
Session -3-
Dr-emad
Thyroid gland
Which is common goiter or CA thyroid?
-
Goitre.
Is it important to ask about age in thyroid diseases?
-
yes,as thyroid diseases mostly affect young female pts.
Classification of thyroid disorders
1) Multinodular .
2) Solitary.
3) diffuse.
Approach to pt with thyroid problem
:
C.c:-
Most common
swelling in the neck.
-Pain.
-Dysphagia / dyspnea(pressure symptoms).
-Hoarseness of voice .

if
painful
either
Hemorrhage in a nodular goiter/Riedel's
thyroiditis/Hashimoto's thyroiditis/anaplastic CA.
Review of system
CVS:-
palpitation , dyspnea.
GIT:-
diarrhea.
CNS:-
agitation,nervousness,insomnia,lethargy,fatigue.
Endocrine:-
heat intolerance"preference of cold weather in
hyperthyroidism " ,excessive sweating.
Gynecological :-
menstrual Hx"amenorrhea in
hyperthyroidism,amenorrhegia in hypothyroidism".
Medical Hx:-
HTN, D.M"any other autoimmune diseases".
Drug Hx:-
amiodarone,anithyroid drugs,estrogens, propanolol.
Family Hx:-
hx of thyroid diseases in the family/CA thyroid
**any familial thyroid diseasesthink of "medullary CA".
Social Hx:-
iodine salts in the food/cabbages/smoking"increase the
chance of CA".
Examination
inspection :

1.
any swelling in the neck.
2.Ask the pt to swallow sip of water , look for movement with
swallowing.
3.Ask the pt to protrude the tongue
for thyroglossal cyst.
Palpation :
1)size.
2)position.
3)surface.
4)attachment.
5)tenderness
6)warmth.
7)skin over it.
8)compressible(DDx:
hemangioma).
9)thrill.
10)consistency.
11)edge"lower border of the swelling can get above it or not?
"
retrosternal goiter.
12)L.N palpation .
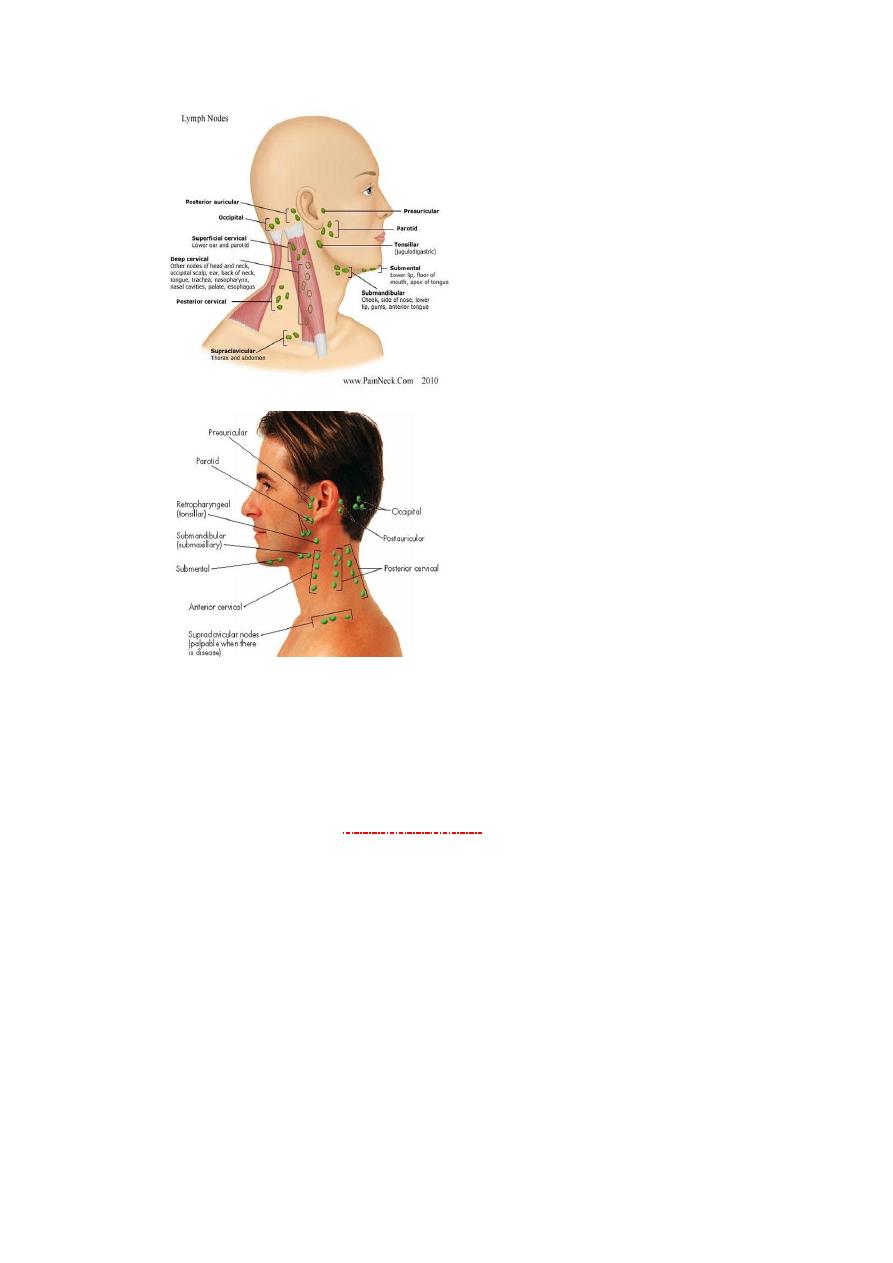
13) pulsation of carotid artery:avoid testing both arteries vasovagal
faint.
Impalpable carotid pulse occurs in :-CA thyroid extending to
carotid sheath
(( berry's sign )).
Percussion :
over the sternum for dullness in retrosternal goiter.
What tests you can do for retrosternal goiter?
1.by palpation the edge of the swelling "lower border" can get
above it or NOT.
2.percussion : dullness over the sternum.

3.pemberton sign:-flushing of the face when the pt holds his arms
slowly upward ,because of thoracic inlet obstruction "pressure" ….
(Do this test with precaution).
Auscultation :-
Auscultate for
bruit sites of auscultation :-
-
over upper fold of thyroid
-
over the sac of mass.
Eyes examination :signs of eyes in thyoid disease
1)exophthalmos .
2)chemosis
3)ophthalmoplegia"double vision".
4)lid lag.
5)lid retraction.

Investigations :
1-CBC.
2-X ray.
What we can see in xray ?
a.
retrosternal goiter.
b.
calcification "in
papillary CA & thyroiditis
".
c.
vertebrae (metastatic signs) +OA changes
مثال بالعملية نتجنب
hyperextension of neck or the anaesthesia.
3-TSH,T3,T4.
4-US
cystic or hard lump, L.N ??
5-FNA
cytology (type of CA).
6-Radioisotope scan :
(hot or cold,warm) hot :-
is active , reptake is
occurring, toxic nodule, mostly benign.
cold :-
less reuptake ,mostly malignant .
warm:-
same reuptake with excretion.
7- laryngoscope :
performed preoperatively in pt with hoarseness of
voice or to know if the pt has hoarseness of voice before op or post op.
Rx :- by surgery
Incision :- collar incision :"2"cm above sternal notch:transverse incision.
Types of surgery
1.
total thyroidectomy
2.
subtotal thyroidectomy: we leave 4gm from the lobe.
3.
lobectomy+isthemectomy.
*if solitary nodule
aspiration&surgery.
Anti thyroid drugs
propylthiouracil+carbimazole.
Complications :-
1.hematoma.
2.stridor(due to laryngeal edema or long standing goiter causes
tracheomalacia).
3.R.L.N palsy.
4.wound infection.
5.hypothyroidism
6.parathyroid insufficiency
hypocalcemia
.
7.keloid scar.
Thyroid carcinoma
Classifications :
i.
papillary
most common neoplasm,Hx of radiation exposure is
present.

ii.
Follicular.
iii.
Anaplastic
painful /adult person/treated as palliative RX.
iv.
Medullary
familial CA,part of MEN(multiple endocrine
neoplasm).
Typical complaint :-
wt loss & decrease appetite/bone pain may
present.
Hx of malignancy, metastasis from
bone,GI,brain,liver"jaundice",lung"cough&hemoptysis".
Impalpable carotid pulse is indicator for CA thyroid.
