17
Lec. 6 Pyrimidine Metabolism
Pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway
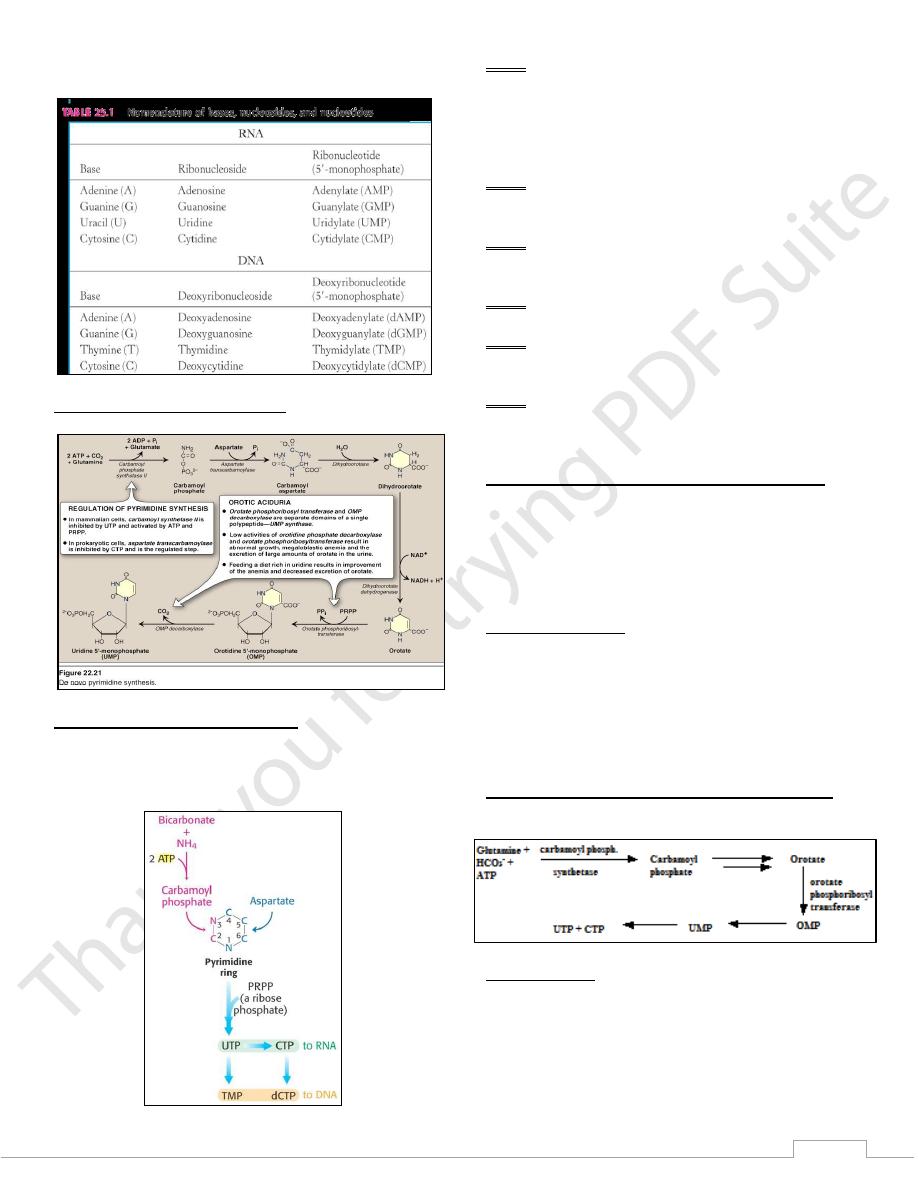
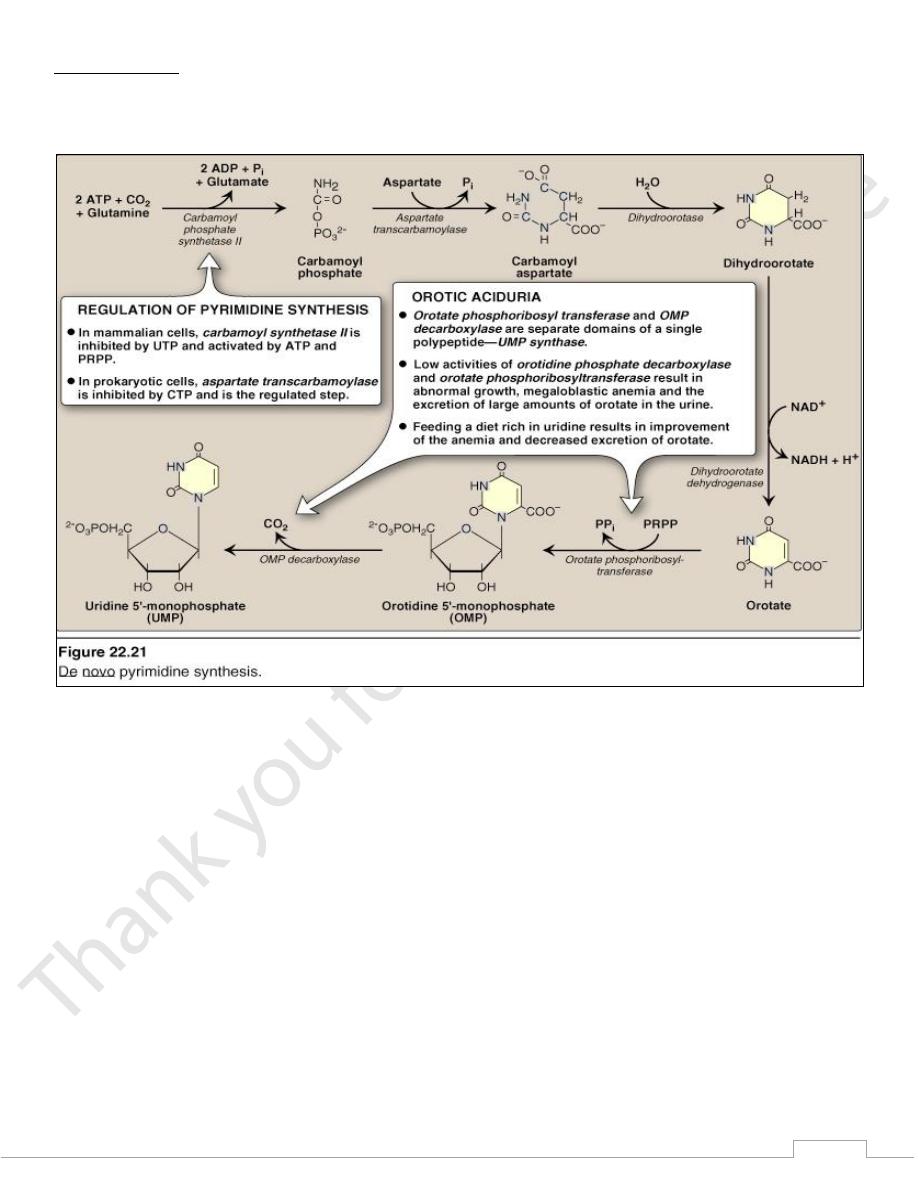
de Novo Synthesis of Pyrimidines
The ring is assembled from bicarbonate, aspartate and
glutamate.
The ring is synthesized first and then added to the ribose.
1) Step 1: Carbamoyl Phosphate synthesis
Carbamoyl phosphate for pyrimidine synthesis is made by
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II)
Substrates are HCO
3
-
, glutamine ,2 ATP
CPS-II can be viewed as the committed step in pyrimidine
synthesis
2) Step 2: Aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase)
catalyzes the condensation of carbamoyl phosphate with
aspartate to form carbamoyl-aspartate
3) Step 3: dihydrootase
ring closure and dehydration via condensation Produce
dihydroorotate
4) Step 4: dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
Synthesis of a pyrimidine (orotate)
5) Step 5: orotate phosphoribosyltransferase
Orotate is joined with a ribose-P to form orotidine-5’-
phosphate (OMP)
6) Step 6: OMP decarboxylase
OMP decarboxylase makes UMP (uridine-5’-
monophposphate)
Synthesis of uridine and cytidine triphosphate
Nucleoside monophosphate kinase
UMP + ATP → UDP + ADP
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase
UDP + ATP → UTP + ADP
CTP sythetase forms CTP from UTP and ATP
Synthesis of dTMP
Methylation of d-UMP by N
5
,N
10
-methylene THF
Nucleotide mono-, di-, and triphospahtes are
interconvertible
Nucleoside monophosphate kinases
UMP is converted to UTP before going on to produce CTP
CTP is formed by amination of UTP.
Regulation of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis
UTP and CTP are feeback inhibitors of CPS II
Orotic aciduria
An inherited human disease caused by a deficiency in the
multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the last 2 steps in the
pyrimidine synthesis
large amounts of orotic acid in urine
retarded growth and severe anemia
treat by administration of uridine and/or cytidine

18
Novo versus salvage pathways
de
Regulation of pyrimidine biosynthesis
UDP and UTP are feedback inhibitors of CPS II
PRPP and ATP are activators
Salvage of pyrimidine
Pyrimidine nucleosides can be salvaged by
Nucleoside kinase that use atp in the phosphorylation of the
nucleoside to nucleotide.
How Are Pyrimidines Degraded?
Pyrimindine rings can be fully degraded to soluble structures
(Compare to purines that make uric acid)
pyrimidines ring is opened and degraded to highly soluble
products as B-alanine,
-aminoisobutyric acid, ammonium,
and CO
2
Degradation pathways are quite distinct for purines and
pyrimidines, but salvage pathways are quite similar
CMP and UMP degraded to bases similarly to purines
Dephosphorylation
Deamination
Glycosidic bond cleavage
Uracil reduced in liver, forming b-alanine
Converted to malonyl-CoA fatty acid synthesis for
energy metabolism
What are the major differences between purine and
pyrimidine pathways? What are the similarities?
similarities:
o both start with R-5-P
o PRPP synthetase catalyzes rate limiting step, most active
during DNA replication
differences:
o pyrimidines use carbomoyl phosphate synthetase II
(CPSII) for the first committed step whereas purines use
glutamine-PRPP-amidotransferase,
o pyrimidine pathway is 4 steps whereas purines is 11
What enzyme catalyzes the rate limiting step and the first
committed step in pyrimidine synthesis?
PRPP synthetase is rate limiting,
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPSII) is 1
st
committed
What is the first pyrimidine and first pyrimidine
nucleotide formed in pyrimidine synthesis?
orotate is first pyrimidine, OMP is first pyrimidine nucleotide
How is CPS II regulated?
Positive effectors: PRPP, ATP
negative effector: UTP
From OMP, what is the process that leads to the formation
of UTP, CTP?
OMP → UMP (Orodylate decarboxylase) → UDP → UTP
(CTP synthetase) → CTP
What percentage of pyrimidines are recycled, and how
does this compare to purines?
30% of pyrimidines are recycled compared to 90% in purines
At what level are pyrimidines recycled and how does this
differ from purines?
pyrimidines are recycled at the level of nucleosides while
purines are recycled as free bases
Do pyrimidine degradation products cause any
pathologies? Why?
No, pyrimidine degradation products are highly water soluble
and excreted in urine
Which nucleotide is an important target in cancer
treatment?
Thymidine (it is only found in DNA, its inhibition will inhibit
replication)
Purine/Pyrimidine
degradation
are
the
same
for
ribonucleotides and deoxyribonucleotides
Biosynthetic pathways are only for ribonucleotide production
Deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized from corresponding
ribonucleotides
Synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from
ribonucleotides
The nucleotides synthesized all contain
ribose(ribonucleotides)
to synthesize DNA we need nucleotides that contain
deoxyribose
ribonucleotide reductase reduce ribonucleotides to
deoxyribonucleotides.(by reduction of ribose sugar )
As UDP to dUDP,GDP to dGDP
Regulation of Nucleotide Biosynthesis
19
Anticancer Drugs
Inhibition of the synthesis of dexoyribonucleotides or
thymidylate will selectively inhibit fast growing cells.
