Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
1
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
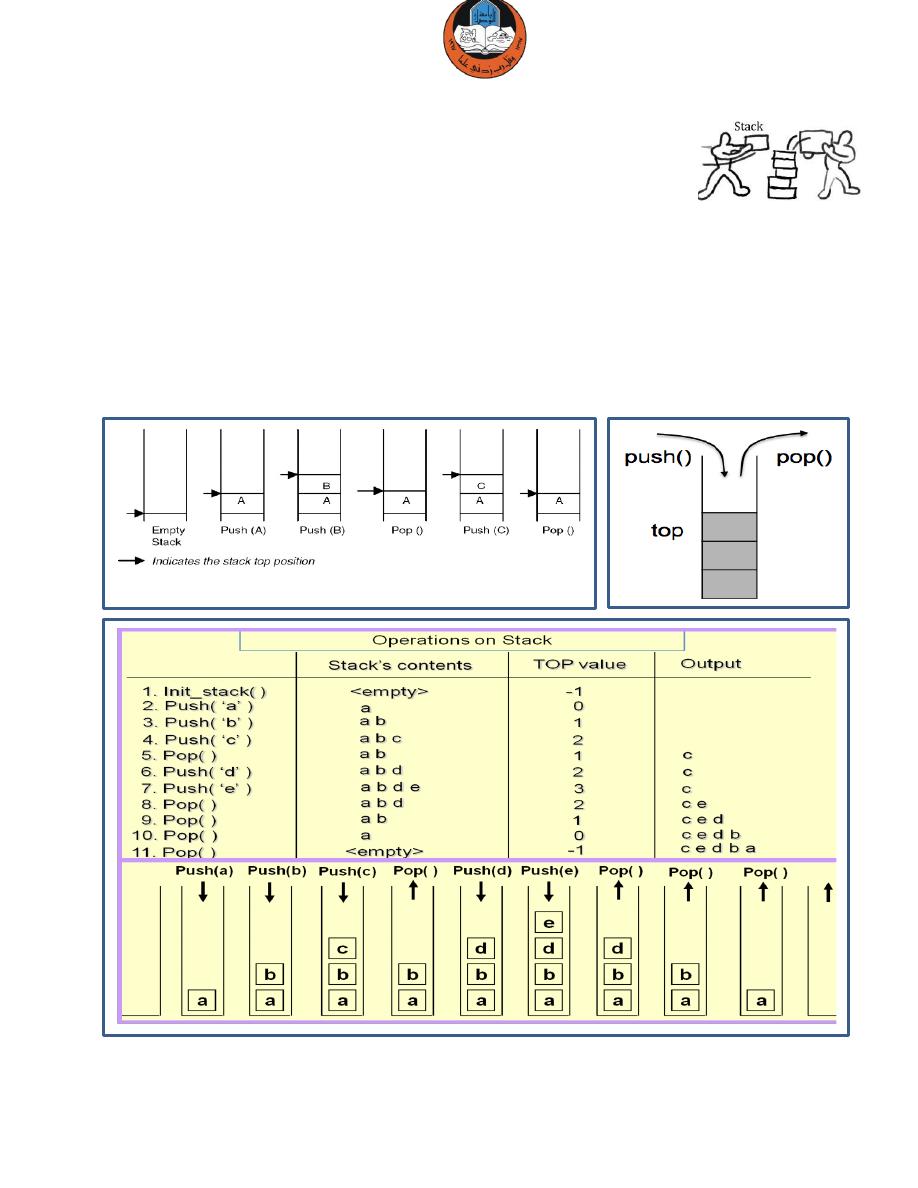
Stack
A stack is a list of data that follows 2 rules:
1. Data can only be accessed by removing the top
(pop)
.
2. A new data element can only be added to the top of the stack
(push)
.
This means that all data in the middle of the stack is hidden.
Note that the last item pushed onto a stack is always the first that will be popped
from the stack. This property is called
last in, first out
, or
LIFO.
In a stack data structure, all insertions and deletions of entries are made at one
end, called the
top
of the stack.
A
stack
is particularly useful in applications involving reversing
Figure: Stack Operation.

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
2
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
Program #7: write a program to implement enter 5-element and print the reverse
using stack.
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#define size 5
int top=-1;
int a[size];
///EMPTY FUNCTION
int empty()
{
if(top==-1)
return(1);
else
return(0);
}
// FULL FUNCTION
int full()
{
if(top==size-1)
return (1);
else
return(0);
}
// PUSH FUNCTION
void push(int k)
{
if(full())
cout<<" FULL STACK";
else
{
top++;
a[top]=k;
}
}

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
3
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
// POP FUNCTION
int pop()
{
if(empty())
cout<<"EMPTE STACK";
else
{
int c=a[top];
top--;
return c;
}
}
// For Main
void main()
{
int i,k,p;
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cout << "Enter a Number to push: ";
cin>>k;
push(k);
}
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
p=pop();
cout<<p<<endl;
}
getch();
}

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
4
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
Program #8: write a program to implement a stack of 5-elements with the choice
to push or pop the stack.
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#define size 5
int top=-1;
int a[size];
///EMPTY FUNCTION
int empty()
{
if(top==-1)
return(1);
else
return(0);
}
// FULL FUNCTION
int full()
{
if(top==size-1)
return (1);
else
return(0);
}
// PUSH FUNCTION
void push(int k)
{
if(full())
cout<<"FULL STACK";
else
{
top++;
a[top]=k;
}
}
// POP FUNCTION
int pop()

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
5
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
{
if(empty())
cout<<"EMPTEY STACK";
else
{
int c=a[top];
top--;
return c;
}
}
// For Main
void main()
{
int i,k,p,d=1;
cout<<"1:Push\n2:Pop\n3:Exit\n";
while(d<3)
{
cout<<"\nChoose a number: ";
cin>>d;
if(d==1)
{
cout << "\nEnter a Number to push: (TOP="<<top<<") ";
cin>>k;
push(k);
}
if(d==2)
{
p=pop();
cout<<"\nPop result is: (TOP="<<top<<") "<<p<<endl;
}
if(d<1 || d>2)
break;
}
getch();
}
Homework5:
Write a program to implement 5-element stack to read and print letters with the
choice to push and pop the stack.

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
6
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
Structure
The struct is a very versatile data type. It is a collection of components of any
data type in which the components are given names. The components of a
record are called fields or members. Each field has its own field identifier and
data type.
C++ has its own vocabulary in relation to the general concept of a record.
Structs are called records.
Arrays are one of the most widely used data structures in programming
languages. One downfall of using such a data type is that one must use
homogeneous data types; an array can only hold multiple items of the same
type. Structures overcome this problem by allowing the programmer to have an
unlimited number of items of different data types! Objects contained within the
structure are referred to as a member.
To define a struct, use the keyword struct followed by the name of the structure.
Then use curly braces followed by variable types and names:
struct StructName
{
type1 var1;
type2 var 2;
…
type3 var N;
};
Note the need for a semicolon at the end of the right curly brace!
The above defines a structure named “StructName”. You can use StructName
like it is a new data type. For example, the following will declare a variable to be
of type “StructName”:
StructName myVar;
To access the members (variables) within the structure, use the variable name
followed by a dot and then the variable within the struct. This is called the
member selector:

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
7
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
myVar.var1;
Here is an example structure:
struct Recording
{
string title;
string artist;
float cost;
int quantity;
};
Recording song;
Recording is a pattern for a group of four variables. song is a struct variable with
four members: title, artist, cost, and quantity are the member names. The
accessing expression for members of a struct variable is the struct variable
identifier followed by the member name with a period in between.
song.title is a string variable.
song.artist is a string variable.
song.cost is a float variable.
song.quantity is an int variable.

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
8
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
Program #9: write a program using structure to make a database for 3 students
getting their name, age and year.
#include<iostream>
#include<conio>
#define size 3
struct student
{
char name[10];
int age;
int year;
} ;
void main()
{
int i;
student a[size];
cout<<"\t\t\tEnter the information of students\n\n"<<endl;
for(i=1;i<=size;i++)
{
cout<<"\nEnter the information of student no."<<i;
cout<<"\nname: ";
cin>>a[i].name;
cout<<"age : ";
cin>>a[i].age;
cout<<"year: ";
cin>>a[i].year;
}
cout<<"\n\nYour students are: \n";
for(i=1;i<=size;i++)
{
cout<<"\n\nStudent
no."<<i<<":\nname:
"<<a[i].name<<"\nage
:
"<<a[i].age<<"\nyear: "<<a[i].year;
}
getch();
}
Homework6:
Write a program using structure to create a database of 4 workers with their
information that includes; name, year of birth and monthly salary.
Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
9
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
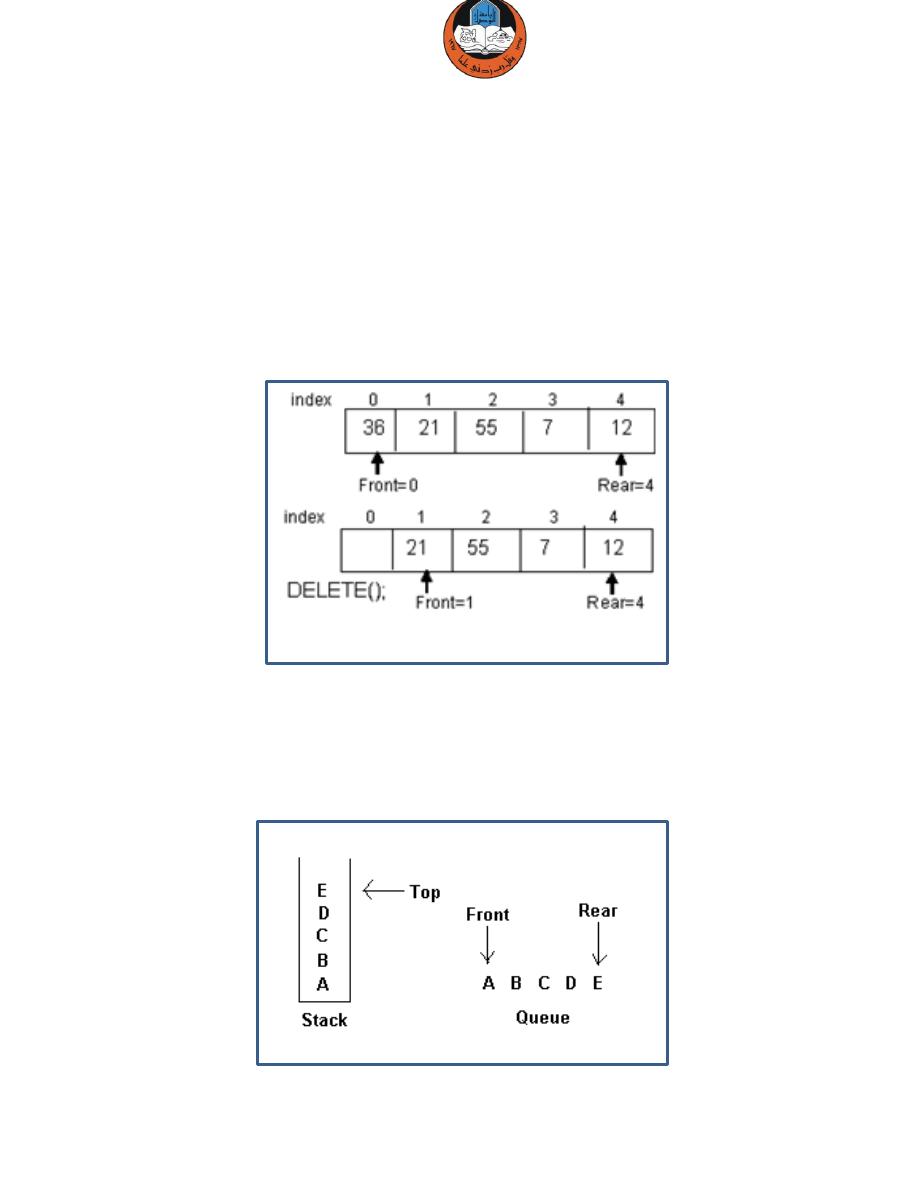
Queue
Queue is also an abstract data type or a linear data structure, in which the first
element is inserted from one end called
REAR
(also called tail), and the deletion
of existing element takes place from the other end called as
FRONT
(also called
head).
This makes queue as First In First Out (FIFO) data structure, which means that
element inserted first will also be removed first.
The process to add an element into queue is called Enqueue and the process of
removal of an element from queue is called Dequeue.
The easiest way of implementing a queue is by using an Array. Initially the front
(head) and the rear (tail) of the queue points at the first index of the array
(starting the index of array from 0). As we add elements to the queue, the rear
keeps on moving ahead, always pointing to the position where the next element
will be inserted, while the front remains at the first index.
Queue operation
Enqueue Dequeue

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
10
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
Program #10: write a program to implement the queue data structure with 5
elements.
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#define size 5
int front = -1;
int rear = -1;
int a[size];
// Empty check function
int isempty()
{
if(front == rear)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Full check function
int isfull()
{
if(rear == size-1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Enqeueu (adding element to the queue) function
void enqueue(int x)
{
if(isfull())
{
cout<<"Queue is FULL !!!No insertion allowed further.";
}
else
{
a[rear] = x;
rear++;
}
}

Lecture2: Stack, Structure, Queue.
11
2
Computer Algorithms
& Programming
Mustafa Al-Qassab
2016-2017 Kirkuk
// Dequeue (removing element from the queue) function
int dequeue()
{
int c;
if(isempty())
cout<<" Queue is Empty !!! ";
else
{
c=a[front];
front++;
return(c);
}
}
// main body
void main()
{
int x,y;
cout <<”Enter the 5 elements of the queue: “;
for(int i=0; i< 5 ; i++)
{
cin >> x;
enqueue(x);
}
for(int i=0; i< 5 ; i++)
{
y=dequeue();
cout << y << "\t";
}
getch();
}
Homework7:
Write a program to implement the queue with 6 elements with the choice to
enqueue or dequeue from the main body.
