Baghdad College of Medicine / 5
th
grade
Student’s Name :
SURGERY
LEC.8
Dr. Mahmood
Lec.4
Sub. Complications of
fractures
Sun. 9-10-2016
DONE BY : Mustafa Naser
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
2016 – 2017
Orthopedics (4)

Complications of fractures Dr. Mahmood
9-10-2016
2
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
— General complications
o Hemorrhage and shock.
o Fat embolism.
o Venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
o Crush syndrome.
o Complications of prolonged bed rest and recumbancy, especially in elderly and
aged patients. . e.g. DVT, bedsores, hydrostatic pneumonia and UTI.
—
— Local complications
Early
o Infection.
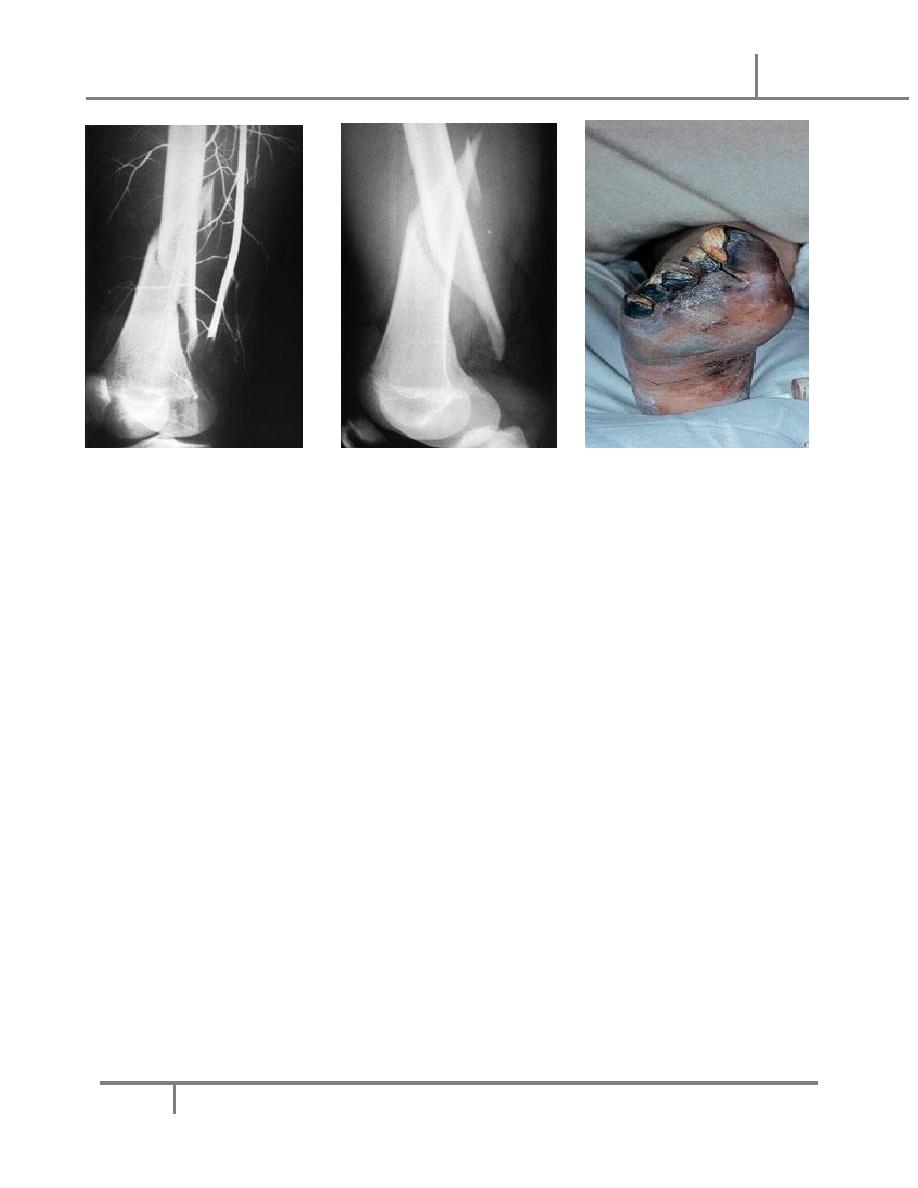
o Vascular injury.
o Nerve injury.
o Visceral injury.
o Heamarthrosis (bleeding inside a joint).
o Compartment syndrome.
Complications of fractures Dr. Mahmood
9-10-2016
3
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
Late local
o Delayed union and nonunion, those may need surgical treatment with Refreshment
of the bony ends, Re-reduction of the fr. Reinforcement by rigid internal fixation
and Replacement by bone graft (the four R principles).
o Mal-union, if its sever and affect function or show severe deformity it may need
surgery in form of Osteotomy at site of deformity, Reduction to normal position,
Internal fixation and sometimes Bone graft.
o Joint stiffness, this needs good physiotherapy and exercises and sometimes
manipulation or even surgical soft tissue release.
o Myositis ossificans around a joint or of the muscles which causes sever stiffness
and it’s difficult to treat.
o Algodystrofy or reflex sympathetic dystrophy where the limb get swollen and
painful with excessive loss of bone mass and functional disturbances, this usually
treated with physiotherapy and exercises with symptomatic treatment but still it can
be sever and very disturbing and difficult to treat.
o Avascular necrosis of nearby bony end or segment, this occurs in certain regions
where the blood supply of a bony end (usually inside a joint) is critical and

Complications of fractures Dr. Mahmood
9-10-2016
4
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
seriously affected by the fr. this leads to serious changes which may ends in
damage to nearby joint and serious functional deficit.
o
Osteoarthritis, it’s a degenerative joint disease associated with pain and limitation
of movement.
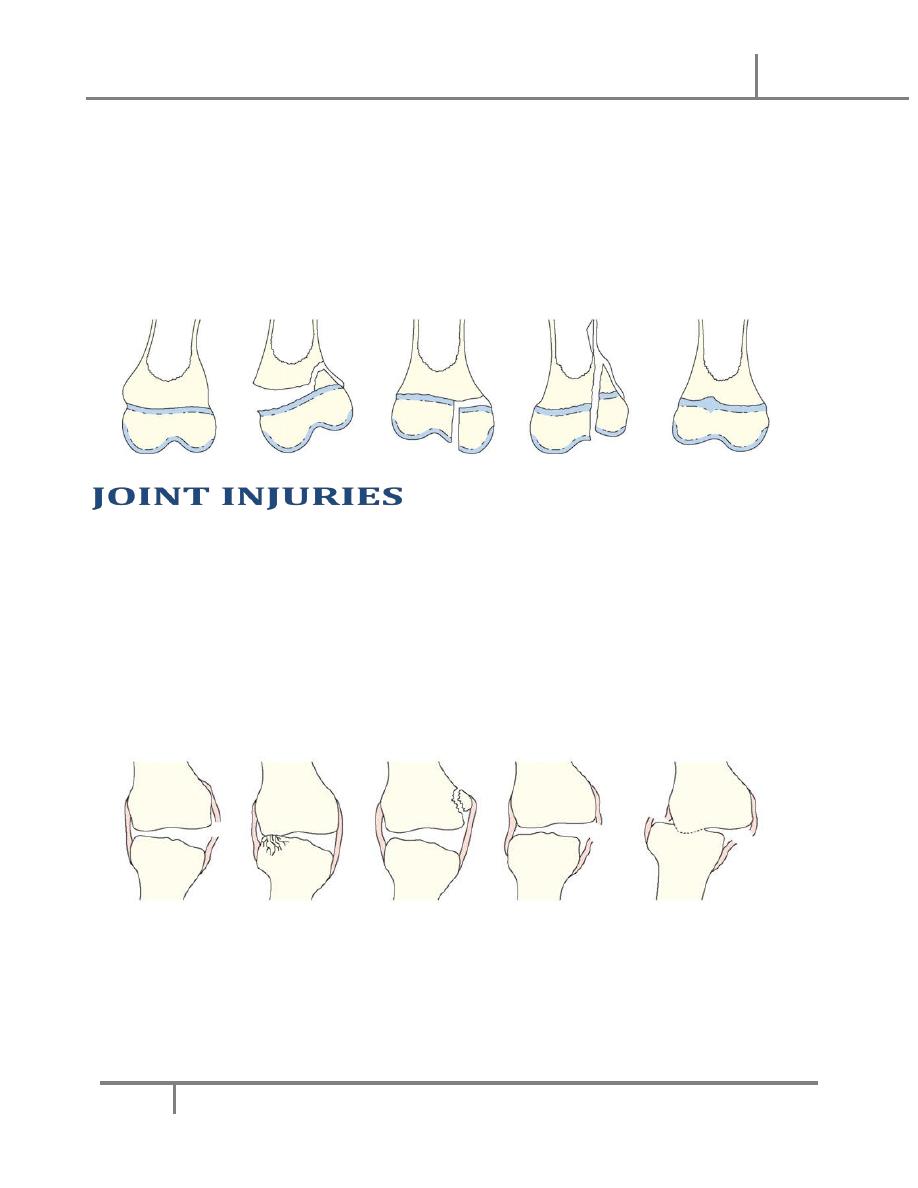
— 1.Green stick (incomplete) fractures:
— 2.Epiphysial inj
— SALTER-HARRIS classification into:
—
— Type1; the fracture pass through the Epiphysial plate only and there is no
displacement.
—
— Type 2; fr line pass through most of the epiphysis and cuts partly on the metaphysis
displacing the epiphysis and the attached small metapliyesial triangular segment.
—
— Type 3; partial epiphysial plate fracture that will continue through the epiphysis
separating epiphysial fragment.
—
— Type 4; the fracture line cuts through the epiphysis and the metaphysis separating
an epiphysial fragment with its opposed epiphysial plate and metaphysis.
—
— Type 5; its compression fr of the epiphysis that does not usually seen in x-ray. It
carries the worst prognosis, as it’s commonly lead to growth disturbances.
Complications of fractures Dr. Mahmood
9-10-2016
5
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
—
— Type 1 and 2 are commoner and carry good prognosis, while type 3 and 4 are less
common and carry poorer prognosis.
— OOOOOOOOO
— uries
o Joint dislocation: it’s the condition of complete displacement of articular surfaces.
o Joint subluxation: it’s the condition of incomplete (partial) displacement of
articular surfaces.
o medical emergency,
o MUA and rested for 2-3 weeks with pop

Complications of fractures Dr. Mahmood
9-10-2016
6
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
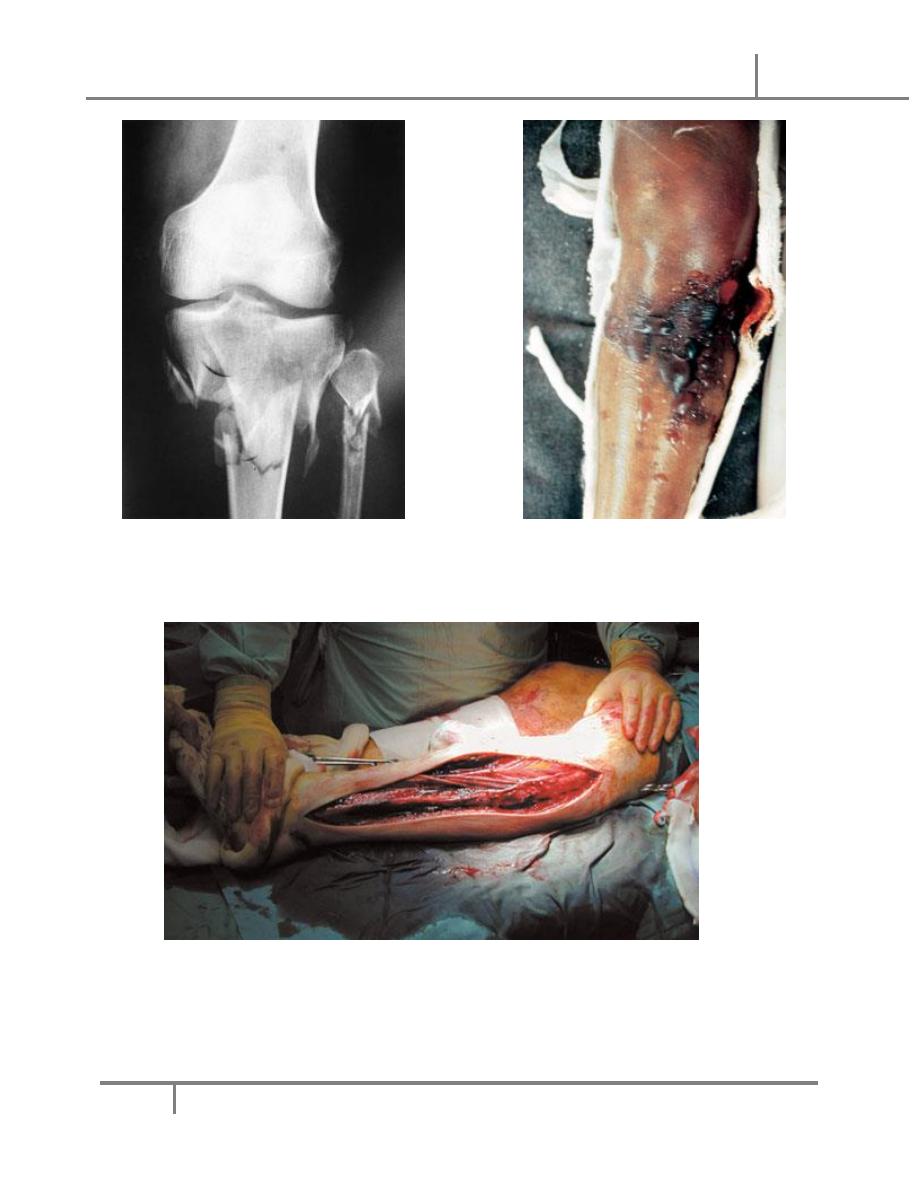
o increased soft tissue pressure within enclosed compartment that leads to failure
of capillary circulation causing tissue ischemia and damage.
o Enclosed compartment
o tight compartments
o The compartment syndrome is a serious condition because it leads to a VICIOUS
CIRCLE where tissue ischemia causes soft tissue swelling and as the swelling
occurs and increase in a closed compartment there further increase in local tissue
pressure until its more than local capillary pressure causing failure of capillary
circulation with hypoxia and lactic acidosis that cause further edema and further
increase in tissue pressure with further ischemia . . . and so on.
o
The ischemia will cause tissue death; the most sensitive tissues affected are
the nerves and the muscles that will die. After control of the compartment syndrome
the nerves can regenerate and regain some or all of its function but not the muscles
that after ischemia and death will heal with fibrous tissue that will contracts later
giving a chronically deformed limb with serious functional impairment (the
Volkman’s contracture
(
Clinical features:
o There are FIVE cardinal clinical features of ischemia are the FIVE Ps:
o Painful limb (pain is much greater than expected from the injury itself despite good
management) or sometimes the limb is tender to stretch because of tender muscles.

Complications of fractures Dr. Mahmood
9-10-2016
7
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
o Pale or plum colored skin, sometimes its cyanosed skin.
o Parasthesia due to disturbed nerve function.
o Paralysis or weakness due to muscle ischemia.
o Pulseless limb, only at late stage after serious pressure increase with impairment
of major vessel circulation, PRESENCE OF PULSE DOES NOT EXCLUDE
COMPARTMENT SYNDROME, it’s a crime to wait until the pulse is absent.
Diagnosis
must be made at earlier stages, and it’s not important to have all the signs
and a symptom to say there is a compartment syndrome. For example we must keep it
in mind after any possible cause of compartment syndrome and frequently look for it,
as limb is in sever unexpected pain with local muscle tenderness on stretch or if skin
gets pale or dusky we must check for compartment syndrome and this is done very
simply by measuring the local tissue pressure and if its more than 40mm Hg it means
there is compartment syndrome that needs management, sometimes we do continues
tissue pressure monitoring for expected compartments
Management of compartment syndrome:
o The primary cause must be removed if possible e.g. removal of tight POP cast,
bandages or dressings. Control of main vessel insufficiency, and measure the
pressure. If it’s present and there is no relief THE CLOSED COMPARTMENT
MUST BE OPENED by surgical FASCIOTOMY by opening of the tight deep fasciae
all over the closed compartment to decrease the local pressure and break the circle of
progressive tissue death and improve capillary circulation.
o Fascitomy is an urgent simple surgical procedure that can save a limb from serious
consequences as deformity and functional losses.
Complications of fractures Dr. Mahmood
9-10-2016
8
@Mustafa Naser 2016-2017
Done By: Mustafa Naser …
