CUTANEOUS MYCOSES
Dr. Mohammed H. Mushrif
Lecturer of Medical Mycology
By

Dermatophytes
• More than 100 species have been described for
dermatophytes, only about 40 are considered and less
than half of these are associated with human disease.
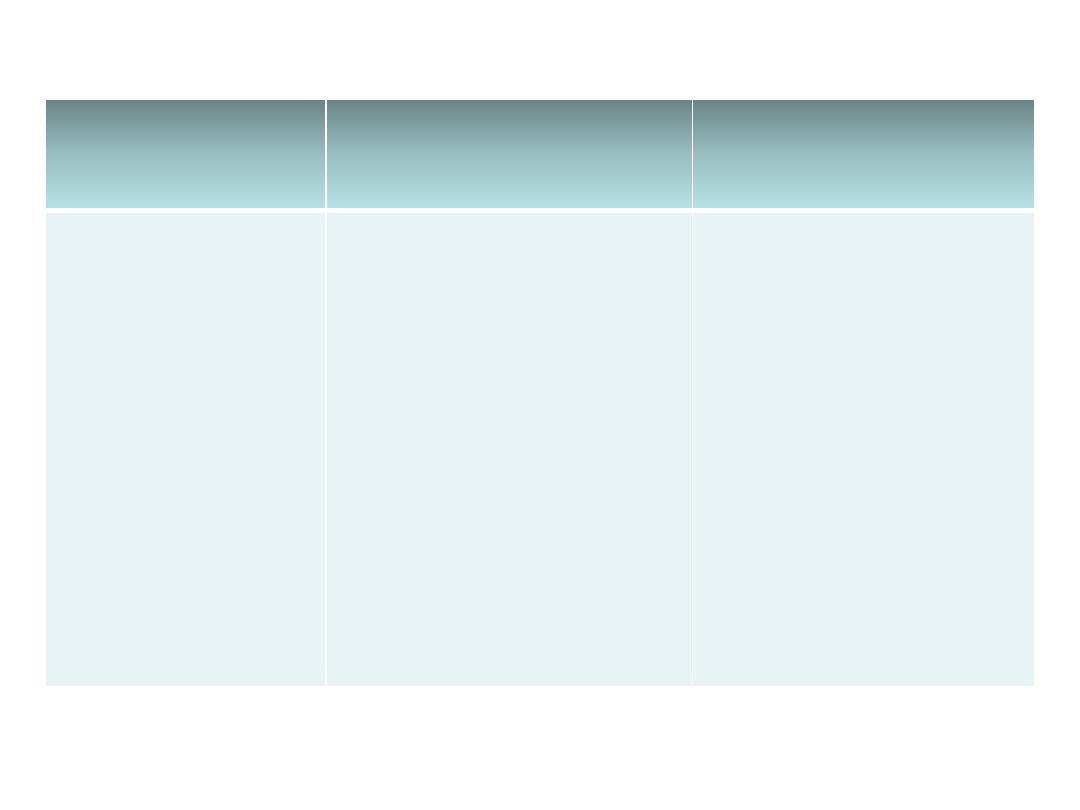
• Dermatophytes include three genera which are:
trichophyton, microsporum and epidermophyton.
• According to sporulation:
Asexual (anamorphic state): chains of arthroconidia.
Sexual (teleomorphic state): trichophyton and microsporum
are ascomycetes but that of epidermophyton is not observed.
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes2

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes3
Epidermophyto
n
Trichophyton
Microsporu
m
E. floccosum
T. mentagrophytes
T. rubrum
T. tonsurans
T. schoenleinii
T. verrucosum
T. violaceum
M. canis
M. gypseum
M. audouinii
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes4
Trichophyton
• Skin
• Hair
• Nails
Affect
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes5
Microsporum
• Skin
• Hair
Affect
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes6
Epidermophyton
• Skin
• Nails
Affect

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes7
• Dermatophytes affect keratinized tissues (skin, hair and
nails) as they produce keratinase enzyme which digests
the keratin.
• The intact skin is an important barrier against infection.
• Heat and humidity enhance the infection.
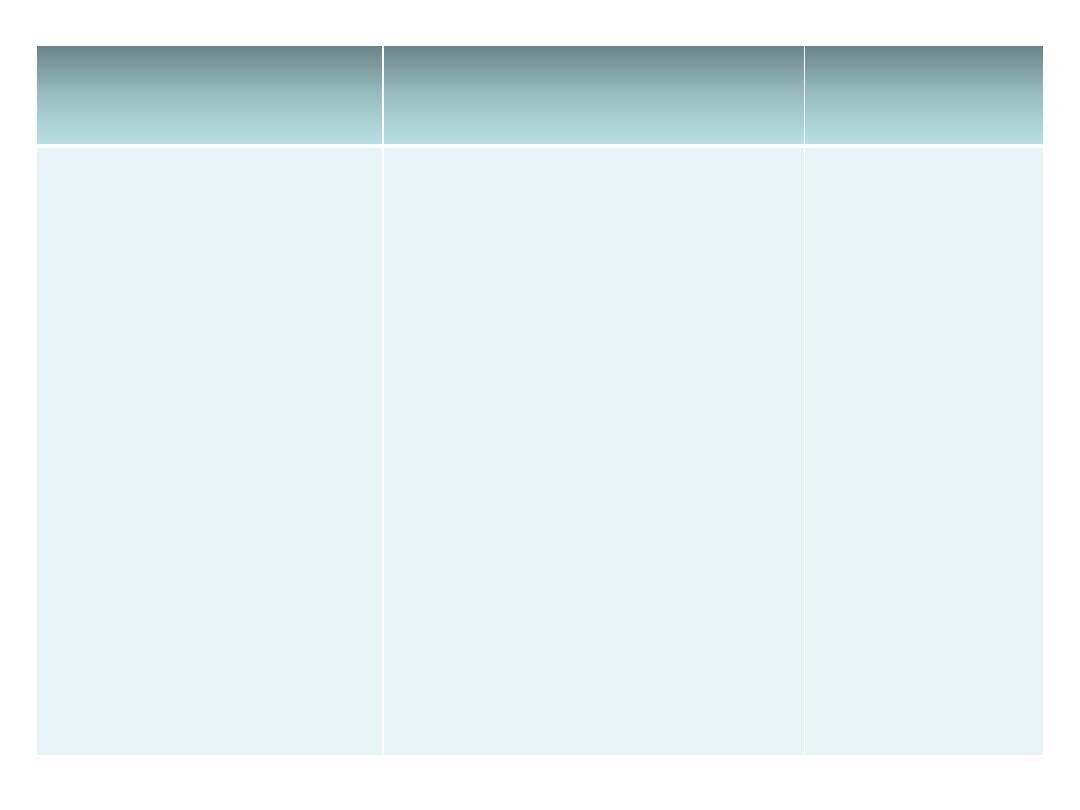
• Infection may be:
Anthropophilic: from man to man by direct contact.
Zoophilic: from the animals.
Geophilic: from the soil.
Pathogenesis

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes8
• Anthropophilic group tends to cause
chronic infections which are difficult to
cure.
• Zoophilic and geophilic groups tend to
cause acute inflammatory lesions that
respond well to therapy.

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes9
Geophilic
Zoophilic
Anthropophilic
M. gypseum
M. canis (dogs, cats)
M. equinum (horses)
M. gallinae (fowls)
T. verrucosum (cattle)
M. audouinii
T. mentagrophytes
var interdigitale
T. rubrum
T. tonsurans
T. schoenleinii
T. violaceum
E. Floccosum

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes10
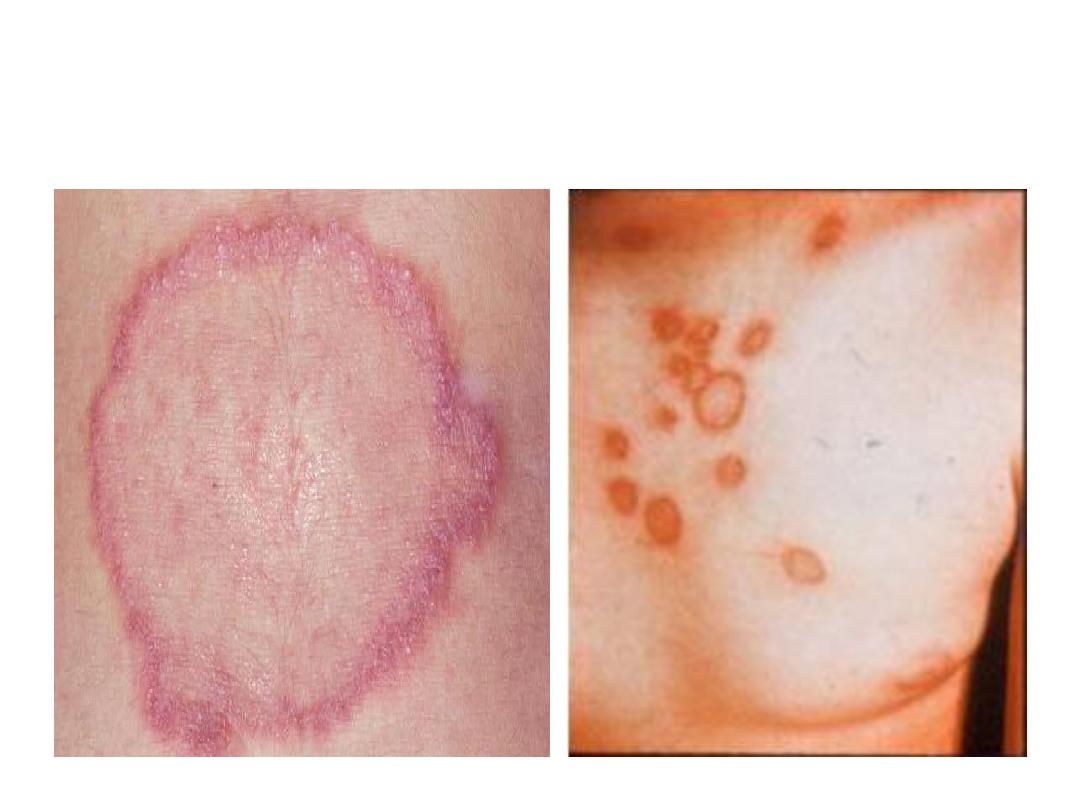
• The lesion is called ring worm or tinea.
• Tinea comes from the latin word moth.
• The lesion is called ring worm because it is ring
shaped with red raised border of active
inflammation and a healing center.
• The clinical forms of the disease are:
Tinea capitis (head) & tinea cruris (groin
area) & tinea corporis (body) & tinea
unguium (nails) & tinea pedis (feet) & tinea
barbae (beard) & tinea manus (hands).
Clinical picture
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes11
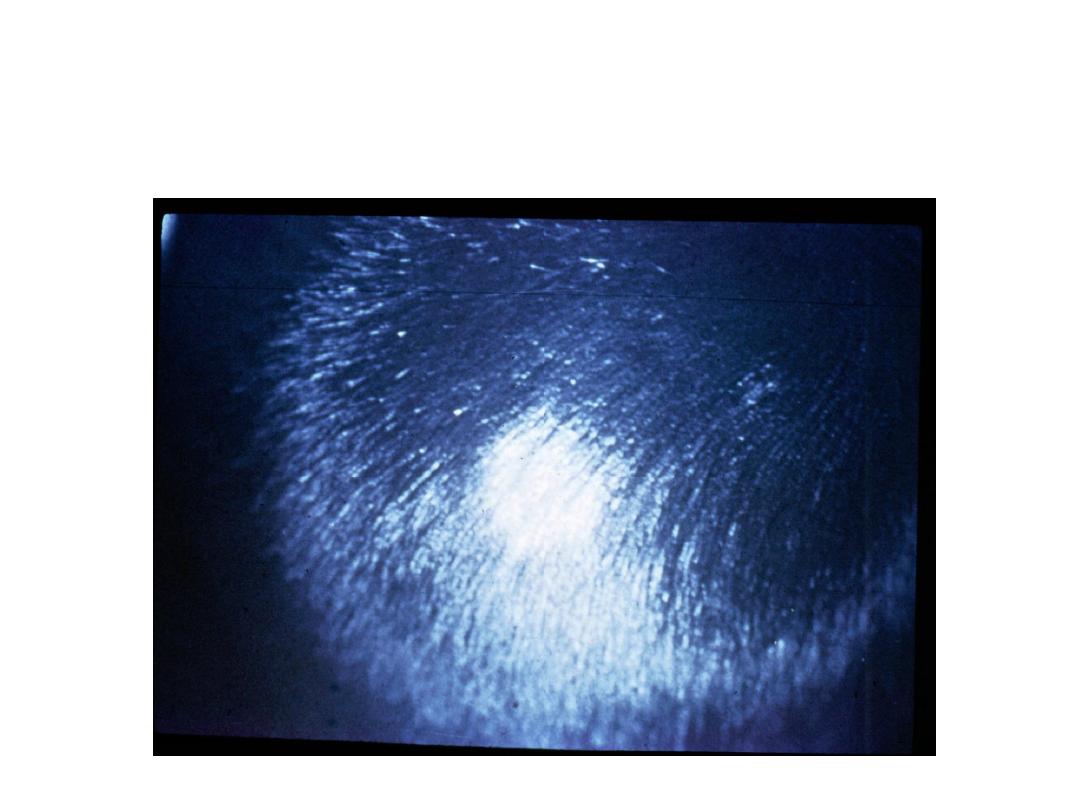
Tinea capitis
(scalp)
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes12
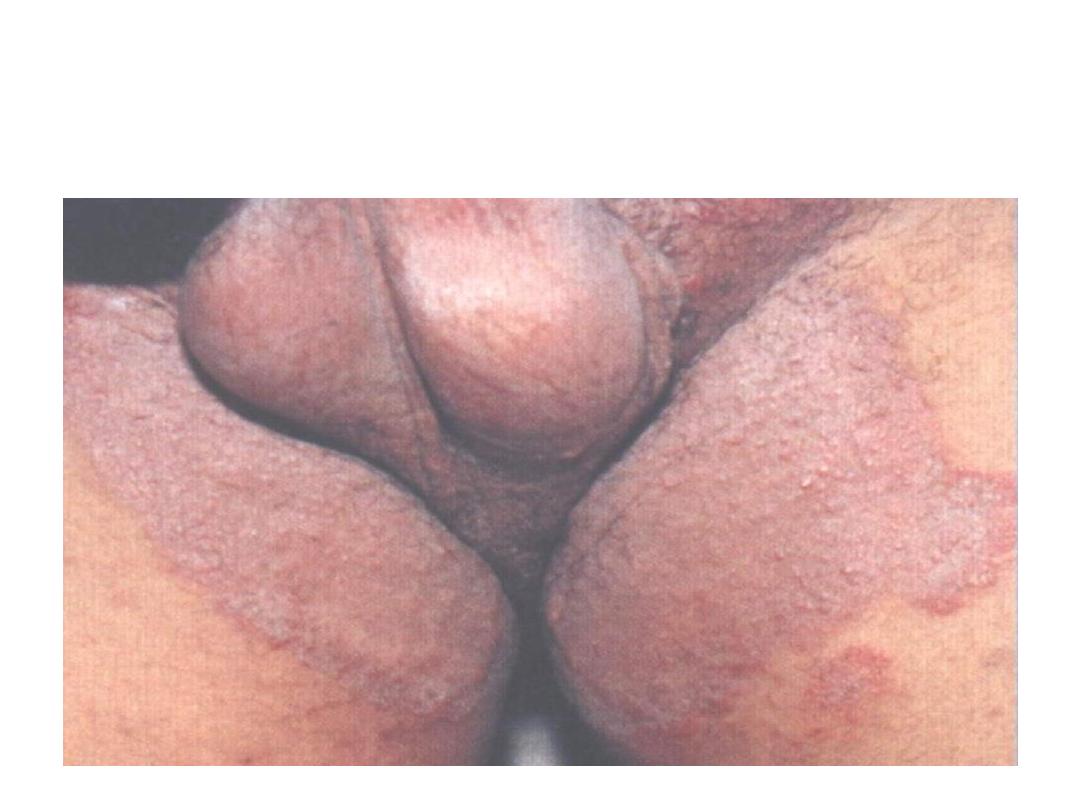
Tinea cruris
(jock itch)
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes13
Tinea corporis
(the body)
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes14
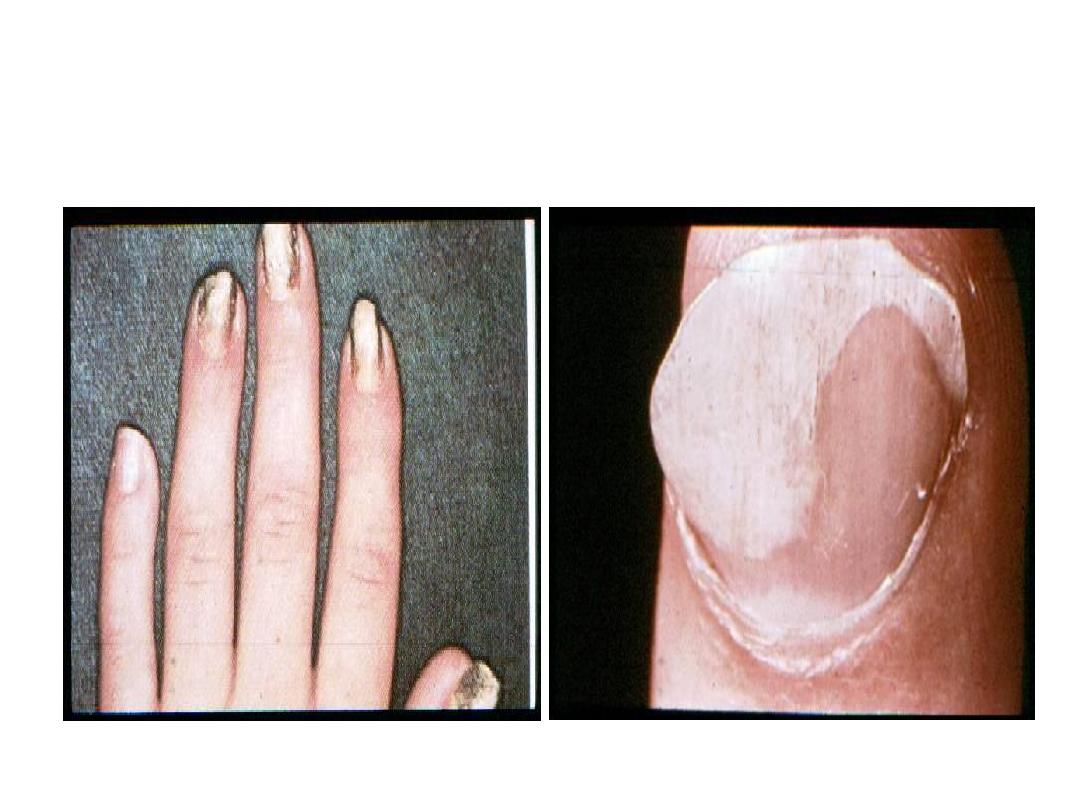
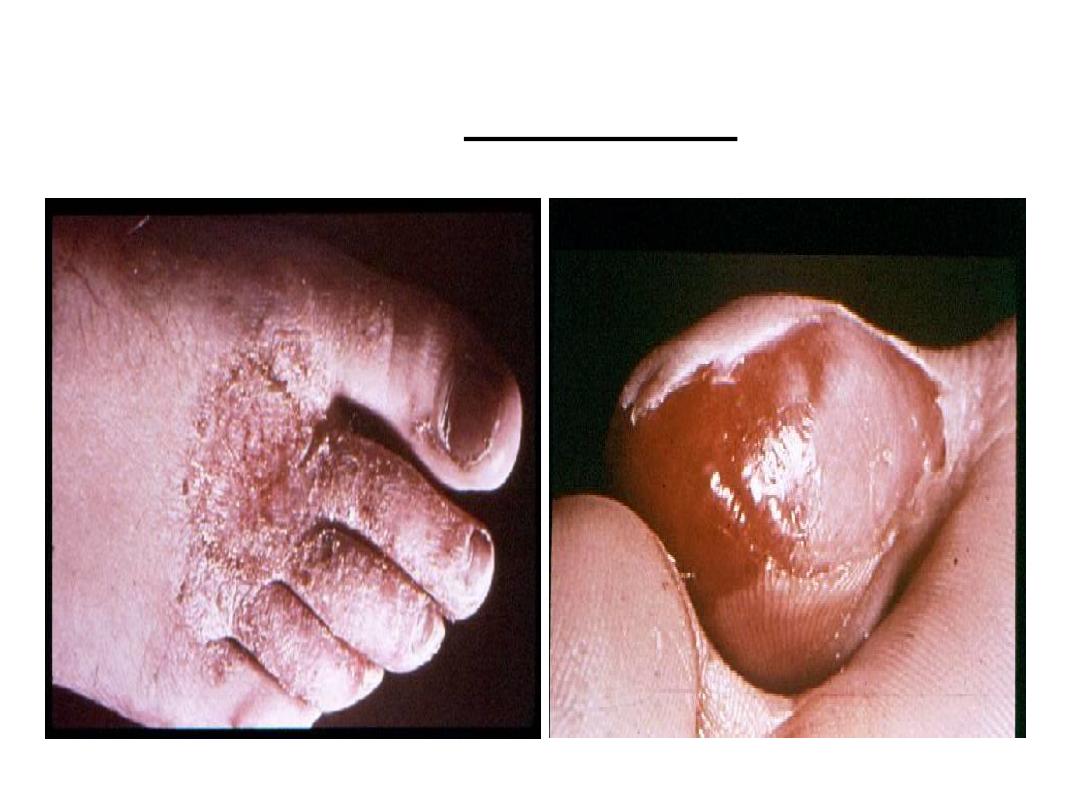
Tinea unguium (onychomycosis)
Nails are thickened, discolored and brittle
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes15
Tinea pedis
The lesion is called
athlete’s foot that occurs in
those wearing shoes
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes16
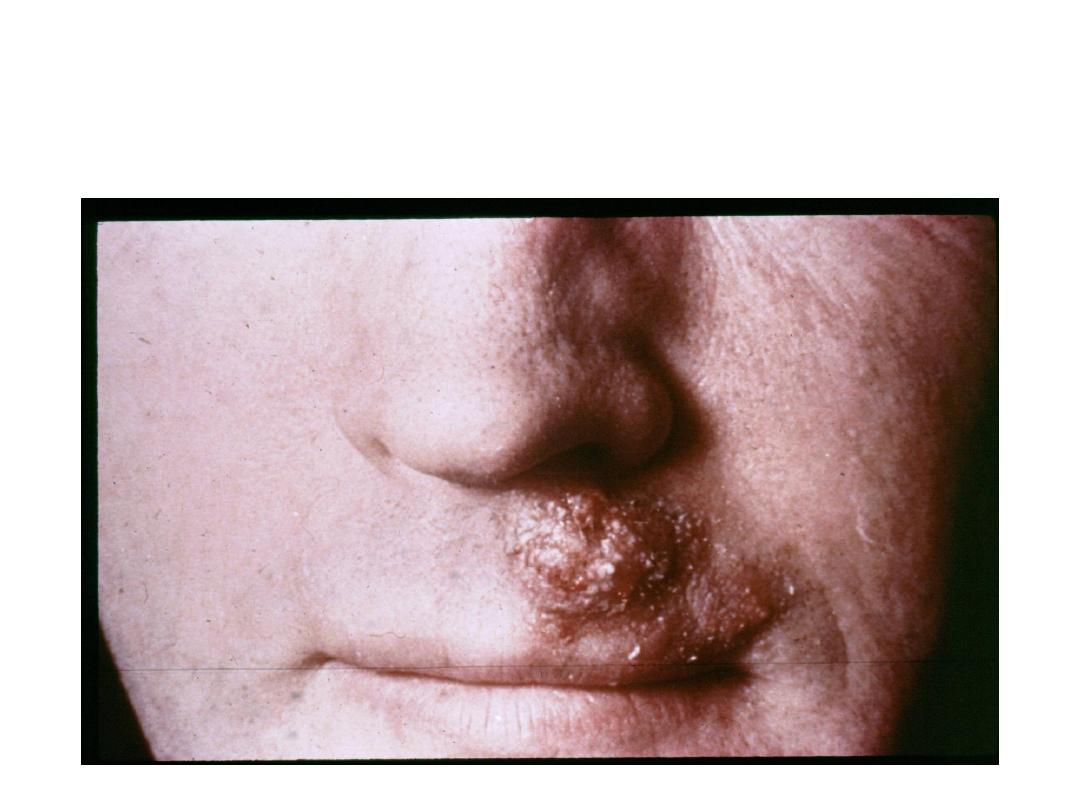
Tinea barbae
(bearded area)

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes17
• Dermatophytid reaction:
in the
course of dermatophytosis
,
the individual
may become hypersensitive to fungal
elements and develop allergic
manifestations called dermatophytids
usually vesicles elsewhere in the body
most often on the hand. Trichophytin skin
test is markedly positive.

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes18
Wood’s light (UV light at wave length 365 nm):
Microsporum lesions will fluoresce brilliant green.
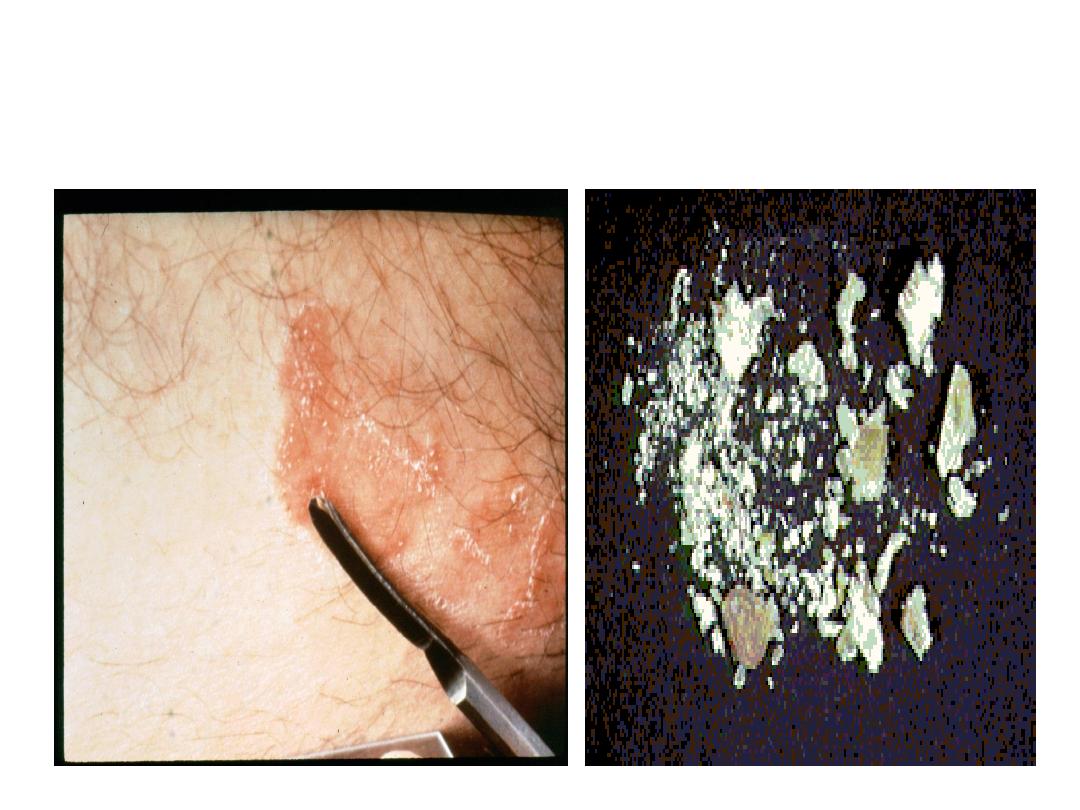
Specimen:
Skin scales, nails, hair.
Microscopic examination of these specimens using
KOH 10%:
KOH dissolves keratin but does not affect fungi.
Branching septate hyphae are detected among epithelial
cells.
Spores (arthroconidia) may be detected outside the hair
shaft (ectothrix) or inside the hair shaft (endothrix). An
exception is favus in which hyphal elements are seen in
the hair shafts.
Laboratory diagnosis
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes19
Specimen collection
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes20
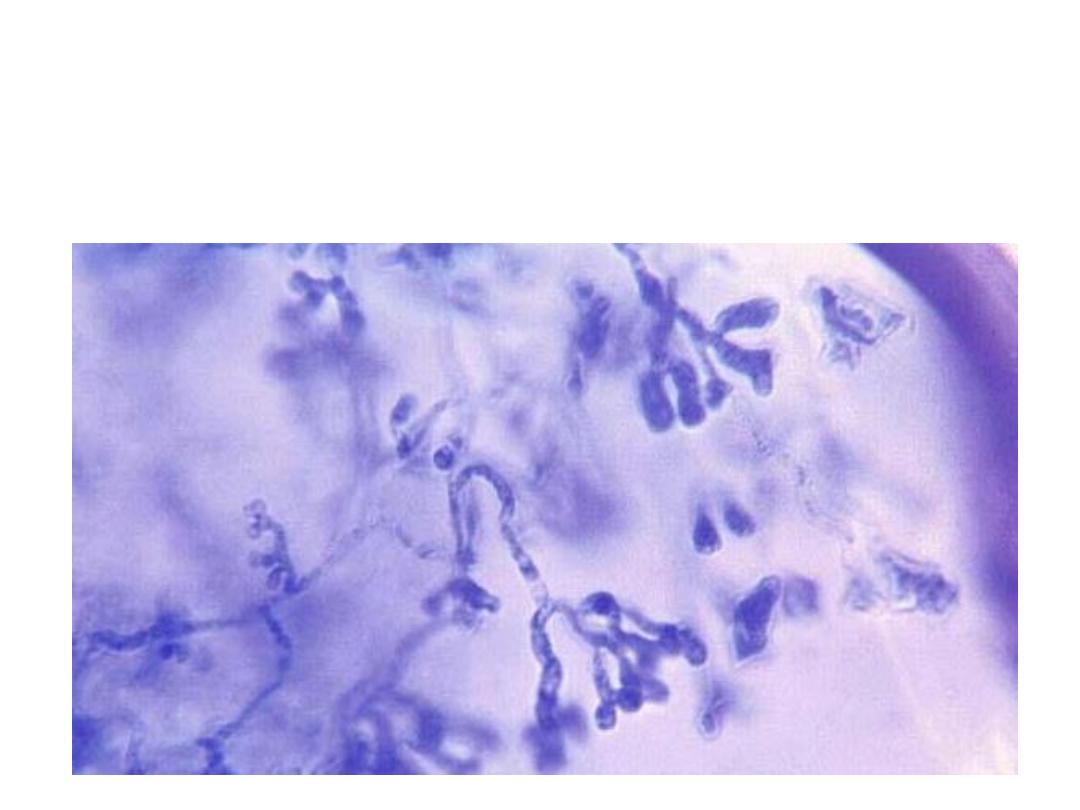
Dermatophytes in KOH mount of skin scraping
(Branching hyphae + arthroconidia)
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes21
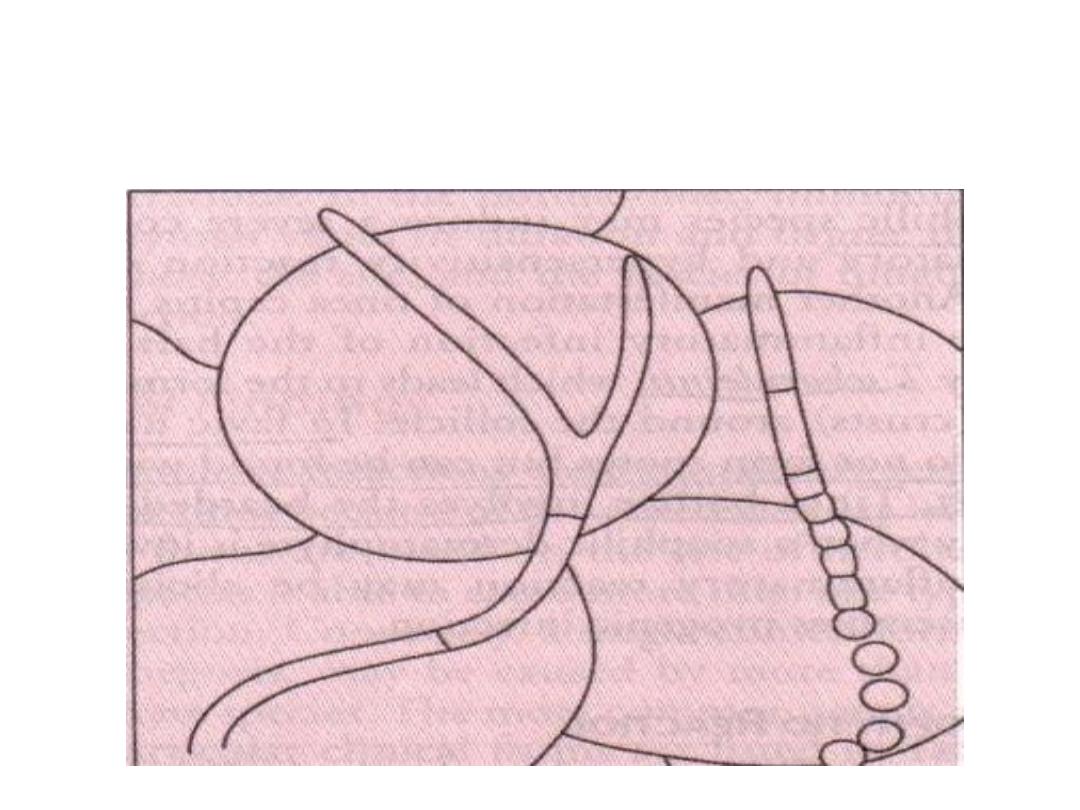
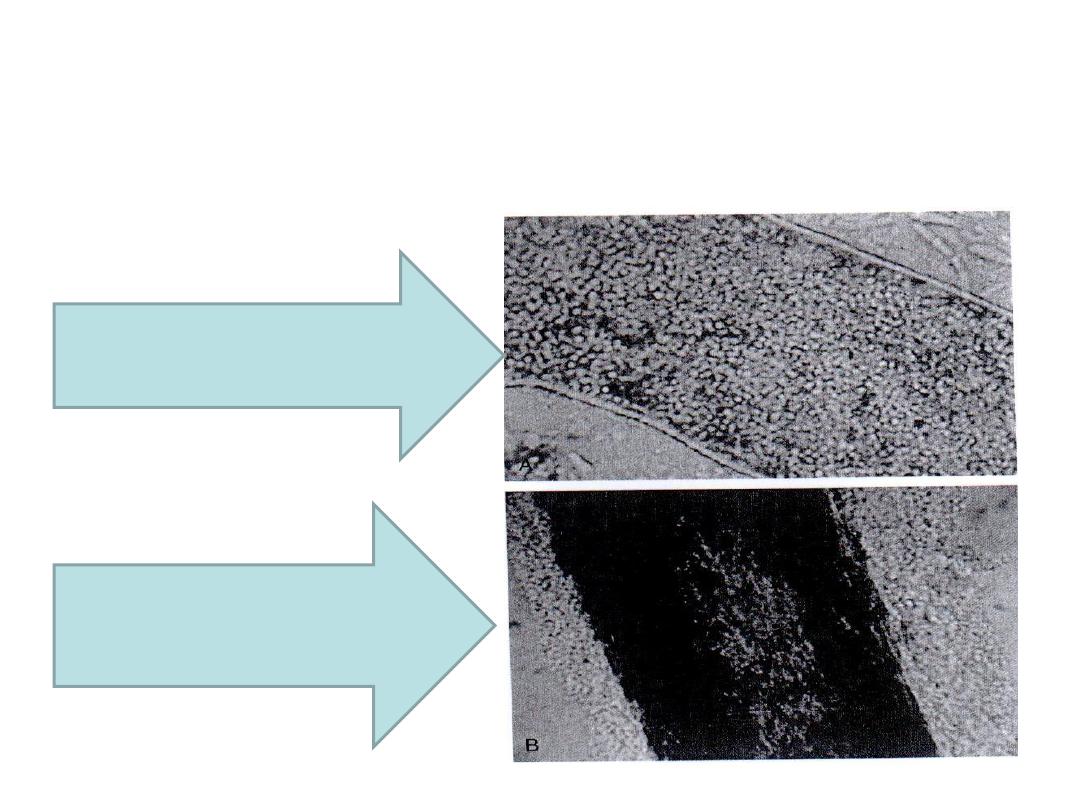
Ectothrix and endothrix infection
Endothrix spores
(T. tonsurans)
Ectothrix spores
(Microsporum)
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes22
(Favic hair)
In favic hair, hyphae do not form spores but
can be found within the hair shaft

Culture:
o Medium:
Sabouraud’s dextrose agar to which we add
chloramphenicol and cycloheximide.
o Incubation: at the room temperature.
o Duration: Up to 4 weeks.
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes23
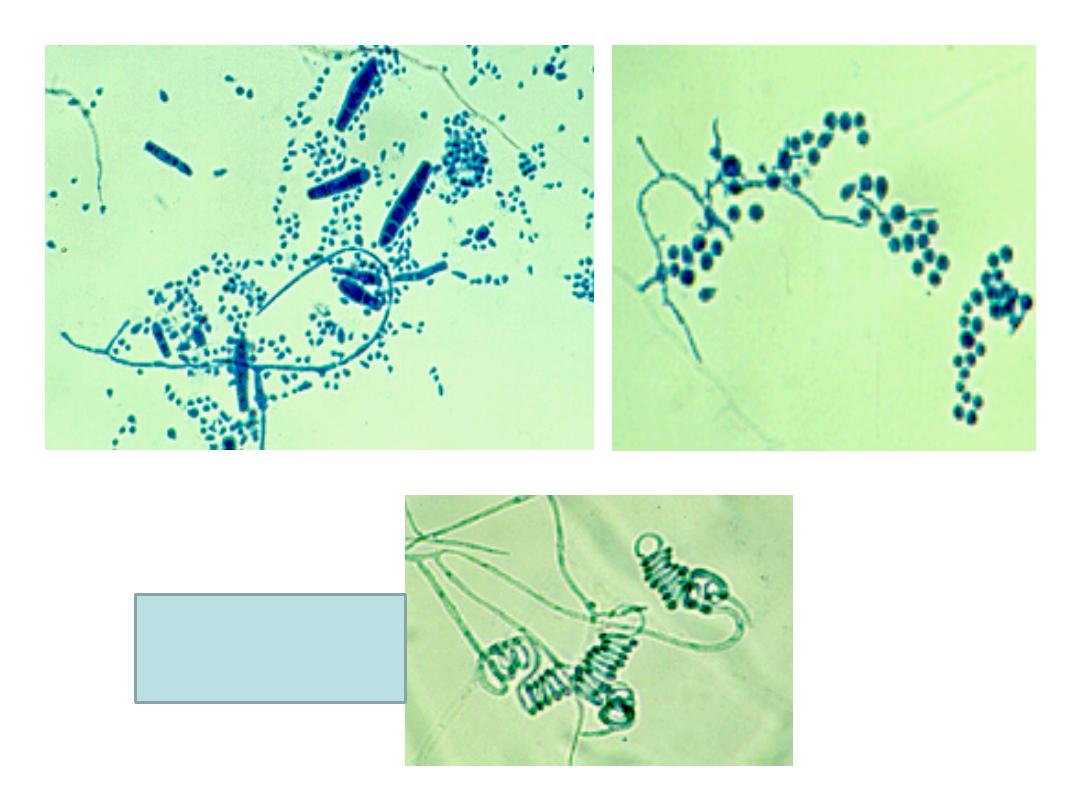
Identification is done by:
Morphology and color on the observe and reverse
surfaces.
Slide culture to study the morphology and color of conidia
using lactophenol cotton blue.
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes24
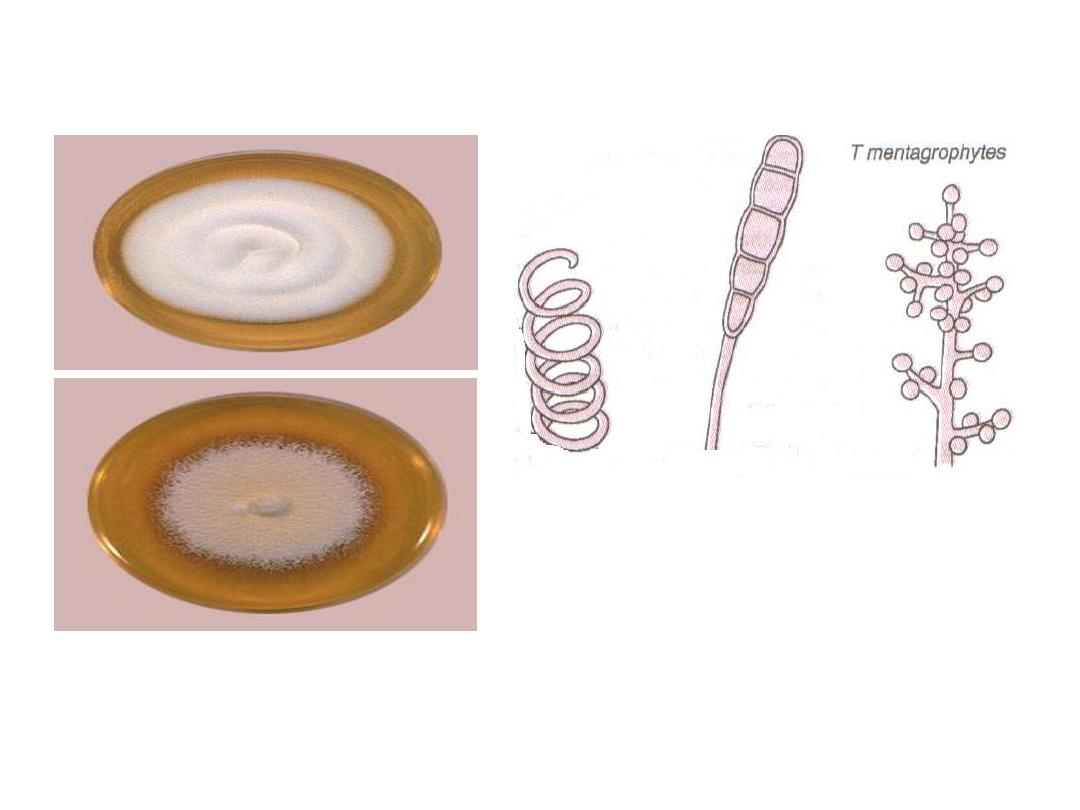
Trichophyton
mentagrophytes
Conidia: are macroconidia
which are smooth, thin walled
and cylindrical and
microconidia which are grape
like clusters on terminal
branches.
Colonies may be cottony
to granular.
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes
25
Spiral
hyphae
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes26
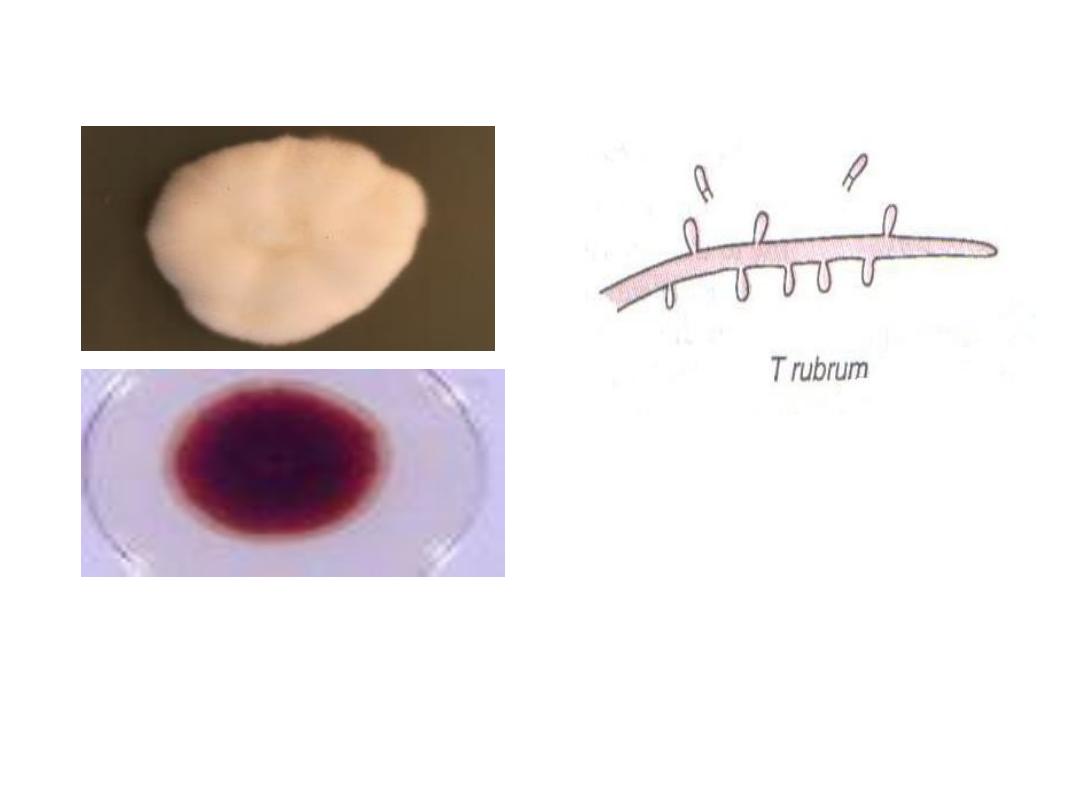
Trichophyton rubrum
Conidia: are microconidia
which are small and
piriform in shape
.
The fungus has white cottony observe
surface + deep red non diffusible
pigment on the reverse surface
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes
27
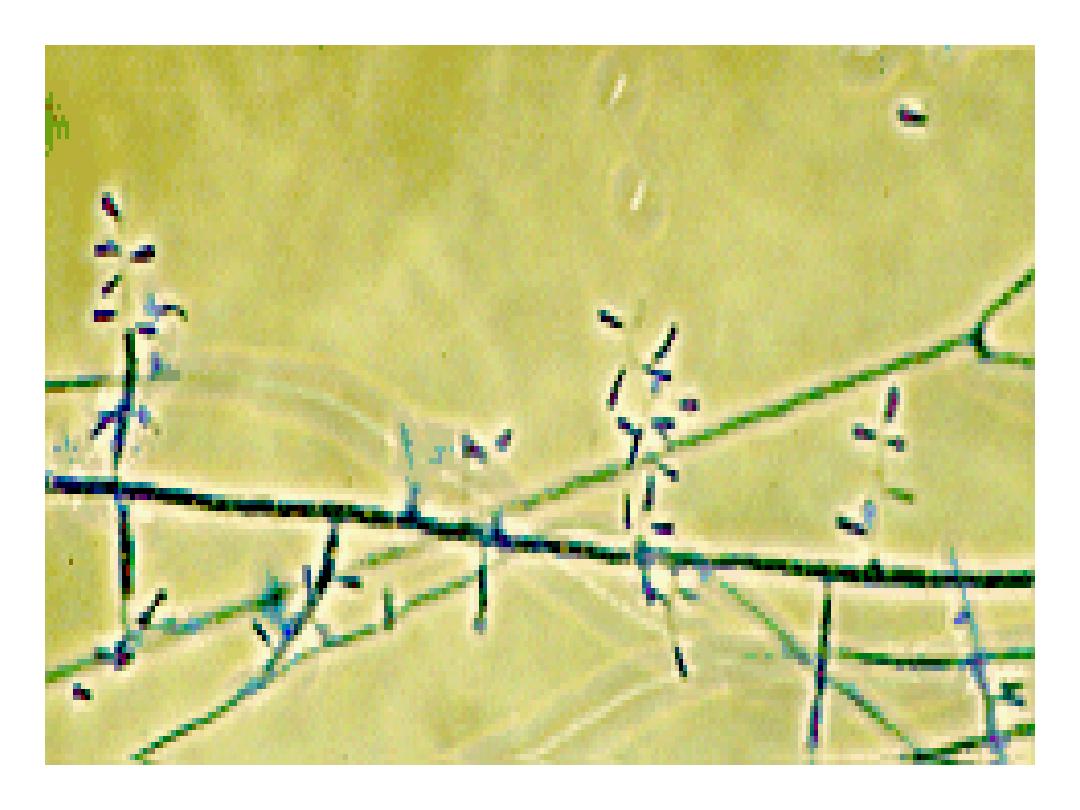
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes28
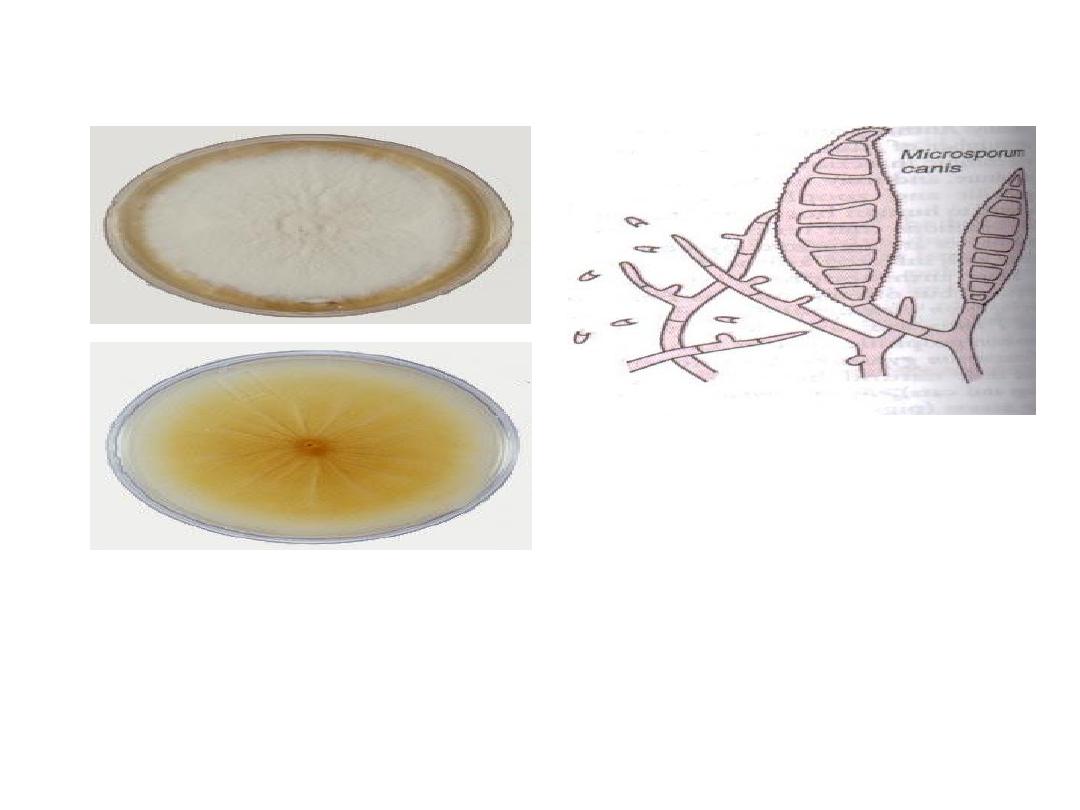
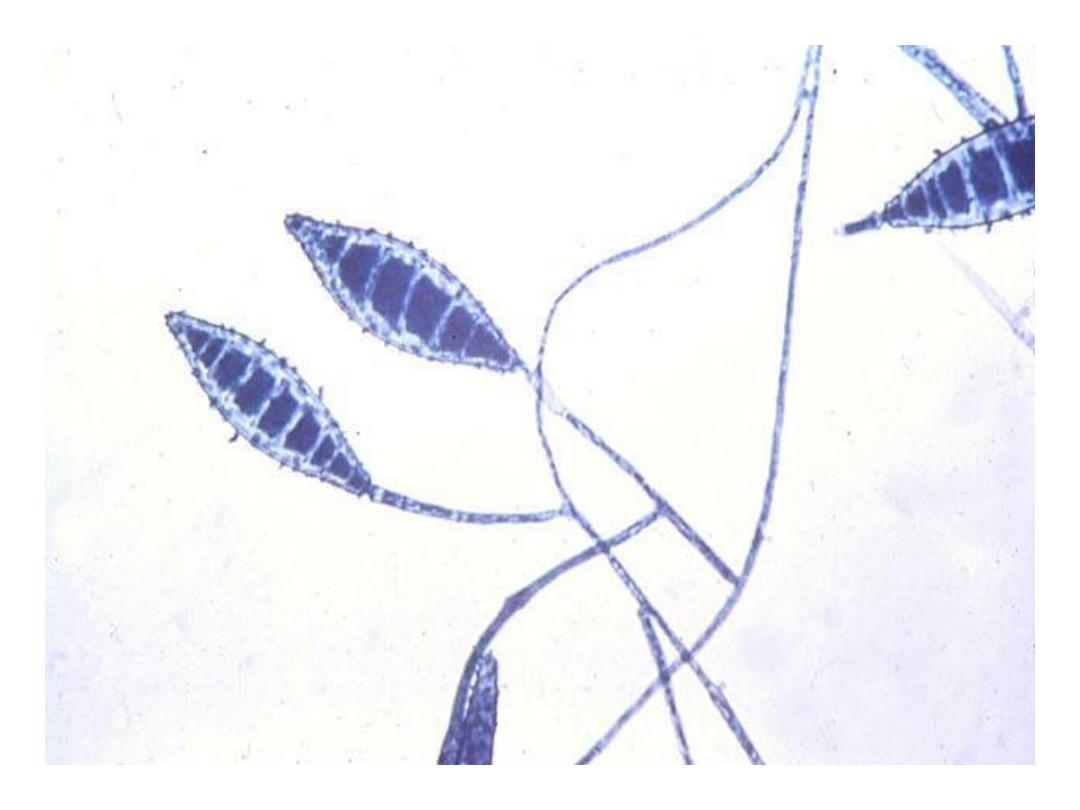
Microsporum canis
Conidia: are macroconidia
which are thick echinulate
walled, 8-15 cells + curved
tip
The fungus has white cottony
observe surface + deep yellow on
the reverse surface
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes
29

4/30/2016
Dermatophytes30
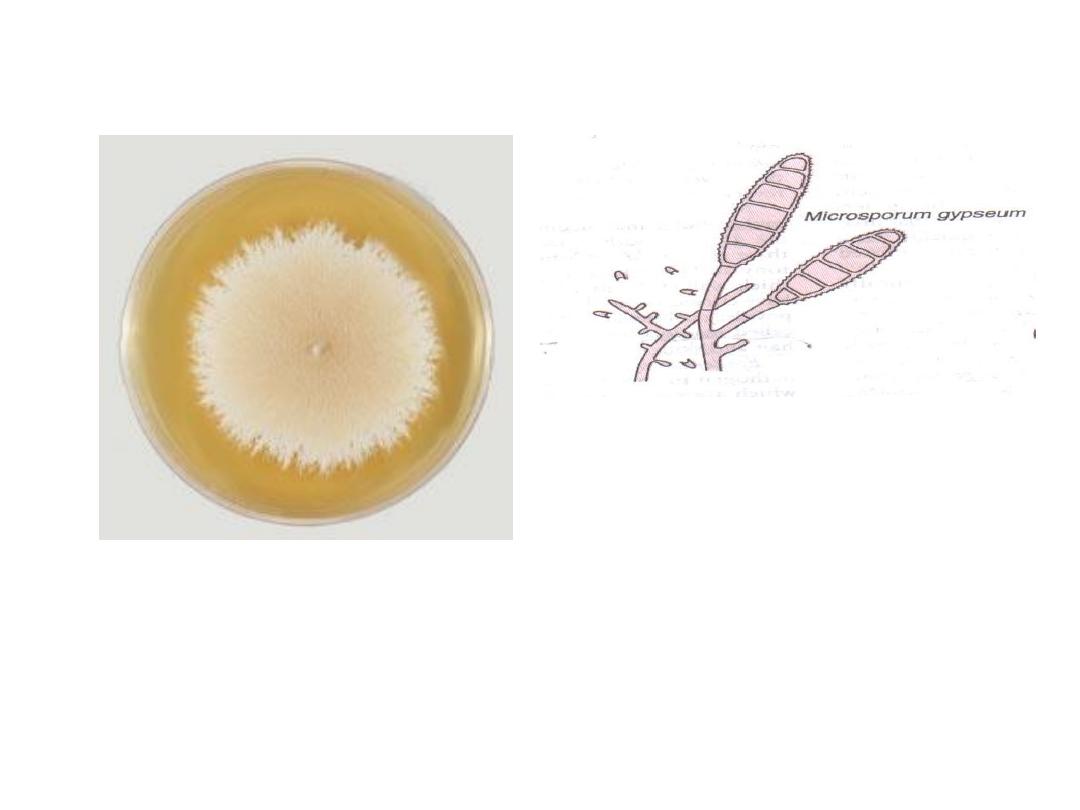
Microsporum gypseum
Conidia: are macroconidia
which are thin echinulate
walled, 4
– 6 cells
Colonies of the fungus are tan
powdery.
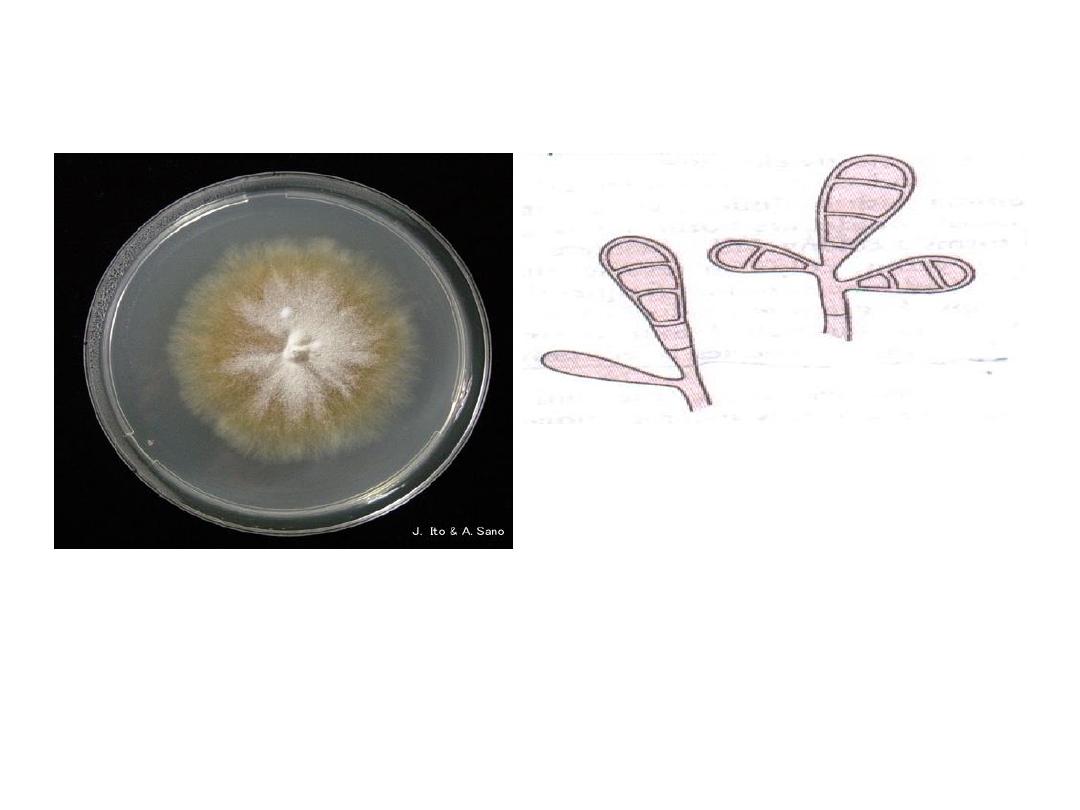
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes31
Epidermophyton
floccosum
Conidia: are macroconidia
which are smooth walled,
clavate, 2
– 4 cells, groups of
two or three
Colonies of the fungus are
flat, velvety with olive
green tinge.
4/30/2016
Dermatophytes32
• For skin infections: topical azoles
(miconazole, clotrimazole). They act by
inhibiting ergosterol synthesis.
• For hair infections: griseofulvin. It acts
by inhibiting the microtubule function in the
fungus.
Treatment
