Baghdad College of Medicine / 5
th
grade
Student’s Name :
SURGERY
LEC.6
Dr. Mahmood
Lec.3
Sub. Factors affect and
help bone healing
Wed.
5-10-2016
DONE BY : Mustafa Naser
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
2016 – 2017
Orthopedics (3)

Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
2
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
1-Proper contact and apposition of fr fragments.
2-Good local blood supply.
3-Adequate immobility or fixation of the fr.
4-Absence of infection.
5-Early and good management.
Diagnosis of fr
:
Clinical diagnosis;
A-There is history of injury or trauma.
B-Patient has pain.
C-Inability to move or use of the limb (loss of function).
By local examination :
1-Local tenderness.
2-Swelling by heamatoma or soft tissue edema.
3-Deformity, the limb may acquire an abnormal posture like abnormal angulation,
rotation... etc
4-Abnormal movements can occur at the fr site when it’s complete fr.
5-CREPITUS its characteristic of fr where an abnormal friction sound can be
elicited between the fr fragments when they are moved.
Radiological diagnosis;
o The fr line can be shown by a good x-ray exam. specially with application of the
role of two, the fr line can be seen and we can describe the fr site, shape and
displacement exactly.

Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
3
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
o problems of union:
o Sometimes bone healing is delayed and takes more than usual time here we
call it DELAYED UNION.
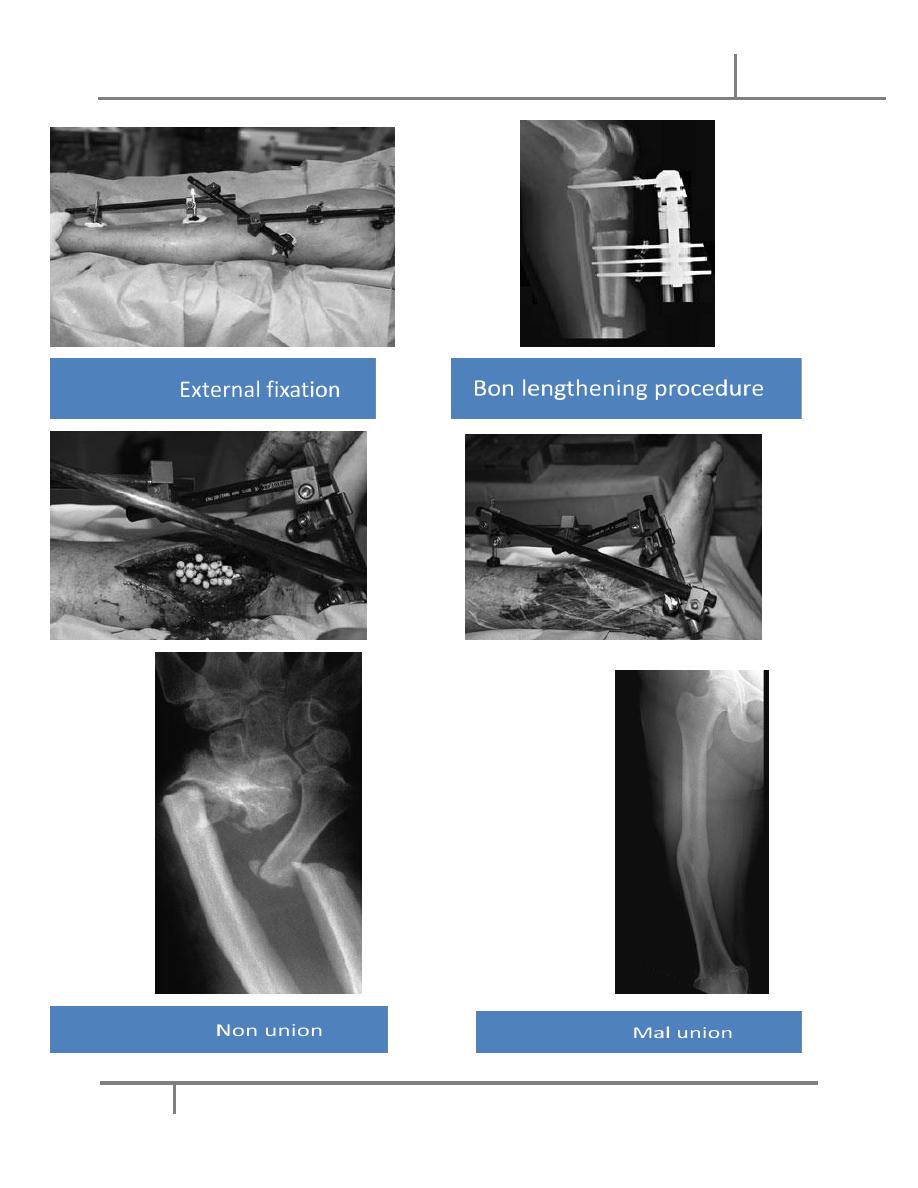
o Sometimes the fracture fail to unite and the problem is called NON-UNION, this
can be atrophic non-union where bone completely fail to form around the
fracture,
o or its called hypertrophic non-union where there is excessive large callus that
cannot pass
o through the fr line and bridge the fr fragments.
Causes of non-union can be
o Wide separation of fr fragments.
o Soft tissue interposition between the fragments.
o Poor local blood supply.
o Excessive movement of the fr fragments.
o Local infection as in compound fracture or after surgical operation.
o Continuous pull of the fragments by a muscle as in avulsion fr of patella
or olecranon.
o Delayed or poor management.
o In debilitated, elderly or sometimes chronically diseased patients.
Clinical symptoms and signs of non-union are nearly the same as for fractures
unless at later stages the gap is filled with fibrous tissue (fibrous union) and the
fracture area becomes painless with the presence of abnormal movements
(pseudoarthrosis = false joint).
Radiologically atrophic nonunion shows;
o Maintenance of the fr line.
o Resorbtion of the ft end that will show a rounded appearance rather
than the sharp fr ends.

Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
4
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
o Local sclerosis of the fr ends.
o Sometimes abnormal position or displacement of the fragments.
Hypertrophic non-union gives the radiological appearance of maintenance of the fr
line with extensive callus proximal and distal to it, also abnormal position of the
fragments may be seen. The appearance sometimes refereed to as elephant foot or
hours hoof appearance.
Sometimes bone unites in an abnormal position, this is called MAL-UNION, this can
lead to various deformities and functional impairments.
We must always think of possible associated injuries of the patient so we must
examine the patient as a whole and do the urgent resuscitation or treatment
before we think of the fracture.
The golden rule is TREAT THE PATIENT AND NOT SIMPLY THE PART.
The two main procedures in treating closed fr are:
a, reduction;
1. Closed reduction
by manipulation of the fr under anesthesia or sometimes analgesia; this
Aincludes:
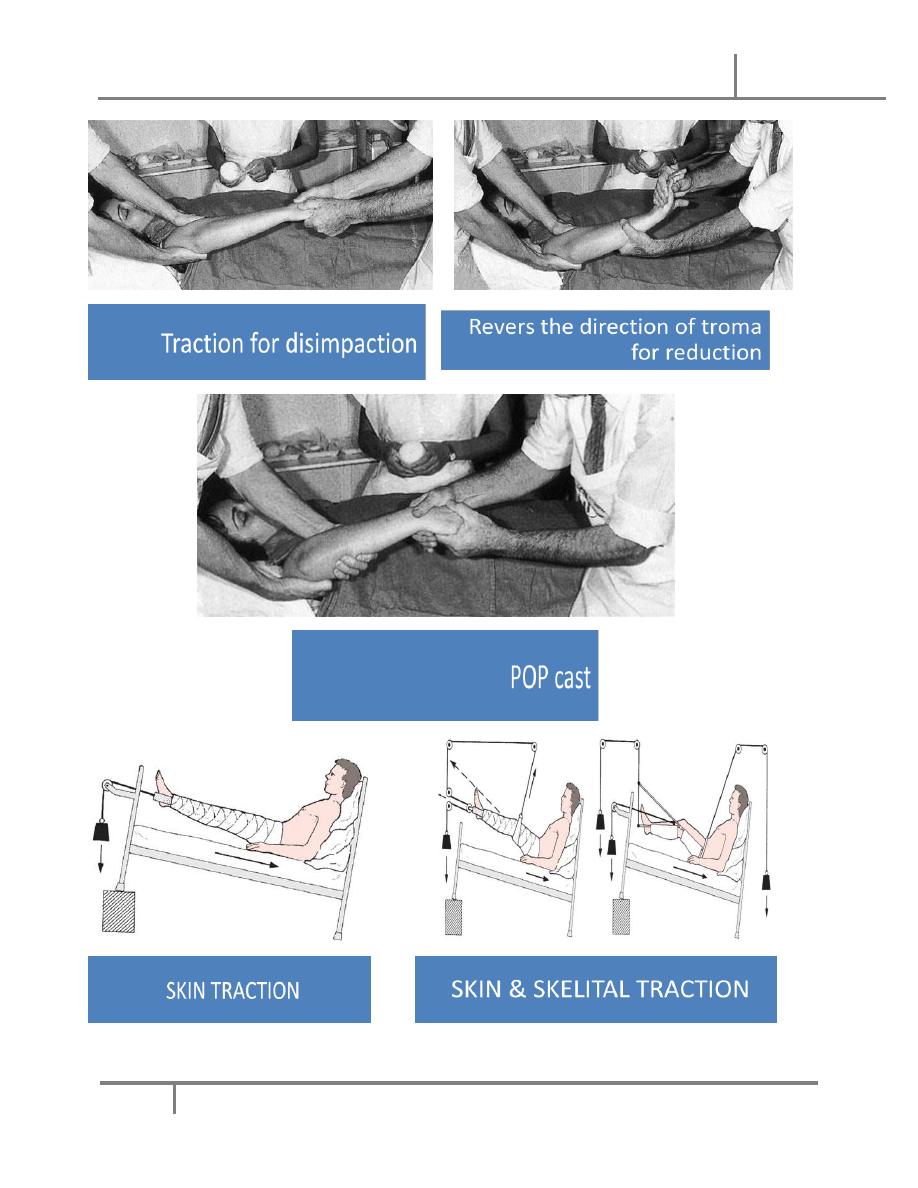
Traction of the fragments (always use a counter traction of the assistant)
to disimpact the fr.
Move the distal segment in a way to reverse the mechanism of injury so
that we can get proper realignment of the displaced fragments.

Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
5
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
2. open reduction
through surgical operation this is done in cases of failure of closed reduction or
in special occasions when closed reduction is not useful or not applicable, it’s
also preferred for intraarticular fr.
b. Hold the reduction in the proper position for a suitable period to allow
union; this can be achieved by variable ways:
1. Cast immobilization: by using the plaster of Paris (POP) where we try to
immobilize the reduced fr in position together with a proximal and a distal
joint., this takes longer time and cause stiffness of the involved joints. very
good choice in upper limb fracture s .
2. Maintained traction: this can be
askin traction
balanced traction.
skeletal tractions
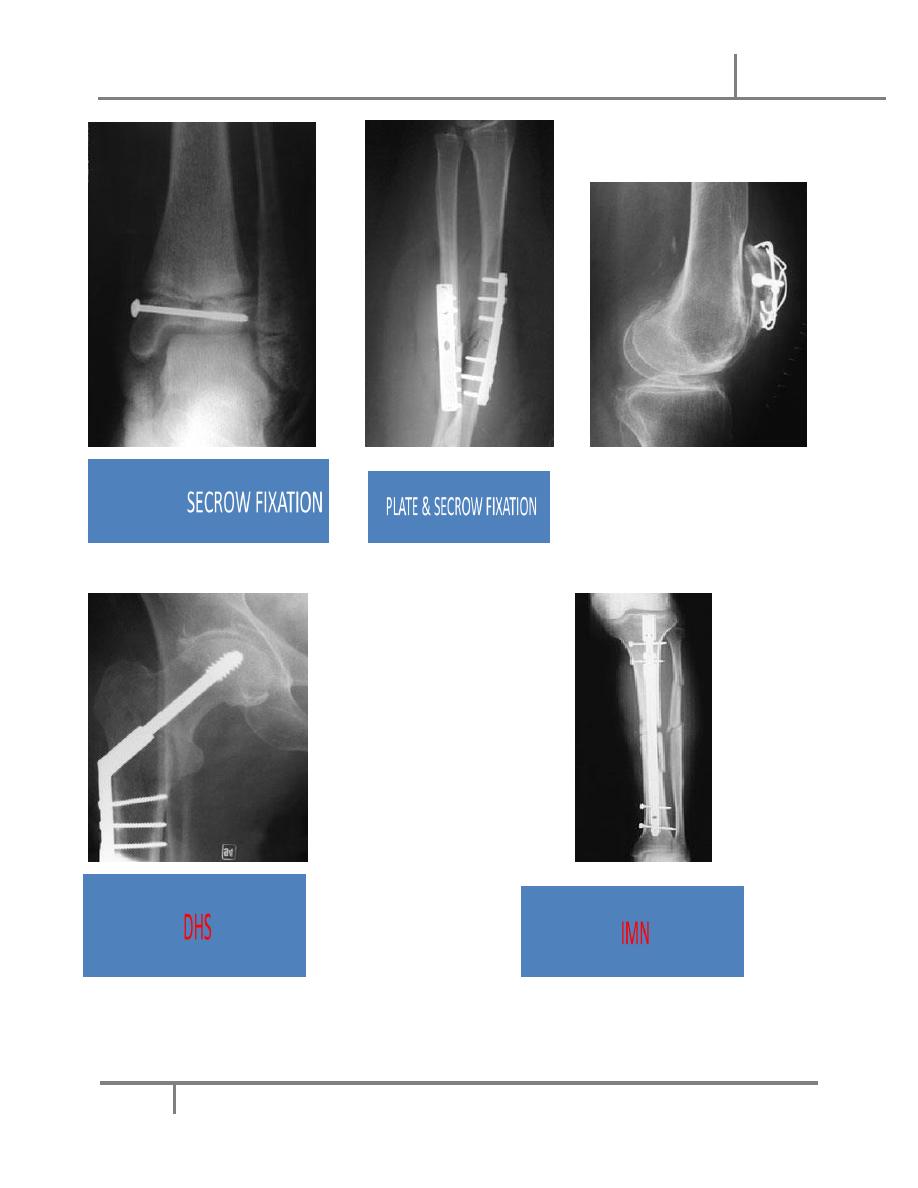
3. Interna1 fixation.
o Fractures that cannot be reduced only by operation.
o Failure of conservative treatment.
o Unstable fr that frequently redisplaces after closed reduction e.g. fr of
forearm or mid shaft of femur.
o Fr that poorly heals and takes long time to do so in conservative way e.g.
femoral neck fr.
o Pathological fractures.

Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
6
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
o Polytraumatized patient with multiple fr.
o Patients that have nursing difficulties as in elderly, paraplegics, chronically
diseased...etc
o Fr with vascular injury that needs surgical intervention.
5. External fixation: its usually used in compound fr it means that we use a
metal pins that pass through the skin from outside proximal and distal to the fr
and after proper reduction the pins are joined together outside the skin by
special long bars.
The indications of external fixation:
o Compound fractures.
o Infected fractures as after internal fixation.
o Multiple fractures, as an urgent way to stabilize a seriously ill patient.
o Fr with nerve or vessel injury.
o Fr with extensive soft tissue damage.
o Fr of pelvis.
o Seriously comminuted and unstable fr.
o For bone lengthening.
o For joint arthrodesis.
The treatment of closed fr always includes physiotherapy, exercises and
rehabilitation.
A. In multiple injured patients the basic priorities is to be followed; the
ABCDE
o Airway clearance.
o Breathing control.

Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
7
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
o Circulation and hemorrhage control.
o Disability—neurological status.
o Exposure of the whole body to assess injuries.
o All above done at the same time and a good multiple venous access secured
for patient resuscitation and replacement.
o System priorities we care to vital systems according to importance for life
according to this sequence:
o Head injury.
o Chest injury
o Abdominal and pelvic visceral injury.
o Skeletal injuries i.e. bonny fr and dislocation which can be multiple as well.
Those injuries can be closed or open.
B.For open fr the definitive treatment: includes first aids
and operation
first aid treatment
o Patient clothes are removed, limbs are washed and wounds are sterilized
and dressed.
o Temporary splintage (immobilization by splints) of fractured limbs
o At the same time SHOCK is treated and patient is resuscitated and replaced
with blood, fluids.. .etc to stabilize his general condition.
o Anti tetanus prophylaxis.
o Anti gas gangrene prophylaxis.
o Combined prophylactic antibiotic treatment until results of culture and
sensitivity show the specific antibiotics to be used.
o Prepare the patient for urgent anesthesia and surgery.
o Operation (wound excision or called debridemcnt)
o Patient must take general anesthesia.
o Tourniquet must be used when needed.

Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
8
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
o Skin must be prepared.. i.e, hair is shaved, skin around the wound is washed
very well, wound sterilization.
o The surgical procedure is called wound debridemcnt, which is the technique
that include exploration of the wound, excision of dead devitalized tissue,
and removal of foreign material.
o Open reduction of the fr and fixing the fracture with external fixator.
o starts from the skin down to the bone:
◦ Skin is excised few millimeters away from the wound until regular
healthy wound margin is gained.
◦ Deep fascia if dead is removed widely and extensively opened all
through the wound and beyond its limits as well.
◦ Foreign and dirty materials are carefully removed from the wound
and proper wound cleaning and sterilization is achieved.
o Muscles which are dead removed until healthy muscle is reached,
doubtful muscles are examined well, normal muscle looks pink while
dead muscle looks darker, healthy muscle have bleeding margin but
dead muscle does not bleed, and viable muscle contracts when
stimulated as by an artery or other tool during operation but it dose not
contract when dead
o Nerves and tendons are dealt with carefully, in the early treatment we
usually don’t do immediate repair, we try to clean and minimally cut the
dead damaged edges. We approximate the two ends by a black silk
suture that will act as marker in later explorations when we do
secondary suture or repair.
o The fractured bone is gently displaced and the bone ends are cleaned
with a curette and washed then we replace it back in normal position
and alignment (open reduction). Any small fragment that has a soft
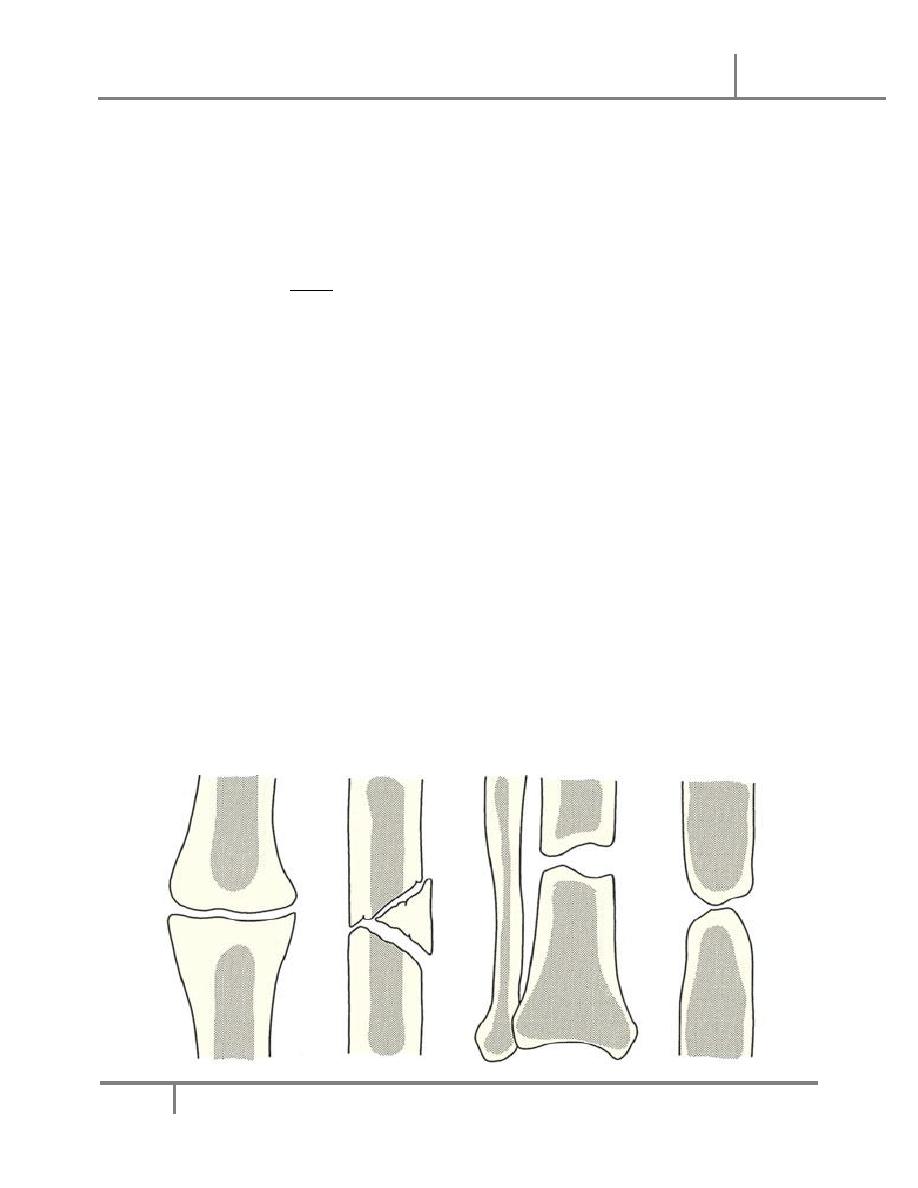
Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
9
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
tissue or periosteal attachment that ensures blood supply must be
preserved. Very small segments that are completely displaced and have
no attachment can be removed with precautions.
o Fractures then stabilized by external fixation until there is good skin
cover or until union.
o The wound must left open to avoid serious infections and other
complications.we use sterile packing and dressings.
o Wounds usually re-explored 5-7 days later and anther debridement is
done, this is repeated until we decide wound closure.
Wound closure varies according to the degree of primary skin damage and
loss.
o Sometimes we do delayed primary suture, or secondary suture, if the defect
is large it may need a graft that can be a simple skin graft or even a
combined fasciocutaneous, myocutaneous or other grafts all depends on
the degree of skin loss.
o Before, during and after surgery we should use specific antibiotics
according to frequent wound swab cultures; also we support the patient
general health and condition.
o Physiotherapy and muscle exercises with rehabilitation are all part of the
treatment.
Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
10
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
11
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
Factors affect bone healing Dr. Mahmood
5-10-2016
12
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
