
The Foot # 1
Bones, Ankle retinacula
& Sole
Lab Session 10
Dr. Hayder Jalil Al-Assam
MBChB (Iraq), MRes Anatomy (UK)
: dr_hayder_anatomy@yahoo.com
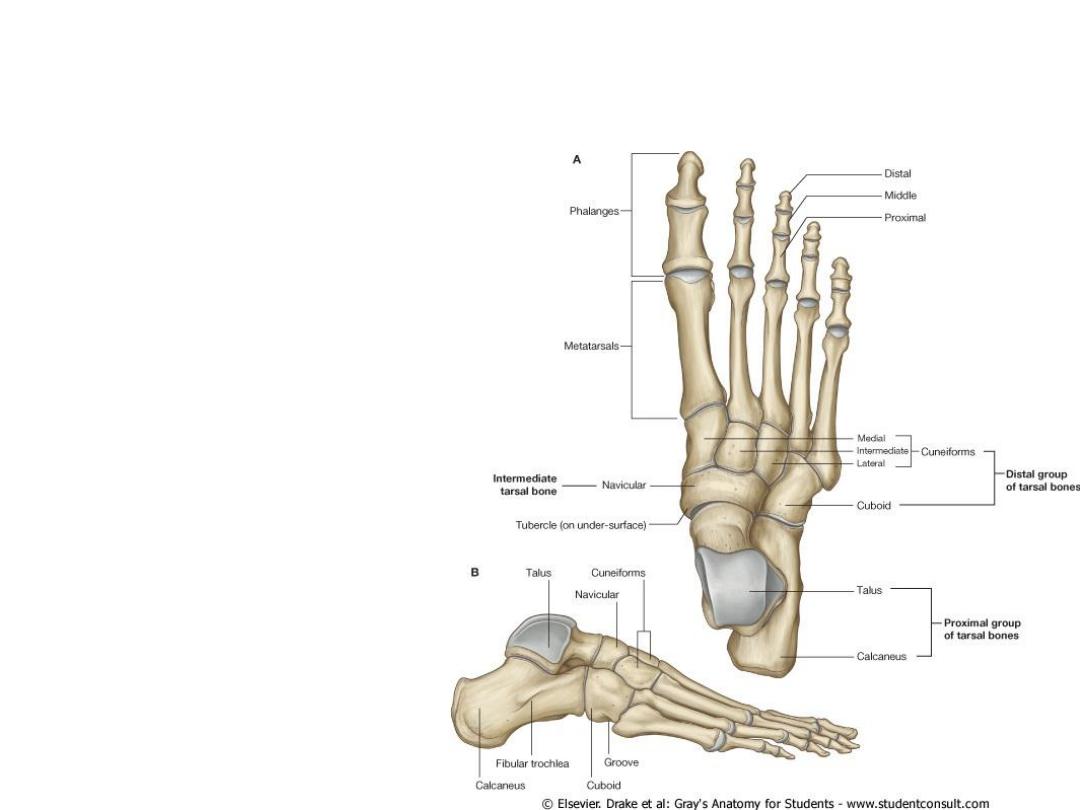
Bones of the foot
• Tarsus
1. Calcaneum
2. Talus
3. Navicular bone
4. 3 Cuniform bones
• Metatarsus
• Phalanges
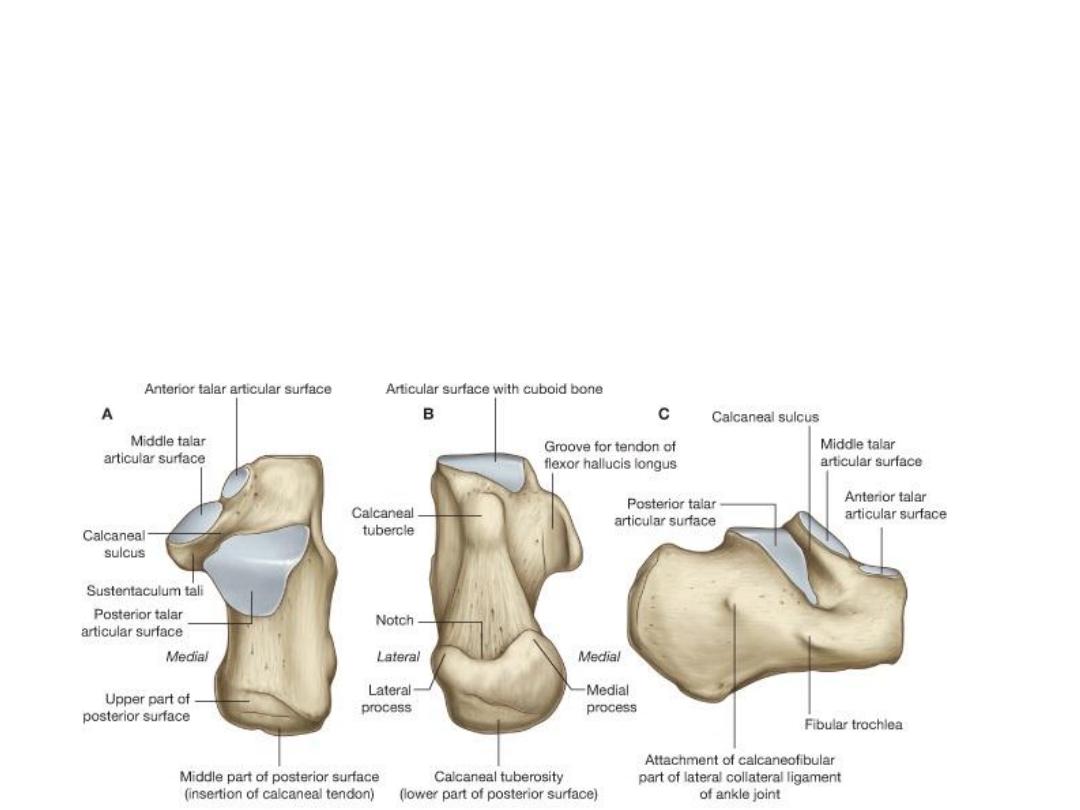
Calcaneum
•
The largest bone, forms the prominence of the heel.
•
It has six surfaces.
1.
The anterior surface is small and articulates with the cuboid bone.
2.
The posterior surface (prominence of the heel & gives tendo calcaneus attachment).
3.
The superior surface (two articular facets separated by a sulcus calcanei).
4.
The inferior surface (has an anterior tubercle, large medial & a smaller lateral tubercle at the junction of the
inferior and posterior surfaces).
5.
The medial surface possesses a large, shelflike process (sustentaculum tali)
6.
The lateral surface (flat with anterior small elevation - peroneal tubercle)
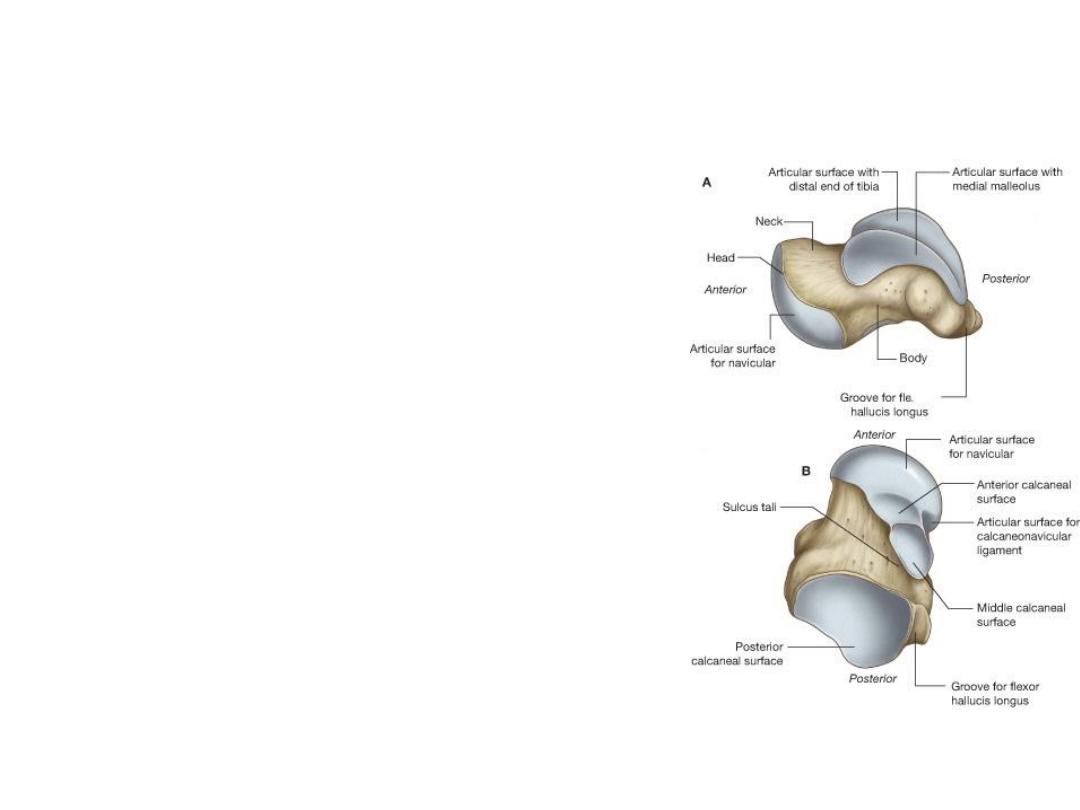
Talus
• It has head, neck & body.
• The head has an oval convex articular surface for
articulation with the navicular bone & this
articular surface rests on the sustentaculum tali.
• The neck of the talus (slightly narrowed with
inferior deep groove, the sulcus tali).
• The sulcus tali and the sulcus calcanei in the
articulated foot form a tunnel, the sinus tarsi,
which is occupied by talocalcaneal ligament.
• The body of the talus is cuboidal & articulates
1.
Superiorly - distal end of the tibia.
2.
Laterally - lateral malleolus of the fibula by
triangular facet
3.
Medially - medial malleolus of the tibia by a
small, comma-shaped articular facet
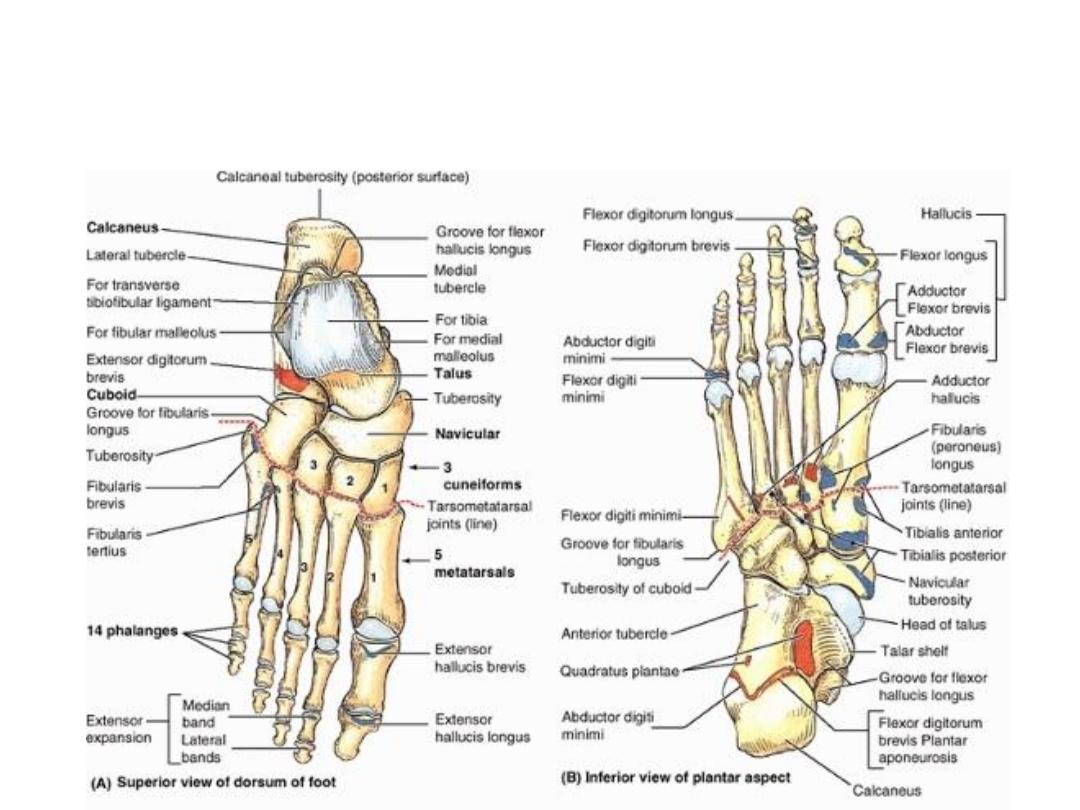
Bones of the foot
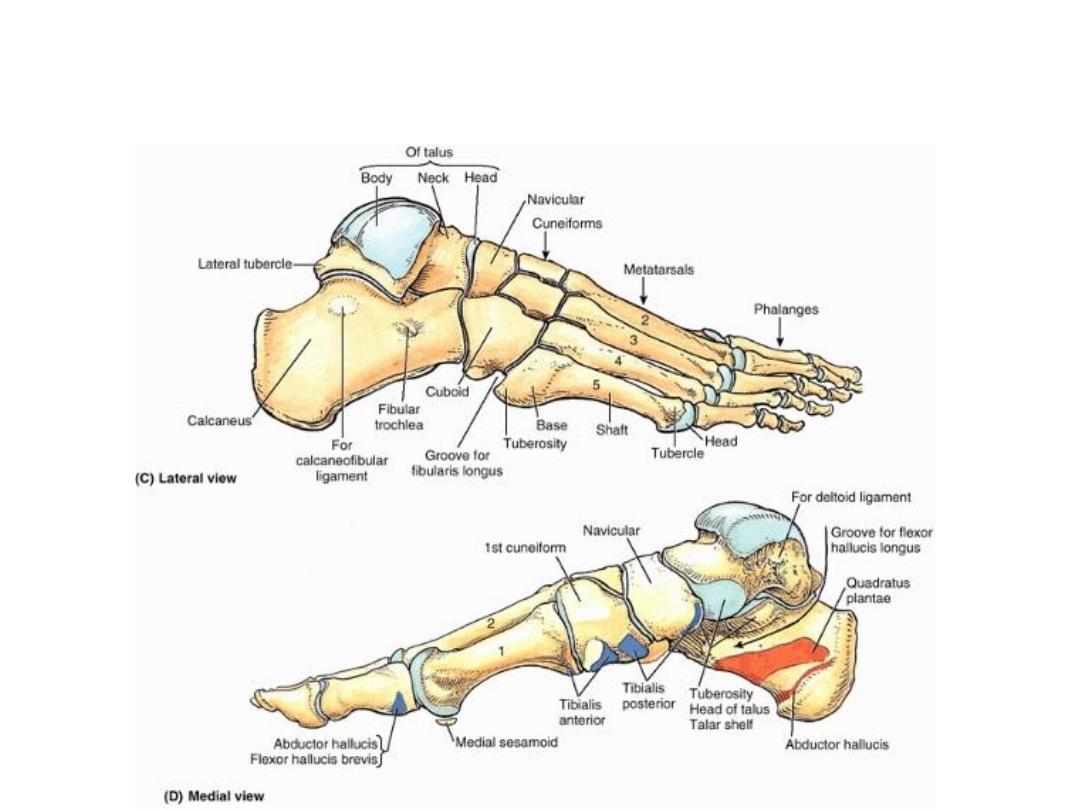
Bones of the foot

Retinacula of the ankle
• Extensor Retinacula
1. Superior
2. Inferiors
• Flexor Retinaculum
• Peroneal Retinacula
1. Superior
2. Inferiors
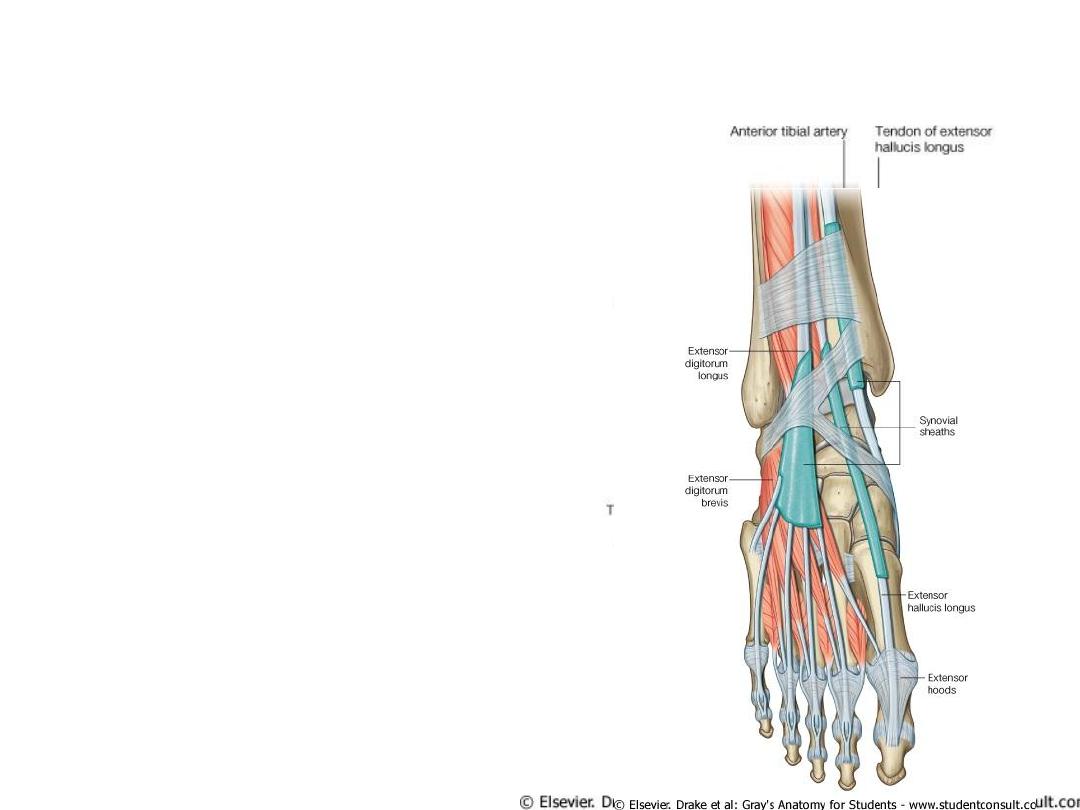
Sup. & Inf. Extensor Retinacula
• Structures That Pass Anterior to the Extensor
Retinacula
1.
Saphenous nerve
2.
Great saphenous vein
3.
Superficial peroneal nerve
• Structures That Pass Beneath or Through the
Extensor Retinacula
1.
Tibialis anterior tendon
2.
Extensor hallucis longus tendon
3.
Anterior tibial artery with venae comitantes
4.
Deep peroneal nerve
5.
Extensor digitorum longus tendons
6.
Peroneus tertius
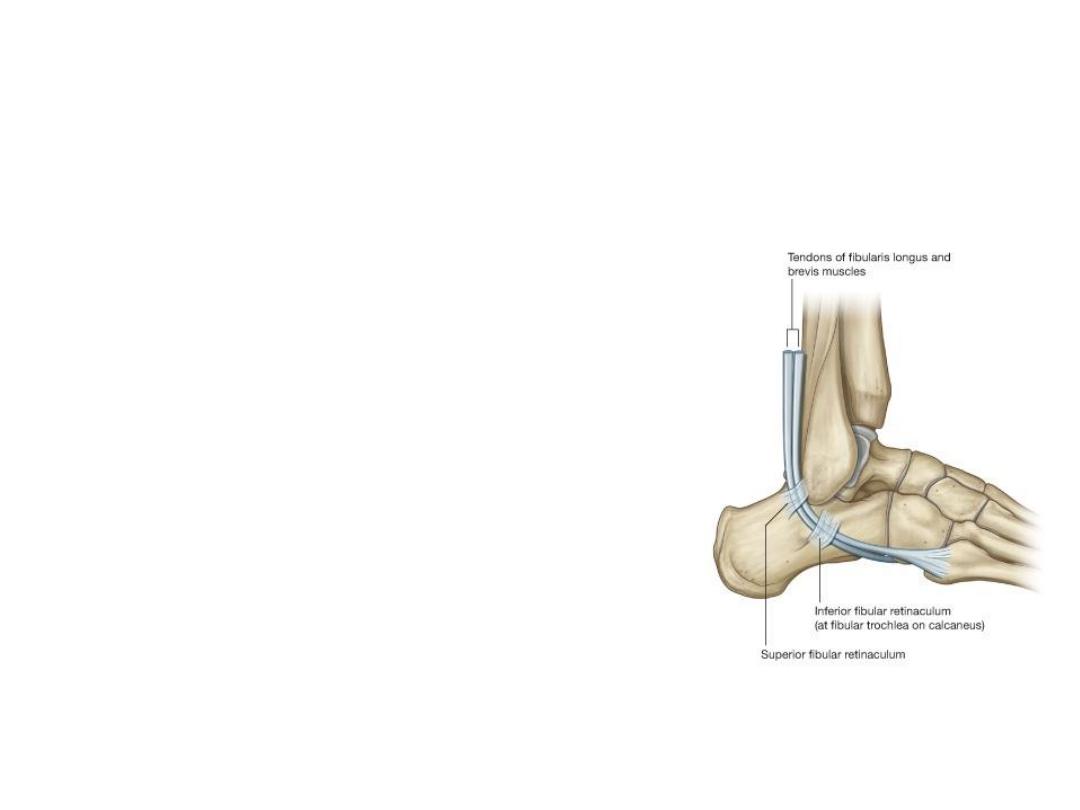
Peroneal (Fibular) Retinacula
• Structures That Pass Superficial
to the Superior Peroneal
Retinaculum
1. The sural nerve
2. Small saphenous vein
• Structures That Pass Beneath
the Superior Peroneal
Retinaculum
1. The peroneus longus tendon
2. The peroneus brevis tendon
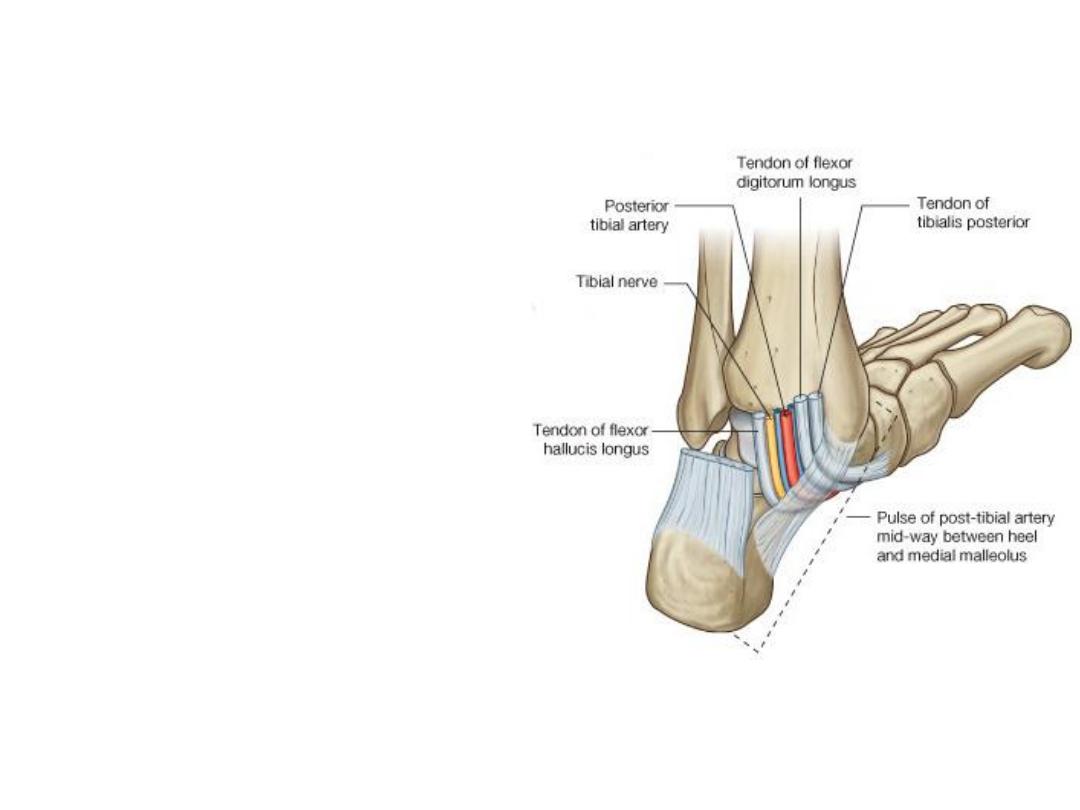
Flexor Retinaculum
• Structures That Pass
Beneath the Flexor
Retinaculum
1. Tibialis posterior tendon
2. Flexor digitorum longus
3. Posterior tibial artery with
venae comitantes
4. Tibial nerve
5. Flexor hallucis longus

Sole of the foot
• Superficial fascia (adherent & thick)
• Deep fascia ( plantar aponerosus)
• Muscles (4 layers)
• Nerve supply ( medial & lateral plantar nerve
& medial calcaneal nerve)
• Blood supply (medial & lateral planter arteries
& dorsalis pedis artery)
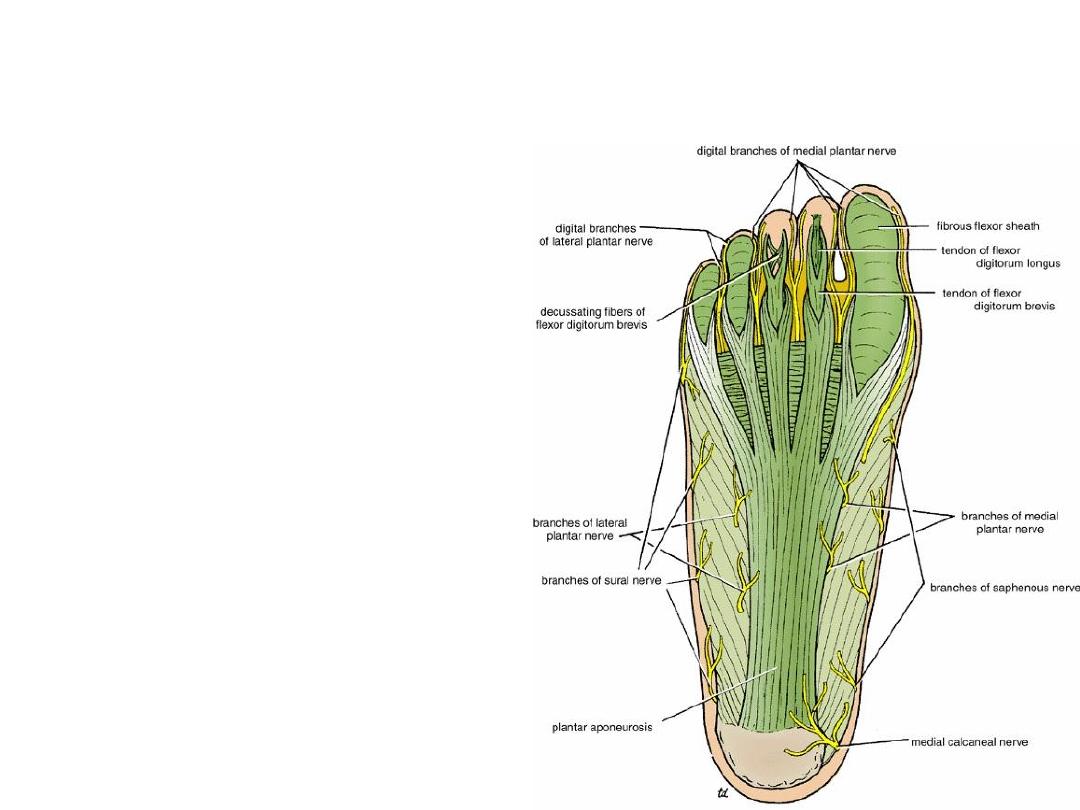
Plantar aponerosus
• The plantar aponeurosis is triangular
thickening of the deep fascia of foot
sole.
• The apex is attached to the medial
&lateral tubercle of the calcaneum.
The base of the aponeurosis divides
at the bases of the toes into five slips.
Each slip divides into two bands, one
passing superficially to the skin & the
other passing deeply to the root of
the toe; here, each deep band
divides into two parts, which diverge
around the flexor tendons & finally
fuse with the fibrous flexor sheath &
deep transverse ligament.
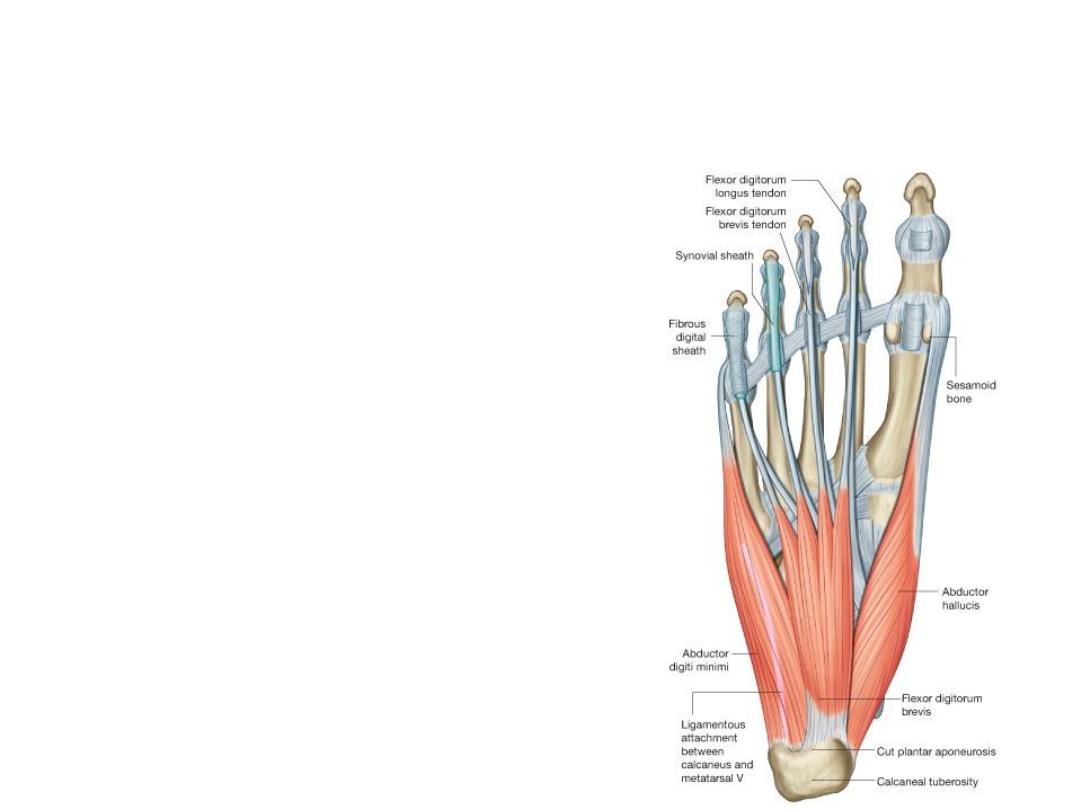
Muscles of the foot sole
• First layer
1. Abductor hallucis
2. Flexor digitorum brevis
3. Abductor digiti minimi
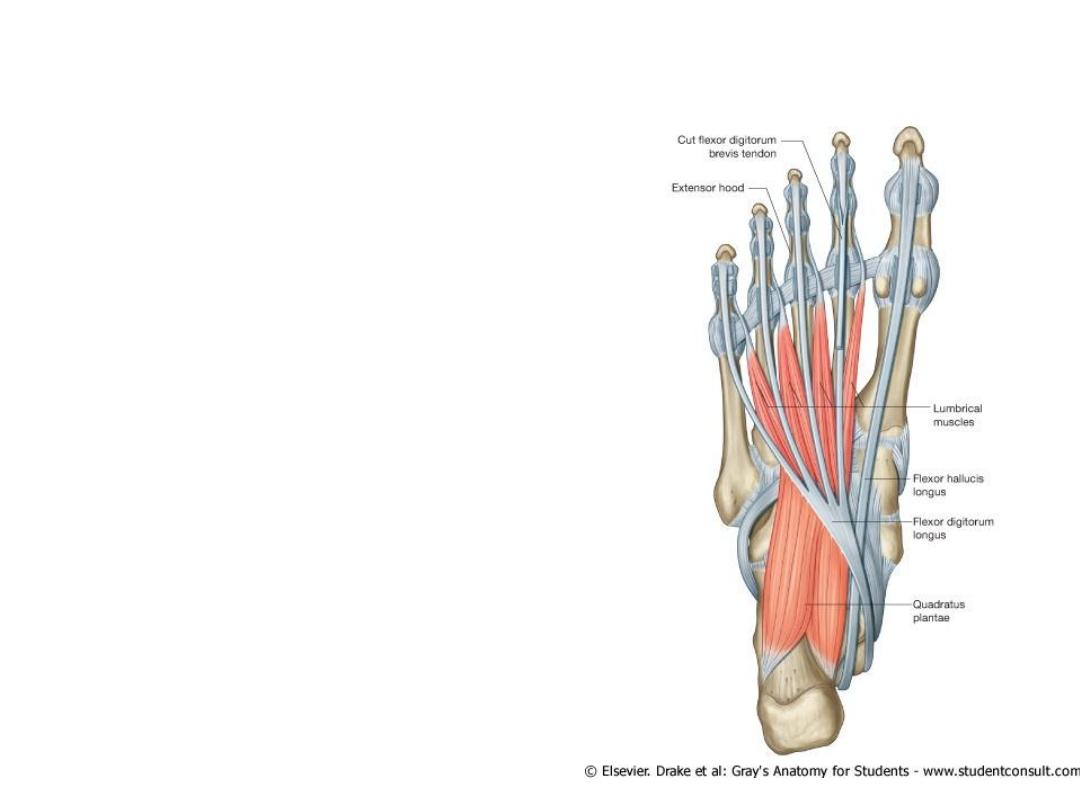
Muscles of the foot sole
• Second Layer
1. Quadratus plantae
2. Lumbricals (4)
3. Flexor digitorum longus tendon
4. Flexor hallucis longus tendon
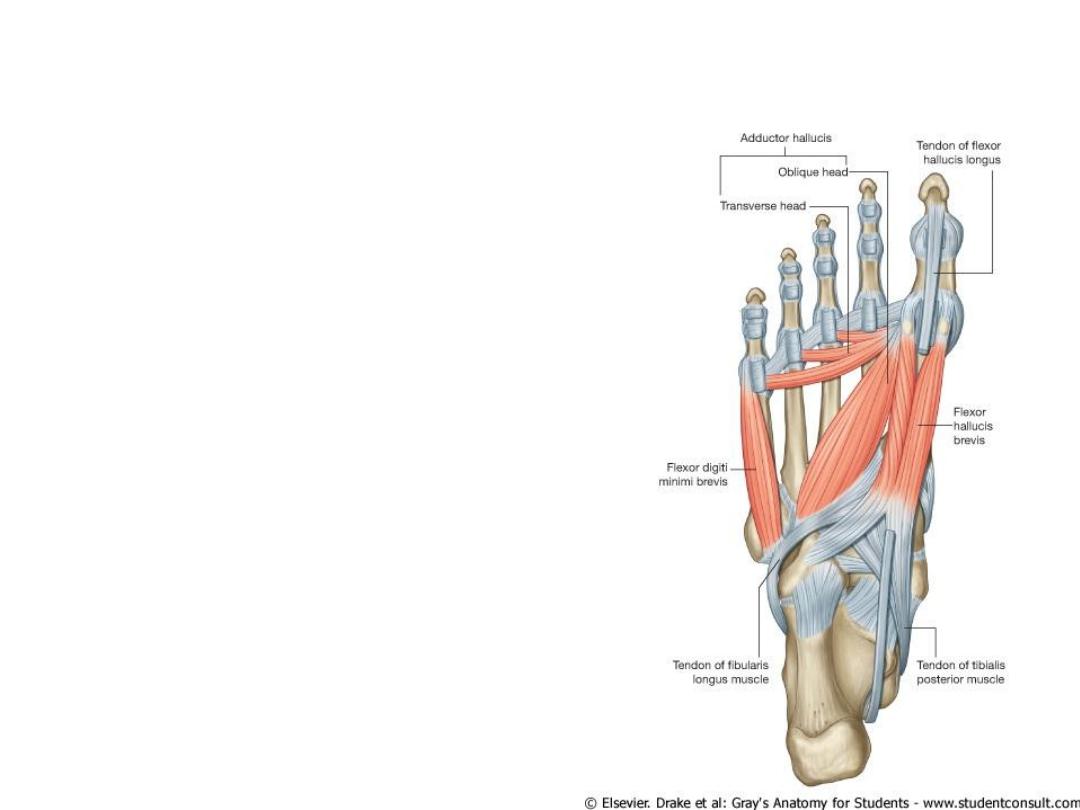
Muscles of the foot sole
• Third Layer
• Flexor hallucis brevis
• Adductor hallucis
• Flexor digiti minimi brevis
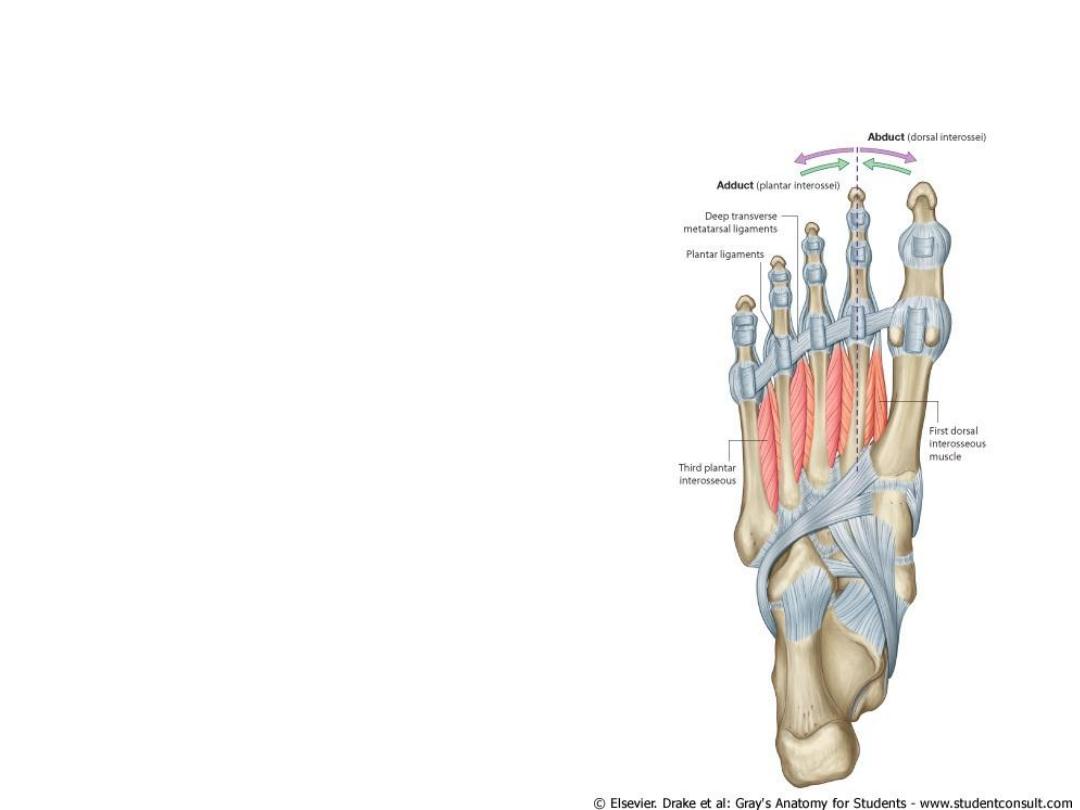
Muscles of the foot sole
• Fourth layer
• Dorsal interossei
• Plantar interossei
• Peroneus longus tendon
• Tibialis posterior tendon
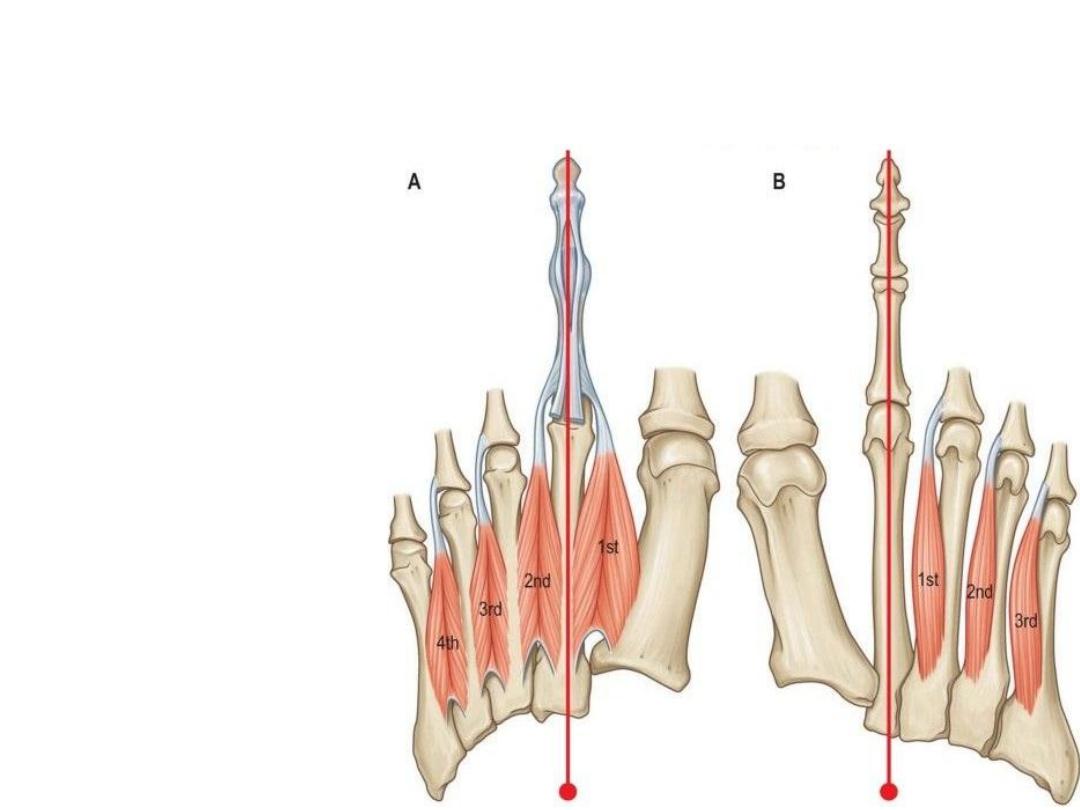
Dorsal & Plantar interossei
• Dorsal – Abduction
• Plantar - Adduction
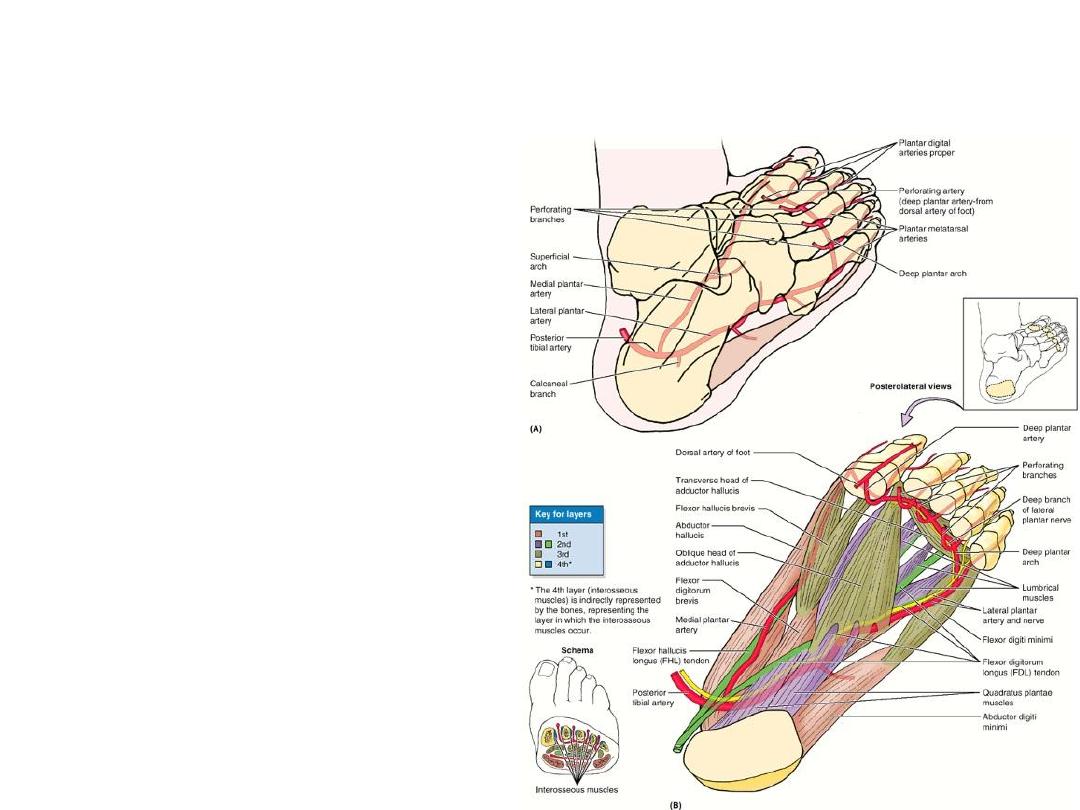
Arteries of the foot sole
• Medial Plantar artery
• Lateral Plantar artery
• Branch of Dorsalis Pedis
artery.

Thank You
