63
, and this genetic activity in
activity of specific genes
An expression of changes in
*
turns is influenced by a variety of factors inside and outside the cell..
* It is differential gene expression that is responsible for variation in chemistry,
behavior and structure among cells.
with a
Differentiation development of a relatively unspecialized cell or tissue into one
*
more specific structure and function.
* Through this process, an embryo develops into an organism composed of more
than 200 types of cells, each specialized to perform specific functions.
* Cell differentiation by itself does not explain development.
become progressively organized , shaping the intricate pattern of
The diff. cell must
*
.
imal
tissue and organs that characterizes a multicellular an
* In cytopathology the level of cellular diff. is used as a measure of cancer progression.
A cell that is able to diff. into many cell types is known as pluripotent which is
meristematic cell in higher plants & stem cells in animals
Totipotent A cell that is able to diff. into all cell types ex. Zygote and early embryonic cell
are totipotent
* Pluripotent stem cells go further specialization multipotent progenitor cell
functional cells.
* During diff. certain genes are turned on, while other genes are switched off
Mammalian cell type
* Each of about 10
14
cells in an adult human has its own copy, or copies , of the
genome , except a red blood cell.
* The majority of the cells are diploid (have 2 copies of each chromosome). This
category of cells called
1- Somatic cells: A) skin B) muscle cell
2- Germ line cell: are any line of cells that give rise to gametes , egg and sperm-and are
continuous through the generation
3- Stem cells : are unspecialized and have the capacity to divide, giving rise to more stem
cell and to one or more specialized types
64
Stem cells permit the body to repair both normal wear and tear injury tissue.
ex. 1- Stem cells in the skin continuous divide and some differentiated to replace skin
cell that are constantly being wear off.
2- Stem cells in the lining of the intestine reproduce themselves to replace cell that
wear off.
3- Stem cell in the bone marrow differentiates to restore the various types of blood
cells.
If ES cells could be cultured in laboratory and then implanted in damaged hearts, brains,
spinal cord, or livers they could potentially provide the cells needed for repairing injuries
or for reversing the ravages of disease processes. Stem cells will eventually be used to
treat disorders like Parkinson’s disease , Alzheimer’s disease , diabetes and spinal cord
injury.
Development
Fertilization zygote cleaves tiny ball of cells called blastula
undergoes a mitotic division gastrula ,with either two or three layers( germ
layers) in all vertebrates , these are the forerunners of all adult tissues and organs.
* In most multicellular organisms, not all cells are alike ex. Cells that make up the
human skin are different from cells that make up the inner organs
nervous system and nervous system and sense organs.
Ectoderm;
* Outer layer of skin (epidermis) and its associated structure (nails, hair, etc.).
Pituitary gland, pigment cells.
Mesoderm:
Notochord --- Skeleton (bone and cartilage)--- Muscle --- Circulatory system --- Excretory
system --- Reproductive system --- Inner layer of skin (dermis)
the pharynx, esophagus and the stomach.
cavity,
oral
,
foregut
Endoderm
Hindgut, rectum and large intestine.
Midgut, small intestine.
Epithelial parts of trachea , lungs. The lining cells of all the glands which
open into the digestive tube.
65
Stem Cells, & Differentiation of blood cells
, and consequently the
Mature blood cells have a relatively short life span
population must be continuously replaced with the progeny of stem cells produced in
the hematopoietic
* In the earliest stages of embryogenesis, blood cells arise from the yolk sac
mesoderm.
* Sometime later, the liver and spleen serve as temporary hematopoietic tissues, but
by the second month the clavicle has begun to ossify and begins to develop bone
marrow in its core
* As the prenatal ossification of the rest of the skeleton accelerates, the bone
marrow becomes an increasingly important hematopoietic tissue.
* After birth and on into childhood, erythrocytes, granular leukocytes, monocytes,
and platelets are derived from stem cells located in bone marrow. The origin and
maturation of these cells are termed, respectively, erythropoiesis), granulopoiesis,
monocytopoiesis, and megakaryocytopoiesis (give platelets).
* The bone marrow also produces cells that migrate to the lymphoid organs,
producing the various types of lymphocytes
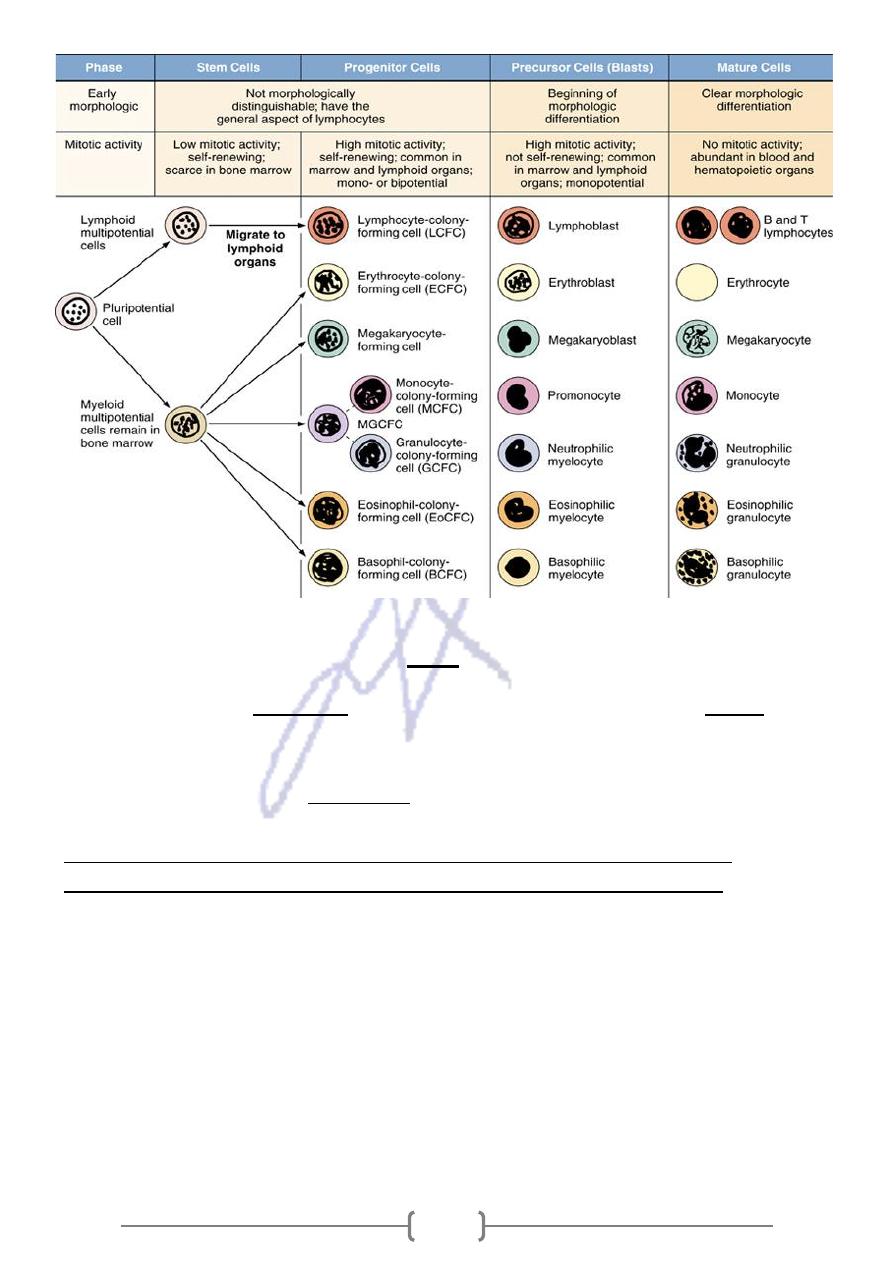
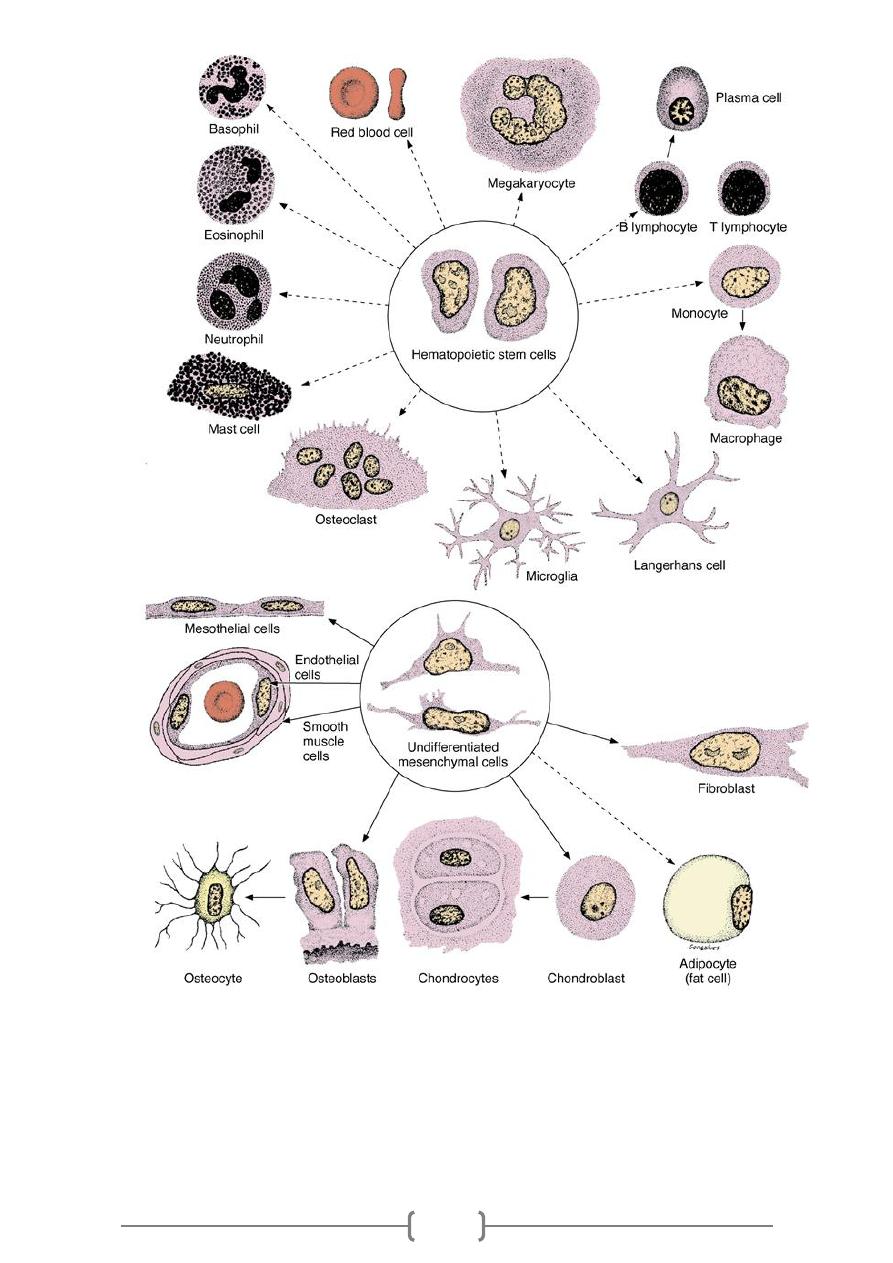
Pluripotential Hematopoietic Stem Cells
* It is believed that all blood cells arise from a single type of stem cell in the bone
pluripotential
a
alled
marrow. Because this cell can produce all blood cell types, it is c
1)
–
(Figure 13
stem cell
cell lineage that will become lymphocytes
one
These cells proliferate and form
*
in
that develop
the myeloid cells
lineage that will form
another
and
lymphoid cells)
(
bone marrow (granulocytes, monocytes, erythrocytes, and megakaryocytes). Early in
their development, lymphoid cells migrate from the bone marrow to the thymus, lymph
nodes, spleen and other lymphoid structures where they proliferate
66
Figure 13—1. Differentiation of pluripotential stem
cells during hematopoiesis.
Skin
, a
dermis
an epithelial layer of ectodermal, and the
epidermis,
It is composed of the
*
layer of connective tissue of mesodermal origin in 2
nd
week of embryogenesis..
* Epidermal derivatives include hairs, nails, and sebaceous and sweat glands.
, or subcutaneous tissue, a loose connective
hypodermis
* Beneath the dermis lies the
tissue that may contain a pad of adipose cells. .
.
, fibroblasts, vessel and adipose cells derive from mesoderm
Langerhans cells
*
Neurons, and sensory ending derive from neural ectoderm and neural crest.
*
* The mature epidermis begin as a simple cuboidal epitheliul then squamous layer
called peridern in 4
th
week.
* Keratinization begins in basal layer of cells appear after 5
th
month.
* Melanocytes enter the epidermis during the 8
th
week . and by the 6
th
month they
have begun pigmenting the epidermis.
* Dermis begins as diffuse mesenchyme cells and extracellular matrix which develop
fibroblasts and collagen fibers.
* Neuron processes begin to penetrate the dermis in 5
th
week . capillary bed form
during 3
rd
month . In 4
th
month dermis has appeared.
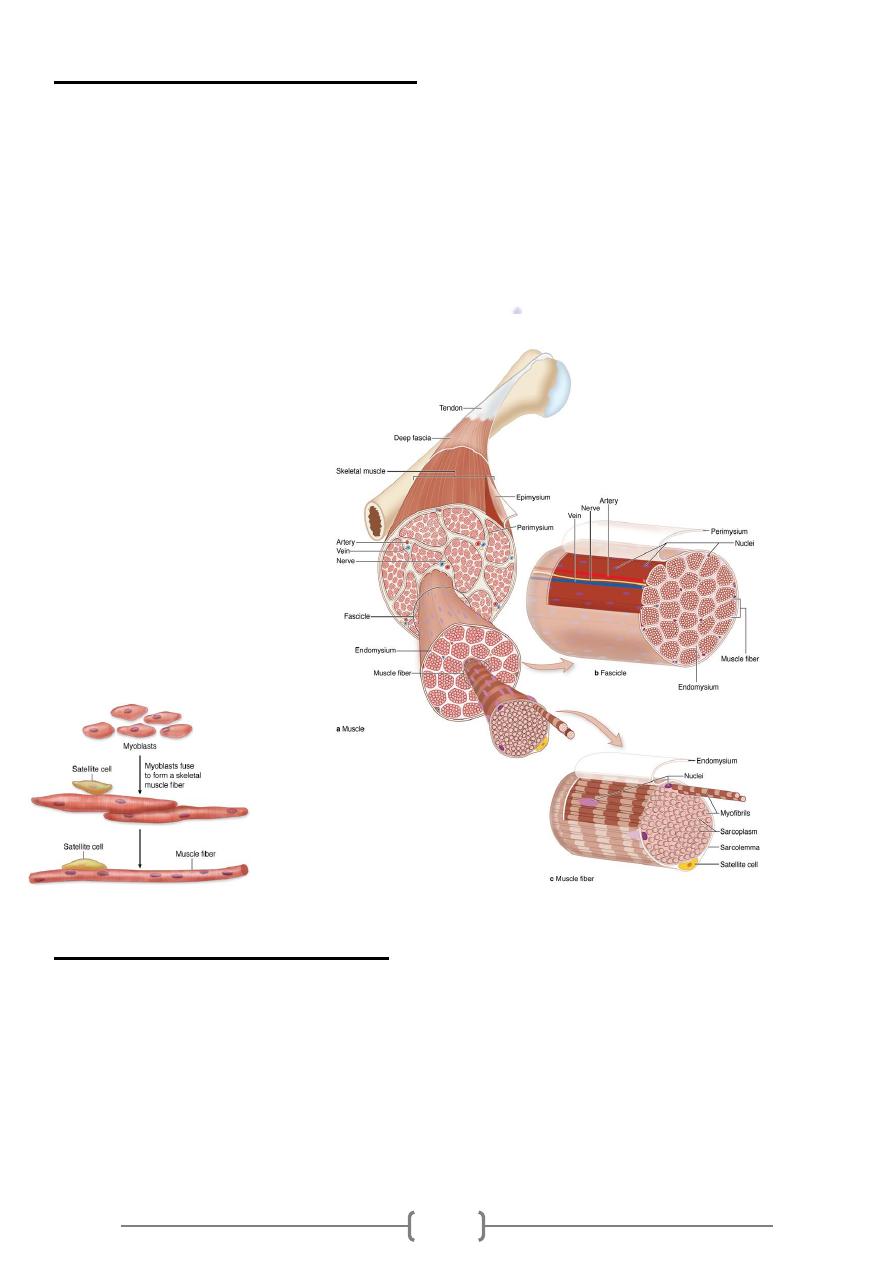
67
ac muscle cells
Skeletal and cardi
* Also derived from mesoderm, there is synthesis and intracellular accumulation of
large amount of muscle cell protein, including
a- Actin b- Myosin c- Troponin d- Tropomycin
* These proteins are then arranged within the cells into organized semi crystalline
arrays called Sacromeres, so increasing the functional efficiency of muscle protein for
generating contraction
Nervous tissue differentiation
* In human, nervous tissue has become highly differentiated to utilize the property of
excitability for detection of changes in the environment.
* Neuroepithelium , in primitive embryo contains a groups of undifferentiated highly
Proliferative cells , among them is undifferentiated cell population that continues to
divide and give rise to a series of progeny that undergo subsequent differentiation
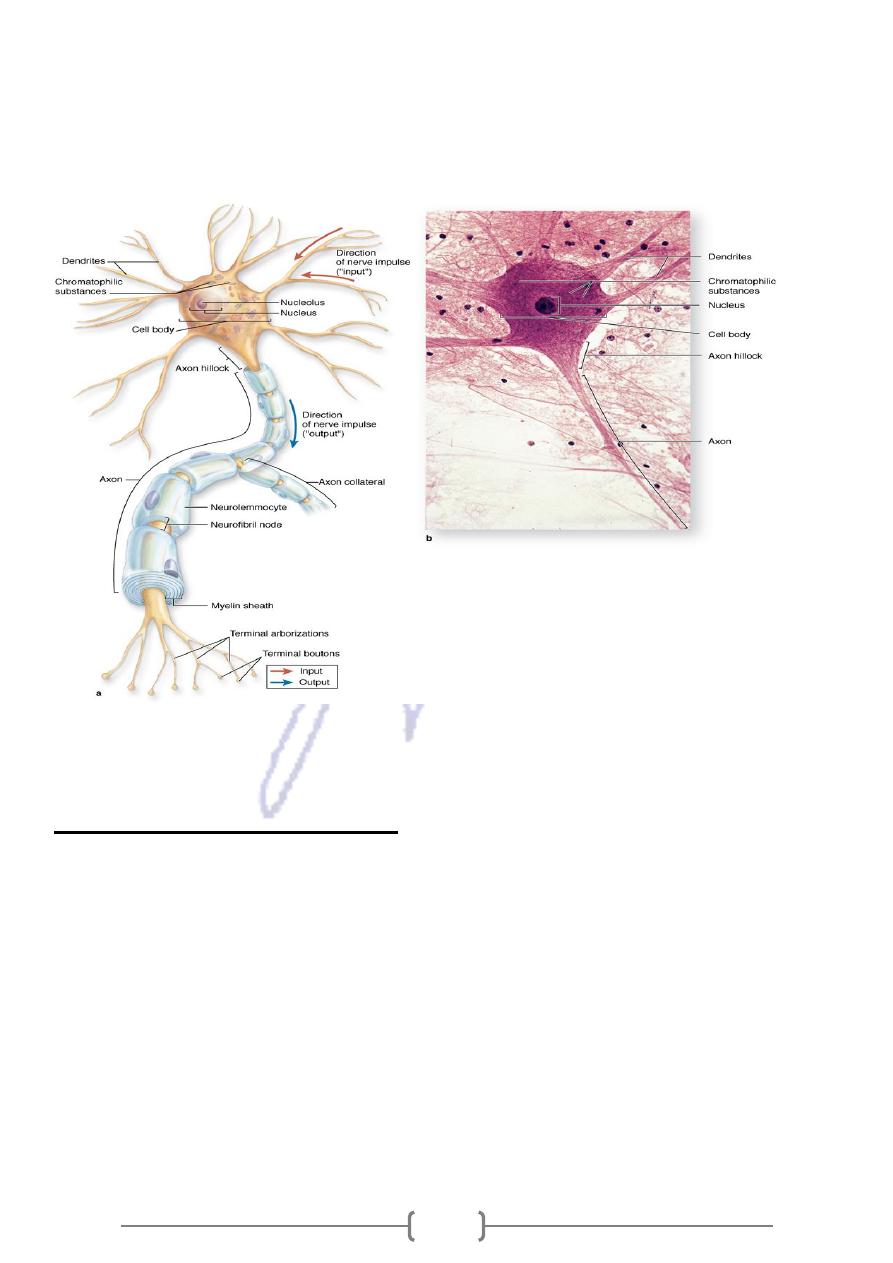
68
and produce a Neuroblast, which differentiate into NEURON the main functional
communicating cells of the nerve system.
* GLIBOBLASTS, which diff. into Glial cells , that serve a supporting function in nerve
system.
Osteocytes (cell of bone) and chondrocyte (cells of cartilage).
Chondrocytes differentiation :
* An undifferentiated mesenchymal cell becomes committed to the chondrocyte
pathway. As a result, chondrocyte begins to secrete large amount of several kinds of
proteins and other macromolecules characteristics of cartilage such as:-
A- collagen b- cartilage proteoglycan c- hayluronic acid d- glycoprotein.
* At first, the chondrocytes differentiate by elaborating synthetic enzymes (proteins),
and then it recognizes these enzymes, into secretory organelles. ex. ER & GA.
* Other cells also synthesize collagen and proteoglycan, but only chondro.
manufacture and secrete large amount of them
69
