3
Biology
Is the study of life. Basic themes of biology include the evolution of life, the transmission of
information, & the flow of energy through organisms.
OR
Study of life from the microscopic &sub microscopic levels of cells & molecules to the global
distribution of biological communities & stretches back over vast spans of time.
Application to human life:
1- Provide us with technology to transplant kidney, liver, heart, manipulate genes
treat many diseases & increase world food production.
2- Human genome project: is mapping the complete set of gene (the genome) &
studying the proteins for which the genes code.
3- stem cell project's] that are unspecialized, have the capacity to divide & giving rise
one or more specialized types cells ex:- in the skin ,in the lining of intestine, in bone.
give rise to all of the types of cells .In 1970 & 1980
(ES)
Embryonic stem cells
culturing ES cells from mouse embryo
: is the process of producing genetically identical cells or organisms by a
Cloning
sexual reproducing of a single cell or organism.
transgenic animals produce needed
-
oning techniques & genetic engineering
Cl
human proteins such as blood clotting factors
II
- All living organism is able to grow & develop, carry on self-regulated metabolism,
move, respond to stimuli &reproduce. Species evolve & adapt to their environment.
A- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
B- Organisms grow by increasing the size & number of their cells.
C- Metabolism refers to all the chemical activities that take place in the organism,
including the chemical reactions essential to nutrition, growth, repair &
conversion of energy to usable forms.
* Homeostasis is the tendency of organisms to maintain a constant internal
environment ex. Concentration of glucose in the blood.
D- Movement, though not necessarily locomotion , is characteristic of living
organisms , some organisms use tiny extensions of the cell called cilia or longer
flagella to move from place to place. Other organisms are sessile & remain
rooted to some surface.
4
E-Organisms respond to stimuli , physical or chemical changes in their external or
internal environment ex. Changes in temperature , pressure , or sound.
F- In asexual reproduction, offspring are typically identical to the single parent; in
sexual reproduction, offspring are typically the product of the fusion of gametes &
genes are typically contributed by two parents.
G - Populations evolve & become adapted to their environment Adaptations are
traits that increase an organism's ability to survive in its environment ex. The flexible
tongue of the frog
cell.
eukaryotic
cells; all other organisms have
aryotic
prok
have
* Bacteria
* Organisms can be classified into three domains: Archaea , Eubacteria & Eukaryote ,
& six kingdoms: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protiasta, (protozoa, algae, water molds
& slime molds) , Fungi (molds & yeasts) plantae & Animalia
& behaviorally
mation chemically,electrically
Organisms transmit infor
-
III
A- DNA, which makes up the genes, contains the instructions for the development of
an organism & for carrying out life processes.
* Information encoded in DNA is transmitted from one generation to the next.
* DNA codes for proteins, which are important in determining the structure &
function of cells & tissue. They are different from organ to other ex.
1-proteins are important in communication within & among cells.
2-Proteins on the surface of a cell serve a markers, or receptors.
B- Hormones, chemical messengers that transmit messages from one part of an organism
to another, are one type of cell signaling.
C- Many organisms use electrical signals to transmit information; most animals have
nervous systems that transmit electrical impulses & release neurotransmitters (chemical
signal) used by neuron to transmit impulses across alpha synapse
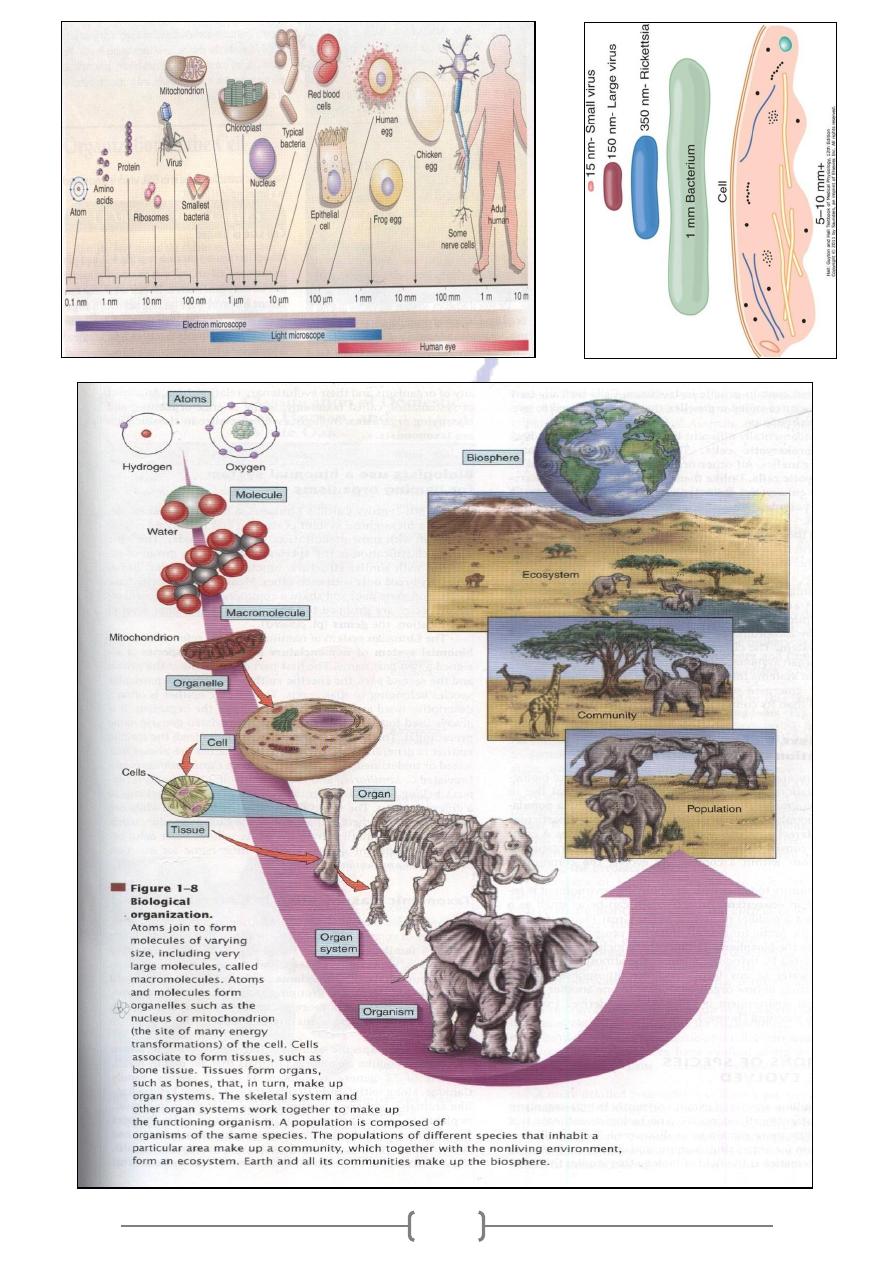
ganization is hierarchica
Biological or
-
IV
A- A complex organism is organized at the chemical, cellular, tissue, organ & organ
system levels.
B- The basic unit of ecological organization is the population. Various population
form communities; a community & its physical environment are referred to as an
ecosystem, all of Earths communities & ecosystems together make up the biosphere.
5
6
ons of species have evolved.
Milli
-
V
A- Taxonomic classification is hierarchical; it includes species, genus, family, order, class ,
phylum , kingdom & domain. Each grouping is referred as a taxon.
B- Biologist uses a binomial system nomenclature in which the name of each species
includes a genus name & a specific epithet.
VI- Evolution
A- Natural selection, the mechanism by which evolution proceeds, favors individuals
with traits that enable them to cope with environmental changes. These individual
are most likely to survive & to produce offspring
B- Charles Darwin based his theory of natural selection on his observations that
individuals of a species vary ; organisms produce more offspring than survive to
reproduce, individuals that are best adapted to their environment are more likely to
survive & reproduce ; as successful organisms pass on their hereditary information ,
their traits become more widely distributed in the population
Activities of living cells require energy , life depends on continuous
-
VII
from the sun.
energy input
A- During photosynthesis plants, algae "& certain bacteria use the energy of sunlight
to synthesized complex molecules from carbon dioxide & water.
which make their
producers, or autographs
sufficient ecosystem includes
–
A self
-
B
, which eat producers or organisms that have eaten producers;
consumers
own food;
, which obtain energy by breaking down wastes & dead organisms.
decomposers
&
Consumers & decomposers are heterotrophy, which are organisms that depend on
producers as an energy source & for food & oxygen
C-All cells carry on cellular respiration, a biochemical process in which they capture
the energy stored in nutrients by producers. Some of that energy is then used to
synthesize needed materials or to carry out other cell activities.
