Drug interaction: one dug interact or interfere with the action
of another drug e.g. :
Anti-acid with oral tetracycline the action of tetracycline
due to delay the absorption of tetracycline into the blood
stream.
The drug drug interaction can produce effects called:
1. Addition (additive effect): 1+1=2
2. Summation: 1+1=3
3. Potentiation(synergistic): 1+1=4
4. Antagonism: 1+1=5
Additive effect: combine of two drugs is equal to the summation
e.g.: propoxyphene + aspirin = added analgesic effect.
Synergistic: combine of two drugs is greater than the
summation e.g.: codeine + aspirin = greater analgesic effect.
Antagonistic effect: one drug interfere with the action of
another drug the result is decrease the effect of another drug
e.g.: tetracycline + anti-acid = the absorption of tetracycline.

Drug food interaction: interact of the food with drugs e.g.:
tetracycline + dairy products.
Notes:
Some drug take on empty stomach, it’s absorbed more
quickly into blood stream than be taking with food, and it’s
benefit than giving it with food due to it gives an optimal
effect e.g.: captopril.
Drugs that should take with an empty stomach are took (1 or
2) hours before meal.
Drugs that cause irritation to stomach and cause epigastric
distress (nausea, vomiting), the best way is give them with
food to decrease the gastric distress e.g. : NSAIDs, salicylate.
NSAID: non steroidal anti inflammatory drug.
Other drugs like tetracycline combine with food like milk
(dairy products) the dug will be unabsorbable, or no
pharmacological effects and the result will be toxic and cause
therapeutic failure.
Factors effect on the movement of the drugs in the body:
1. Size of drug.
2. Lipids.
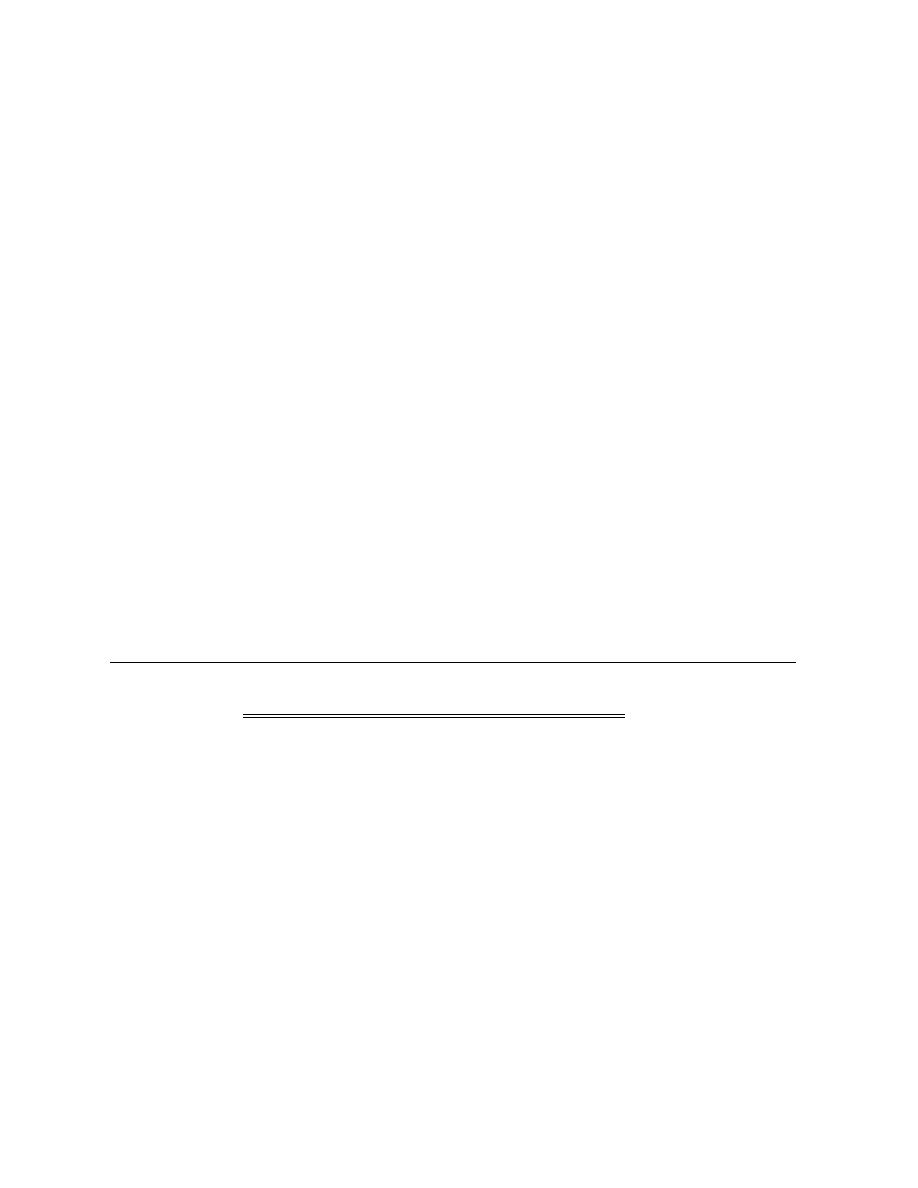
3. Degree of ionization: a)Aspirin = 3.5pka
b)Ascorbic acid = 11.5pka
c)Diazepam = 3pka
d)Atropine = 10pka
Factors effect on drug absorption:
1. Drug solubility.
2. Root of drug administration.
3. States of G.I.T.
4. Variation of species.
5. Drug interaction.
6. Blood circulation.
C.N.S. pharmacology
Receptors: 1. Muscarinic (smooth m.), nicotinic (skeletal m.)
(Parasympathetic).
2.
α
1
(blood)
,
α
2
(C.N.S.)
,
β
1
(heart)
,
β
2
(bronchus)
(Sympathetic).
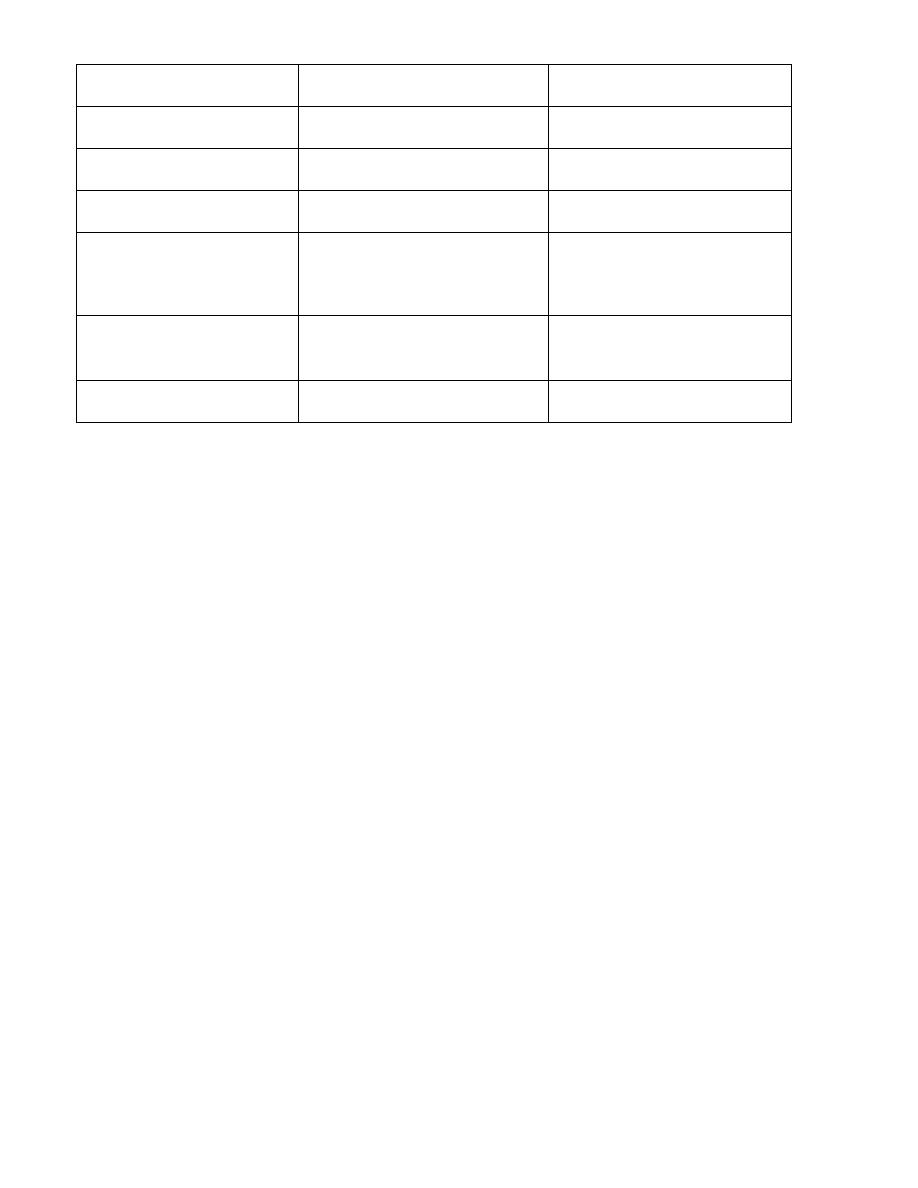
Effector organ
Cholinergic effect
Adrenergic effect
Eye
Constriction of pupil of eye Dilitation of pupil of eye
Heart
Decrease heart rate Increase heart rate
Bronchus
Bronchoconstriction Bronchodilitation
Increase secretion &
motility of G.I.T.
Decrease secretion
& motility of G.I.T.
Smooth muscle
Constriction of smooth m.
of urinary bladder
Dilitation of smooth m. of
urinary bladder
Salivary gland
Increase secretion Decrease secretion
Cholinergic agonist:
1. Directly: acetylcholine, carbachol, pilocarpine.
2. Indirectly: neostigmine, physostigmine, edrophonium,
pyridostigmine, distigmine.
Acetylcholine: neurotransmitter of parasympathetic &
cholinergic nerves, therapeutically it’s not important because
it’s rapid inactivation by an enzyme called (acetylcholine
esterase), and it’s not stabile in lab and room temperature.
Carbacol: neuromuscular purgative (make diarrhea), &
decrease intraocular pressure.
G.I.T.

Pilocarpine: drug of choice for glyoma for emergency cases it
decreases intraocular pressure.
Physostigmin: for glycoma ( pilocarpine is more effect),
increases G.I.T. motility and bladder.
Neostigmine: increases G.I.T. motility and bladder,
myasthenigravis.
Edrophonium: like neostigmine, short duration action (10-20)
minutes.
Pyridostigmine: like edrophonium.
Distigmine: myasthenigravis, urinary retention.
