Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 1
Digital Image
Processing
4th Class –IT Department
(2014-2015)-(Part I)
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 2
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
Digital image processing deals with manipulation of digital images through
a digital computer. It is a subfield of signals and systems but focus
particularly on images. DIP focuses on developing a computer system that is
able to perform processing on an image. The input of that system is a digital
image and the system process that image using efficient algorithms, and
gives an image as an output. The most common example is Adobe
Photoshop. It is one of the widely used applications for processing digital
images.
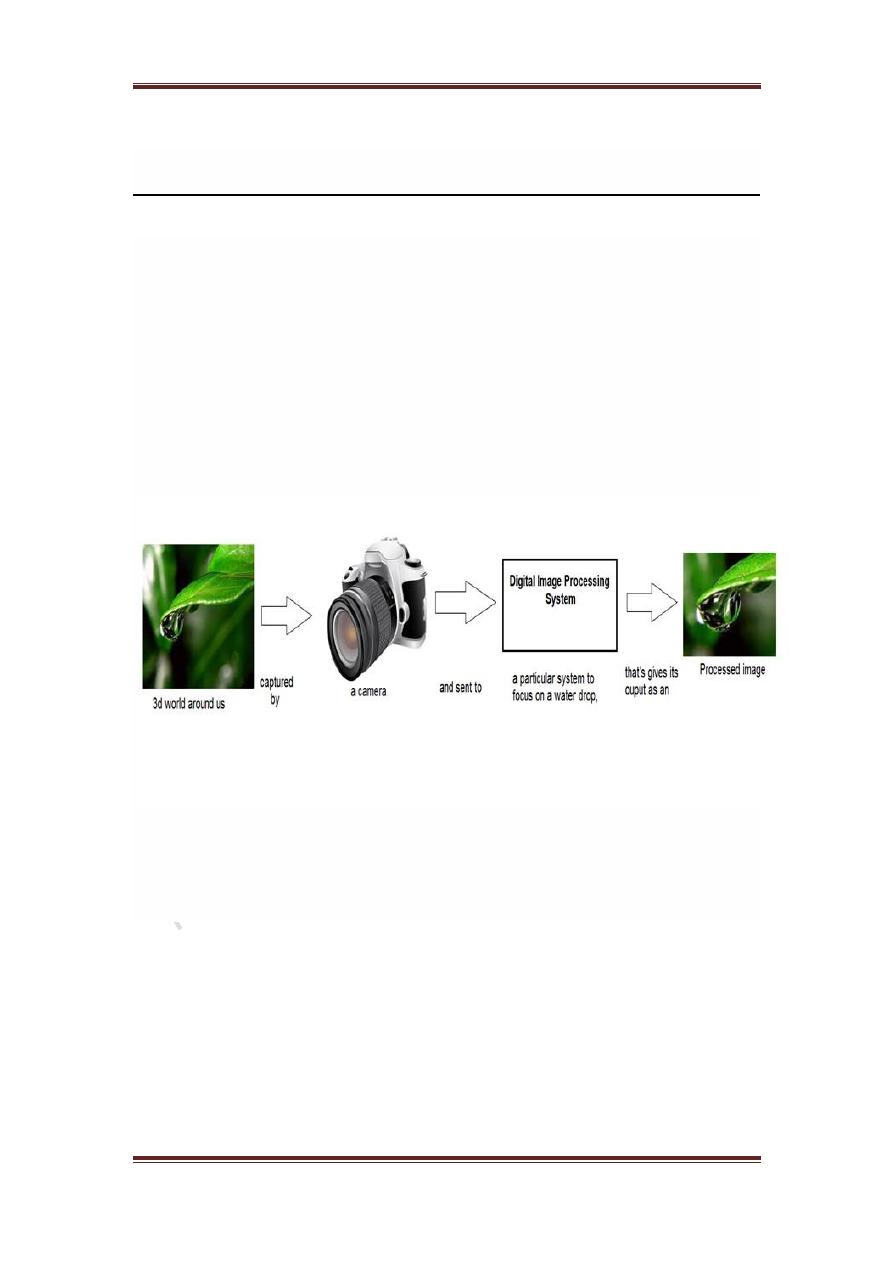
How it works.
In the above figure , an image has been captured by a camera and has been
sent to a digital system to remove all the other details , and just focus on the
water drop by zooming it in such a way that the quality of the image remains
the same

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 3
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
INTRODUCTION
Introduction
Signal processing is a discipline in electrical engineering and in
mathematics that deals with analysis and processing of analog and digital
signals , and deals with storing , filtering , and other operations on signals.
These signals include transmission signals , sound or voice signals , image
signals , and other signals e.t.c.
Out of all these signals , the field that deals with the type of signals for
which the input is an image and the output is also an image is done in image
processing. As it name suggests, it deals with the processing on images.
It can be further divided into analog image processing and digital image
processing.
Analog image processing
Analog image processing is done on analog signals. It includes processing
on two dimensional analog signals. In this type of processing, the images are
manipulated by electrical means by varying the electrical signal. The
common example include is the television image.
Digital image processing has dominated over analog image processing with
the passage of time due its wider range of applications.
Digital image processing
The digital image processing deals with developing a digital system that
performs operations on an digital image.
What is an Image
An image is nothing more than a two dimensional signal. It is defined by the
mathematical function f
x,y
where x and y are the two co-ordinates
horizontally and vertically.
The value of f
x,y
at any point is gives the pixel value at that point of an
image.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 4
The above figure is an example of digital image that you are now viewing
on your computer screen. But actually , this image is nothing but a two
dimensional array of numbers ranging between 0 and 255.
128
30
123
232
123
221
123
77
89
80
255
255
Each number represents the value of the function f
x,y
at any point. In this
case the value 128 , 230 ,123 each represents an individual pixel value. The
dimensions of the picture is actually the dimensions of this two dimensional
array.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 5
Relationship between a digital image and a signal
If the image is a two dimensional array then what does it have to do with a
signal? In order to understand that , We need to first understand what is a
signal?
Signal
In physical world, any quantity measurable through time over space or any
higher dimension can be taken as a signal. A signal is a mathematical
function, and it conveys some information. A signal can be one dimensional
or two dimensional or higher dimensional signal. One dimensional signal is
a signal that is measured over time. The common example is a voice signal.
The two dimensional signals are those that are measured over some other
physical quantities. The example of two dimensional signal is a digital
image.
Relationship
Since anything that conveys information or broadcast a message in physical
world between two observers is a signal. That includes speech or
human
voice
or an image as a signal. Since when we speak , our voice is converted
to a sound wave/signal and transformed with respect to the time to person
we are speaking to. Not only this , but the way a digital camera works, as
while acquiring an image from a digital camera involves transfer of a signal
from one part of the system to the other.
How a digital image is formed
Since capturing an image from a camera is a physical process. The sunlight
is used as a source of energy. A sensor array is used for the acquisition of
the image. So when the sunlight falls upon the object, then the amount of
light reflected by that object is sensed by the sensors, and a continuous
voltage signal is generated by the amount of sensed data. In order to create a
digital image , we need to convert this data into a digital form. This involves
sampling and quantization. The result of sampling and quantization results
in an two dimensional array or matrix of numbers which are nothing but a
digital image.
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 6
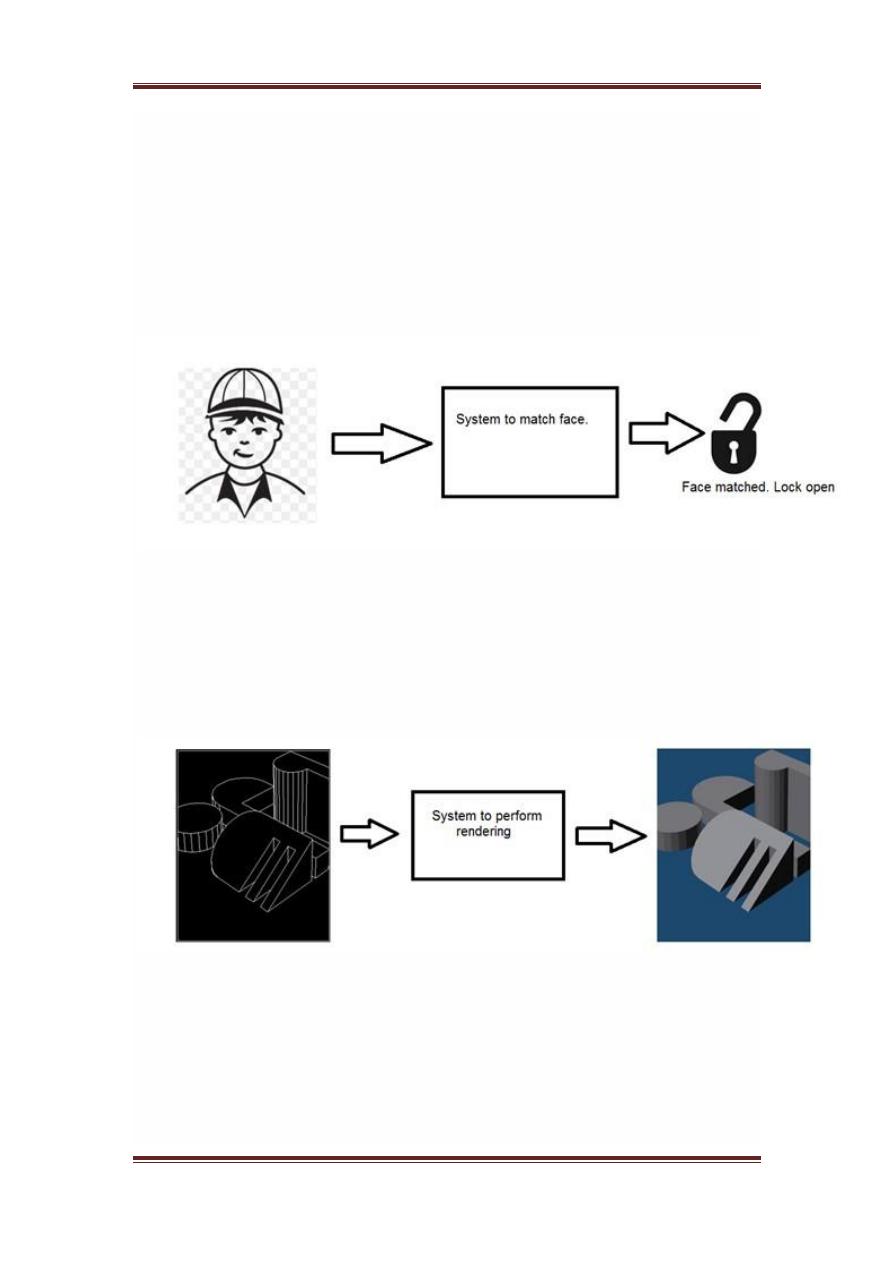
Overlapping fields
Machine/Computer vision
Machine vision or computer vision deals with developing a system in which
the input is an image and the output is some information. For example:
Developing a system that scans human face and opens any kind of lock.
This system would look something like this.
Computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with the formation of images from object models,
rather then the image is captured by some device. For example: Object
rendering. Generating an image from an object model. Such a system would
look something like this.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is more or less the study of putting human intelligence
into machines. Artificial intelligence has many applications in image
processing. For example: developing computer aided diagnosis systems that
help doctors in interpreting images of X-ray , MRI e.t.c and then
highlighting conspicuous section to be examined by the doctor.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 7
Signal processing
Signal processing is an umbrella and image processing lies under it. The
amount of light reflected by an object in the physical world
3dworld
is pass
through the lens of the camera and it becomes a 2d signal and hence result in
image formation. This image is then digitized using methods of signal
processing and then this digital image is manipulated in digital image
processing.
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
INTRODUCTION
This tutorial covers the basics of signals and system necessary for
understanding the concepts of digital image processing. Before going into
the detail concepts , lets first define the simple terms.
Signals
In electrical engineering, the fundamental quantity of representing some
information is called a signal. It doesn't matter what the information is
i-e: Analog or digital information. In mathematics, a signal is a function that
conveys some information. In fact any quantity measurable through time
over space or any higher dimension can be taken as a signal. A signal could
be of any dimension and could be of any form.
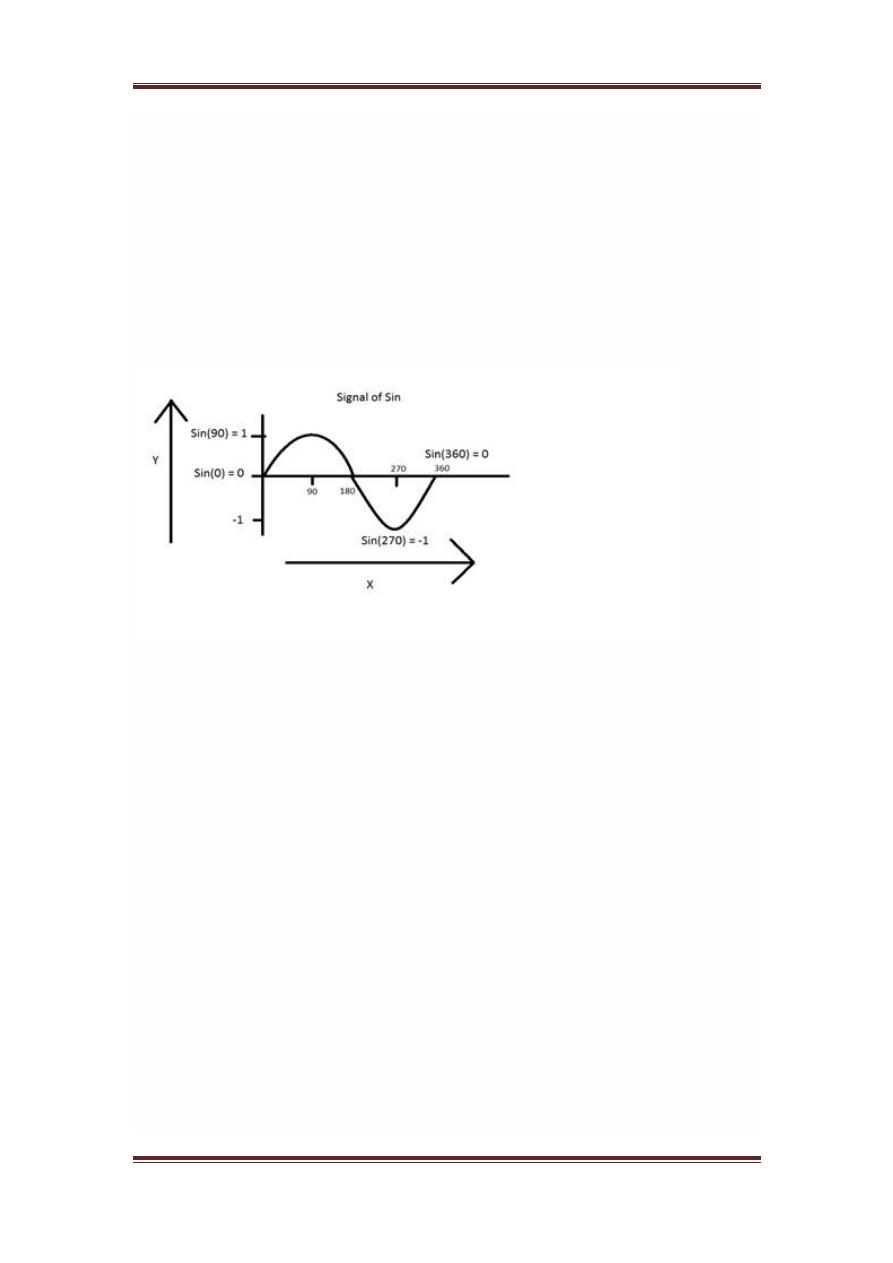
Analog signals
A signal could be an analog quantity that means it is defined with respect to
the time. It is a continuous signal. These signals are defined over continuous
independent variables. They are difficult to analyze, as they carry a huge
number of values. They are very much accurate due to a large sample of
values. In order to store these signals , you require an infinite memory
because it can achieve infinite values on a real line. Analog signals are
denoted by sin waves.
For example:
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 8
Human voice
Human voice is an example of analog signals. When you speak , the voice
that is produced travel through air in the form of pressure waves and thus
belongs to a mathematical function, having independent variables of space
and time and a value corresponding to air pressure.
Another example is of sin wave which is shown in the figure below.
Y = sin
x
where x is indepedent
Digital signals
As compared to analog signals, digital signals are very easy to analyze.
They are discontinuous signals. They are the appropriation of analog
signals.
The word digital stands for discrete values and hence it means that they use
specific values to represent any information. In digital signal , only two
values are used to represent something i-e: 1 and 0
binary values
. Digital
signals are less accurate than analog signals because they are the discrete
samples of an analog signal taken over some period of time. However digital
signals are not subject to noise. So they last long and are easy to interpret.
Digital signals are denoted by square waves.
For example:
Computer keyboard
Whenever a key is pressed from the keyboard , the appropriate electrical
signal is sent to keyboard controller containing the ASCII value that
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 9
particular key. For example the electrical signal that is generated when
keyboard key a is pressed, carry information of digit 97 in the form of 0 and
1, which is the ASCII value of character a.
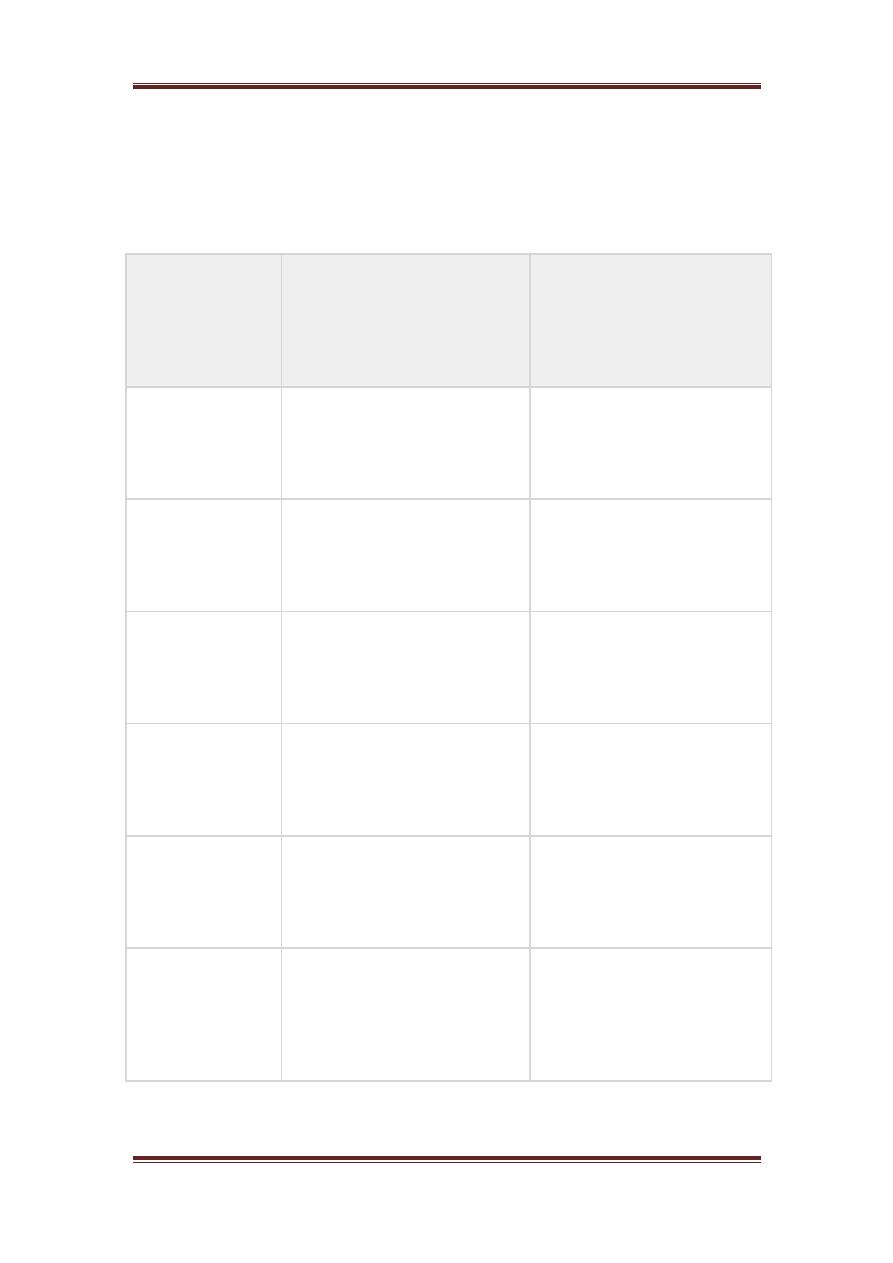
Difference between analog and digital signals
Comparison
element
Analog signal
Digital signal
Analysis
Difficult
Possible to analyze
Representation
Continuous
Discontinuous
Accuracy
More accurate
Less accurate
Storage
Infinite memory
Easily stored
Subject to Noise
Yes
No
Recording
Technique
Original signal is preserved
Samples of the signal are
taken and preserved
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 10
Examples
Human voice , Thermometer ,
Analog phones e.t.c
Computers , Digital Phones ,
Digital pens , e.t.c
Systems
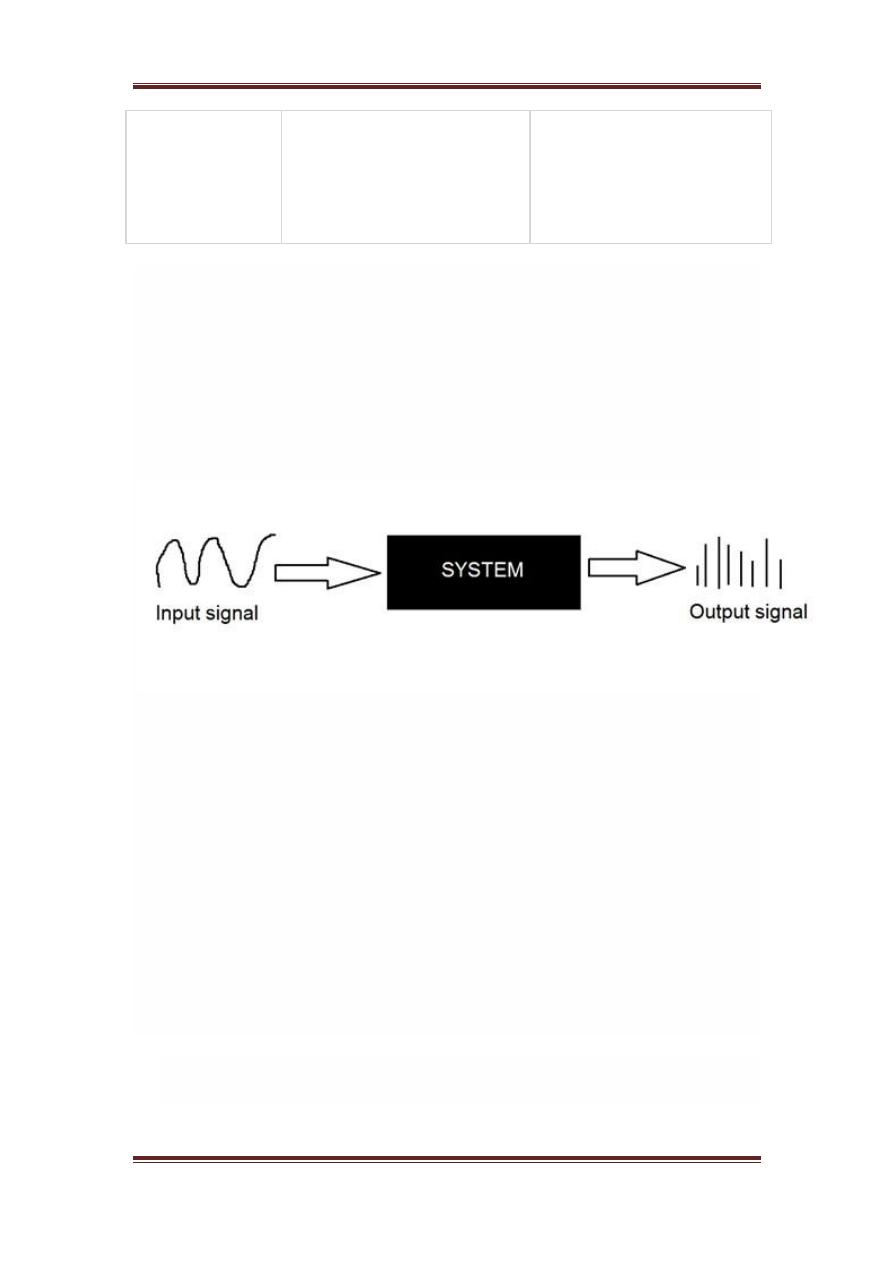
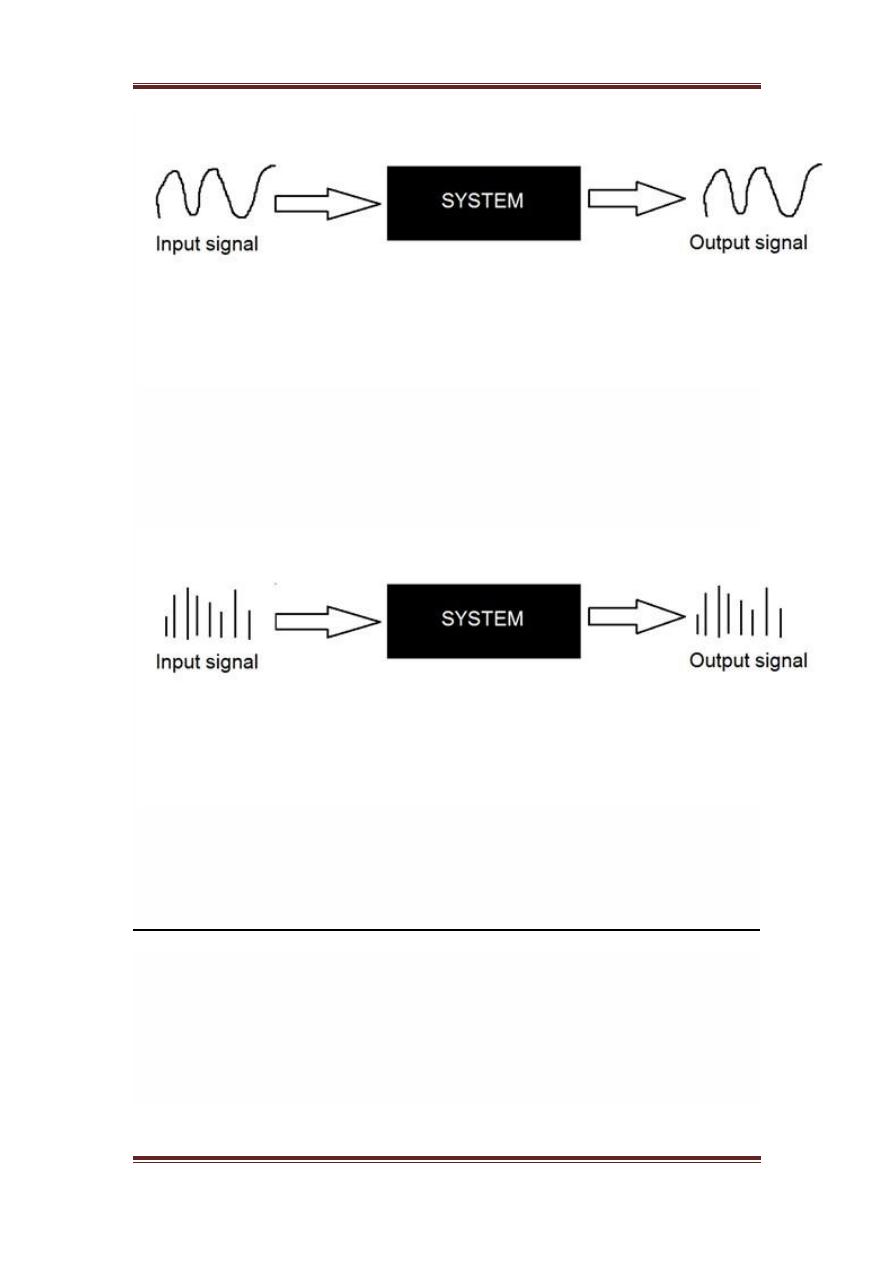
A system is a defined by the type of input and output it deals with. Since we
are dealing with signals , so in our case , our system would be a
mathematical model , a piece of code/software , or a physical device , or a
black box whose input is a signal and it performs some processing on that
signal , and the output is a signal. The input is known as excitation and the
output is known as response.
In the above figure a system has been shown whose input and output both
are signals but the input is an analog signal. And the output is an digital
signal. It means our system is actually a conversion system that converts
analog signals to digital signals.
Lets have a look at the inside of this black box
system
Conversion of analog to digital signals
Since there are lot of concepts related to this analog to digital conversion
and vice-versa. We will only discuss those which are related to digital image
processing. There are two main concepts that are involved in the coversion.
Sampling
Quantization
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 11
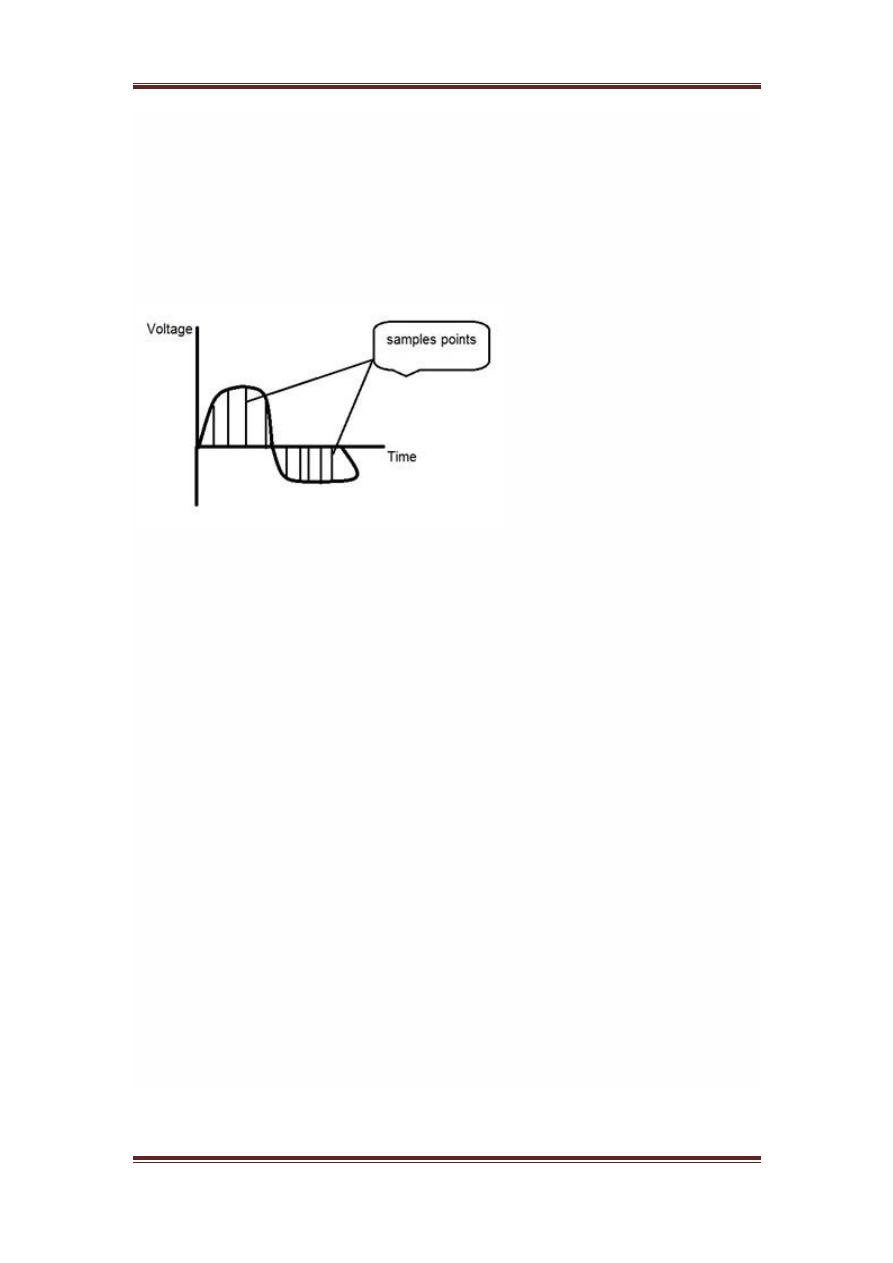
Sampling
Sampling as its name suggests can be defined as take samples. Take samples
of a digital signal over x axis. Sampling is done on an independent variable.
In case of this mathematical equation:
Sampling is done on the x variable. We can also say that the conversion of x
axis
infinite values
to digital is done under sampling.
Sampling is further divide into up sampling and down sampling. If the range
of values on x-axis are less then we will increase the sample of values. This
is known as up sampling and its vice versa is known as down sampling
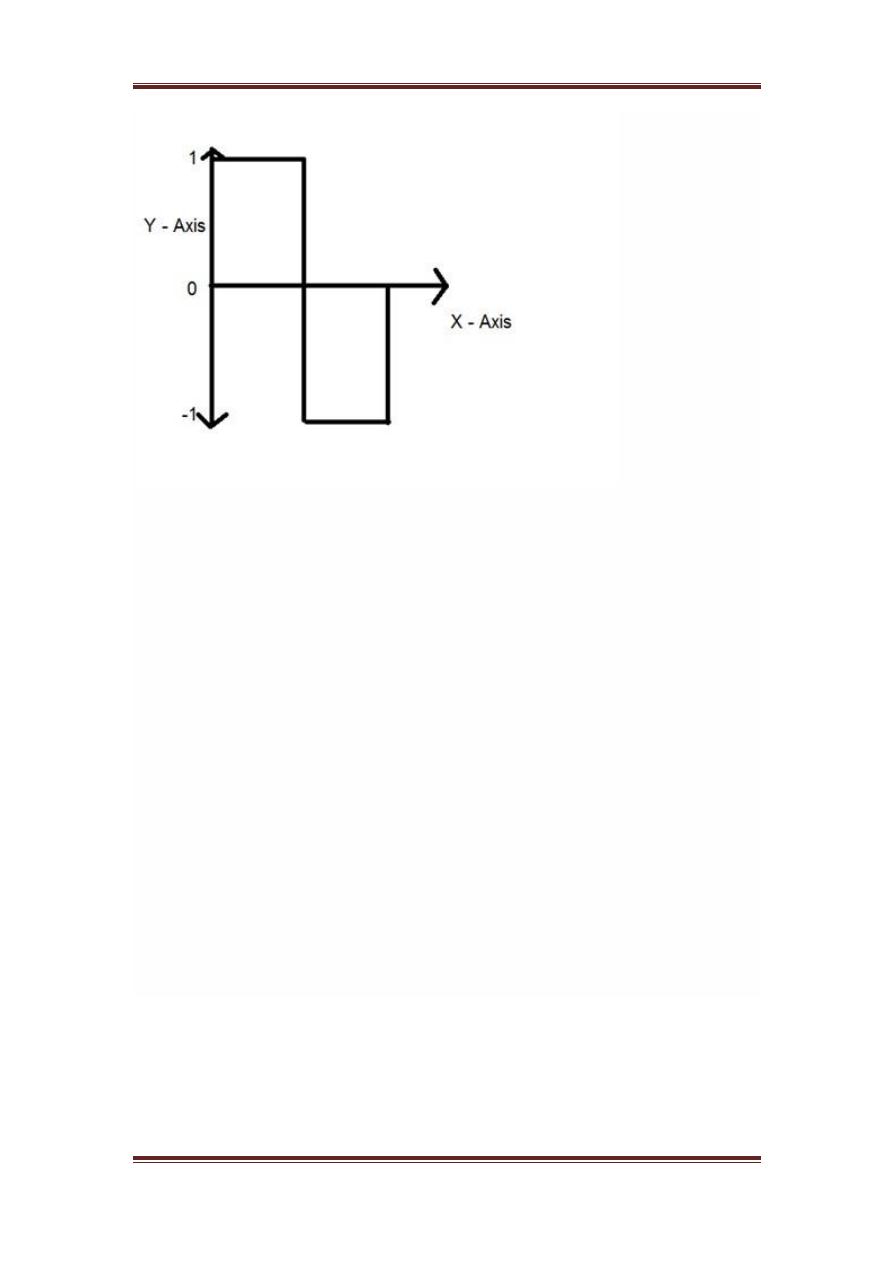
Quantization
Quantization as its name suggest can be defined as dividing into
quanta
partitions
. Quantization is done on dependent variable. It is
opposite to sampling.
In case of this mathematical equation y = sin
x
Quantization is done on the Y variable. It is done on the y axis. The
conversion of y axis infinite values to 1 , 0 , -1
oranyotherlevel
is known
as Quantization.
These are the two basics steps that are involved while converting an analog
signal to a digital signal.
The quantization of a signal has been shown in the figure below.
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 12
Why do we need to convert an analog signal to
digital signal.
The first and obvious reason is that digital image processing deals with
digital images , that are digital signals. So when ever the image is captured ,
it is converted into digital format and then it is processed.
The second and important reason is , that in order to perform operations on
an analog signal with a digital computer , you have to store that analog
signal in the computer. And in order to store an analog signal , infinite
memory is required to store it. And since thats not possible , so thats why we
convert that signal into digital format and then store it in digital computer
and then performs operations on it.
Continuous systems vs discrete systems
Continuous systems
The type of systems whose input and output both are continuous signals or
analog signals are called continuous systems.
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 13
Discrete systems
The type of systems whose input and output both are discrete signals or
digital signals are called digital systems
HISTORY OF PHOTOGRAPH
Origin of camera
The history of camera and photography is not exactly the same. The
concepts of camera were introduced a lot before the concept of photography
Camera

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 14
The principles of the camera were first introduced by a Chinese philosopher
MOZI. It is known as camera obscura. The cameras evolved from this
principle.
The word camera obscura is evolved from two different words. Camera and
Obscura. The meaning of the word camera is a room or some kind of vault
and Obscura stands for dark.
The concept which was introduced by the Chinese philosopher consist of a
device, that project an image of its surrounding on the wall. However it was
not built by the Chinese.
The creation of camera obscura
The concept of Chinese was bring in reality by a Muslim scientist Abu Ali
Al-Hassan Ibn al-Haitham commonly known as Ibn al-Haitham. He built the
first camera obscura. His camera follows the principles of pinhole camera.
He build this device in somewhere around 1000.
Portable camera
In 1685, a first portable camera was built by Johann Zahn. Before the advent
of this device , the camera consist of a size of room and were not portable.
Although a device was made by an Irish scientist Robert Boyle and Robert
Hooke that was a transportable camera, but still that device was very huge to
carry it from one place to the other.
Origin of photography
Although the camera obscura was built in 1000 by a Muslim scientist. But
its first actual use was described in the 13th century by an English
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 15
philosopher Roger Bacon. Roger suggested the use of camera for the
observation of solar eclipses.
Da Vinci
Although much improvement has been made before the 15th century , but
the improvements and the findings done by Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci
was remarkable. Da Vinci was a great artist , musician , anatomist , and a
war enginner. He is credited for many inventions. His one of the most
famous painting includes, the painting of Mona Lisa.
Da vinci not only built a camera obscura following the principle of a pin
hole camera but also uses it as drawing aid for his art work. In his work ,
which was described in Codex Atlanticus , many principles of camera
obscura has been defined.
His camera follows the principle of a pin hole camera which can be
described as

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 16
When images of illuminated objects penetrate through a small hole into a
very dark room you will see [on the opposite wall] these objects in their
proper form and color, reduced in size in a reversed position, owing to the
intersection of rays.
First photograph
The first photograph was taken in 1814 by a French inventor Joseph
Nicephore Niepce. He captures the first photograph of a view from the
window at Le Gras, by coating the pewter plate with bitumen and after that
exposing that plate to light.
First underwater photograph
The first underwater photograph was taken by an English mathematician
William Thomson using a water tight box. This was done in 1856.
The origin of film
The origin of film was introduced by an American inventor and a
philanthropist known as George Eastman who is considered as the pioneer
of photography.
He founded the company called as Eastman Kodak , which is famous for
developing films. The company starts manufacturing paper film in 1885. He

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 17
first created the camera Kodak and then later Brownie. Brownie was a box
camera and gain its popularity due to its feature of Snapshot.
After the advent of the film , the camera industry once again got a boom and
one invention lead to another.
Leica and Argus
Leica and argus are the two analog cameras developed in 1925 and in 1939
respectively. The camera Leica was built using a 35mm cine film.
Argus was another camera analog camera that uses the 35mm format and
was rather inexpensive as compared by Leica and became very popular.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 18
Analog CCTV cameras
In 1942 a German engineer Walter Bruch developed and installed the very
first system of the analog CCTV cameras. He is also credited for the
invention of color television in the 1960.
Photo Pac
The first disposable camera was introduced in 1949 by Photo Pac. The
camera was only a one time use camera with a roll of film already included
in it. The later versions of Photo pac were water proof and even have the
flash.
Digital Cameras
Mavica by Sony

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 19
Mavica
themagneticvideocamera
was launched by Sony in 1981 was the
first game changer in digital camera world. The images were recorded on
floppy disks and images can be viewed later on any monitor screen.
It was not a pure digital camera , but an analog camera. But got its
popularity due to its storing capacity of images on a floppy disks. It means
that you can now store images for a long lasting period , and you can save a
huge number of pictures on the floppy which are replaced by the new blank
disc , when they got full. Mavica has the capacity of storing 25 images on a
disk.
One more important thing that mavica introduced was its 0.3 mega pixel
capacity of capturing photos.
Digital Cameras
Fuji DS-1P camera by Fuji films 1988 was the first true digital camera
Nikon D1 was a 2.74 mega pixel camera and the first commercial digital
SLR camera developed by Nikon , and was very much affordable by the
professionals.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 20
Today digital cameras are included in the mobile phones with very high
resolution and quality.
APPLICATIONS AND USAGE
Since digital image processing has very wide applications and almost all of
the technical fields are impacted by DIP, we will just discuss some of the
major applications of DIP.
Digital Image processing is not just limited to adjust the spatial resolution of
the everyday images captured by the camera. It is not just limited to increase
the brightness of the photo, e.t.c. Rather it is far more than that.
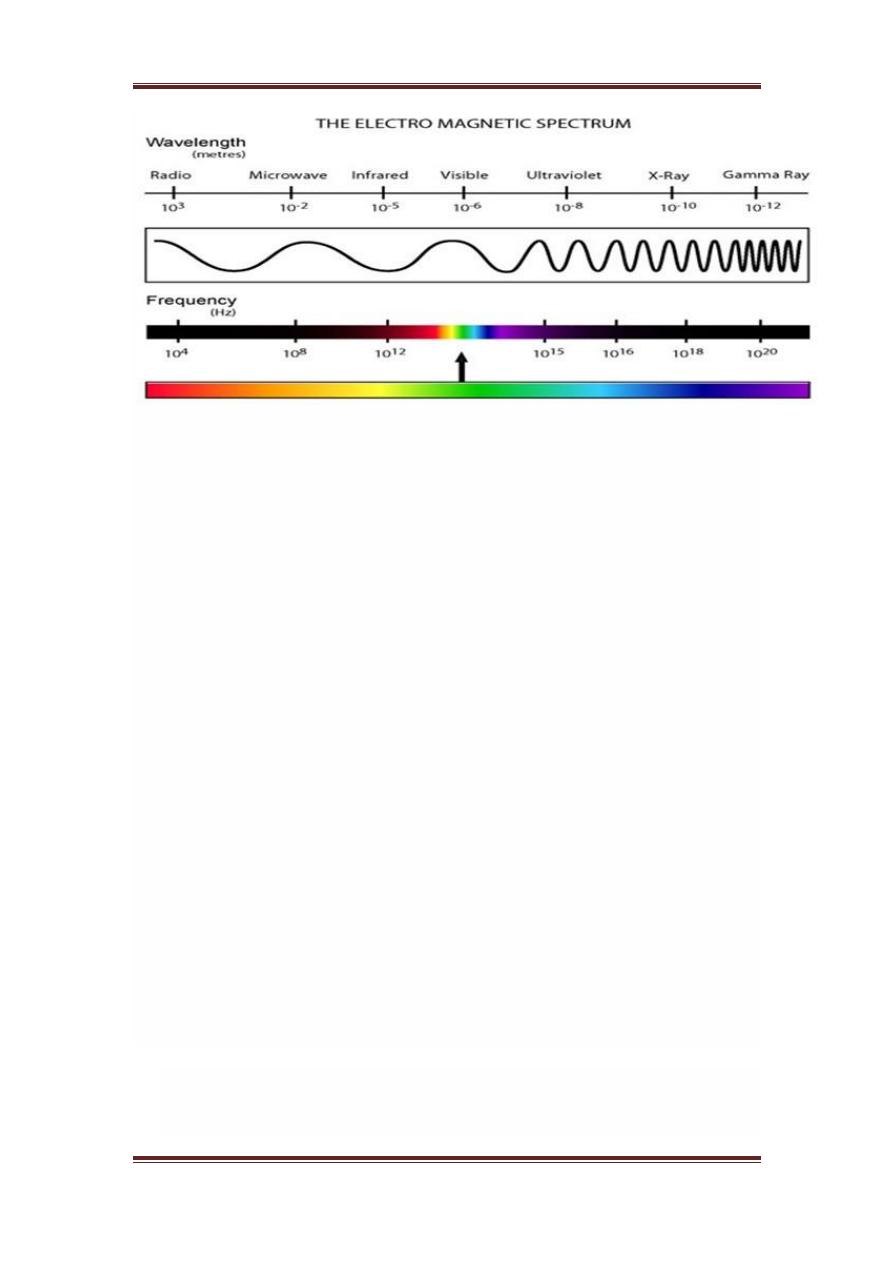
Electromagnetic waves can be thought of as stream of particles, where each
particle is moving with the speed of light. Each particle contains a bundle of
energy. This bundle of energy is called a photon.
The electromagnetic spectrum according to the energy of photon is shown
below.
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 21
In this electromagnetic spectrum, we are only able to see the visible
spectrum. Visible spectrum mainly includes seven different colors that are
commonly term as
VIBGOYR
. VIBGOYR stands for violet , indigo , blue
, green , orange , yellow and Red.
But that doesnot nullify the existence of other stuff in the spectrum. Our
human eye can only see the visible portion, in which we saw all the objects.
But a camera can see the other things that a naked eye is unable to see. For
example: x rays , gamma rays , e.t.c. Hence the analysis of all that stuff too
is done in digital image processing.
This discussion leads to another question which is
why do we need to analyze all that other stuff in EM
spectrum too?
The answer to this question lies in the fact, because that other stuff such as
XRay has been widely used in the field of medical. The analysis of Gamma
ray is necessary because it is used widely in nuclear medicine and
astronomical observation. Same goes with the rest of the things in EM
spectrum.
Applications of Digital Image Processing
Some of the major fields in which digital image processing is widely used
are mentioned below
Image sharpening and restoration
Medical field
Remote sensing

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 22
Transmission and encoding
Machine/Robot vision
Color processing
Pattern recognition
Video processing
Microscopic Imaging
Others
Image sharpening and restoration
Image sharpening and restoration refers here to process images that have
been captured from the modern camera to make them a better image or to
manipulate those images in way to achieve desired result. It refers to do
what Photoshop usually does.
This includes Zooming, blurring , sharpening , gray scale to color
conversion, detecting edges and vice versa , Image retrieval and Image
recognition. The common examples are:
The original image
The zoomed image

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 23
Blurr image
Sharp image
Edges

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 24
Medical field
The common applications of DIP in the field of medical is
1. Gamma ray imaging
2. PET scan
3. X Ray Imaging
4. Medical CT
5. UV imaging
UV imaging
In the field of remote sensing , the area of the earth is scanned by a satellite
or from a very high ground and then it is analyzed to obtain information
about it. One particular application of digital image processing in the field of
remote sensing is to detect infrastructure damages caused by an earthquake.
As it takes longer time to grasp damage, even if serious damages are
focused on. Since the area effected by the earthquake is sometimes so wide ,
that it not possible to examine it with human eye in order to estimate
damages. Even if it is , then it is very hectic and time consuming procedure.
So a solution to this is found in digital image processing. An image of the
effected area is captured from the above ground and then it is analyzed to
detect the various types of damage done by the earthquake.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 25
The key steps include in the analysis are
1. The extraction of edges
2. Analysis and enhancement of various types of edges
Transmission and encoding
The very first image that has been transmitted over the wire was from
London to New York via a submarine cable. The picture that was sent is
shown below.
The picture that was sent took three hours to reach from one place to
another.
Now just imagine , that today we are able to see live video feed , or live cctv
footage from one continent to another with just a delay of seconds. It means
that a lot of work has been done in this field too. This field doesnot only
focus on transmission , but also on encoding. Many different formats have
been developed for high or low bandwith to encode photos and then stream
it over the internet or e.t.c.
Machine/Robot vision
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 26
Apart form the many challenges that a robot face today , one of the biggest
challenge still is to increase the vision of the robot. Make robot able to see
things , identify them , identify the hurdles e.t.c. Much work has been
contributed by this field and a complete other field of computer vision has
been introduced to work on it.
Hurdle detection
Hurdle detection is one of the common task that has been done through
image processing, by identifying different type of objects in the image and
then calculating the distance between robot and hurdles.
Line follower robot
Most of the robots today work by following the line and thus are called line
follower robots. This help a robot to move on its path and perform some
tasks. This has also been achieved through image processing.
Color processing
Color processing includes processing of colored images and different color
spaces that are used. For example RGB color model , YCbCr, HSV. It also

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 27
involves studying transmission , storage , and encoding of these color
images.
Pattern recognition
Pattern recognition involves study from image processing and from various
other fields that includes machine
learning
abranchofartificialintelligence
. In pattern recognition , image
processing is used for identifying the objects in an images and then machine
learning is used to train the system for the change in pattern. Pattern
recognition is used in computer aided diagnosis , recognition of handwriting
, recognition of images e.t.c
Video processing
A video is nothing but just the very fast movement of pictures. The quality
of the video depends on the number of frames/pictures per minute and the
quality of each frame being used. Video processing involves noise reduction
, detail enhancement , motion detection , frame rate conversion , aspect ratio
conversion , color space conversion e.t.c.
CONCEPT OF DIMENSIONS
We will look at this example in order to understand the concept of
dimension.
Consider you have a friend who lives on moon, and he wants to send you a
gift on your birthday present. He ask you about your residence on earth. The
only problem is that the courier service on moon doesnot understand the
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 28
alphabetical address, rather it only understand the numerical co-ordinates.
So how do you send him your position on earth?
Thats where comes the concept of dimensions. Dimensions define the
minimum number of points required to point a position of any particular
object within a space.
So lets go back to our example again in which you have to send your
position on earth to your friend on moon. You send him three pair of co-
ordinates. The first one is called longitude , the second one is called latitude,
and the third one is called altitude.
These three co-ordinates define your position on the earth. The first two
defines your location , and the third one defines your height above the sea
level.
So that means that only three co-ordinates are required to define your
position on earth. That means you live in world which is 3 dimensional. And
thus this not only answers the question about dimension , but also answers
the reason , that why we live in a 3d world.
Since we are studying this concept in reference to the digital image
processing, so we are now going to relate this concept of dimension with an
image.
Dimensions of image
So if we live in the 3d world , means a 3 dimensional world, then what are
the dimensions of an image that we capture. An image is a two dimensional,
thats why we also define an image as a 2 dimensional signal. An image has
only height and width. An image doesnot have depth. Just have a look at this
image below.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 29
If you would look at the above figure , it shows that it has only two axis
which are the height and width axis. You cannot perceive depth from this
image. Thats why we say that an image is two dimensional signal. But our
eye is able to perceive three dimensional objects , but this would be more
explained in the next tutorial of how the camera works , and image is
perceived.
This discussion leads to some other questions that how 3 dimension systems
is formed from 2 dimension.
How does television works?
If we look the image above , we will see that it is a two dimensional image.
In order to convert it into three dimension , we need one other dimension.
Lets take time as the third dimension , in that case we will move this two
dimensional image over the third dimension time. The same concept that
happens in television, that helps us perceive the depth of different objects on
a screen. Does that mean that what comes on the T.V or what we see in the
television screen is 3d. Well we can yes. The reason is that, in case of T.V
we if we are playing a video. Then a video is nothing else but two
dimensional pictures move over time dimension. As two dimensional
objects are moving over the third dimension which is a time so we can say it
is 3 dimensional.
Different dimensions of signals
1 dimension signal
The common example of a 1 dimension signal is a waveform. It can be
mathematically represented as
F
x
= waveform
Where x is an independent variable. Since it is a one dimension signal , so
thats why there is only one variable x is used.
Pictorial representation of a one dimensional signal is given below:
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 30
The above figure shows a one dimensional signal.
Now this lead to another question, which is, even though it is a one
dimensional signal ,then why does it have two axis?. The answer to this
question is that even though it is a one dimensional signal , but we are
drawing it in a two dimensional space. Or we can say that the space in
which we are representing this signal is two dimensional. Thats why it looks
like a two dimensional signal.
Perhaps you can understand the concept of one dimension more better by
looking at the figure below.
Now refer back to our initial discussion on dimension, Consider the above
figure a real line with positive numbers from one point to the other. Now if
we have to explain the location of any point on this line, we just need only
one number, which means only one dimension.
2 dimensions signal
The common example of a two dimensional signal is an image , which has
already been discussed above.
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 31
As we have already seen that an image is two dimensional signal, i-e: it has
two dimensions. It can be mathematically represented as:
F
x,y
= Image
Where x and y are two variables. The concept of two dimension can also be
explained in terms of mathematics as:
Now in the above figure, label the four corners of the square as A,B,C and D
respectively. If we call , one line segment in the figure AB and the other CD
, then we can see that these two parallel segments join up and make a
square. Each line segment corresponds to one dimension , so these two line
segments correspond to 2 dimensions.
3 dimension signal
Three dimensional signal as it names refers to those signals which has three
dimensions. The most common example has been discussed in the beginning
which is of our world. We live in a three dimensional world. This example
has been discussed very elaborately. Another example of a three
dimensional signal is a cube or a volumetric data or the most common
example would be animated or 3d cartoon character.
The mathematical representation of three dimensional signal is:
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 32
F
x,y,z
= animated character.
Another axis or dimension Z is involved in a three dimension, that gives the
illusion of depth. In a Cartesian co-ordinate system it can be viewed as:
4 dimension signal
In a four dimensional signal , four dimensions are involved. The first three
are the same as of three dimensional signal which are:
X,Y,Z
, and the
fourth one which is added to them is T
time
. Time is often referred to as
temporal dimension which is a way to measure change. Mathematically a
four d signal can be stated as:
F
x,y,z,t
= animated movie.
The common example of a 4 dimensional signal can be an animated 3d
movie. As each character is a 3d character and then they are moved with
respect to the time, due to which we saw an illusion of a three dimensional
movie more like a real world.
So that means that in reality the animated movies are 4 dimensional i-e:
movement of 3d characters over the fourth dimension time.
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 33
IMAGE FORMATION ON CAMERA
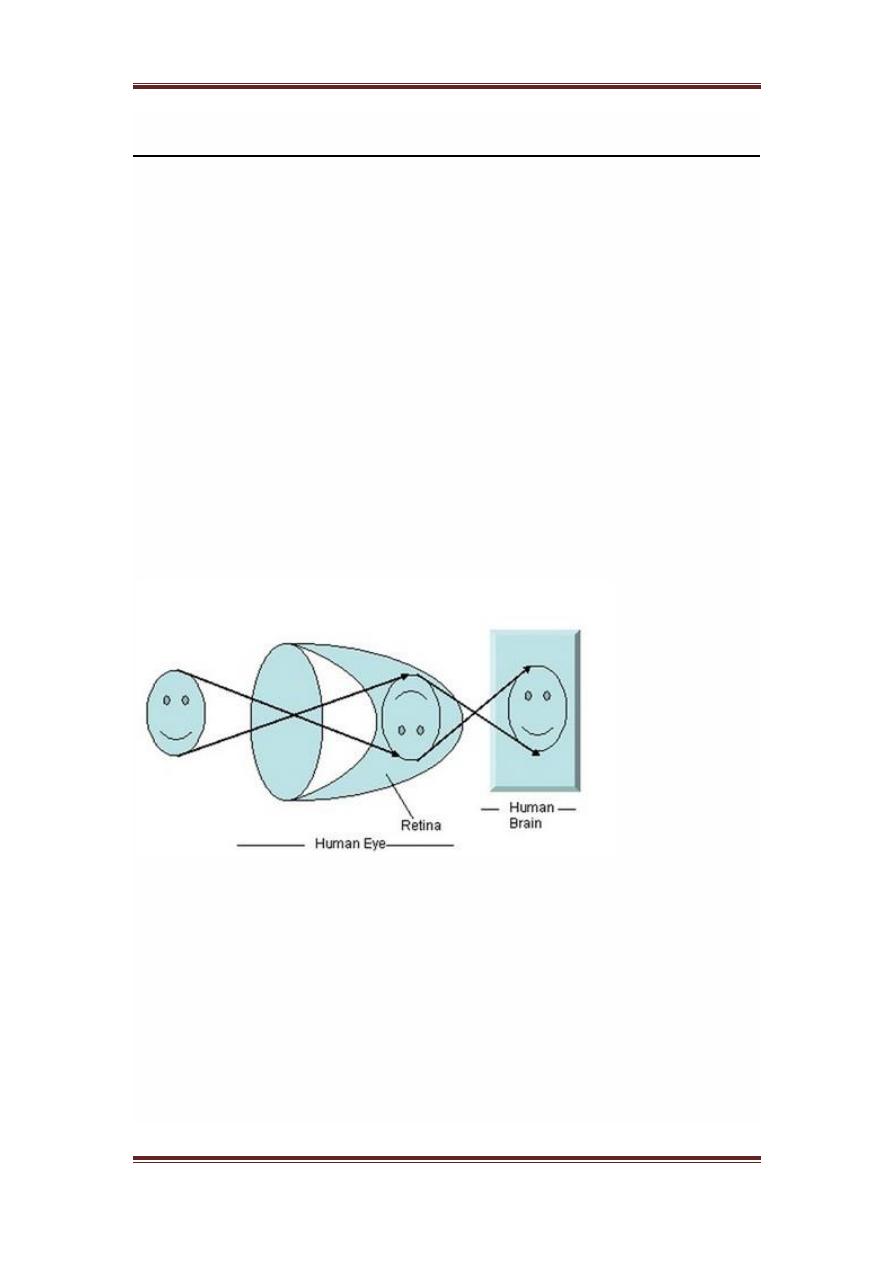
How human eye works?
Before we discuss , the image formation on analog and digital cameras , we
have to first discuss the image formation on human eye. Because the basic
principle that is followed by the cameras has been taken from the way , the
human eye works.
When light falls upon the particular object , it is reflected back after striking
through the object. The rays of light when passed through the lens of eye ,
form a particular angle , and the image is formed on the retina which is the
back side of the wall. The image that is formed is inverted. This image is
then interpreted by the brain and that makes us able to understand things.
Due to angle formation , we are able to perceive the height and depth of the
object we are seeing. This has been more explained in the tutorial of
perspective transformation.
As you can see in the above figure, that when sun light falls on the object
in
this case the object is a face
, it is reflected back and different rays form
different angle when they are passed through the lens and an invert image of
the object has been formed on the back wall. The last portion of the figure
denotes that the object has been interpreted by the brain and re-inverted.
Now lets take our discussion back to the image formation on analog and
digital cameras.
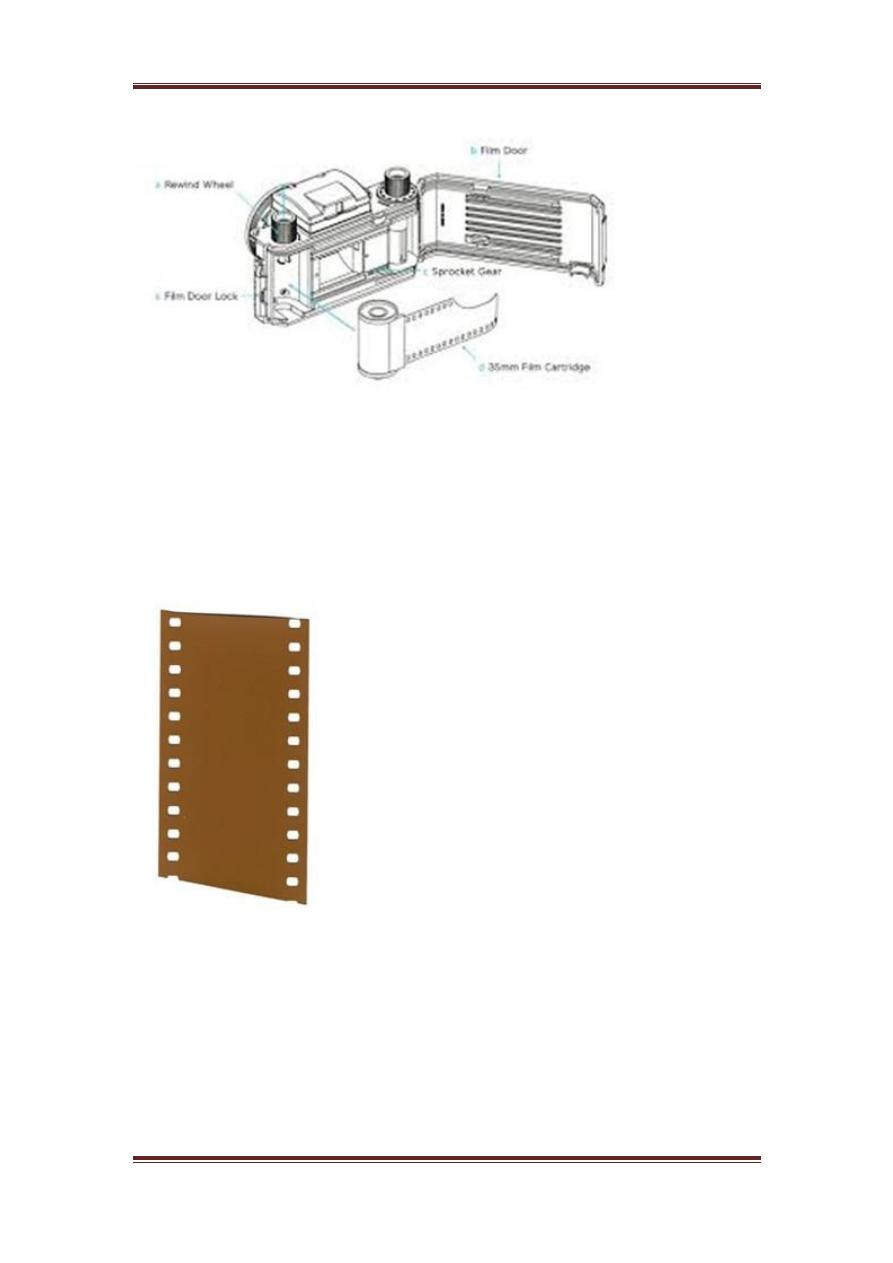
Image formation on analog cameras
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 34
In analog cameras , the image formation is due to the chemical reaction that
takes place on the strip that is used for image formation.
A 35mm strip is used in analog camera. It is denoted in the figure by 35mm
film cartridge. This strip is coated with silver halide
a chemical sub
stance
.
A 35mm strip is used in analog camera. It is denoted in the figure by 35mm
film cartridge. This strip is coated with silver halide
a chemical sub
stance
.
Light is nothing but just the small particles known as photon particles.So
when these photon particles are passed through the camera, it reacts with the
silver halide particles on the strip and it results in the silver which is the
negative of the image.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 35
In order to understand it better , have a look at this equation.
Photons
lightparticles
+ silver halide ? silver ? image negative.
This is just the basics, although image formation involves many other
concepts regarding the passing of light inside , and the concepts of shutter
and shutter speed and aperture and its opening but for now we will move on
to the next part. Although most of these concepts have been discussed in our
tutorial of shutter and aperture.
This is just the basics, although image formation involves many other
concepts regarding the passing of light inside , and the concepts of shutter
and shutter speed and aperture and its opening but for now we will move on
to the next part. Although most of these concepts have been discussed in our
tutorial of shutter and aperture.
Image formation on digital cameras
In the digital cameras , the image formation is not due to the chemical
reaction that take place , rather it is a bit more complex then this. In the
digital camera , a CCD array of sensors is used for the image formation.
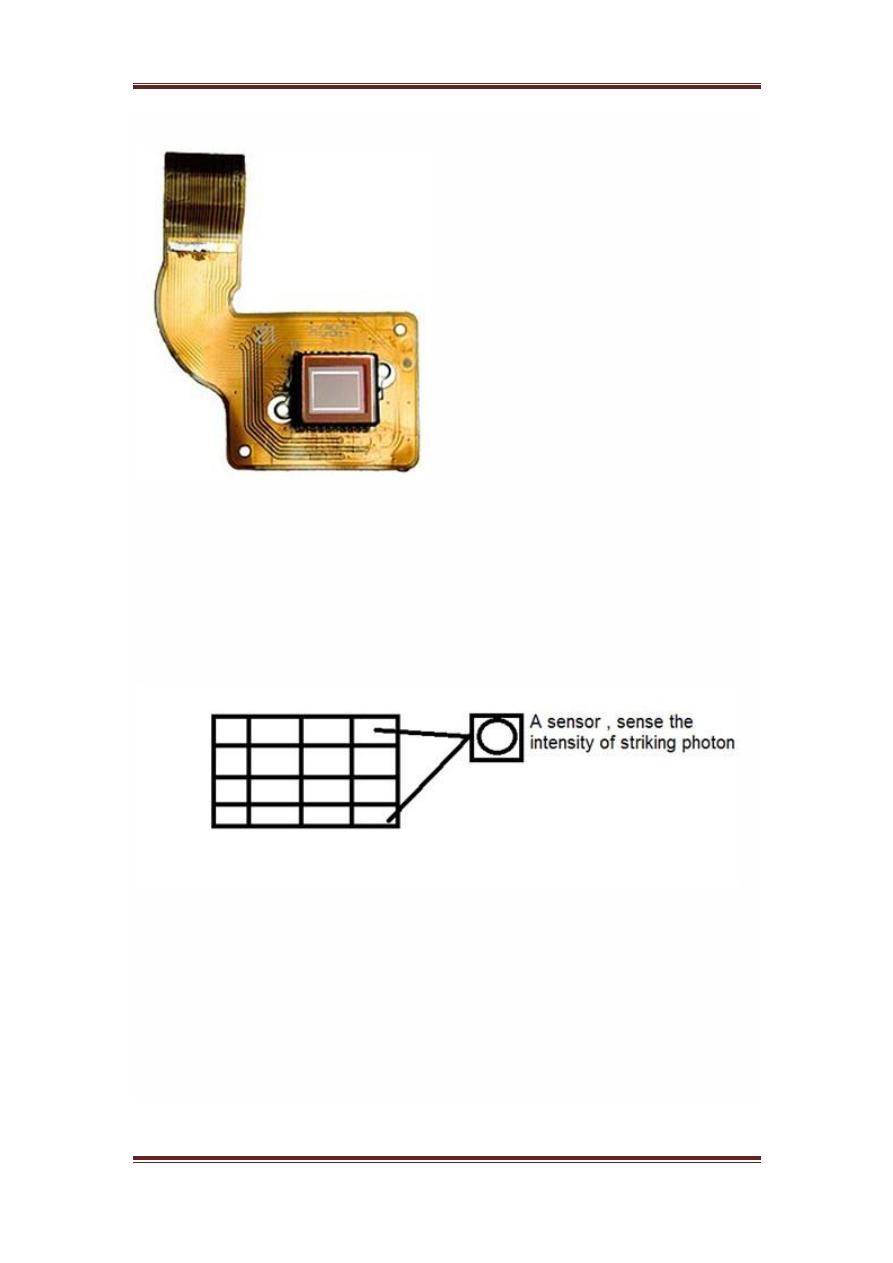
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 36
Image formation through CCD array
CCD stands for charge-coupled device. It is an image sensor, and like other
sensors it senses the values and converts them into an electric signal. In case
of CCD it senses the image and convert it into electric signal e.t.c.
This CCD is actually in the shape of array or a rectangular grid. It is like a
matrix with each cell in the matrix contains a censor that senses the intensity
of photon.
Like analog cameras , in the case of digital too , when light falls on the
object , the light reflects back after striking the object and allowed to enter
inside the camera.
Each sensor of the CCD array itself is an analog sensor. When photons of
light strike on the chip , it is held as a small electrical charge in each photo
sensor. The response of each sensor is directly equal to the amount of light
or
photon
energy striked on the surface of the sensor.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 37
Since we have already define an image as a two dimensional signal and due
to the two dimensional formation of the CCD array , a complete image can
be achieved from this CCD array.
It has limited number of sensors , and it means a limited detail can be
captured by it. Also each sensor can have only one value against the each
photon particle that strike on it.
So the number of photons striking
current
are counted and stored. In order
to measure accurately these , external CMOS sensors are also attached with
CCD array.
Introduction to pixel
The value of each sensor of the CCD array refers to each the value of the
individual pixel. The number of sensors = number of pixels. It also means
that each sensor could have only one and only one value.
Storing image
The charges stored by the CCD array are converted to voltage one pixel at a
time. With the help of additional circuits , this voltage is converted into a
digital information and then it is stored.
Each company that manufactures digital camera, make their own CCD
sensors. That include , Sony , Mistubishi , Nikon ,Samsung , Toshiba ,
FujiFilm , Canon e.t.c.
Apart from the other factors , the quality of the image captured also depends
on the type and quality of the CCD array that has been used.
CAMERA MECHANSIM
In this tutorial, we will discuss some of the basic camera concepts, like
aperture , shutter , shutter speed , ISO and we will discuss the collective use
of these concepts to capture a good image.
Aperture
Aperture is a small opening which allows the light to travel inside into
camera. Here is the picture of aperture.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 38
You will see some small blades like stuff inside the aperture. These blades
create a octagonal shape that can be opened closed. And thus it make sense
that , the more blades will open, the hole from which the light would have to
pass would be bigger. The bigger the hole , the more light is allowed to
enter.
Effect
The effect of the aperture directly corresponds to brightness and darkness of
an image. If the aperture opening is wide , it would allow more light to pass
into the camera. More light would result in more photons, which ultimately
result in a brighter image.
The example of this is shown below
Consider these two photos
Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 39
The one on the right side looks brighter, it means that when it was captured
by the camera , the aperture was wide open. As compare to the other picture
on the left side , which is very dark as compare to the first one, that shows
that when that image was captured, its aperture was not wide open.
Size
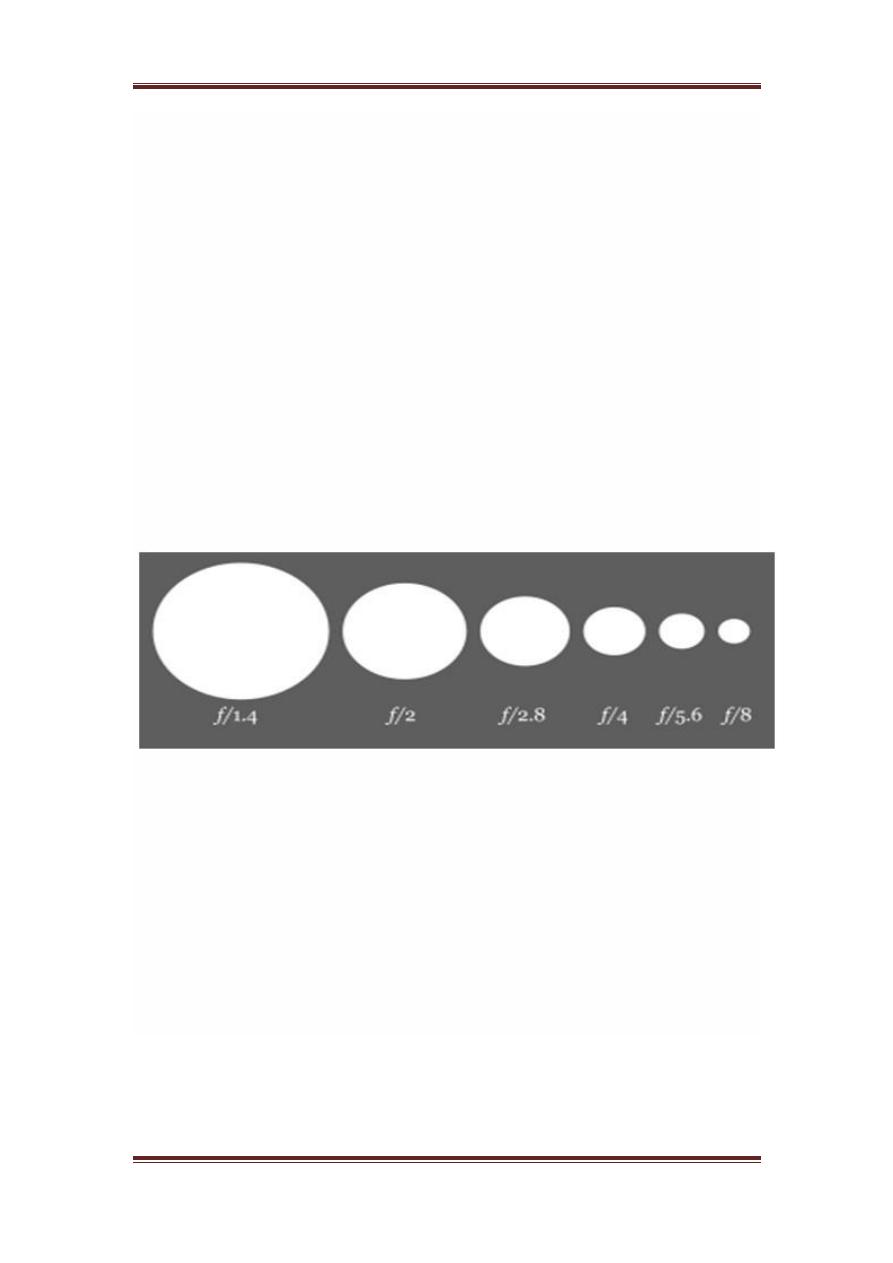
Now lets discuss the maths behind the aperture. The size of the aperture is
denoted by a f value. And it is inversely proportional to the opening of
aperture.
Here are the two equations , that best explain this concept.
Large aperture size = Small f value
Small aperture size = Greater f value
Pictorially it can be represented as:
Shutter
After the aperture , there comes the shutter. The light when allowed to pass
from the aperture , falls directly on to the shutter. Shutter is actually a cover,
a closed window , or can be thought of as a curtain. Remember when we
talk about the CCD array sensor on which the image is formed. Well behind
the shutter is the sensor. So shutter is the only thing that is between the
image formation and the light , when it is passed from aperture.
As soon as the shutter is open , light falls on the image sensor , and the
image is formed on the array.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 40
Effect
If the shutter allows light to pass a bit longer , the image would be brighter.
Similarly a darker picture is produced , when a shutter is allowed to move
very quickly and hence, the light that is allowed to pass has very less
photons , and the image that is formed on the CCD array sensor is very dark.
Shutter has further two main concepts:
1. Shutter Speed
2. Shutter time
Shutter speed
The shutter speed can be referred to as the number of times the shutter get
open or close. Remember we are not talking about for how long the shutter
get open or close.
Shutter time
The shutter time can be defined as
When the shutter is open , then the amount of wait time it take till it is
closed is called shutter time.
In this case we are not talking about how many times , the shutter got open
or close , but we are talking about for how much time does it remain wide
open.
For example:
We can better understand these two concepts in this way. That lets say that a
shutter opens 15 times and then get closed, and for each time it opens for 1
second and then get closed. In this example , 15 is the shutter speed and 1
second is the shutter time.
Relationship
The relationship between shutter speed and shutter time is that they are both
inversely proportional to each other.
This relationship can be defined in the equation below.

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 41
More shutter speed = less shutter time
Less shutter speed = more shutter time.
Explanation:
The lesser the time required , the more is the speed. And the greater the time
required , the less is the speed.
Applications
These two concepts together make a variety of applications. Some of them
are given below.
Fast moving objects:
If you were to capture the image of a fast moving object , could be a car or
anything. The adjustment of shutter speed and its time would effect a lot.
So , in order to capture an image like this, we will make two amendments:
1. Increase shutter speed
2. Decrease shutter time
What happens is , that when we increase shutter speed , the more number of
times , the shutter would open or close. It means different samples of light
would allow to pass in. And when we decrease shutter time , it means we
will immediately captures the scene, and close the shutter gate.
If you will do this , you get a crisp image of a fast moving object.
In order to understand it , we will look at this example. Suppose you want to
capture the image of fast moving water fall.
You set your shutter speed to 1 second and you capture a photo. This is what
you get

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 42
Then you set your shutter speed to a faster speed and you get.
Then again you set your shutter speed to even more faster and you get.
You can see in the last picture , that we have increase our shutter speed to
very fast, that means that a shutter get opened or closed in 200th of 1 second
and so we got a crisp image.
ISO

Digital image processing
ASSIST PROF. DR. WALEED ABDULLAH
Page 43
ISO factor is measured in numbers. It denotes the sensitivity of light to
camera. If ISO number is lowered , it means our camera is less sensitive to
light and if the ISO number is high, it means it is more senstivie.
Effect
The higher is the ISO , the more brighter the picture would be. IF ISO is set
to 1600 , the picture would be very brighter and vice versa.
Side effect
If the ISO increases, the noise in the image also increases. Today most of
the camera manufacturing companies are working on removing the noise
from the image when ISO is set to higher speed.
