
Chapter 9
Birth Defects and
Prenatal Diagnosis
Birth defects
• Teratology (dysmorphology): The study of Congenital malformations, Congenital
anomalies or birth defects.
• Structural, behavioral, functional & metabolic disorders present at birth.
• Dysmorphologists are usually within a department of clinical genetics.
• Birth defects infant mortality
• Non discriminatory: same for Asians, African Americans, Latin Americans, whites,
and Native Americans.
Causes of birth defects
• 40-60% - unknown cause
• 15% - genetic factors:
– chrm. Abnormalities
– Mutant genes
• 10% - environmental factors
• 20-25% - multi-factorial
• 0.5-1% - twining
Minor anomalies
• 15% of newborns
• Small ears, pigmented spots
• Associated with major defects???
• One Mn.A. 3%chance of Mj.A.
• 2 Mn.A. 10% chance
• 3 or more Mn.A. 20% chance
• Minor anomalies serve as clues for diagnosing
more serious underlying defects
– Ear anomalies:
• easily recognizable
• observed in virtually all children with
syndromic malformations.
Types of abnormalities
• Malformations: result in complete or partial absence of a structure
– have their origin during the third to eighth weeks of gestation
(organogenesis)
– caused by environmental and/or genetic factors
• Disruptions: morphological alterations of already formed structures and
are caused by destructive processes e.g.
– Vascular accidents leading to bowel atresias
– defects produced by amniotic bands
• Deformations: mechanical forces that mold a part of the fetus over a
prolonged period e.g.
– Clubfeet
– involve the musculoskeletal system and may be reversible postnatally.
• A syndrome: a group of anomalies occurring together that have a specific
common cause
• Association: appearance of two or more anomalies, no known cause
– important because recognition of one or more of the components
promotes the search for others in the group.
– VACTERL association (vertebral, anal, cardiac, tracheoesophageal,
renal, and limb anomalies).

Principles of Teratology
•
Factors determining the capacity of an agent to produce birth defects
1.
Genotype of the conceptus
2.
Developmental stage at the time of exposure, third to eighth weeks
–
no stage of development is completely safe
3.
Dose and duration of exposure to a teratogen
4.
Mechanisms
5.
Manifestations of abnormal development are death, malformation,
growth retardation, and functional disorders.
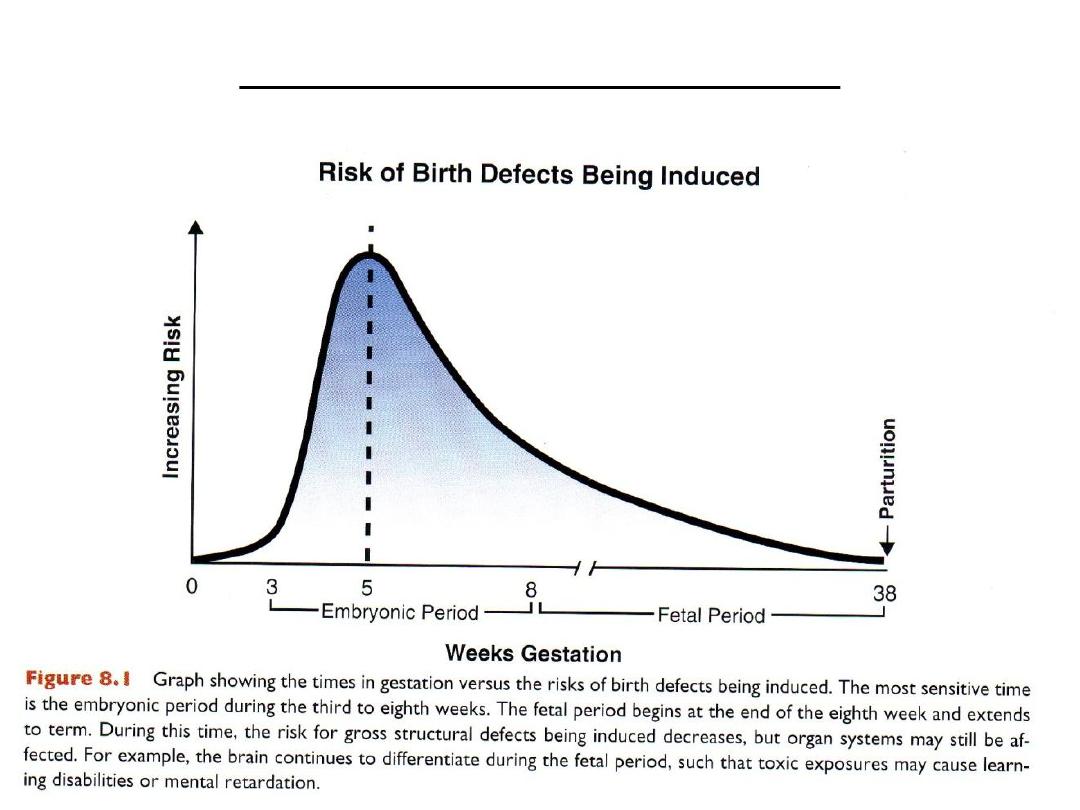
Risk of birth defects being induced
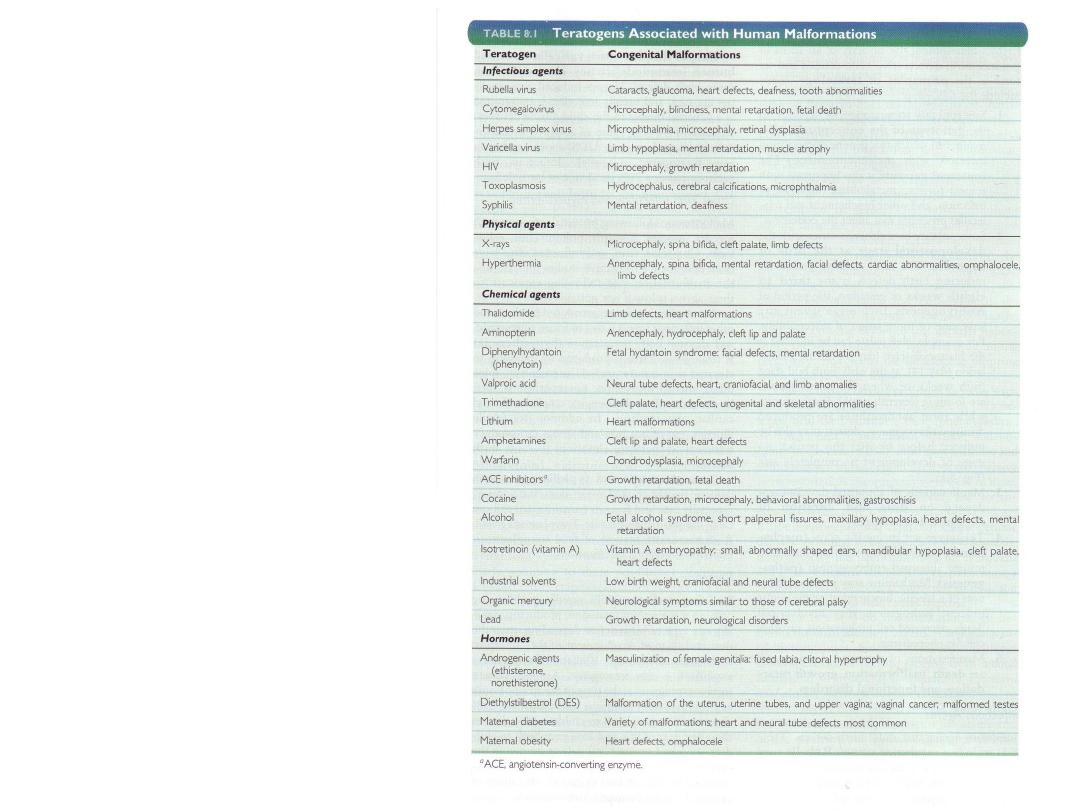
Teratogens
associated with
human
malformations
infectious agents

Physical agents
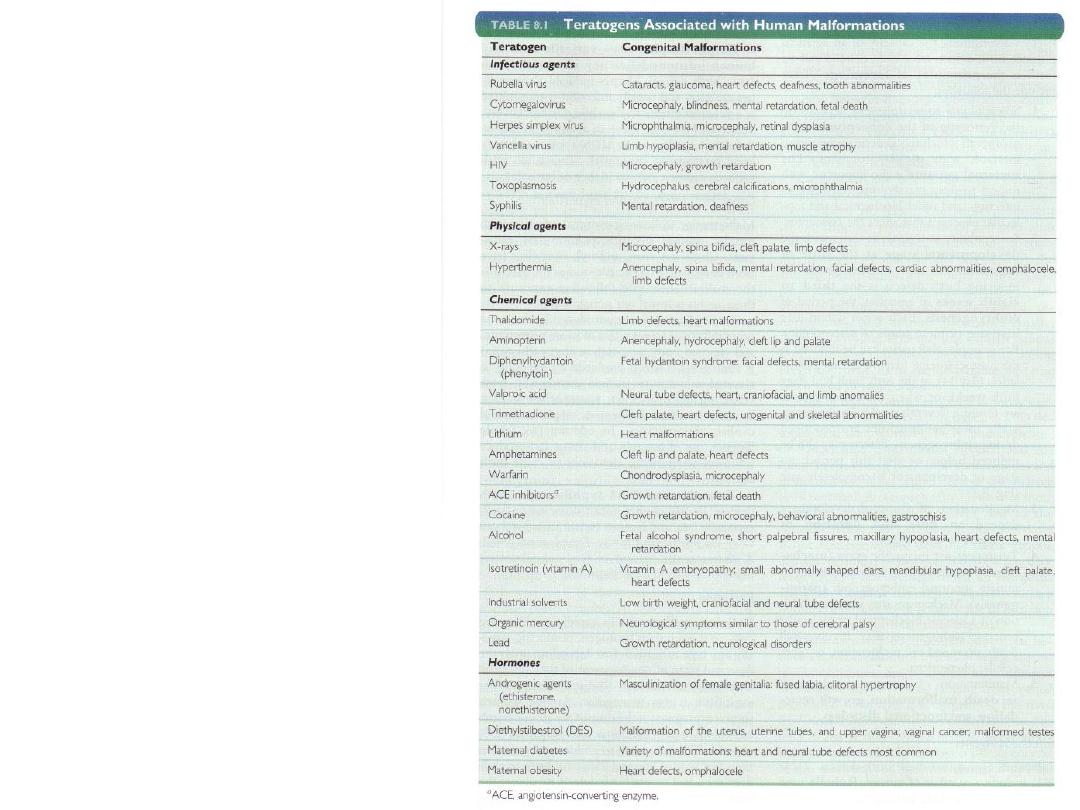
Chemical
agents
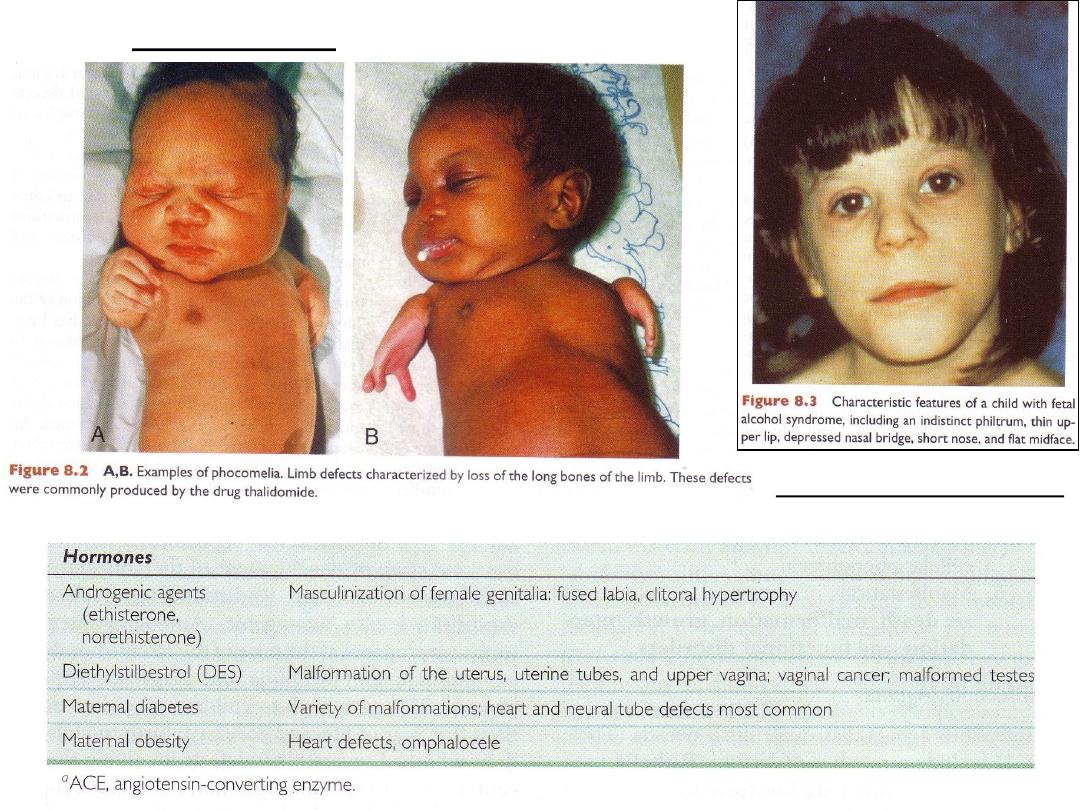
Phocomelia
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Prenatal diagnosis
• Ultrasonography
• Maternal serum screening
• Amniocentesis
• Chorionic villus sampling
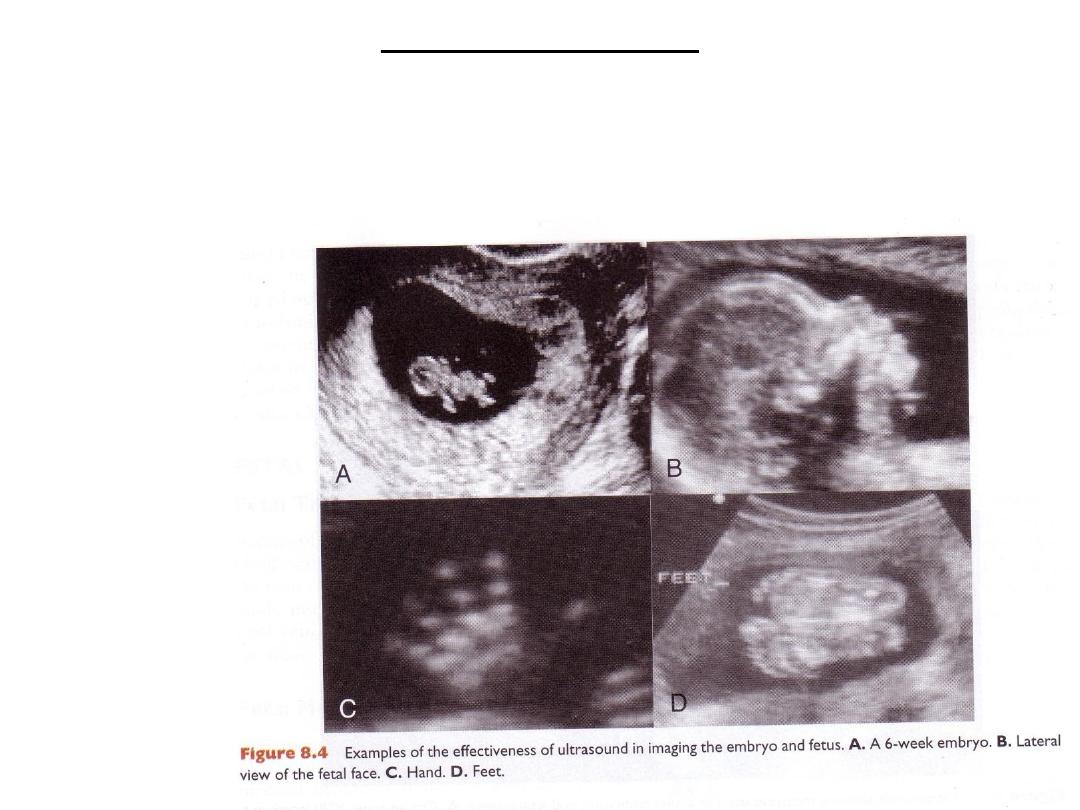
Ultrasound in
imaging the
embryo &fetus
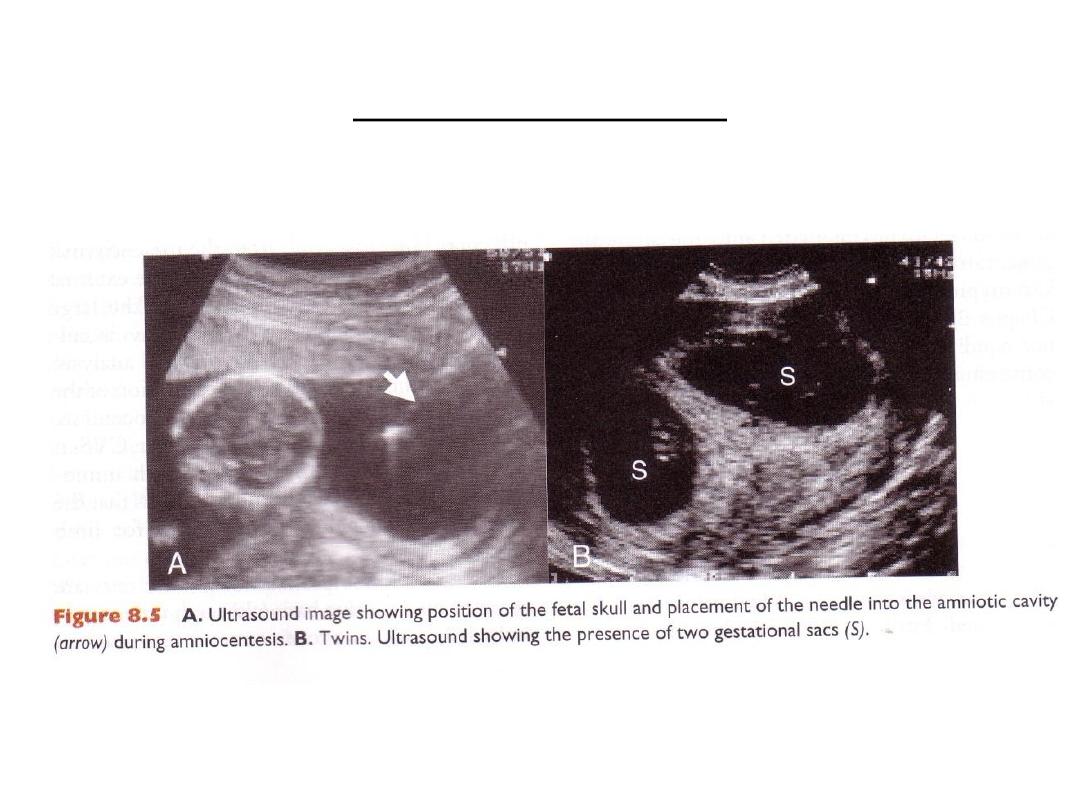
A. Fetal skull b. Twins
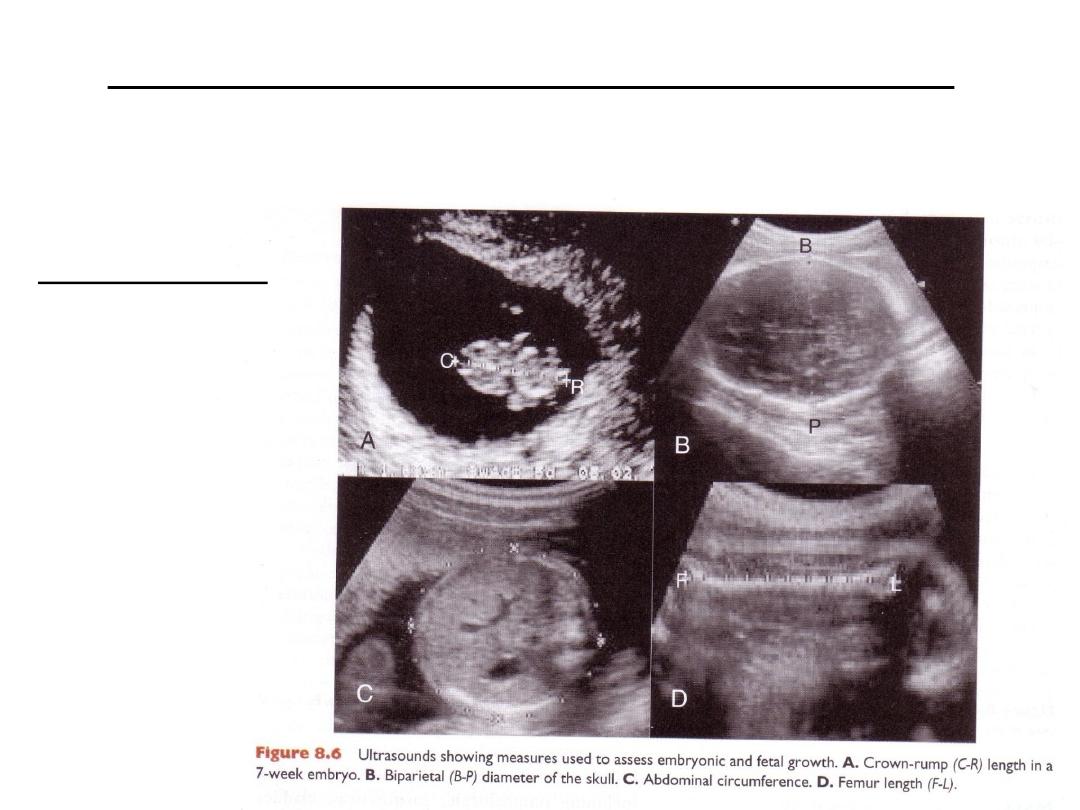
Measurments to asses embryonic & fetal growth
Fetal therapy
• Fetal transfusion
• Fetal medical
treatment
• Fetal surgery
• Stem cell
transplantation &
gene therapy
