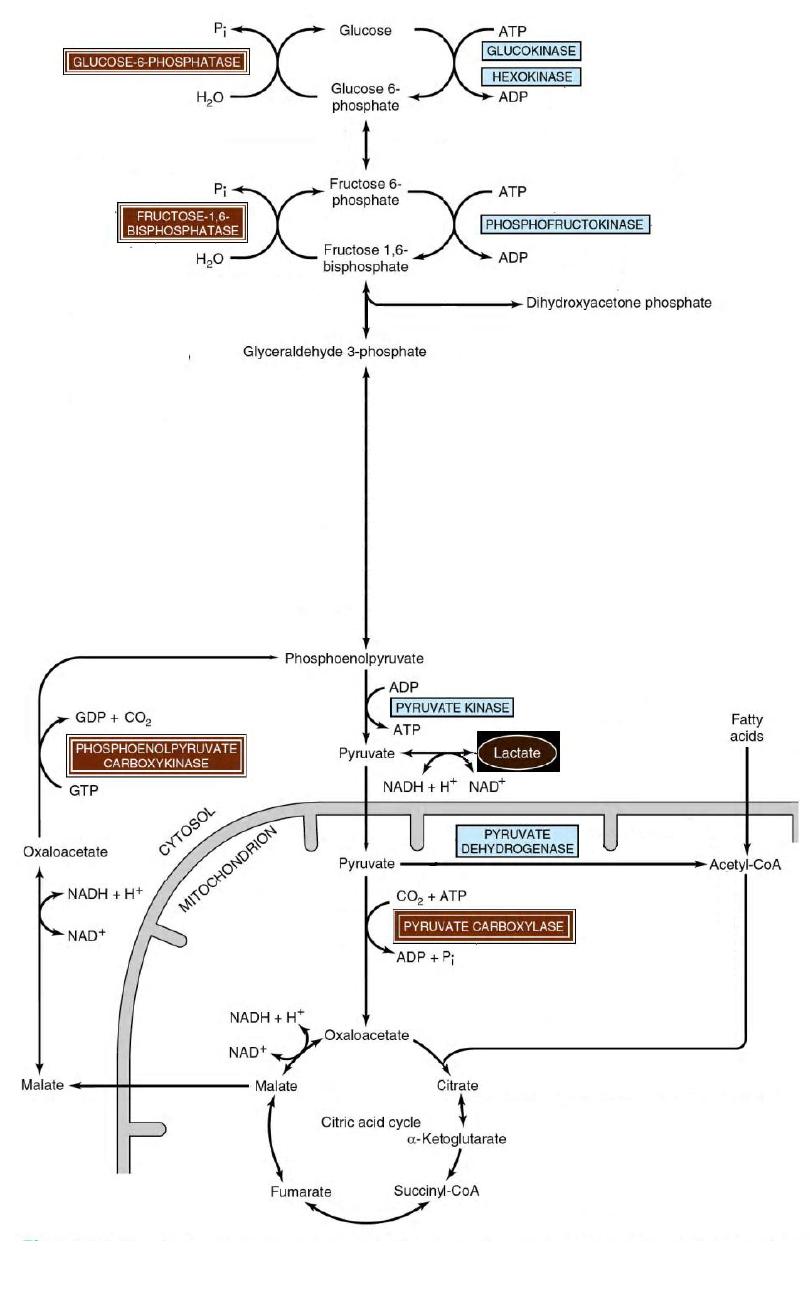
21
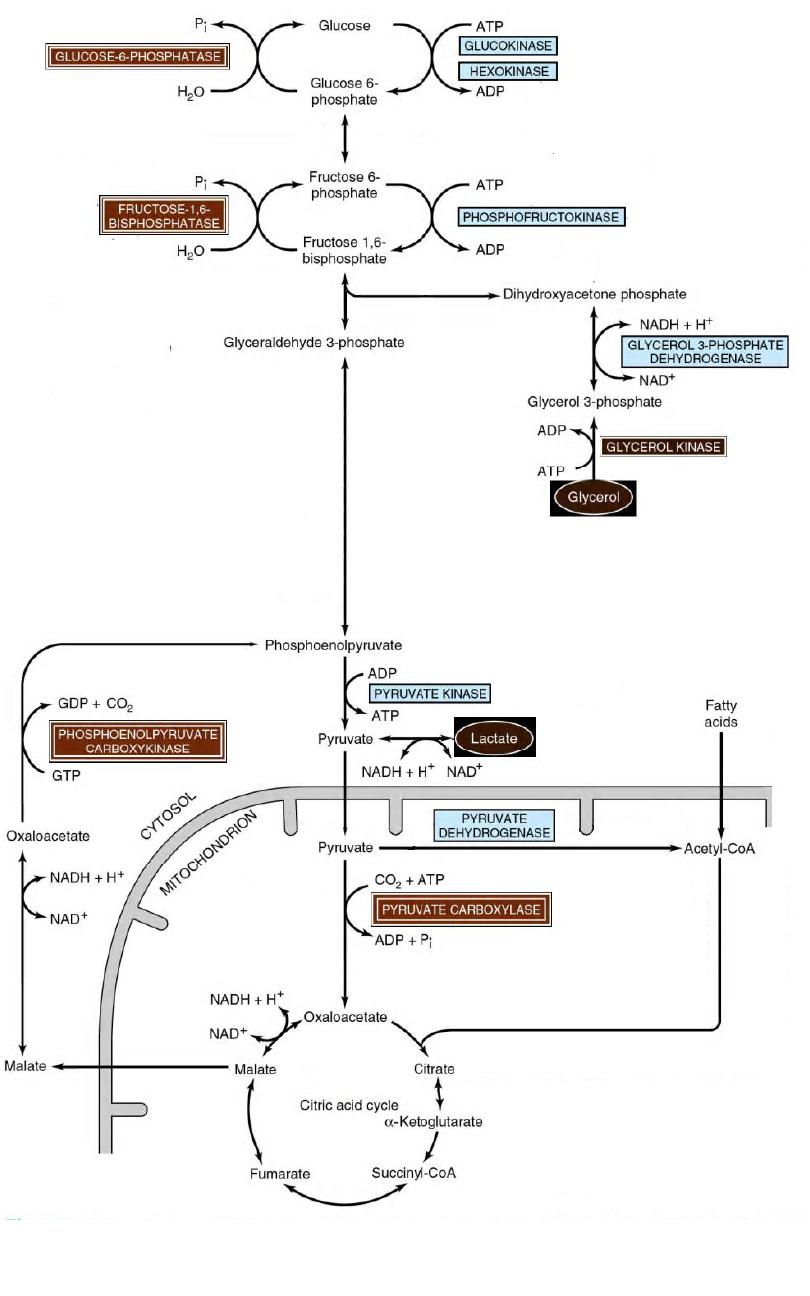
22
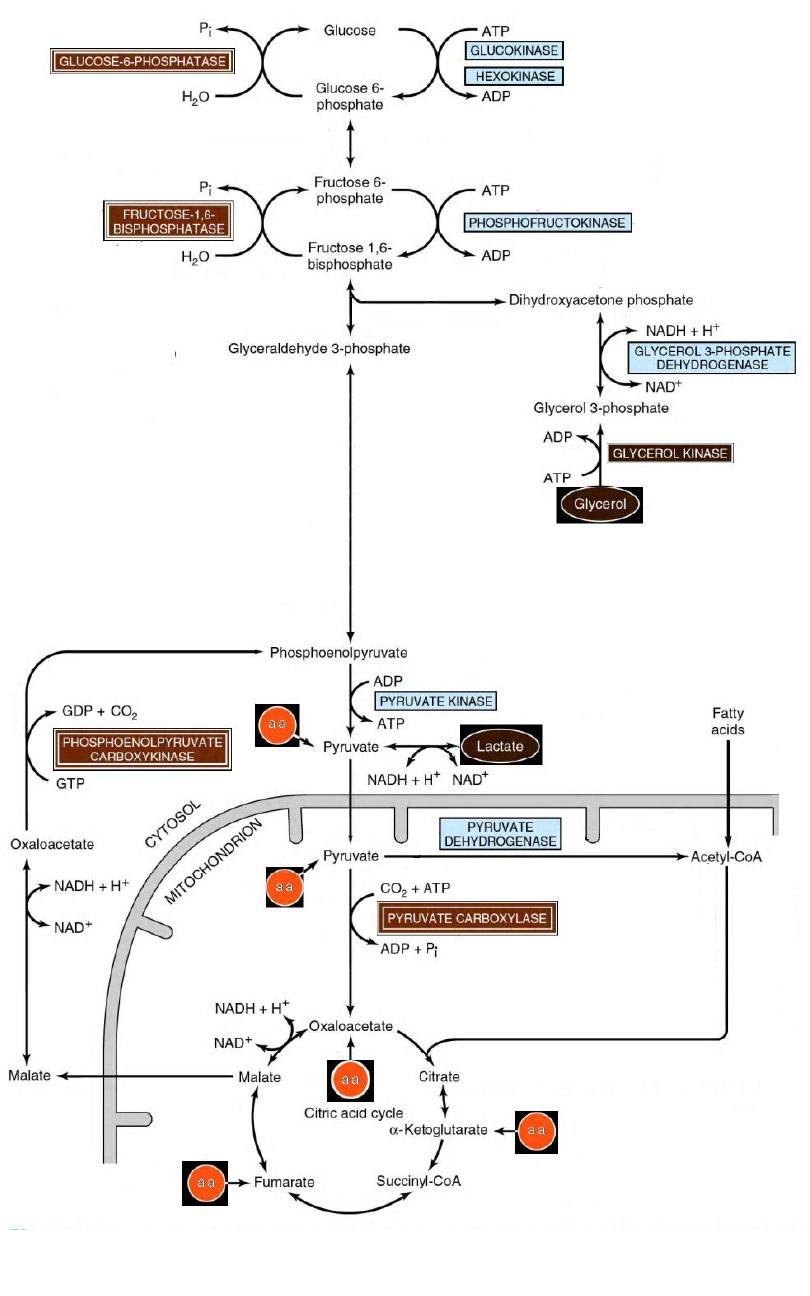
23

Lecture 10
Lactic Acidosis
24
