Lecture 2
Immunoglobulin

Objectives;
To study the secretary IgA
To know the structure & functions of IgM
The antigenic receptor of B lymphocyte
The role of IgE in Atopy
The difference between Isotype, Allotype &
Idiotype
Anti-idiotype Ab
Characterstic of specific Immune response
The difference between primary &
secondary Immune Response

IgA
Constitute 15% of total serum Ig
Main Ig in
the external secretions
as saliva
tears breast milk
Subdivided into IgA1 & IgA2 subclasses
It has 2 forms ;
1-Monomeric in the blood
2- dimeric in the external secretions

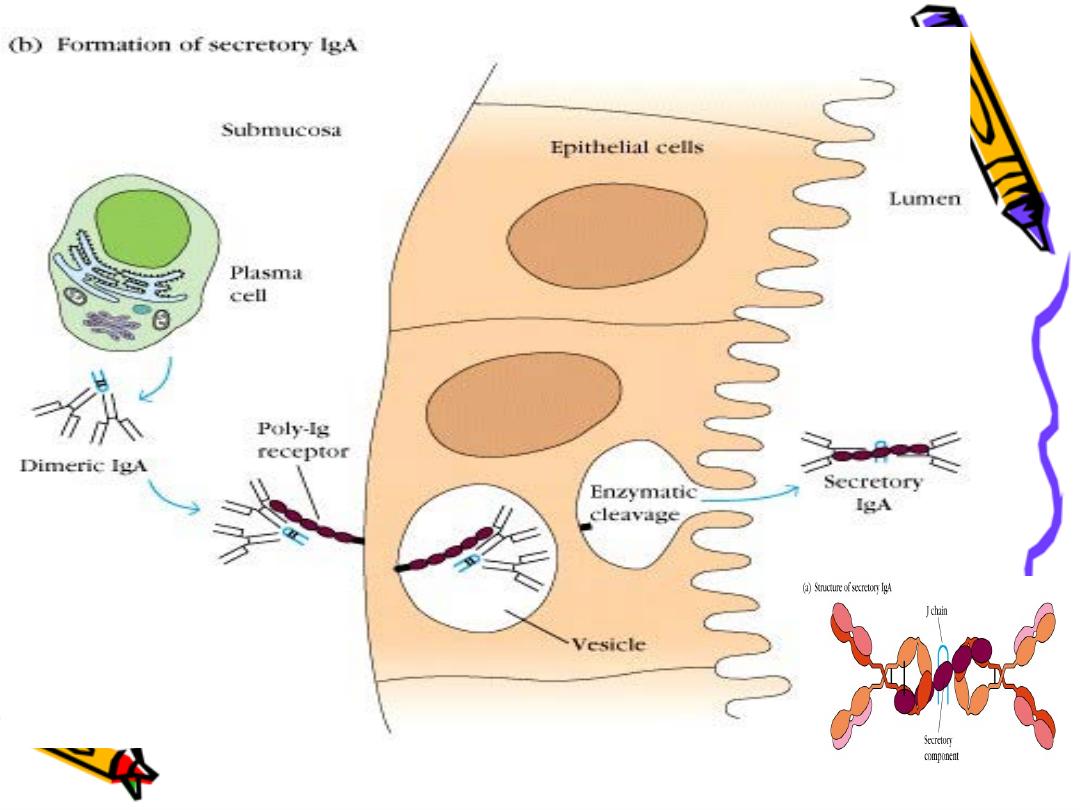
Dimeric IgA
•
IgA synthesized by plasma cell as monomeric
one in the submucosa which will be combine
with another monomeric IgA by a polypeptide
J chain to form dimeric IgA this will be
protected by a secretary piece from the
secretary epithelium to form the
secretary IgA
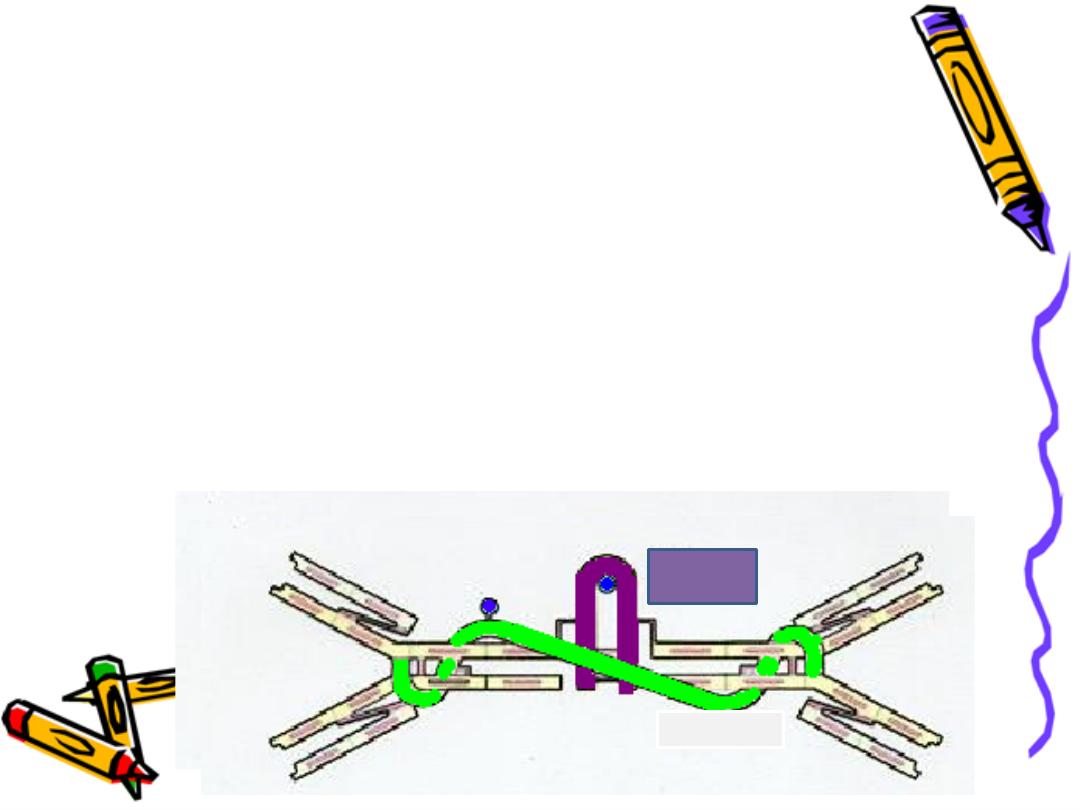
Secretory piece(
SP
):
. Produced by
mucosa epithelial cells
.
Secretory IgA (sIgA)
. Functions:
protect sIgA, resist proteolysis in
extra secretory liquid.
IgA
J chain
SP
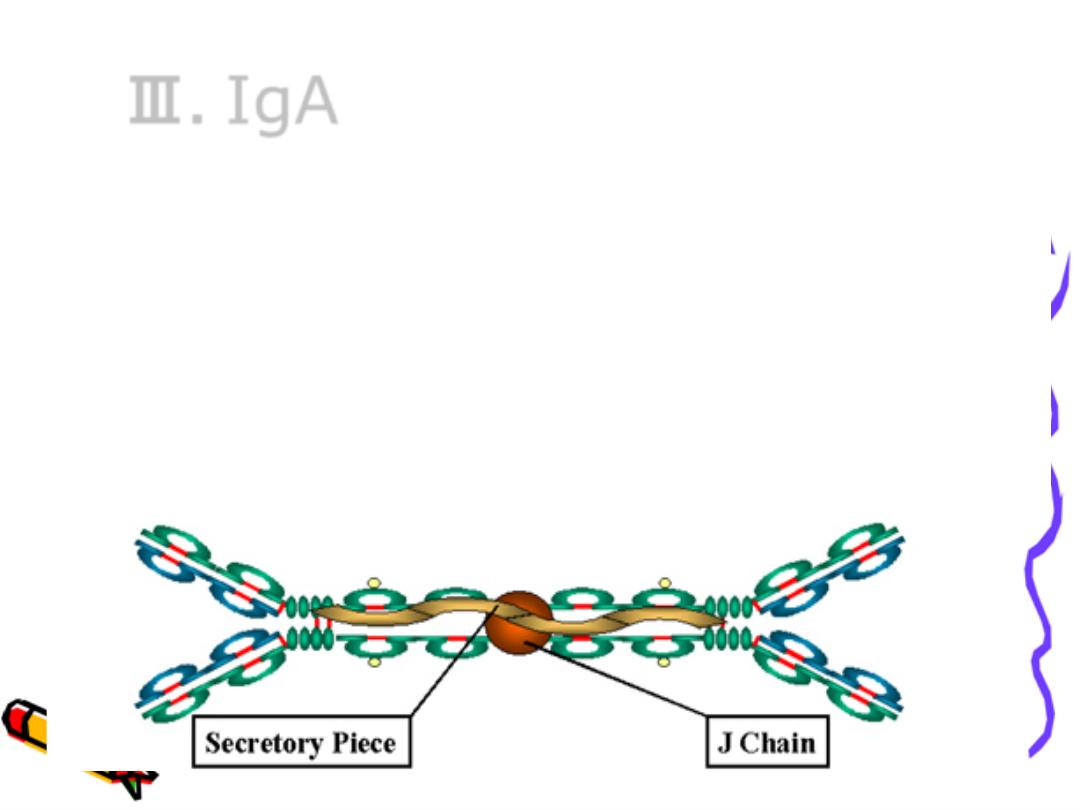
Ⅲ.
IgA
1. Two types
Serum type
:
monomer
Secretary type(sIgA)
: dimer
2. Two subclasses:IgA1,IgA2

Functions of secretary IgA
•
Activation of the complement through the
alternative pathway
•
Blocking & Neutrilization
•
opsonization

IgM
•
Constitute 10% of total serum Ig
•
Its molecular weight 900 000 (
Heavy
)
•
It has 2 forms
1-Monomeric form on the surface of B
lymphocytes as antigen Receptor together
with IgD
2-
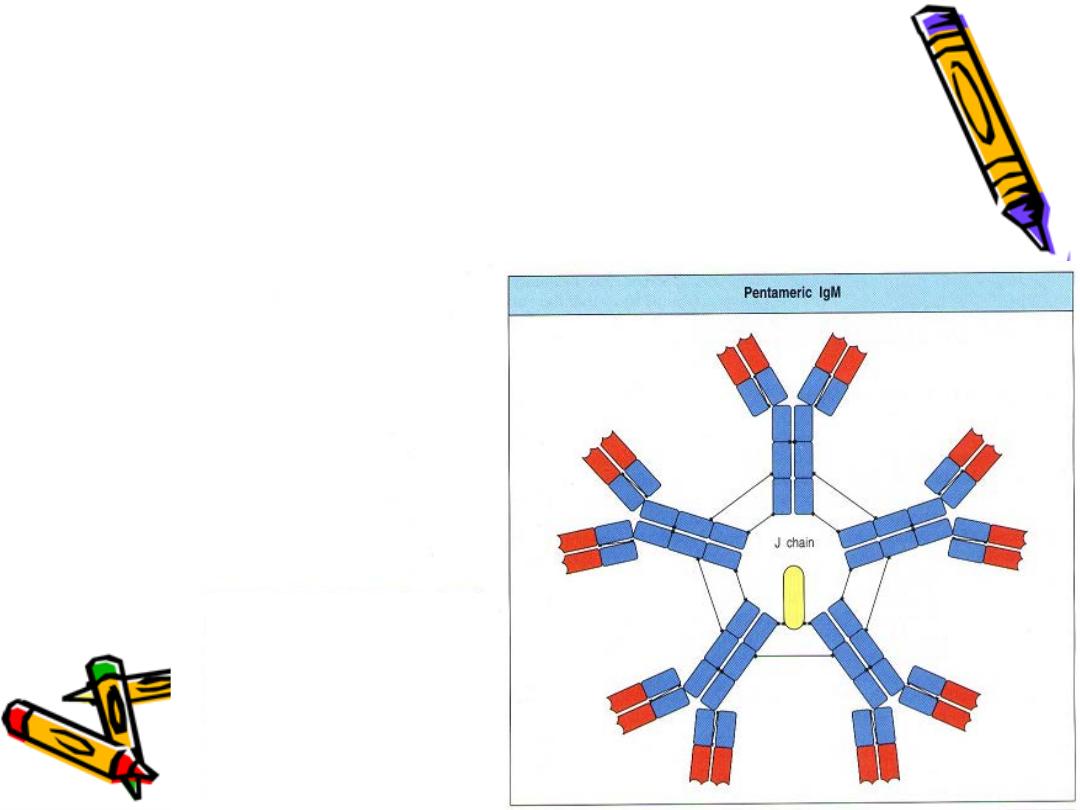
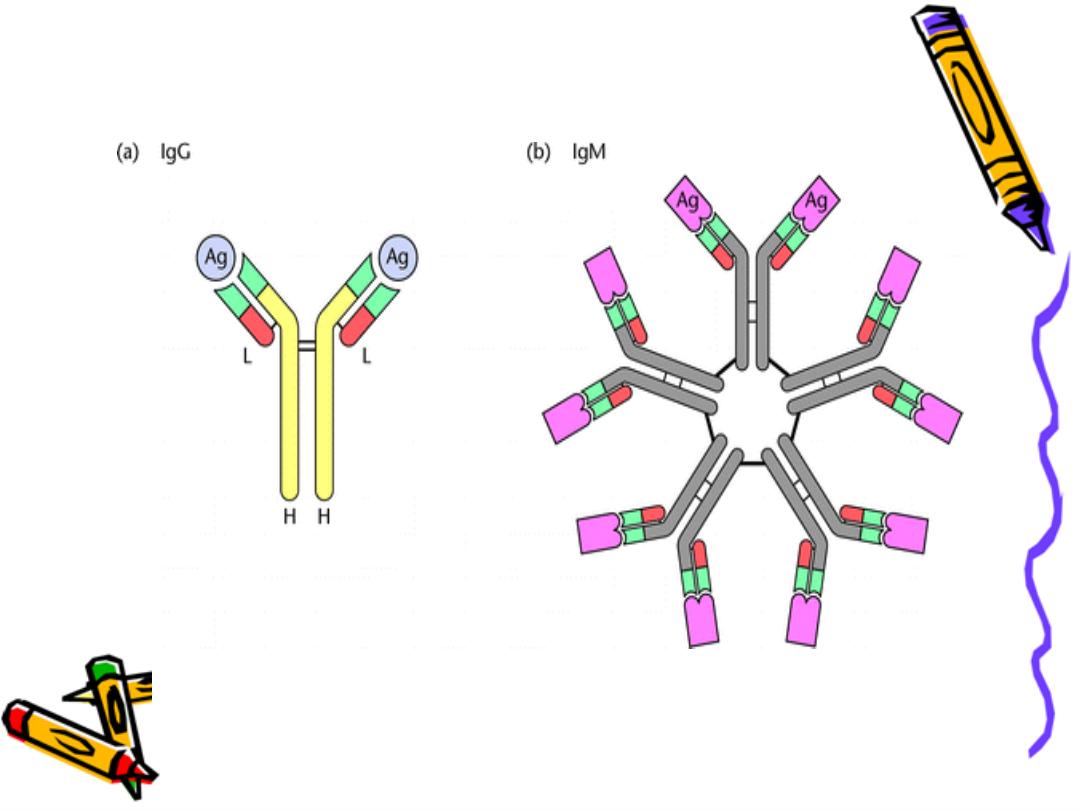
pentameri
c IgM 5 monomeric connected
by J chain
Ⅱ.
IgM
1. Highest MW:pentame ,10 FAB
Pentameric IgM

•
IgM has no hinge region replaced by an
additional domiain(CH2)---CH3,CH4
•
Pentameric IgM has 10 FAB so it is the most
agglutinating & complement fixing Ab
•
It is the main Ig in the primary immune
response
•
It is the 1
st
Ig synthetized by the fetus
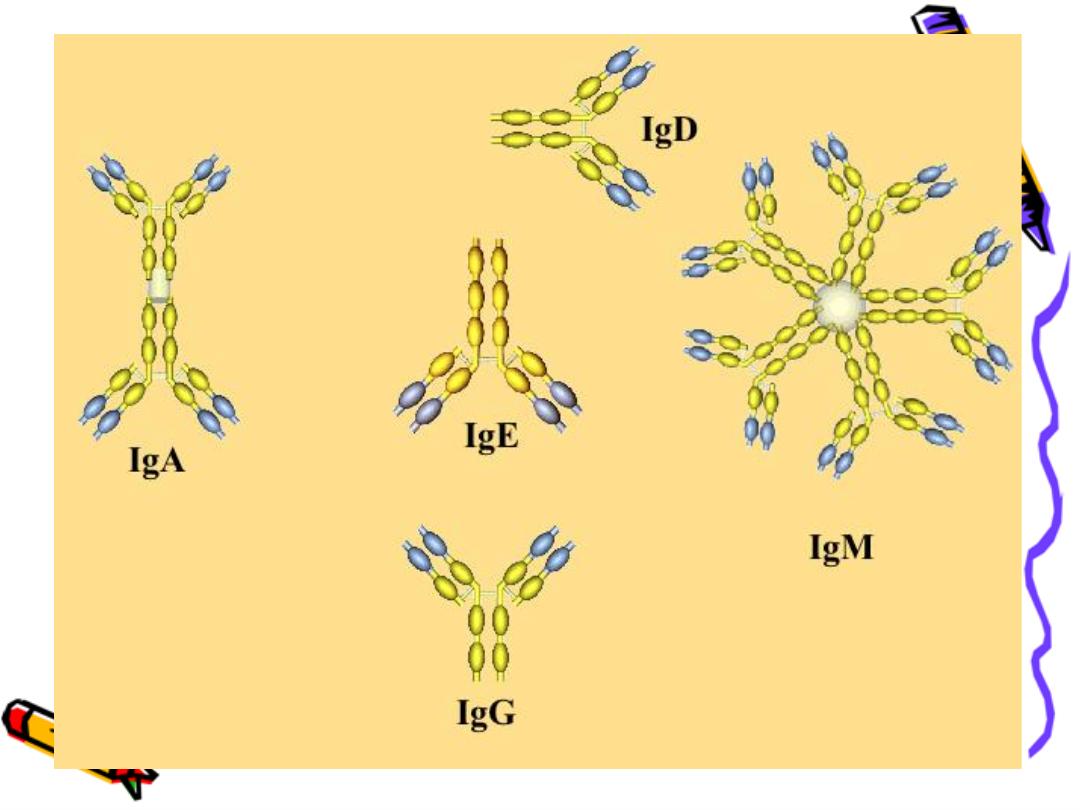

IgD
•
Very low concentration in the blood less than
1%
•
Short half life 2-3 days
•
Present on the surface of B lymphocyte
together with monomeric IgM as a
surface
antigen receptor of B lymphocyte
•
Immature B cell only IgM on its surface
•
Mature B cell IgM+IgD on its surface

IgE
•
0.002 % of serum Ig ( detection by Elisa)
•
In atopic patient the level increase by
handreds
•
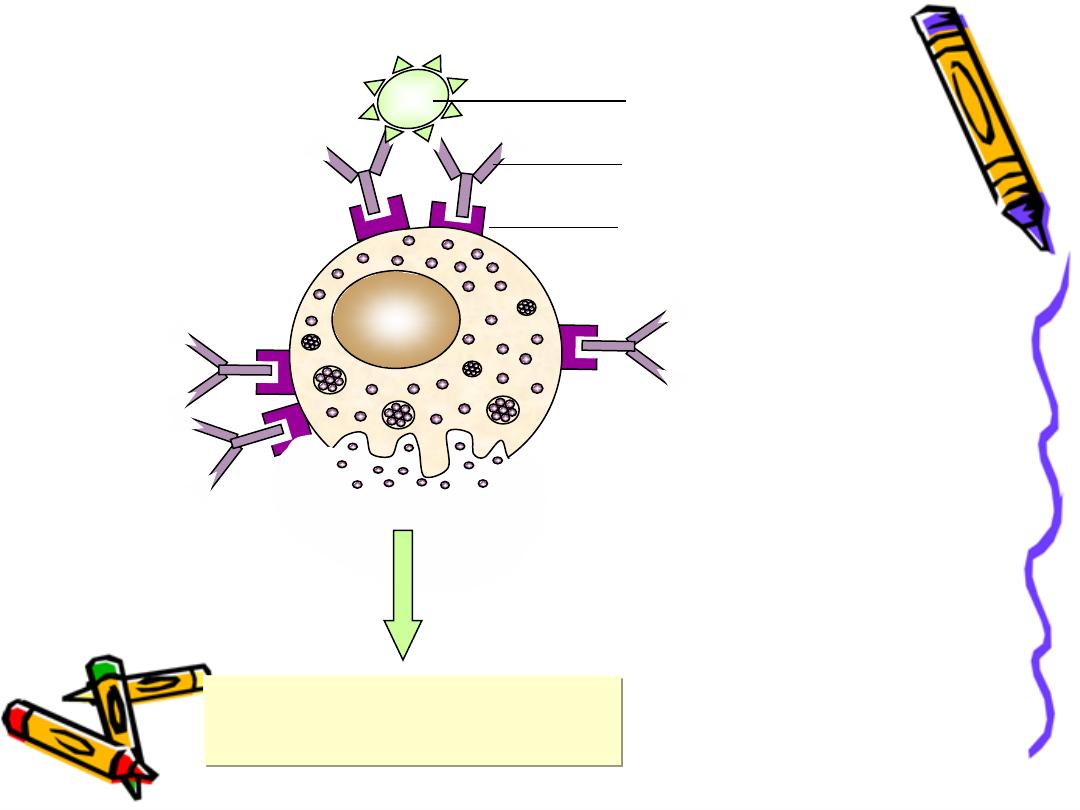
IgE also called
Reagenic or homocytotropic Ab
because of its ability of binding to FC
receptors on the surface of
Mast cells
&
basophiles
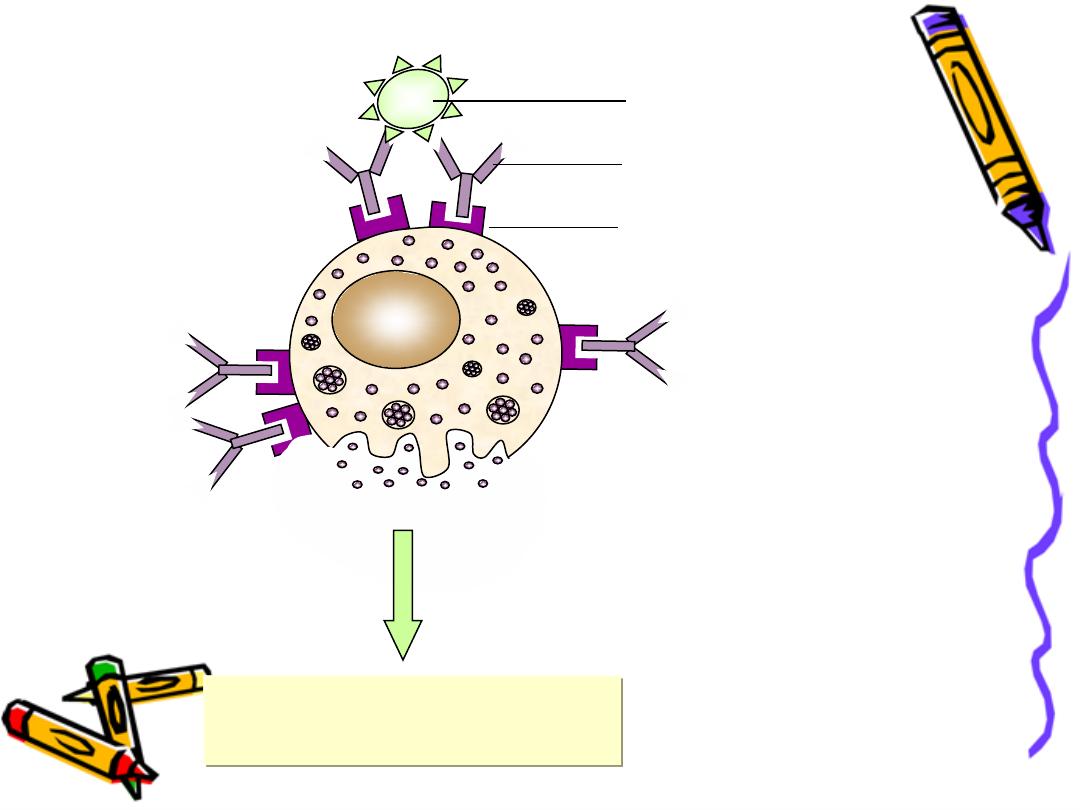
Fc
εRI
degranulation
IgE
allergen
inflammation

Functions of IgE
•
Triggering an acute inflammatory reaction
•
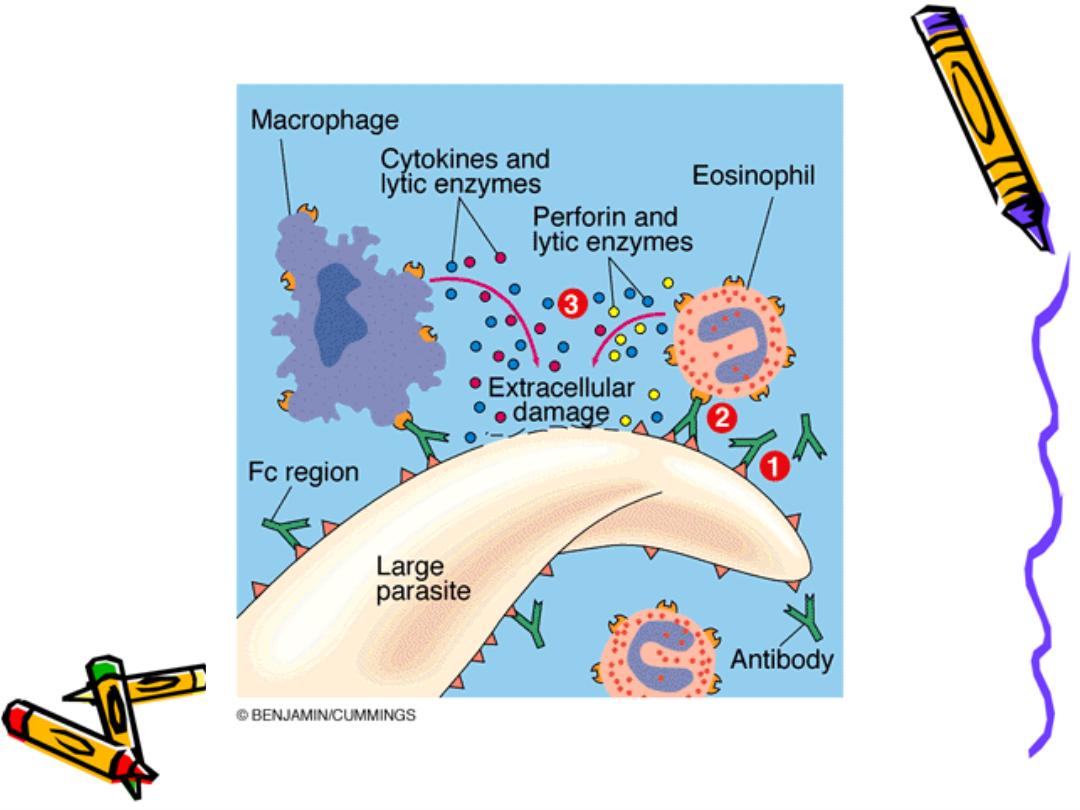
Has the ability to bind to FC receptor on
eosinophils so important against parasitic
infections
eosinophils contain granules that realize cat
Ionic proteins which are toxic to the parasites

IgE increases in
•
Parasitic infections
•
Atopic patients
IL 4 causes switching of Ig to IgE
IL 5 causes eosinophilia
Fc
εRI
degranulation
IgE
allergen
inflammation

Variants of Ig
•
Isotype
all classes ,Subclasses & forms of Ig
which present in normal individual
•
Allotype existence of allelic forms , single a.a.
variation in the peptide chain of Ig ( genetic
marker) IgG =GM, IgA=AM
•
Idiotype
each Ig has its own antigenic
determinant area against which an anti-
idiotype Ab will be formed (Idiotype
•
antiidiotype network)

Characteristics of sp. Immune respond :
1-Discrimination (distinguish) between self &
Foreign Ag
Any Ag when reach the lymphoid tissue during
pre-natal period suppress any further
immunological response to that Ag in future
((self))
_
colonel deletion theory
_
During embryonic dev. All T & B lymphocytes that
carry auto –reactive receptors for self Ag
( (
Auto-reactive cells
) will be deleted by
apoptosis
self tolerance

2- specificity
Ab react specifically with Ag that causes its
production ,sometimes can react with similar
not identical = cross reaction
B haemolytic streptococci can lead to
rheumatic
heart dis
. Because cross reaction between
bacteria Ag & valve tissue in some individuals

3-clonality
We have more that 10 T & B lymphocytic
clones (group) each clone with different Ag
receptor, when the Ag enter the body
lymphocytes bearing receptors that fit the
epitope best are stimulated to divided
(clonal
selection theory)
this response is called
primary immune response
8
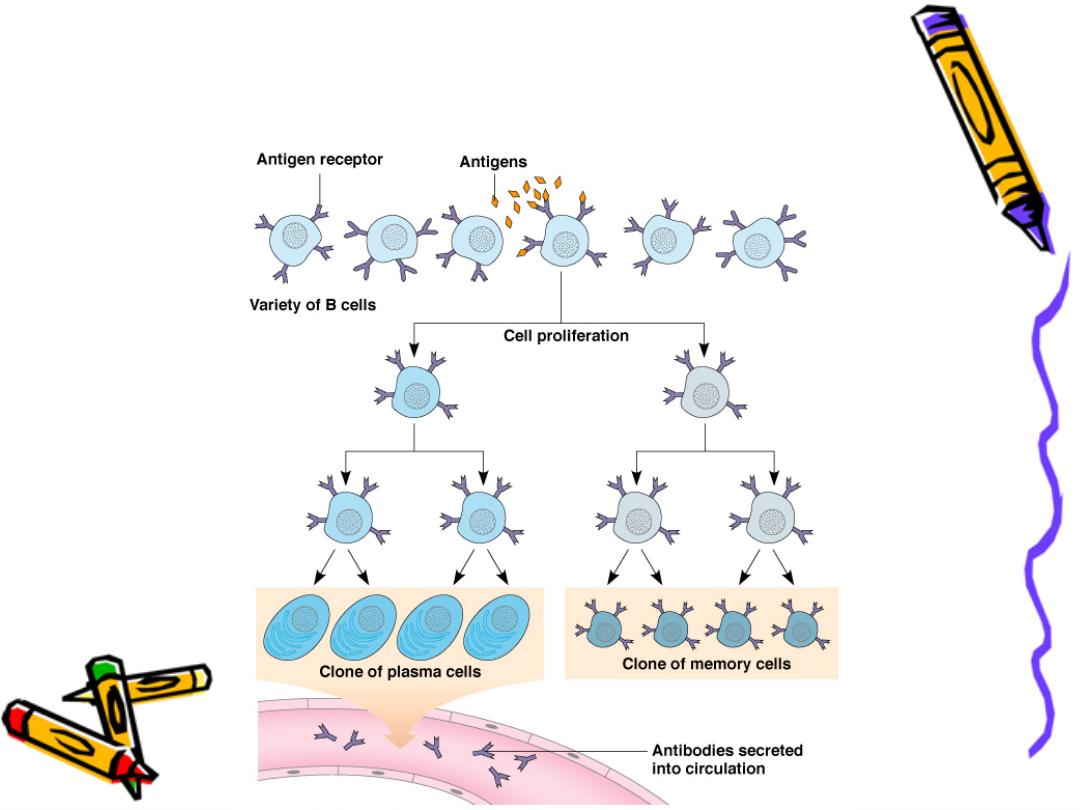
Clonal Selection of B Cells is Caused by
Antigenic Stimulation

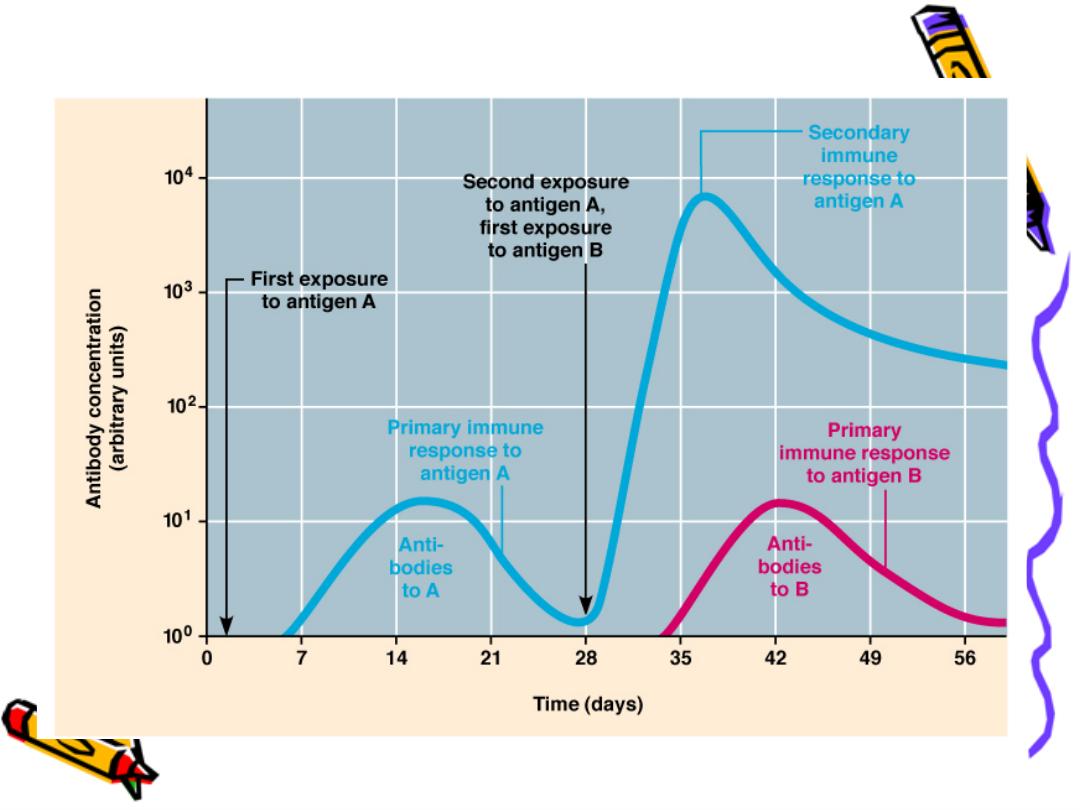
4-Anamnest response :(memory)
The primary I.R. (1
st
exposure)
a-Lag phase (7days) Ab level is zero (time for
finding appropriate Ag receptor) depend on
nature ,routs, immune state
b-Log phase Ab(mainly IgM) start to appear &
increase logarythemly
c-Plateau phase
d-decline phase

Secondary I.R. (2
nd
exposure) there is memory
cell so no lag phase ,Ab titer quickly shooting
up 10-100 times
*There is genetic switching from IgM in the pri.
I.R. to IgG in the 2
nd
I.R.

Primary I.R.
Secondary I.R.
* There is lag phase
*No lag phase
*IgM class
*Ab of IgG class
*Low affinity Ab
*Ab of high affinity
*Ab titer is low
*Ab titer is high
*The host exposure for the
1
st
time so no memory cell
*Host exposure for the 2
nd
time there is memory cell
*Ab titer decline rapidly
*Ab titer decline slowly

Best example is the
vaccination
we give booster
Doses(multiple doses) to shift the I.R. from
primary to secondary I.R.
