
Introduction to
Human Anatomy
Laboratory
Dr. Hayder Jalil Al-Assam
MBChB (Iraq), Mres Anatomy (UK)
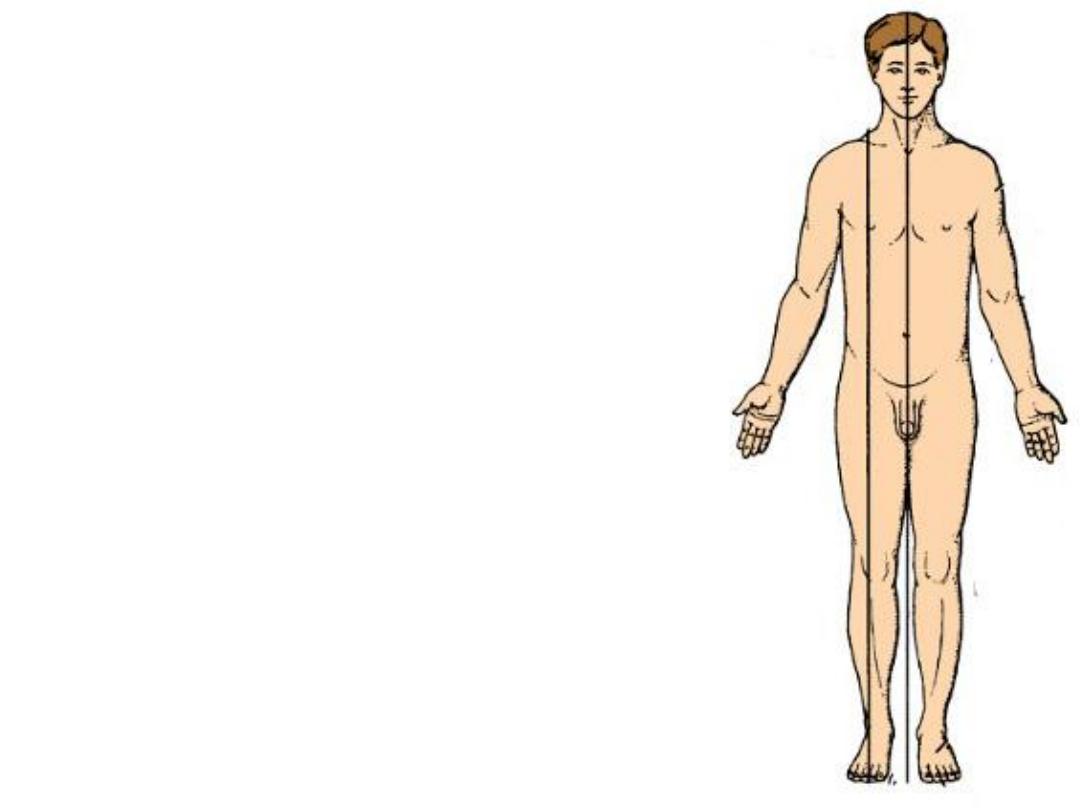
The Anatomical Position
1- Erect
2- Feet together
3-Head and toes pointed forward
4- Arms at the sides of the body
5- Palms facing forward.
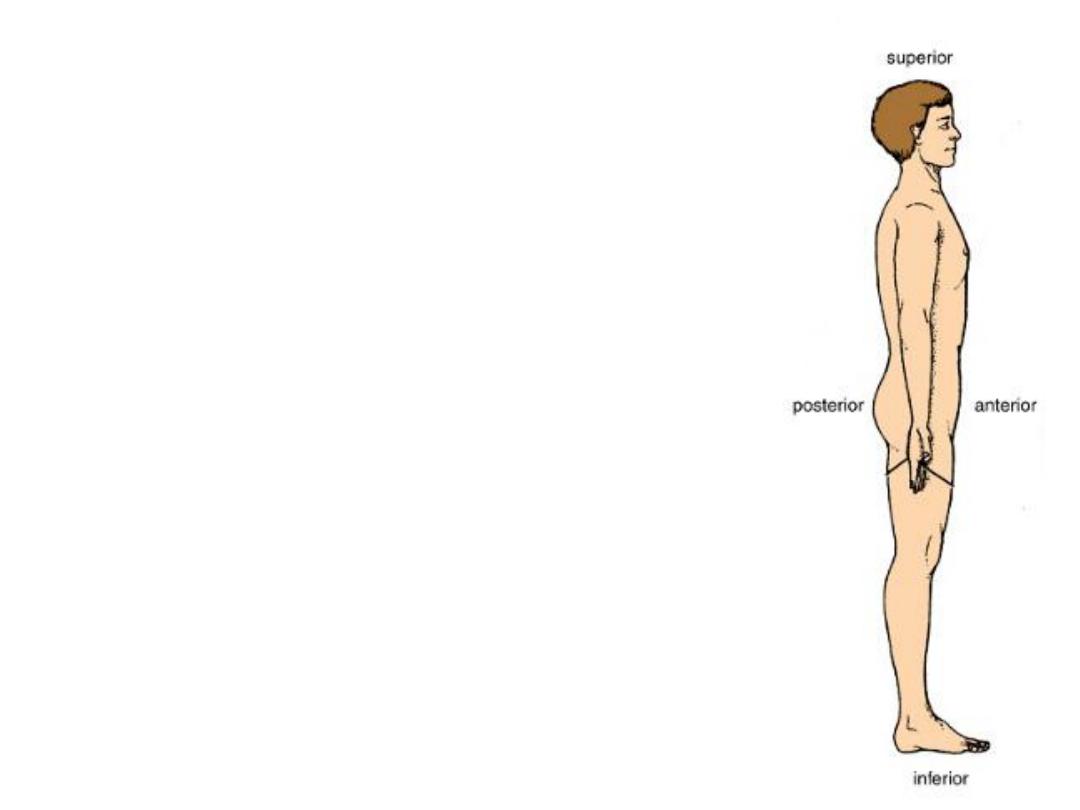
Body orientation
1-
Superior
(Above)
vs
Inferior
(Below)
2-
Anterior
(Front)
vs
Posterior
(Back)
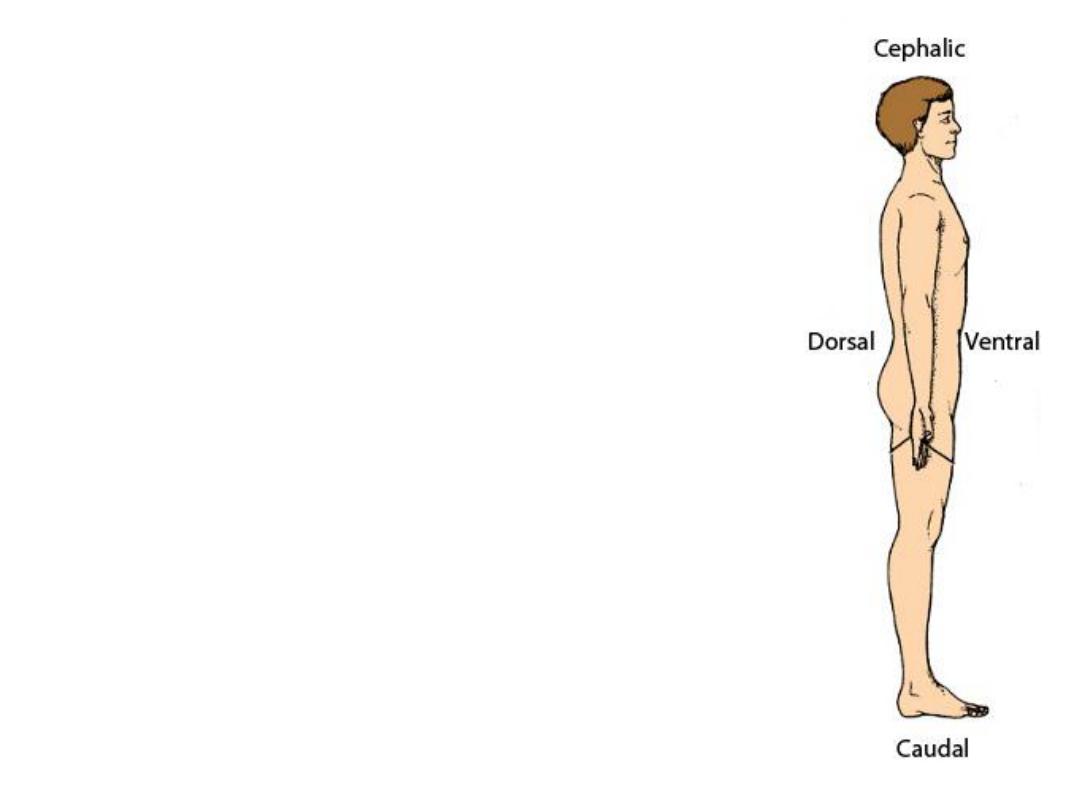
Body orientation
3-
Cephalic
(Toward the head)
vs
Caudal
(Toward the tail)
4-
Dorsal
(Backside of the body)
Vs
Ventral
(belly side of the body)
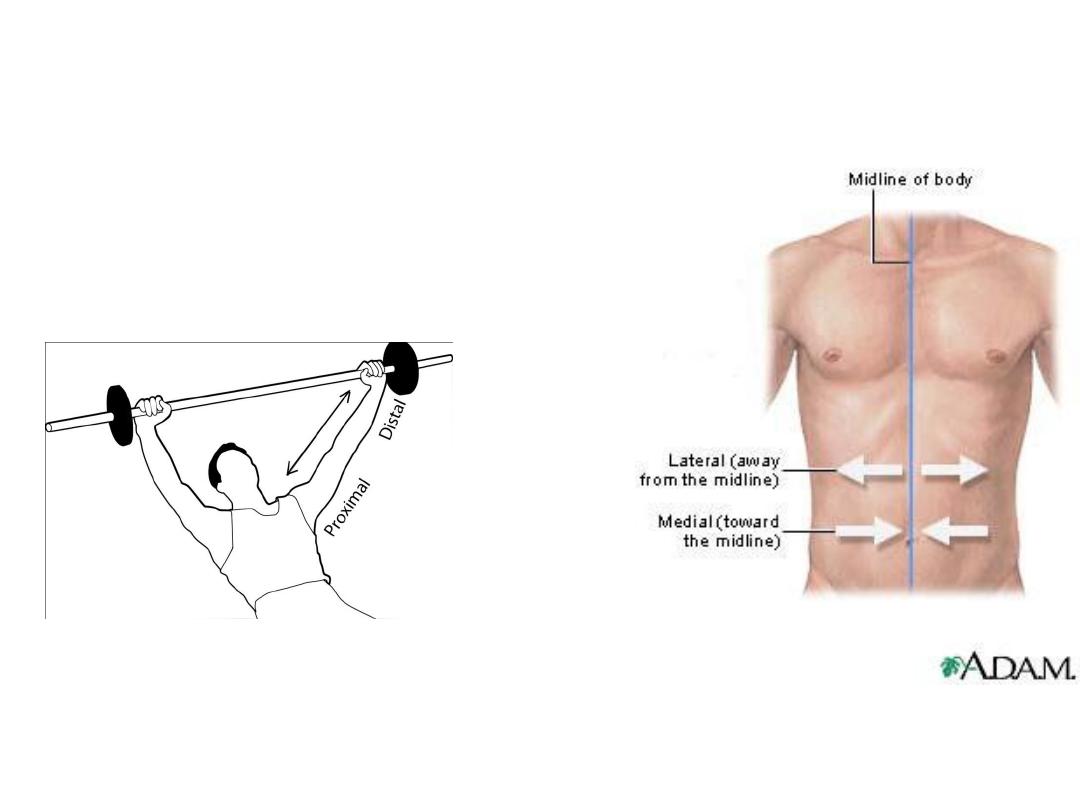
Body orientation
5-
Medial
(Toward the midline)
vs
Lateral
(Away from the midline)
6-
Proximal
(nearer the trunk)
Vs
Distal
(farther from the trunk)

Body orientation
7-
Superficial
(toward or at the surface of the
body)
Vs
Deep
(Away from the body surface toward
the inside)
8-
Internal
( Inside the body)
Vs
External
(Outside the body)
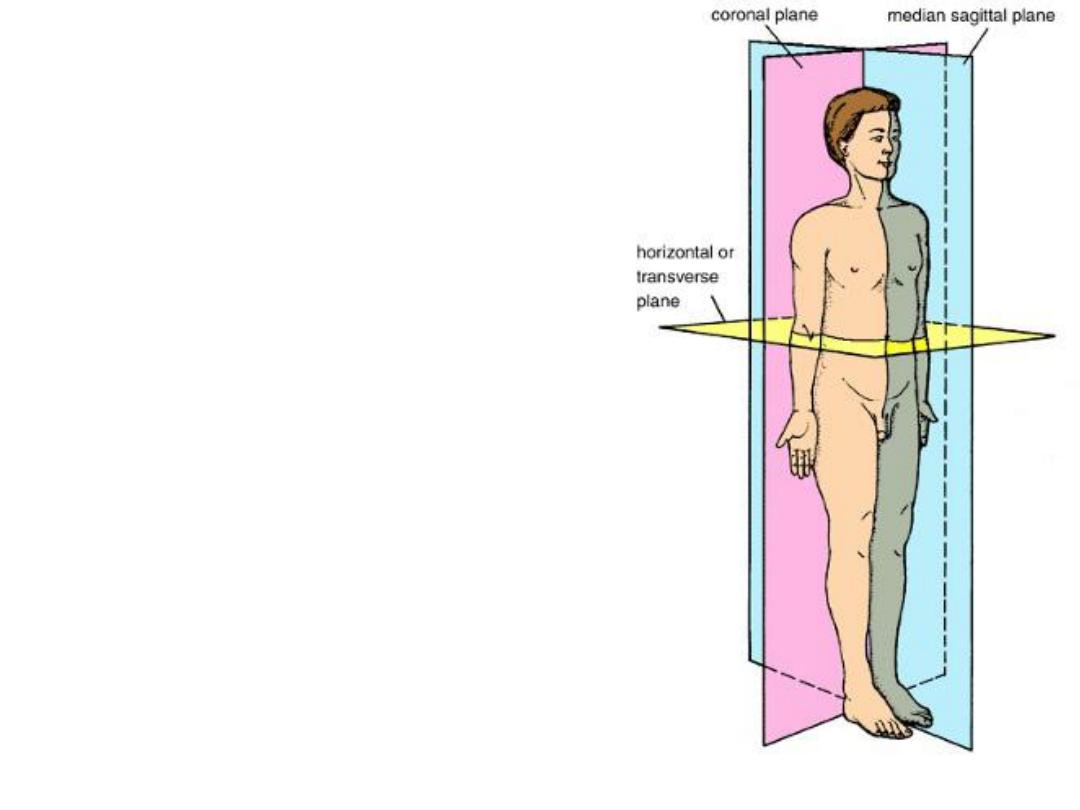
Body Planes
• Sagittal plane
A- Mid-sagittal plane or
median plane
B- Para-sagittal plane.
• Frontal plane
(Coronal plane)
• Transverse plane
(cross section).
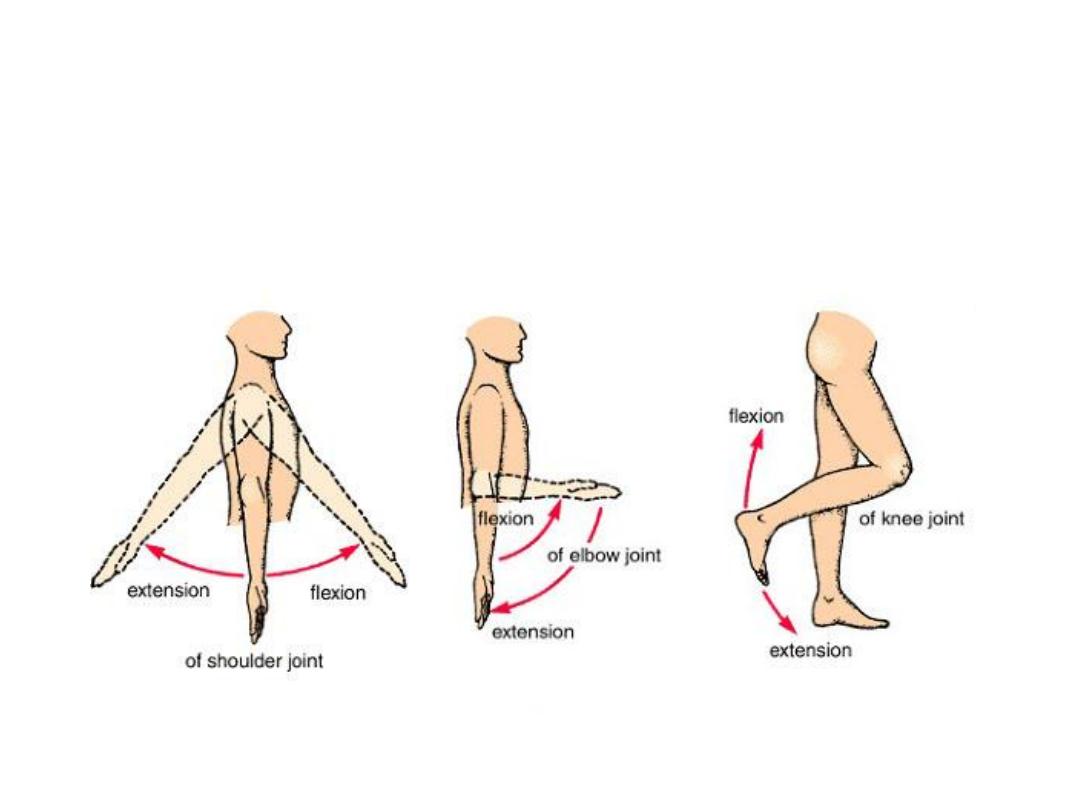
Body movements
• Flexion /Extension
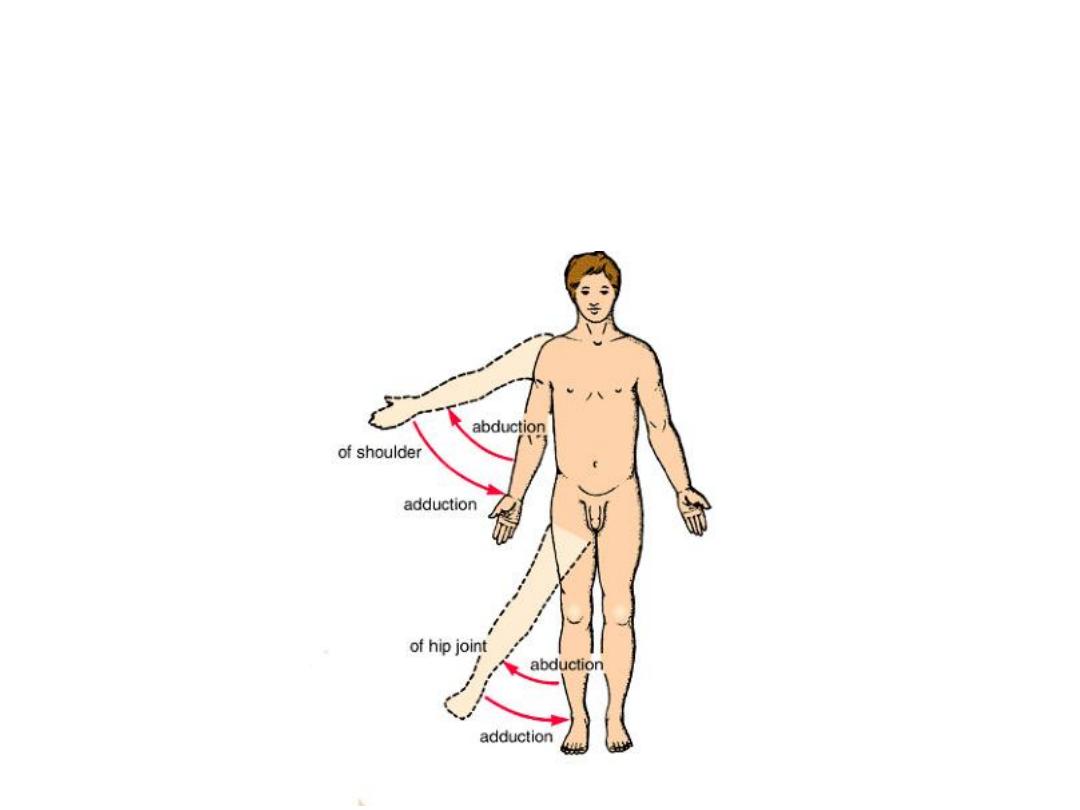
Body movements
• Abduction/adduction
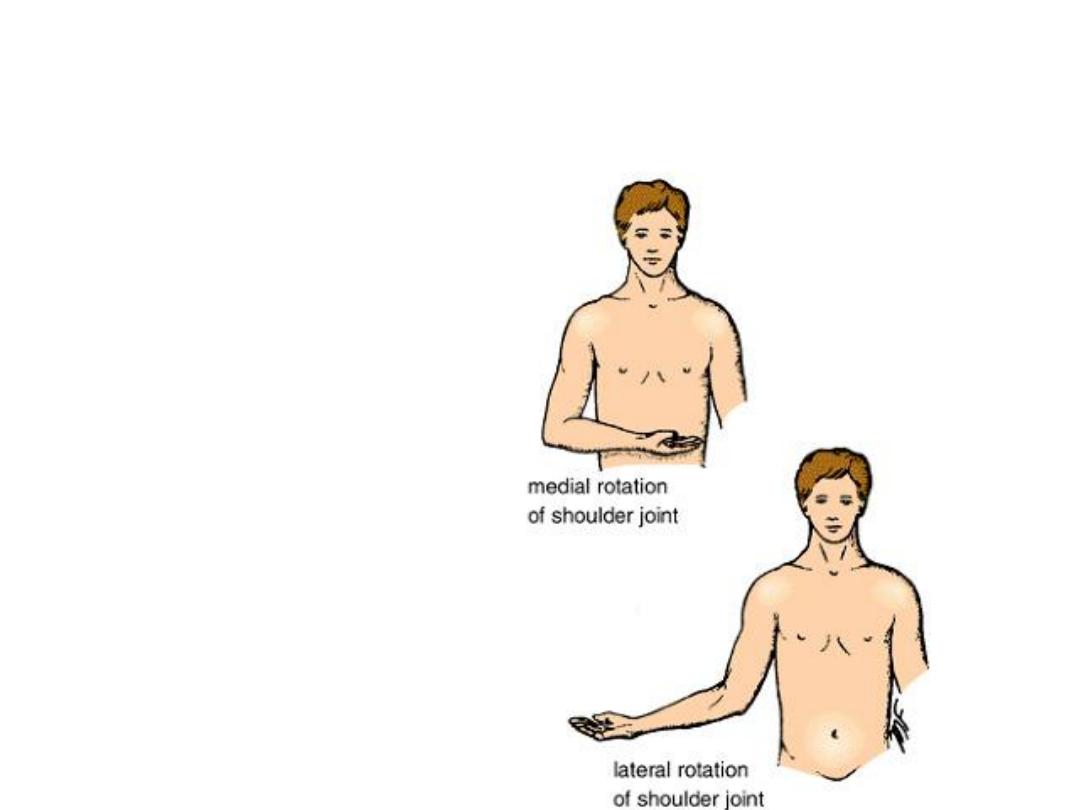
Body movements
• Rotation
- Medial Rotation
- Lateral Rotation
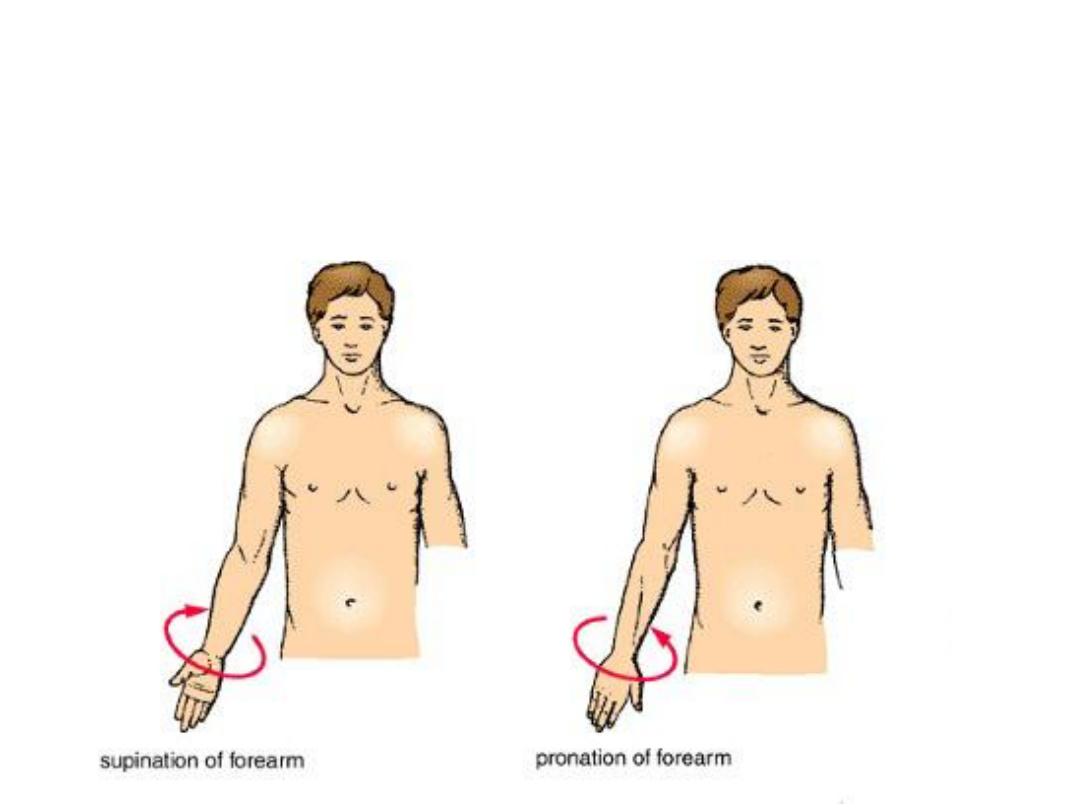
Body movements
• Pronation/supination
Body movements
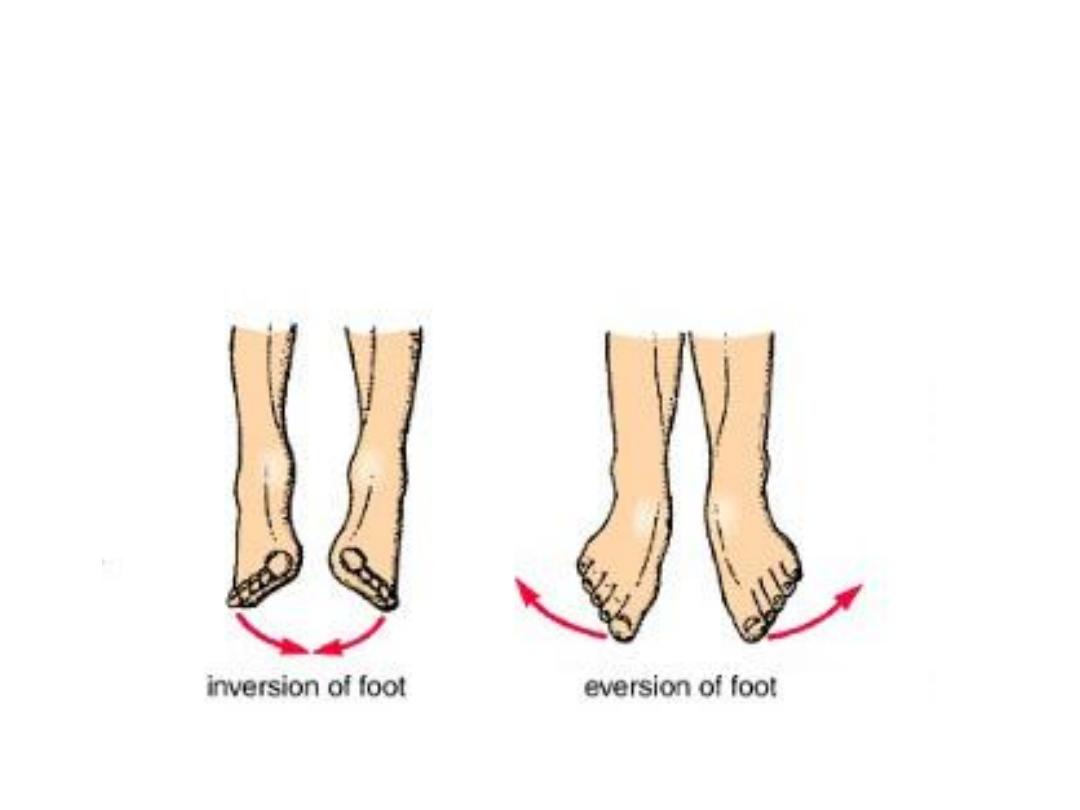
• Eversion / Inversion
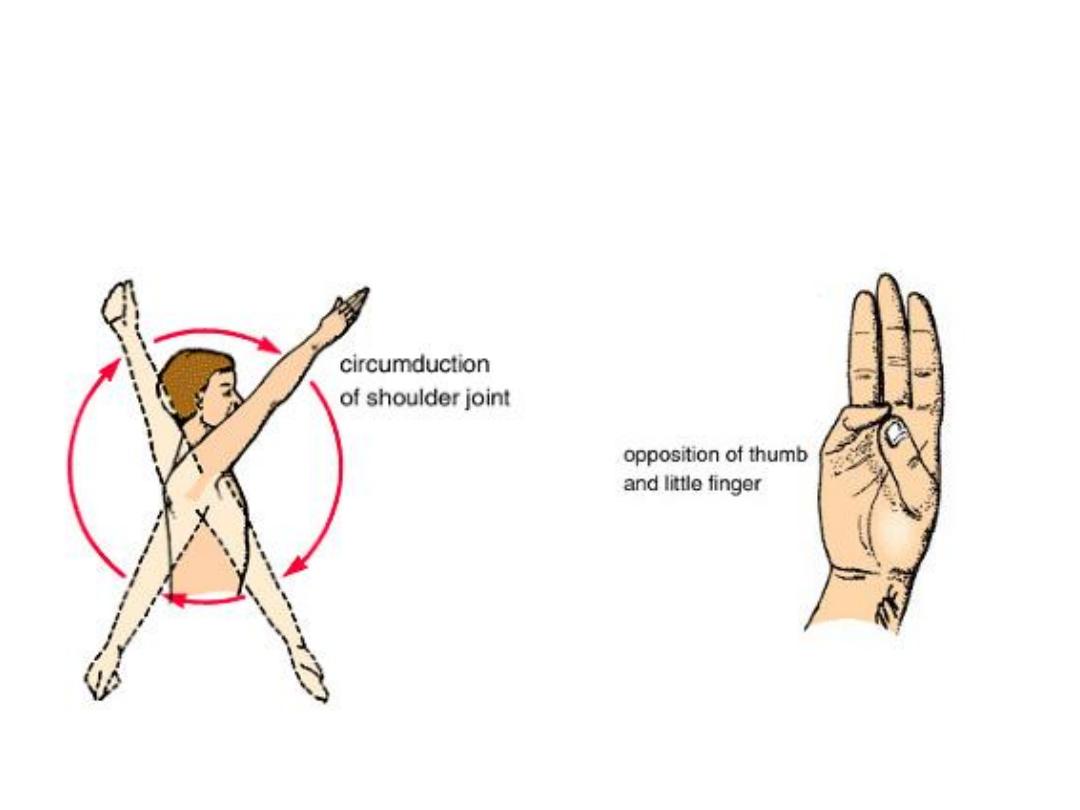
Body movements
• Complex Movement

Basic body composition
• Skin & Fascia
• Muscles
• Bones & Cartilages
• Nerves
• Internal organs (viscera)
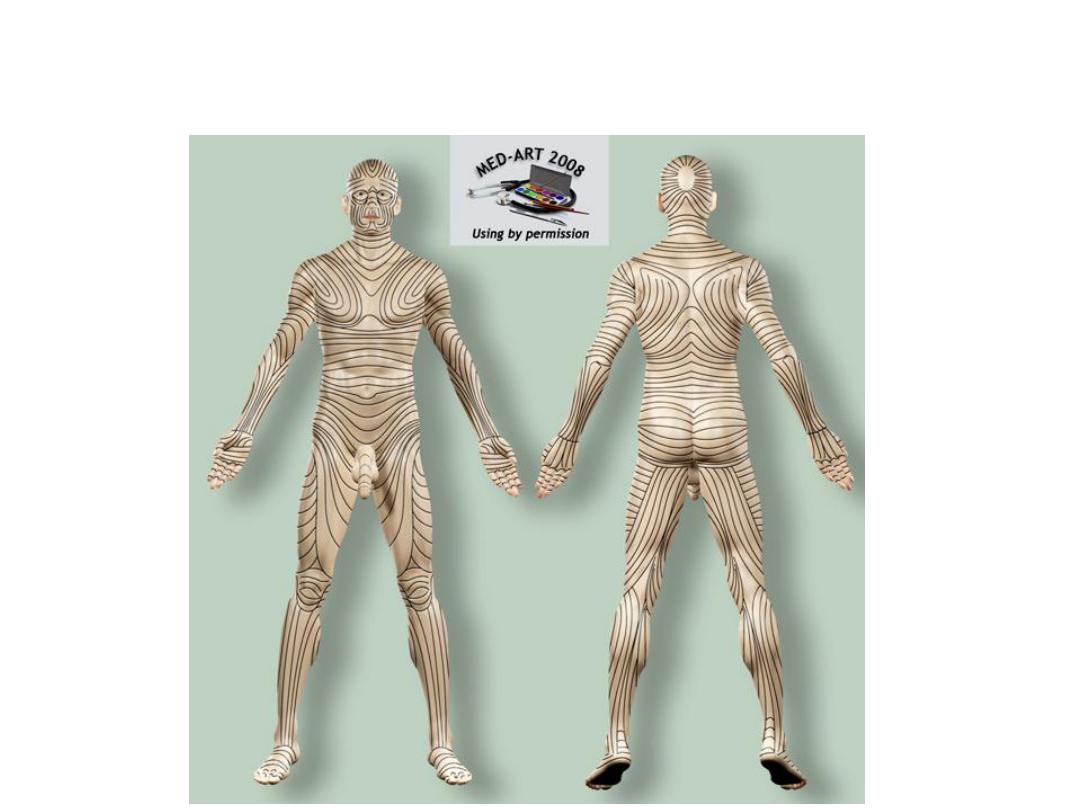
Skin - Langer’s Lines

Muscles
• Types according to voluntary action
1- Voluntary muscle (hand muscles)
2- In-voluntary muscle (heart and intestine)

Muscles
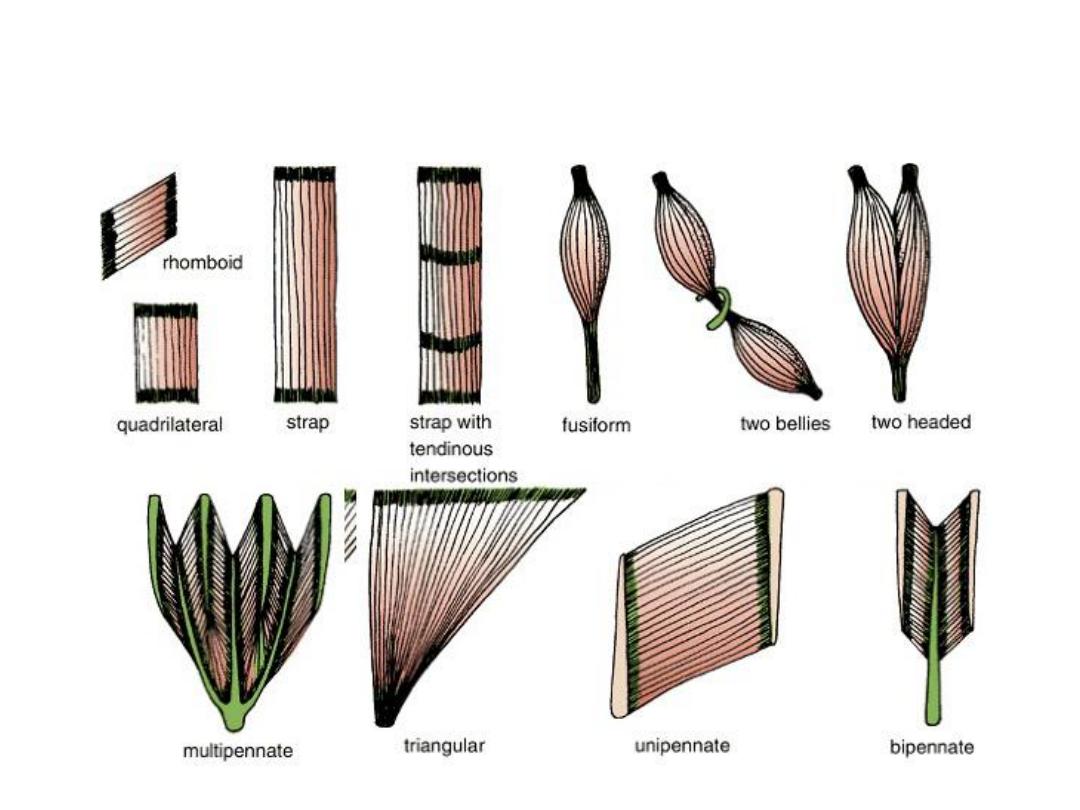
• Types according to shape
1- Strap-like – rectus abdominis
2- Triangular - Pectoralis
3- Rhomboid - Rhomboid major & minor
4- quadrilateral – Pronator quadratus
5- Fusiform – Biceps
6- pennate muscle – different types

Muscles
• Types of obliguly arranged muscle fibers:
1- uni-pennate – extensor digitorum longus
2- bi-pennate – rectus femoris
3- multi-pennate - deltoid
Muscles
Bones
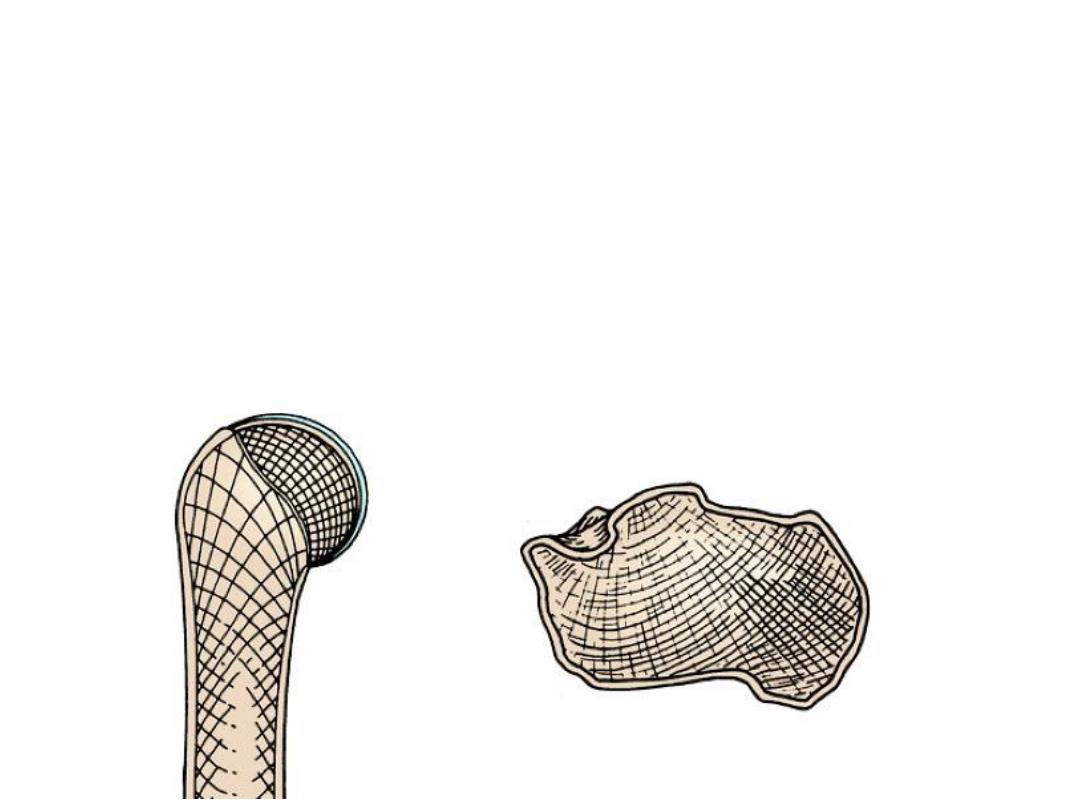
• Types of bony tissue
1- Compact bone
2- Spongy (Cancellous) Bone

Bones
• Types according to shape (relative anatomy)
1- Long bones - femur
2- Short bones – carpal bones
3- Flat bones – Skull
4- Irregular bones – vertebrae
5- Sesamoid bones – patella
6- wormian bones – sutural bones

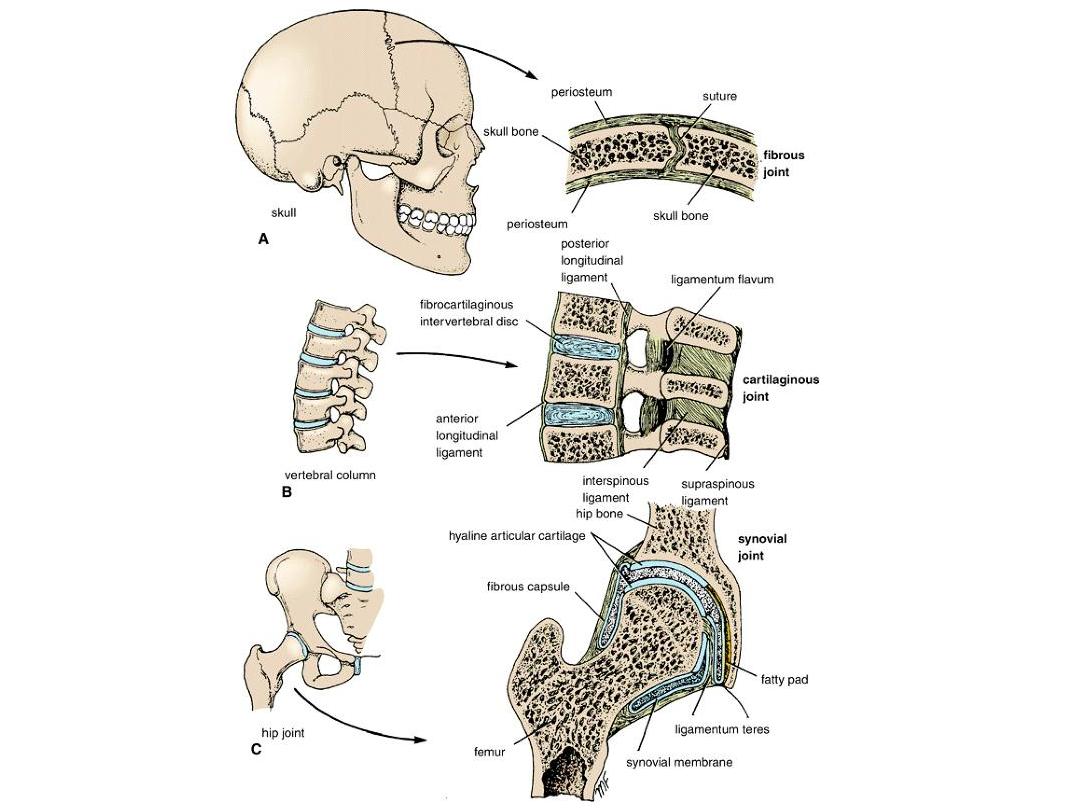
Joints
• Sites where bones come close to each other.
Types:
1- Cartilagenous joints (suturs)
2- Fibrous joints (inter-vertebral disc, tibio-
febullar joint)
3- Synovial joints (Shoulder & hip joints)

Joints
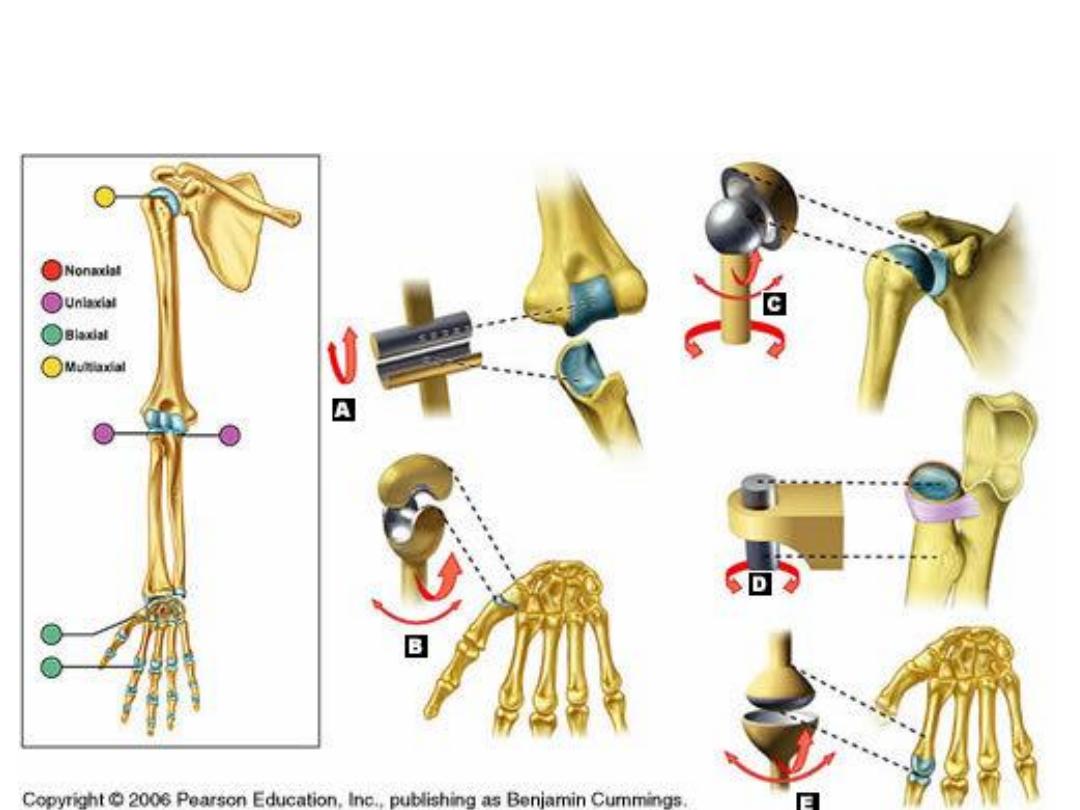
• Types according to direction of movement:
1- Non-Axial – No movement
2- Uni-Axial – One direction
3- Bi-Axial – two directions
4- Multi-Axial – multiple directions

Joints
• Types of Synovial joints
1- plane joint – acromio-claviclular, sternoclavicular
2- Hinge joint – Elbow
3- Ball & Socket joint – Shoulder & Hip
4- Saddle – Carpo-metacarpal
5- Condyloid – Metacarpo-phalangeal joint
6- Pivot joint – atlanto-axial joint, proximal radio-
ulnar joint.
7- Ellipsoid joint – Wrist joint
Joints
