
Baghdad College of Medicine / 5
th
grade
Student’s Name :
Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
Lec. 1
HEAD INJURY
Sun. 16 / 10 / 2016
DONE BY : Ali Kareem
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
2016 – 2017

Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
2
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Head Injury
o Constitute one of the commonest causes of morbidity and mortality in the
community
o In peace time :
- 50% of causes are due to RTA ( road traffic accident )
- 30% of cases are due to FFH ( fall from height )
o In war time :
- 40% of cases are due to bullet and missile injury
CLASSIFICATION OF HEAD INJURY (H.I.)
ž
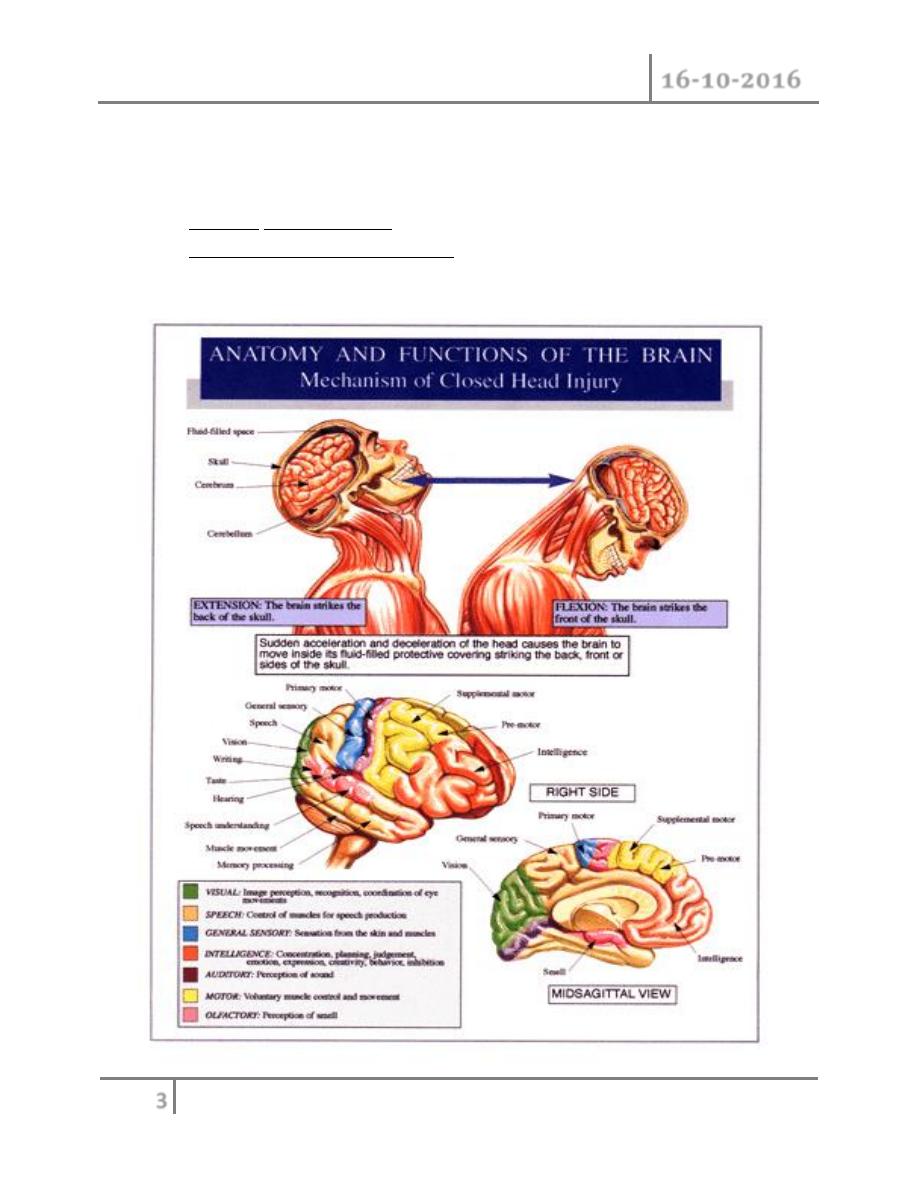
1- Blunt injury
o The head is struck with a blunt object there will be diffuse brain
damage with /without loss of consciousness
o It can occur with minimal external damage ( i.e: without skull fractures or
wounds )
o Are usually closed ones
o It is divided into: ( mechanism of injury )
A. Acceleration injury : where the head is struck by a moving object
B. Decceleration injury : where the moving head is brought to a
deceleration
C. Acceleration-Decceleration injury: combination of the above ; leads
to diffuse brain damage
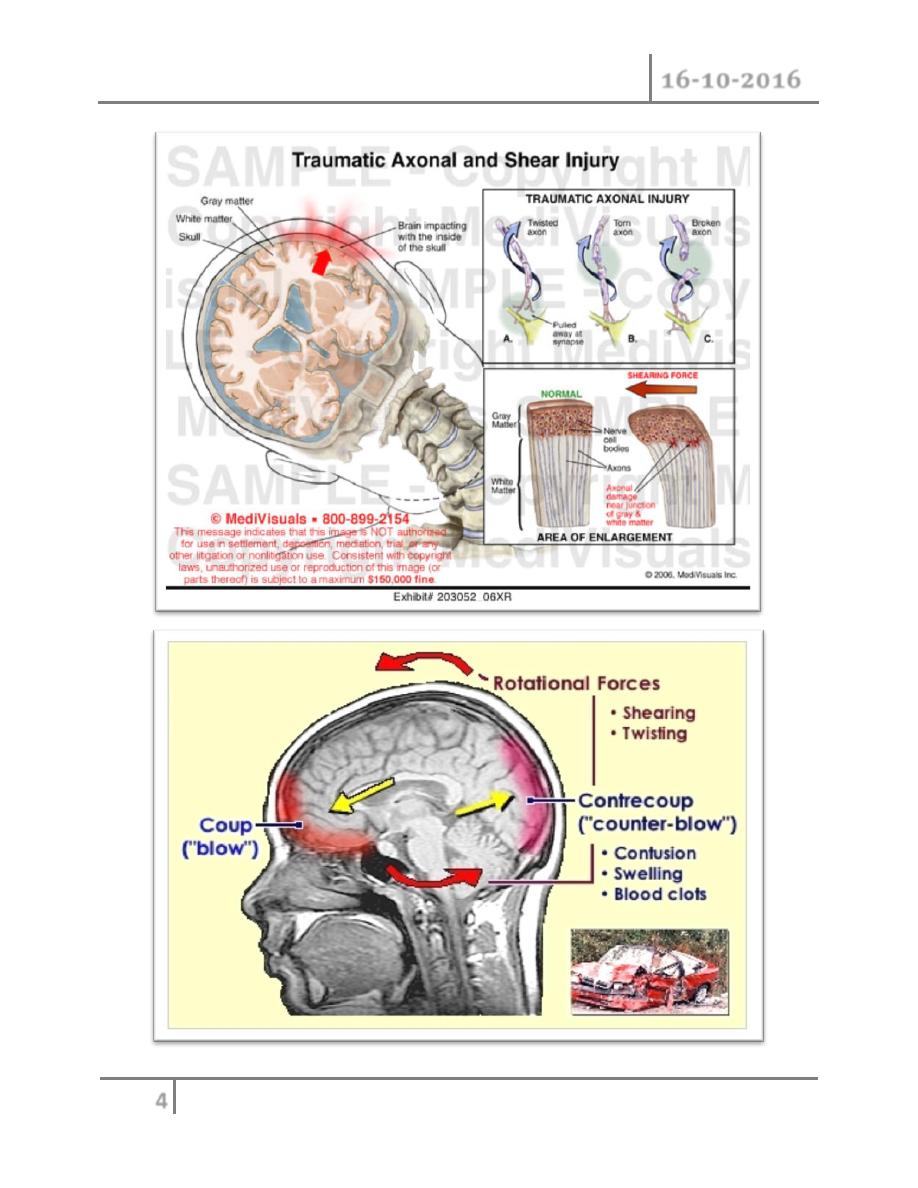
D. Rotational injury : we get eccentric movement of gray and white
matter of brain with different velocities ; leads to cutting and shearing of
the connecting fibers between the two layers . it is the
most serious
2-Penetrating injury
o The head is hit by sharp object like knife , bullet , missle; lead to compound
depressed fractures
o Fracture to the base of the skull when occurred : will involve the paranasal
sinuss , there will be tear to the dura matter also
Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
3
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
o It is of open type
o Damage includes : scalp , skull , meninges , and brain
o Damage to the brain will be either :
1- Primary ( complicated ) : due to direct effect of the trauma
2- Secondary ( non-complicated ) : due to complications following trauma
like : infections ,edema, intra-cranial hemorrhage ( ICH )
Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
4
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
5
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Management of head injury
If the patient presented with shock :
- think of other associated injuries ( like chest , abdomen ) because head
injury alone doesn’t cause sever bleeding
- Deal with the shock , do ABC to the patient in addition to head injury
management
ž
Investigations:
ž
1-Skull X-ray : A-P view , lateral view , towns view ( patient's head 60
0
raised up
) , to paranasal sinuses .
ž
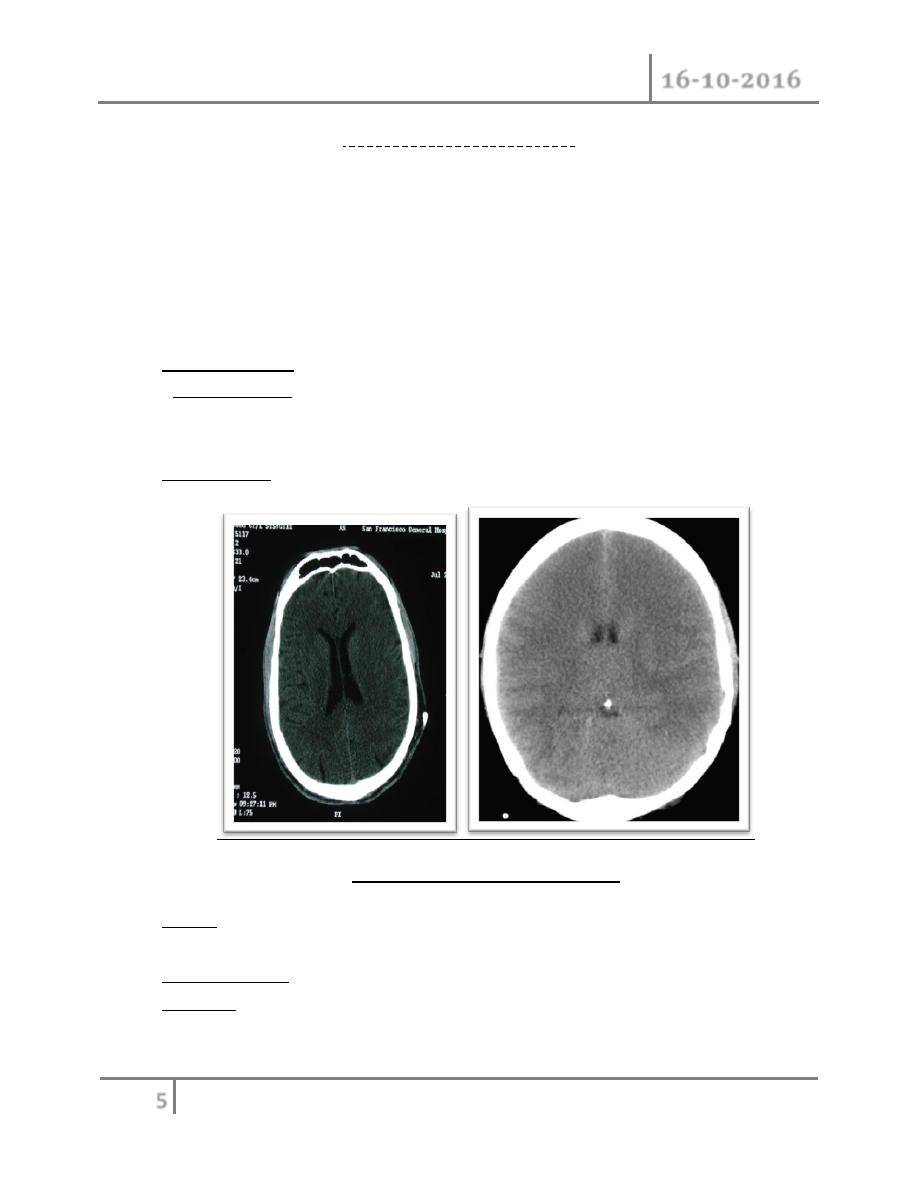
2-CT-Scan: inv. of choice
ž
ž
( Normal Vs. edematous brain )
ž
3-MRI have limited role especially in tired patient because it take more time
than CT-scan , and in head injury we are dealing with soft tissue ( brain )
ž
4-Angiography
ž
5- EEG
to know whether the patient reaches a state of brain death or not
Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
6
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Management of patient with uncomplicated head injury
- Taking a history in head injury
o Mechanism of injury
o Loss of consciousness or amnesia
o Level of consciousness at scene and on transfer
o Evidence of seizures
o Probable hypoxia or hypotension
o Pre-existing medical conditions
o Medications (especially anticoagulants)
o Illicit drugs and alcohol
Then ; think about whether you must admit the patient to hospital or managing
him in an outpatient .
-Indications for admission of a patient with H.I. :
ž
ž 1- unconscious patient or conscious but he didn’t remember the trauma
ž which indicates a brief loss of consciousness
ž 2-skull fracture revealed by x-ray
ž 3- patient on :
ž - epileptic drugs
ž - anti-coagulant drugs
ž 4- convulsions after trauma
ž 5- patient with neurologic deficit like paralysis
ž 6- Persistent vomiting and headache
ž 7- Doubtful cases like : - small child ( we can't take history from him )
ž - Alcoholic patient
ž
-Then after admission we do :
1-Observation of :
ž A- Level of consciousness : according to Glasgow coma scale (GCS)
- Best score is 15/15
- Worst score is 3/15

Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
7
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Glasgow coma scale :
1-
Eyes open
Spontaneously ( 4 points )
To verbal command ( 3 points )
To painful stimulus ( 2 points )
Do not open ( 1 point )
2-
Verbal
Normal oriented conversation ( 5 points )
Confused ( 4 points )
Inappropriate/words only ( 3 points)
Sounds only ( 2 points )
No sounds ( 1 point )
Intubated patient ( T )
3-
Motor
Obeys commands ( 6 points )
Localises to pain (5 points )
Withdrawal/flexion ( 4 points )
Abnormal flexion (decorticate) (3 points )
Extension (decerebrate) ( 2 points )
No motor response ( 1 point )
B- Pupil
ž - If unilat. dilated : indicate ICH at that side so you must interfere
ž - If bilat. dilated : indicate midbrain damage ( 100% mortality )
- If bilat. pinpoint : indicates pontine hemorrhage after exclusion of
ž morphine toxicity
-dilated with trauma to that side of the eye : not very serious
ž because it may be due to that trauma
C- Vital signs :
1- Pulse rate : changeable ; during 1
st
hour after injury : tachycardia ,
then return to normal level , if not ( bradycardia occurred ) : very
serious indicates elevated intracranial pressure , so must interfere

Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
8
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
immediately to avoid loosing the patient
2- Blood pressure : usually increases with / without increased ICP
3- count respiratory rate and observe type of respiration
4- Do blood gases analysis
ž
ž
D- CNS signs (focal signs) : by doing full neurological examination
tone, power, sensation, reflexes
E- Signs of base of skull fracture
o Bilateral periorbital oedaema ( raccoon eyes )
o
Battle’s sign (bruising over mastoid)
o Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea or otorrhoea
o Haemotympanum or bleeding from ear
ž
ž
Manage according to severity :
ž

Head Injury Dr. Ali Al-Shalchy
16-10-2016
9
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
2- Nursing care
ž A-Airway : must be sure that the airways are patent
ž Interfere according to the severity of injury , do either :
ž -airway cleaning from blood , foreign body , retracted tongue
ž - put mouth piece
ž - endotracheal intubation
ž - tracheostomy
B- Management of restless patient : do as simple as possible ; either give
diazepam , Phenobarbital or nothing
ž C- Sphincter care: put drain ( urinary catheter ) ; it is imp. because :
ž - in case of patient can't move
ž - to count urinary output
ž D- Skin care: to prevent bedsore , done by : changing patient's posture
E- Feeding:
ž
- I.V fluid in the first day (
may be more but not fore more than 72
hours
)
ž
- Then put N-G tube and start high calorie balanced diet until
swallowing reflux are returned so remove N-G tube
ž
ž
F- Antibiotics
- Used in cases of catheterization , chest infection
- Steroids are not used in case of head injury because :
1- It can mask the picture
2- It can cause expansion of small hematoma between the dura
matter and skul
Indication for surgery :
1- simple stiching.
2- open H.I. penetrating .
3- I.C.H
#END of this Lecture …
