Practical hematology
Assist.Prof. Dr.Sajeda Al-ChalabiRBC countHEMOCYTOMETER
Hemo: bloodCyto: cell
Meter: measurement/counter
Thus, it is an instrument used to count the blood cells.
It includes:
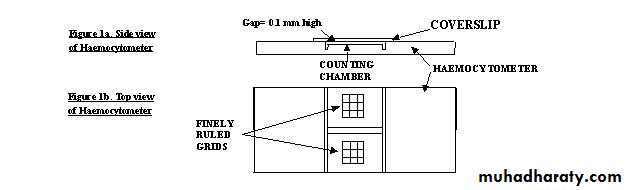
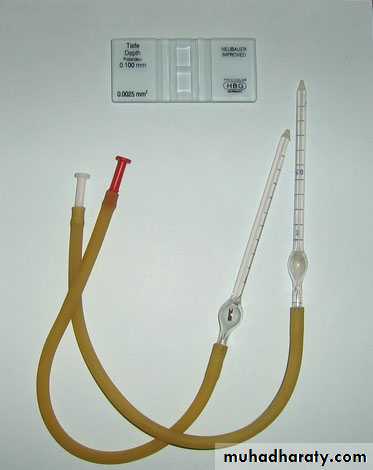
Neubauer’s slide
Cover slip
RBC pipette
WBC pipette
NEUBAUER’S SLIDE
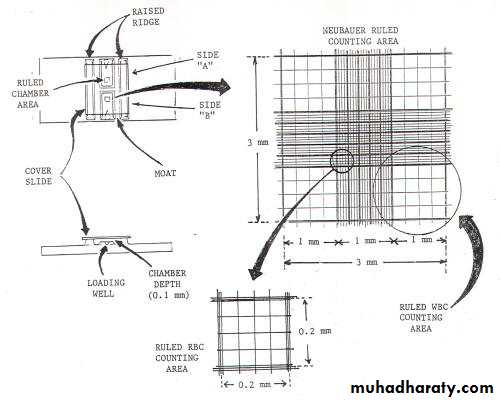
It is the name given to a thick glass slide. In the centre of the slide, there is an H- shaped groove. On the two sides of the central horizontal bar, there are scales for counting the blood cells.The depth of the scales is 1/10mm or 0.1mm.
NeubauerHemocytometer
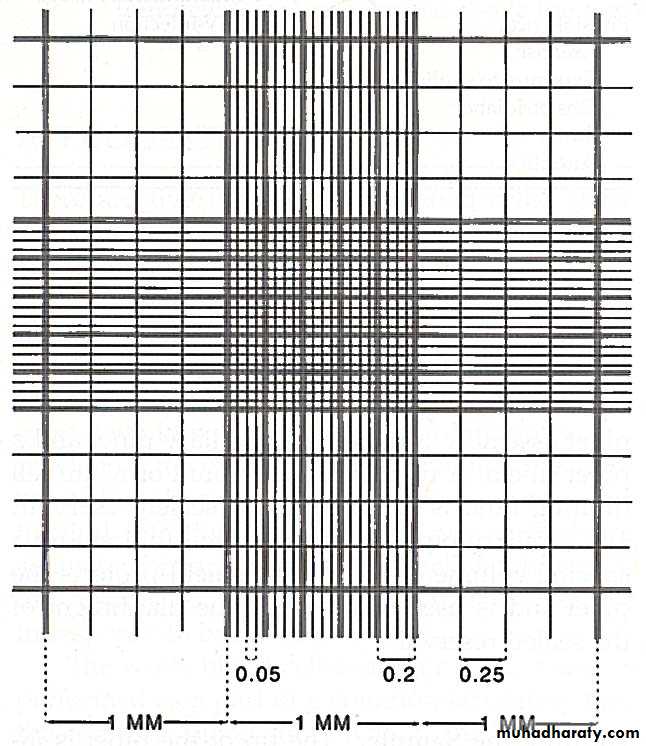
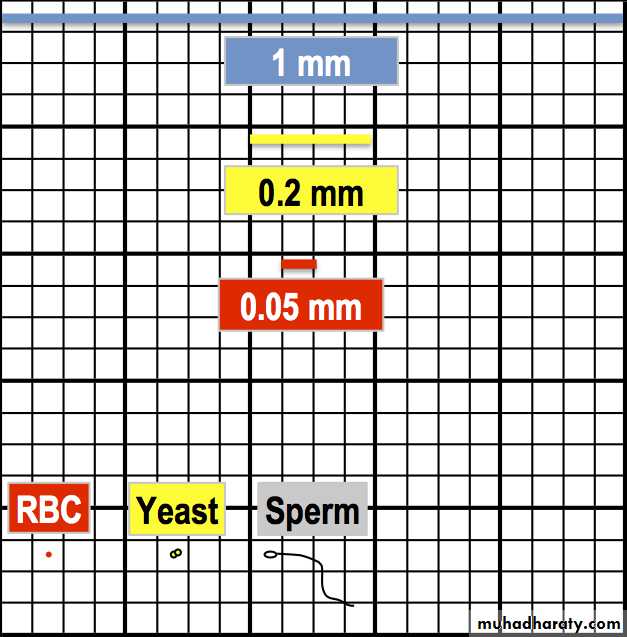
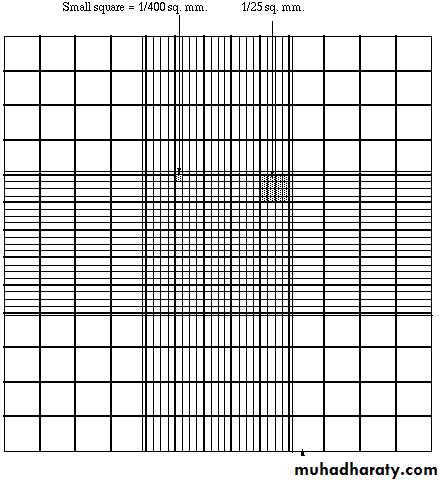
The central square is subdivided into twenty five smaller squares and each of these smaller squares is further subdivided into sixteen smallest squares.
These are meant for platelet and RBC counting.
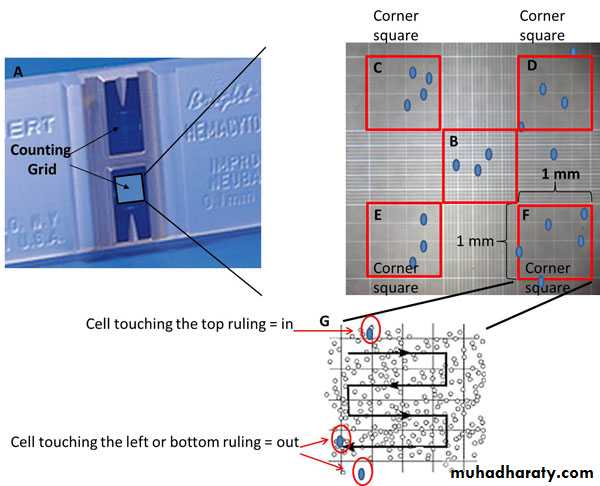
the RBCs are counted in five small squares, four of corners and one of center.
(total of 80 smallest squares)
Each of the smaller squares is further subdivided into sixteen smallest squares.
Length of one smallest square = 1/5 x 1/4 = 1/20mm
Width of one smallest square = 1/20mm
Depth of one smallest square = 1/10mm
Volume of one smallest square
= 1/20 x 1/20 x 1/10
= 1/4000mm³
Cell Counts by Hemocytometer
Procedure
For RBC counting
Blood is filled till mark 0.5 and Hayem’s fluid is then filled till mark 101.Both are thoroughly mixed and then few drops are discarded which contain just the diluting fluid in the stem. Thus, 1 portion out of 101 is discarded. So,
0.5 part of blood is in 100 parts of fluid or,
1 part of blood is mixed in 200 parts of fluid
Thus, dilution factor for RBC counting is 200.
You can count blood cells with as little as a drop of blood. Because the cell density is very high, you have to dilute .
Procedure
Before starting ensure that both the hemocytometer and its coverslip are clean by removing any dust particles with lens paper.
make sure to first place the coverslip over the counting surface before loading the cell suspension. Then place the pipette tip with your sample into one of the V-shaped wells, as in Figure, and gently expel the sample. The area under the coverslip fills by capillary action. Enough liquid should be introduced so that the mirrored surface is just covered
Procedure
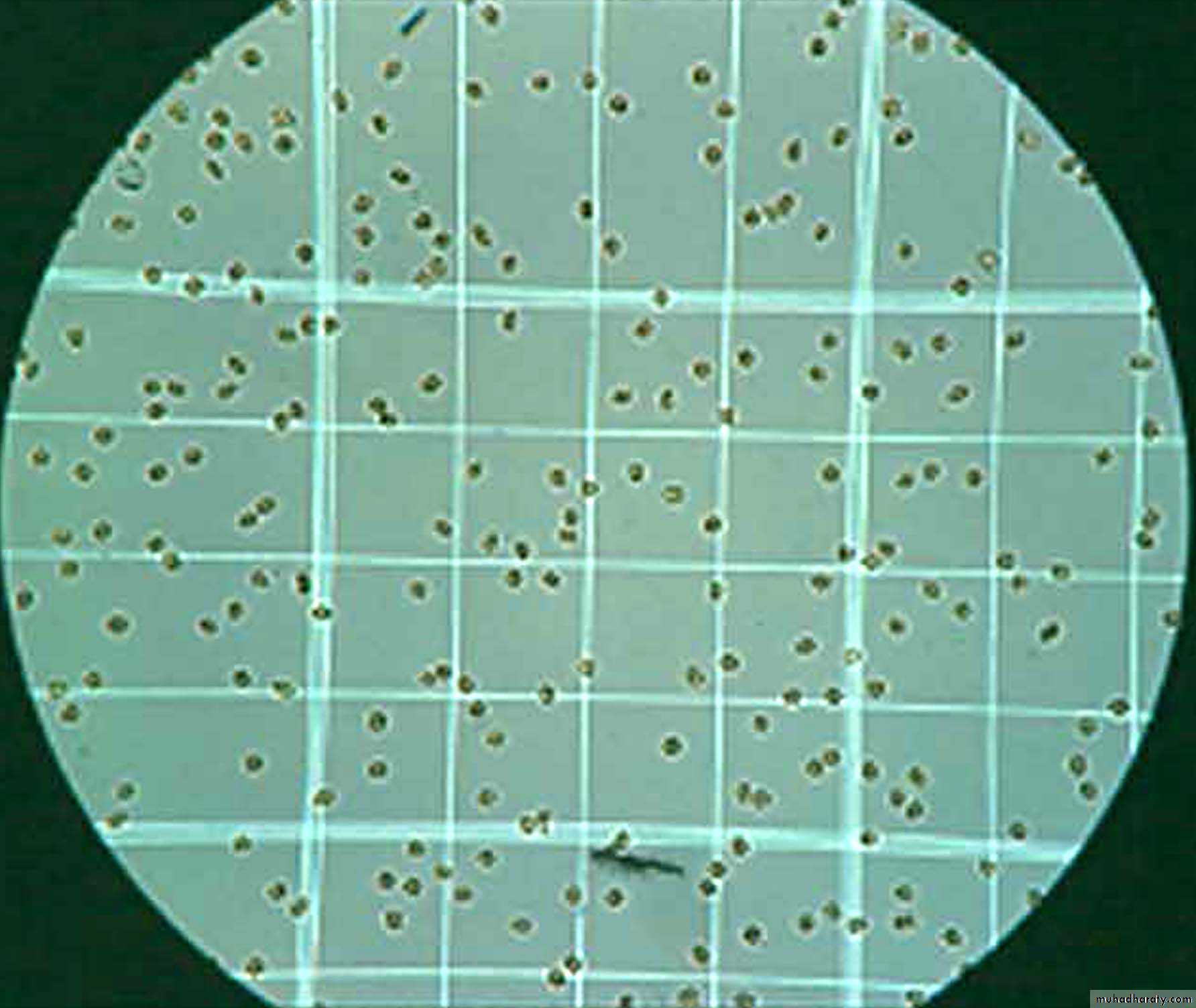
The loaded hemocytometer is then placed on the microscope stage and the counting grid is brought into focus at low power. Allow the sample to settle for a couple of minutes and avoid moving the coverslip as it might introduce air bubbles and make counting difficult
Hayem's solution
Hayem's solution contains: sodium chloride 0.5%, sodium sulphate 2.5% and mercuric chloride 0.25%. The sodium chloride to prevent hemolyses, the sodium sulphate discourages clumping of the erythrocytes and the mercuric chloride is a preservation.
FOCUSING
4X to see the general formation of slide.
10X for WBC counting
40X for RBC counting
Procedure
Counting Rule
Do not count cells touching
Bottom lineRight line
Count cells touching the upper& left lines
This is to avoid double counting.
Calculation
Number of cells/mm³=counted cells in 80 small squares ×
diluting factor ×
volume correction factor.
=N × 200 ×50=N × 10000
Normal Results
Normal RBC ranges are:Male: 4.7 to 6.1 million cells /mm³
Female: 4.2 to 5.4 million cells/ mm³
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher than normal numbers of RBCs(polycythemia)
Your RBC count will increase for several weeks when you are in a higher altitude.
Lower-than-normal numbers of RBCs may be due to
Anemia
By: Mohamad J Rawi