1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Orthopedic
Lec
د.هشام القطان
16/10/2015
Upper limbs 4
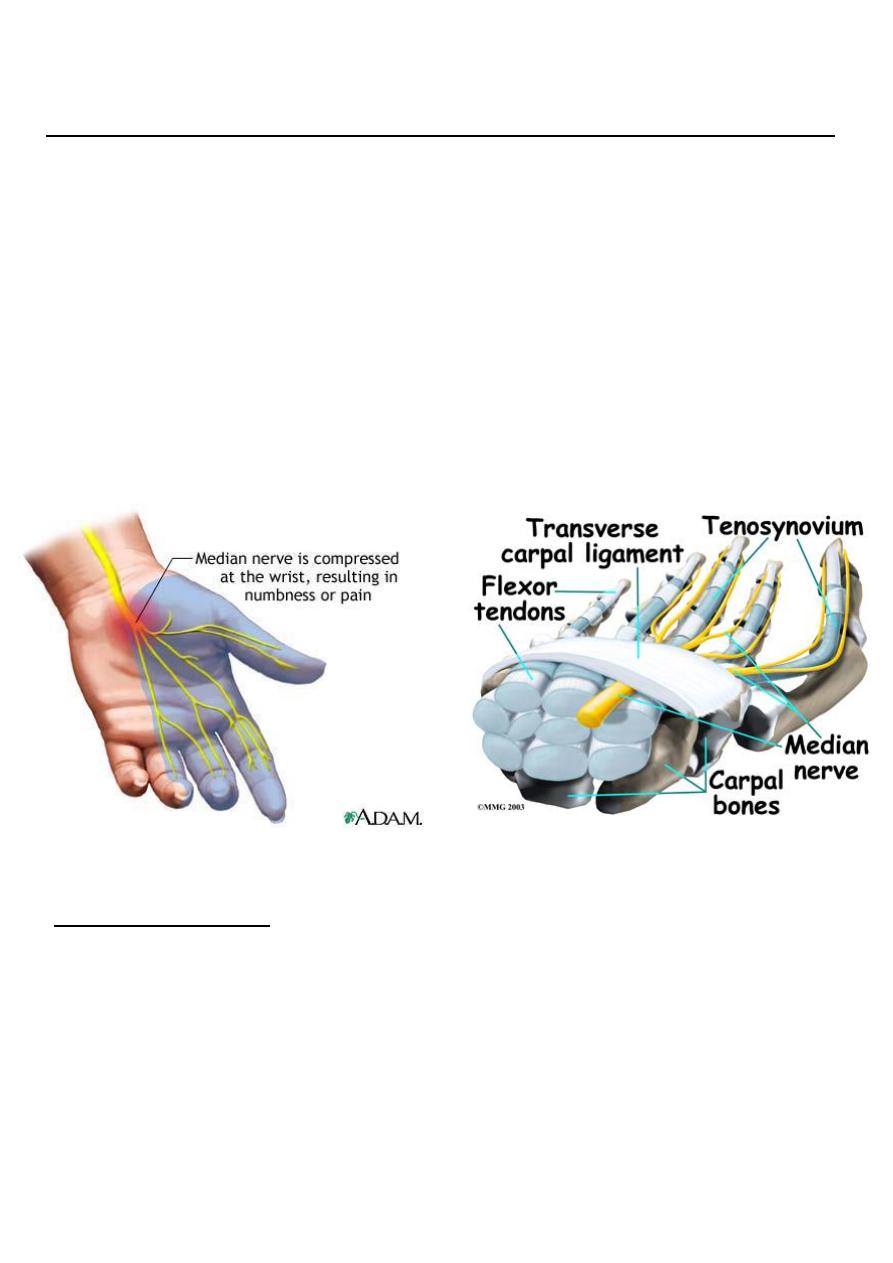
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
This is the commonest and best known of all the nerve entrapment syndromes.
In the normal carpal tunnel there is barely room for all the tendons and the median
nerve .
Any swelling is likely result in compression and ischaemia of the nerve.
Common in women at the menopause, in rheumatoid arthritis, in pregnancy and in
myxoedema.
Clinical features
The usual age group is 40-50 years
The history is most helpful in making the diagnosis.
Pain and paraesthesia occur in the distribution of the median nerve in the hand.
Night after night the patient is woken with burning.
Patients tend to seek relief by hanging the arm over the side of the bed or shaking the
arm.
2
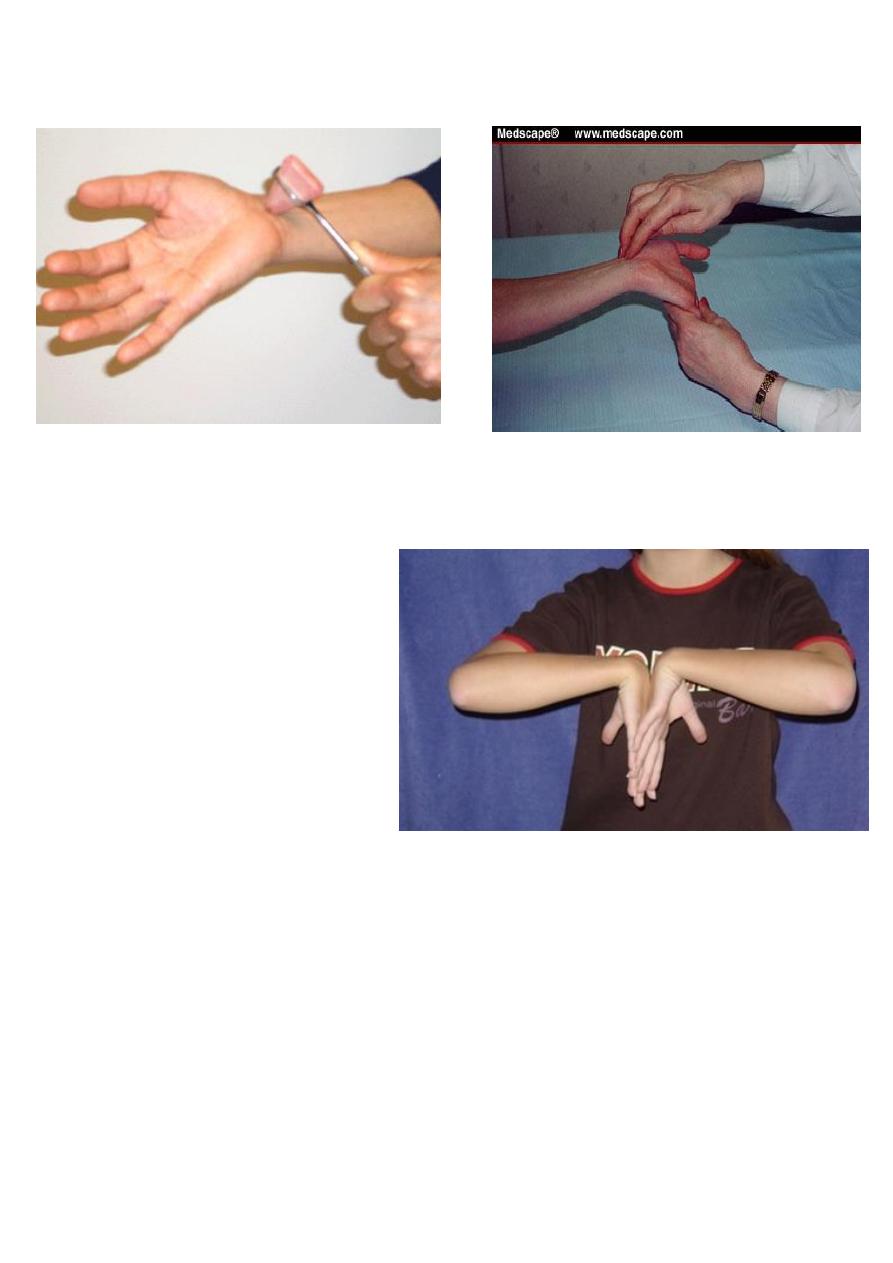
helpful test (Tinels sign) : sensory symptoms can often be reproduced by percussing
over the median nerve.
Phalens test:
Holding the wrist fully
flexed for a minute or two .
In late cases there is wasting of the thenar muscles.
weakness of thumb abduction and sensory dulling in the median nerve territory.
Electrodiagnostic tests. which show slowing of nerve conduction across the wrist.

3
Treatment
Light splints that prevent wrist flexion can help those with night pain or with
pregnancy-related symptoms.
Steroid injection into the carpal canal, likewise, provides temporary relief .
Endoscopic carpal tunnel release offers an alternative with slightly quicker
postoperative rehabilitation.
Open surgical division of the transverse carpal ligament usually provides a quick and
simple cure.
Alternative therapies. Acupuncture . have benefited some patients but their
effectiveness remains unproved.
Hand
Acute Infection of the hand :
Infection of The hand is frequently limited or one of several well-defined compartments:
Nail fold (paronychia).
The pulp space (whitlow).
Subcutaneous tissues elsewhere.
A tendon sheath.
One of the deep fascial spaces or a joint.
Almost invariably the cause is a Staphylococcus which has been implanted by trivial or
unobserved injury
.
Pathology
Acute inflammation and suppuration in small closed compartments (e.g. The pulp
space or tendon sheath) may cause an increase in pressure to levels at which the local
blood supply is threatened.
In neglected cases tissue necrosis is an immanent risk.
Even if this does not occur, the patient may end up with a stiff and useless hand
unless the infection is rapidly control.

4
Clinical features
Usually there is a history of trauma, but it may have been so trivial as to pass
unnoticed.
A thorn prick can be as dangerous as a cut Within a day or two, the finger (or
hand) becomes painful and swollen.
The patient may feel ill.
feverish and the pain becomes throbbing.
obvious redness and tension in the tissues.
exquisite tenderness over the site of infection.
Finger movements may be markedly restricted.
Principles of treatment :
Antibiotics
As soon as the diagnosis is made and specimens have been taken for microbiological
investigation, antibiotic treatment is started - usually with
flucloxacillin and, in severe cases, with fusidic acid
or a cephalosporin as well.
This may later be changed when bacterial
sensitivity is known
-_-
Rest and elevation
In a mild case the hand is rested in a sling.
In a severe case the arm is elevated in a roller towel.
while the patient is kept in hospital under observation.
Analgesics are given for pain.
Drainage
If there are signs of an abscess (throbbing pain, marked tenderness and toxaemia). the
pus should drained.
A tourniquet and either general or regional block anaesthesia are essential.
5
The incision should be made at the site of maximal tenderness, but never across a
skin crease.
Necrotic tissue is excised and the area thoroughly washed and cleansed.
The wound is either
left open
or lightly sutured and then covered with non-stick
dressings.
A pus specimen is sent for microbiological investigation.
Splintage
splint should be applied always with the joints in the position of safe.
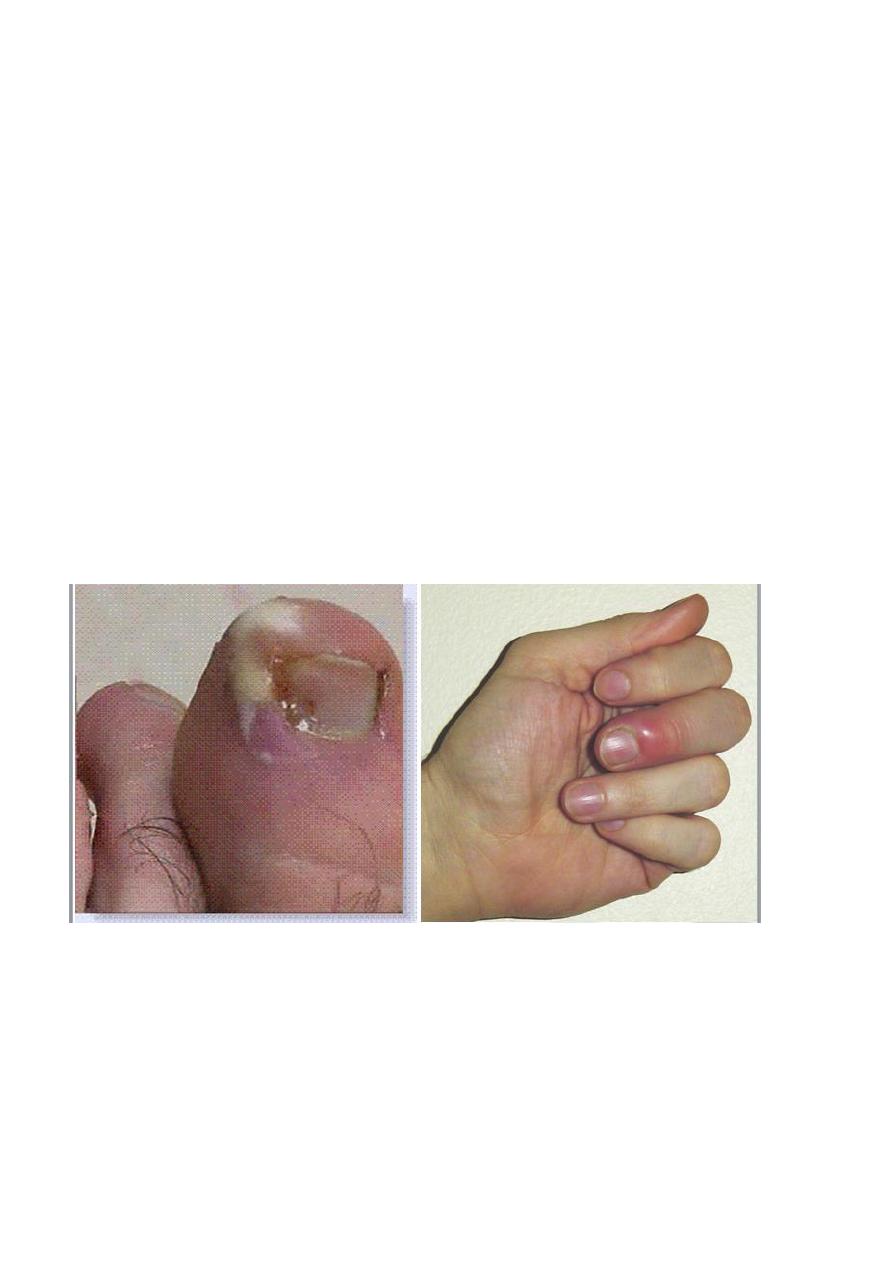
Specific types of Infections
- Paronychia
6
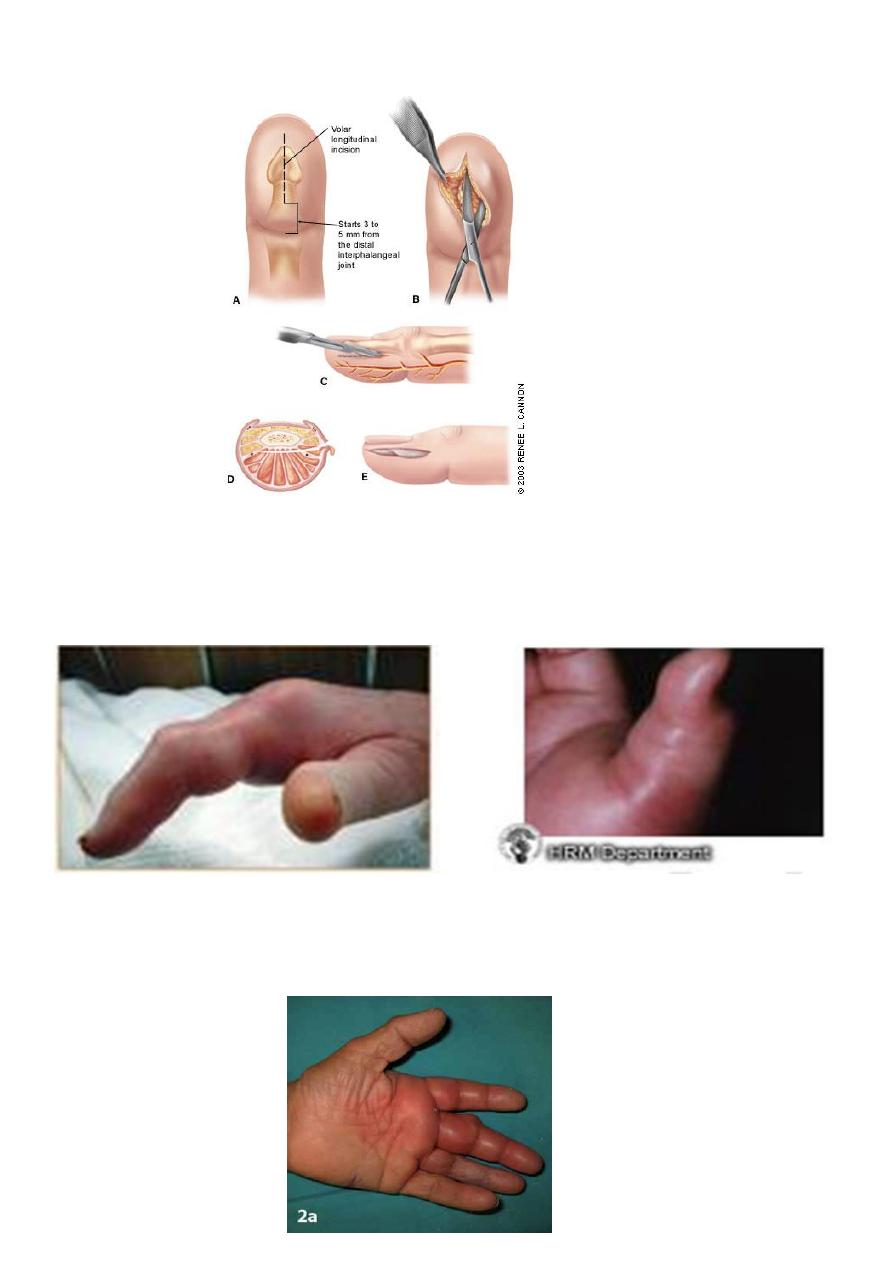
- Pulp-space infection (felon)
- Tendon-sheath infection
- Deep fascial space infection
7
- Human bites
M . O .
o (including anaerobes) are encountered,
o the commonest being Staphylococcus aureus,
o Streptococcus group .
such wounds should be assumed to be infected.
So … NO biting !
Treatment
Surgery to clean the infected tissue.
Antibiotic .
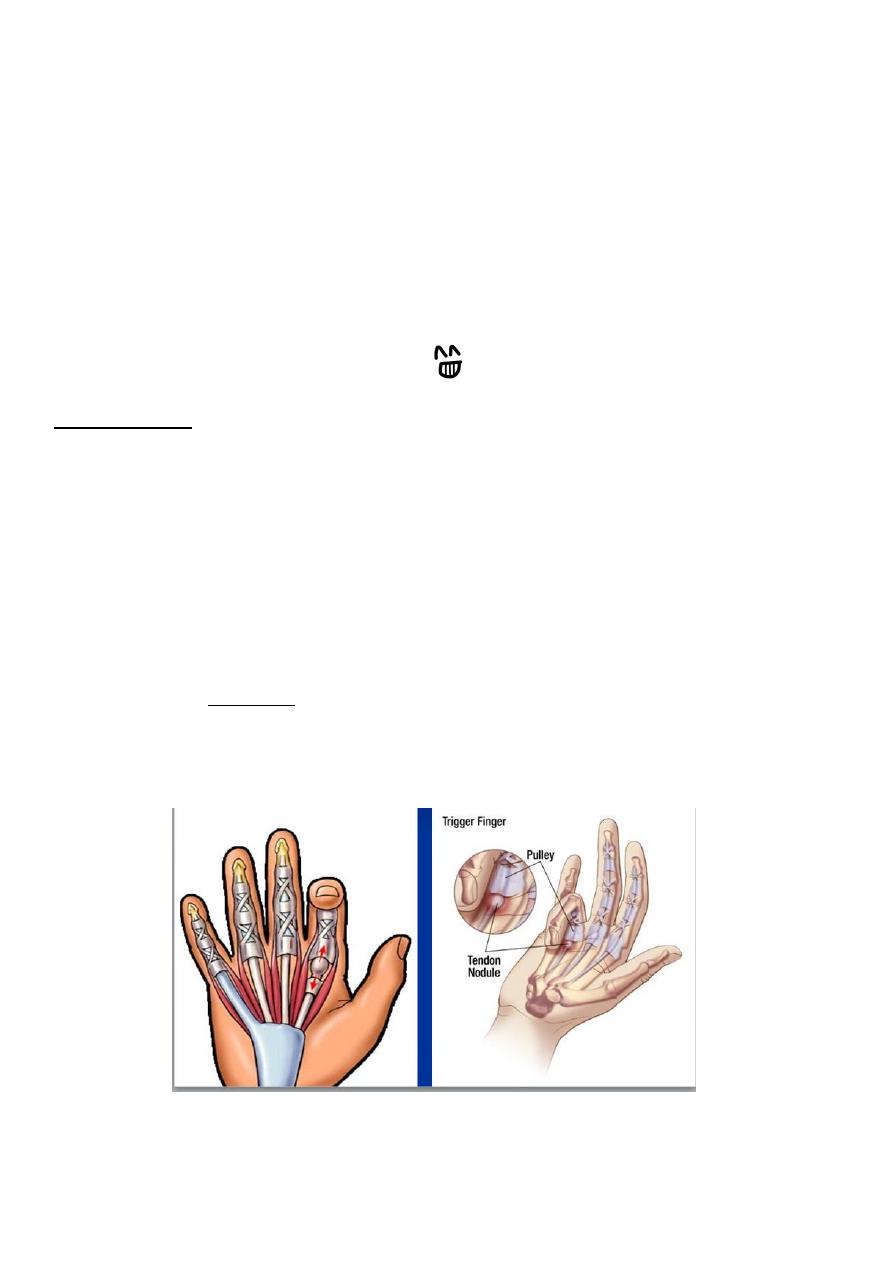
TRIGGER FINGER
Intermittent 'deformity'. usually of the ring or middle finger.
The patient complains that, when the hand is clenched and then opened, the finger (or
thumb) gets stuck in flexion; with a little more effort, it suddenly snaps into fulI
extension

8
Causes are :
1. thickening of the fibrous tendon sheath
2. similar entrapment may occur due to a bulky
Tenosynovitis.
Treatment
Either healed spontaneously.
Local injection steroid
surgery
DUPUYTREN'S CONTRACTURE
This is a nodular hypertrophy and contracture of the
palmar aponeurosis.
The patient - usually a middle-aged man complains of
a nodular thickening in the palm.
If the subcutaneous cords extend into the fingers, they
may produce flexion deformities at the MP and PIP
joints.
Operation is indicated if the deformity is progressive and interferes with function.
DONE
