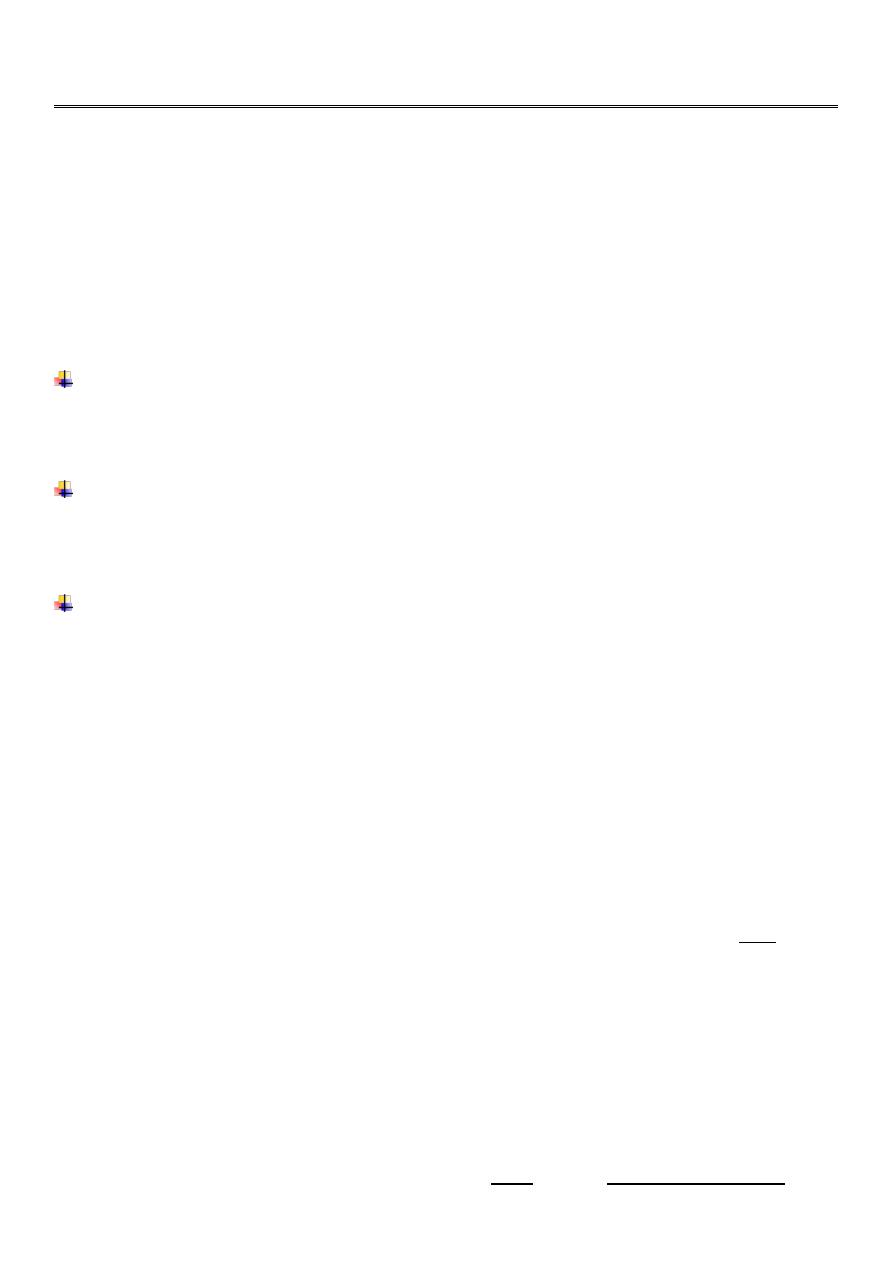
1
Fifth stage
Radiology
) Urinary)
Lec-3
د.أحمد الغبشة
5/11/2016
Obstruction of renal tract
Causes
: of renal tract obstruction
Within the lumen
Calculi
Blood clot
Sloughed papilla (papillary necrosis)
Within the wall of the collecting system
Tumor (transitional cell carcinoma)
Infective stricture (TB or Schistosomiasis)
Intrinsic PUJ obstruction
-Extrinsic pathology:
Tumors (CA cervix or recto-sigmoid junction).
Retroperitoneal fibrosis., Aberrant renal artery or retrocaval ureter.
Renal calculi (stones):
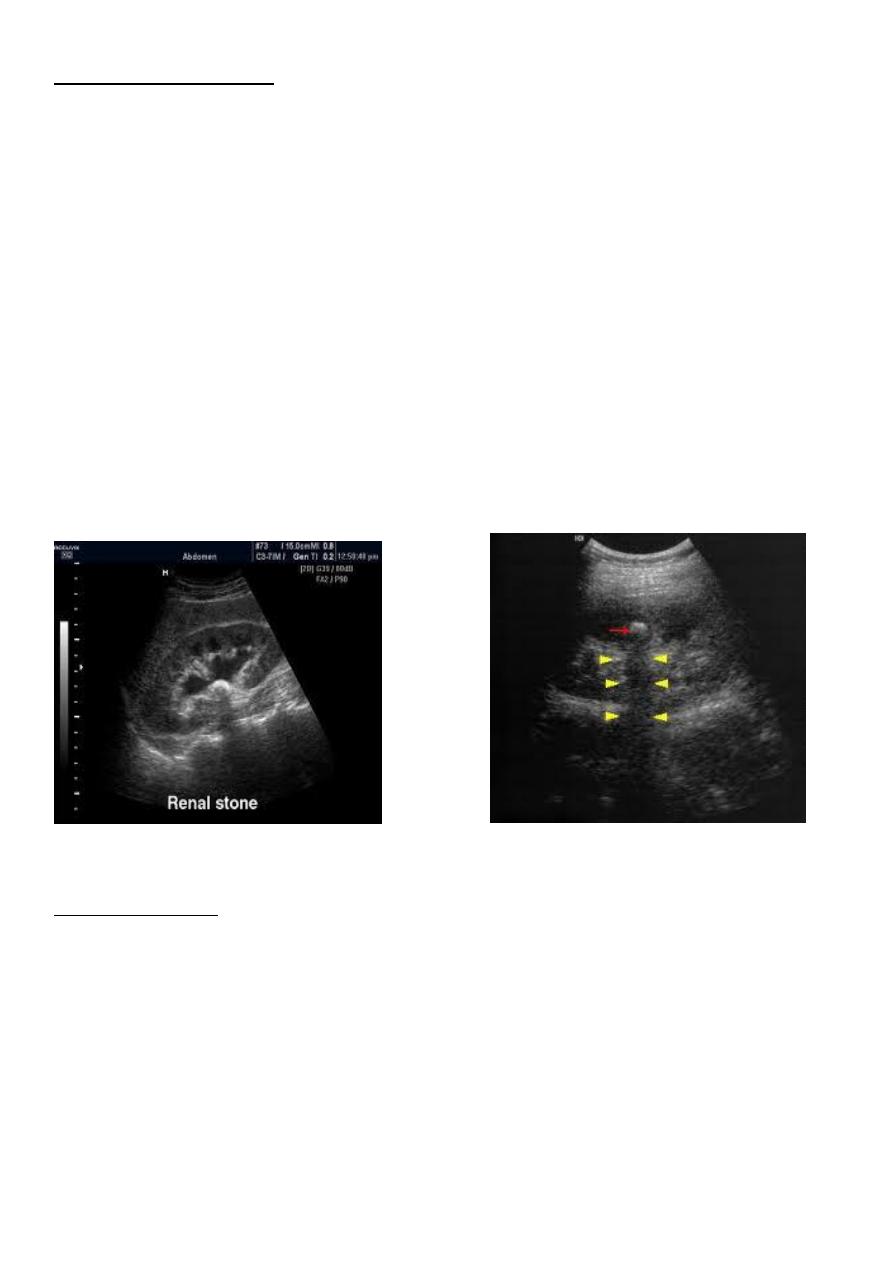
Over 90% of calculi are radiopaque on plain films and virtually all on CT as very
sensitive for detection of calculi, even those that appear radiolucent on plain film.
Most of these stones are a mixture of calcium oxalate and phosphate.
Only pure uric acid and xanthine stones are radiolucent on plain x-ray but CAN be
identified by CT or US , uric acid stones are associated with increased uric acid
excretion in urine as in gout.
Principal feature is dilatation of the pelvicalyceal system and ureter.
• The degree of dilatation depends on chronicity (long standing obstruction=more
dilatation).
• The dilatation is down to the level of pathology
The prime objective of imaging is to determine the level and the cause of obstruction.
2
Ultrasound findings
1-Dilatation of the P.C.S. appears as multilocular fluid collection within central echo
complex.
-With more severe distention, dilated calyces appear as Multiple cysts but communicating
with each other unlike true cysts.
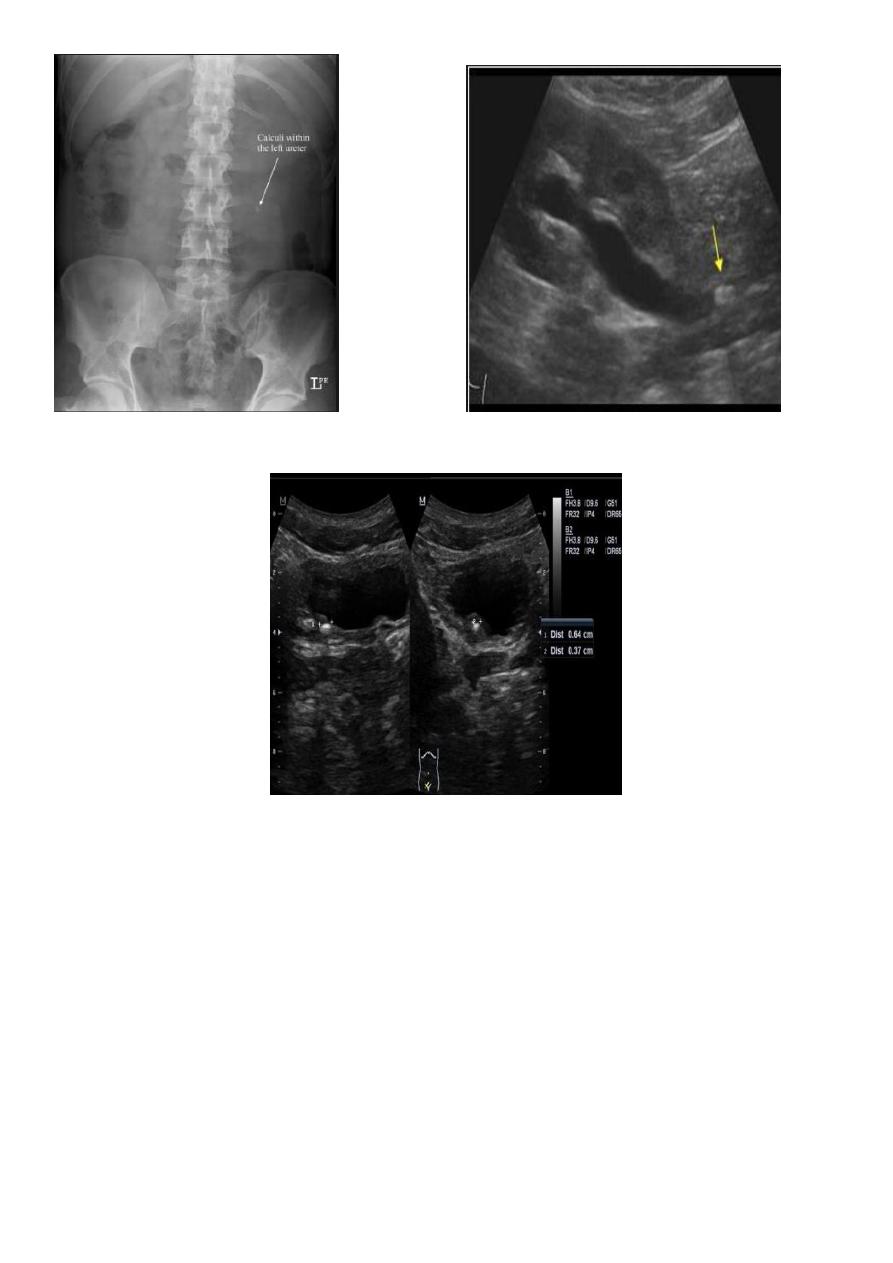
2-Stones larger than 5 mm are easily seen on US but smaller ones may be missed.
-They produce intense echoes (hyperechoic) and cast acoustic shadows.
-Proximal and distal ureteric dilatation can be easily identified unlike mid-ureteric
dilatation, and stones located in the middle third of the ureter are hard to be demonstrated
unlike upper and lower ureteric stones (especially those lodged in the vesico-ureteric
junction or pelvi -ureteric junction) which are easily identified by ultrasound.
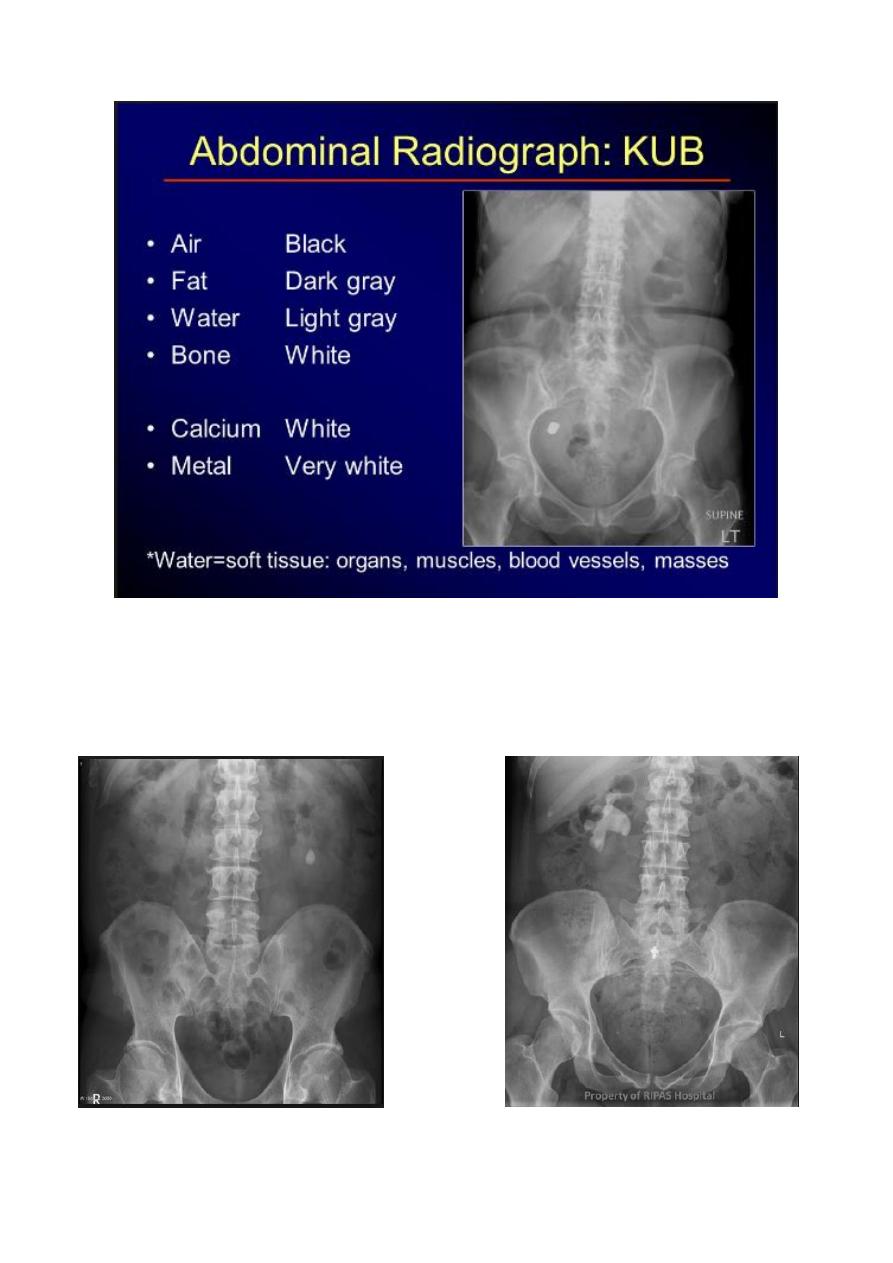
l.V.U. findings:
-
Plain film may be useful in demonstrating calculi.
-After contrast injection:
Acutely obstructed kidney shows a dense nephrogram (dense opacification of the renal
parenchyma).
excretion of contrast (opacification of the collecting system which may take many hours) ,
then the level and degree of obstruction can be determined as dilated pelvi-caliceal system
and ureter are followed down to the point of obstruction (point of hold up).
3
4
Pyeloxinus
may result from rupture of a fornix precipitated by contrast-induced diuresis superimposed
on the increased hydrostatic pressure of an obstructed pelvicaliceal system.
Urine and contrast extravasate into the renal sinus and perirenal space
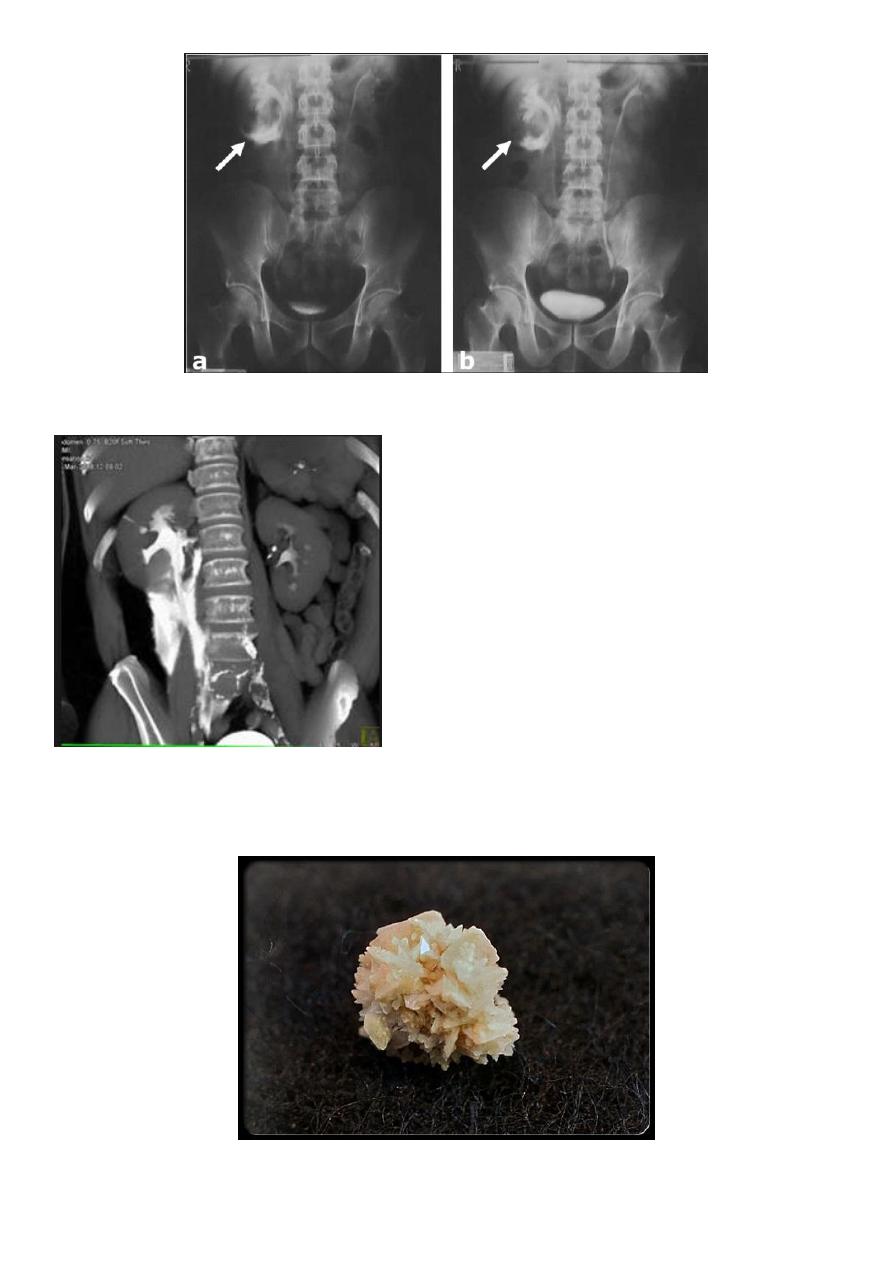
5
6
CT scans used in some hospitals during acute renal stone
-Non contrast CT sensitively identify calculi and non opacified collecting system down to
the level of obstruction. it has a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 96% for detection of
ureteral calculi

7
Ddx of stone on KUB :
1. Gall stone
2. Calcified LN , cartilage ,fibroid,
3. Phlebolith: round, lucent centre.
Infection:
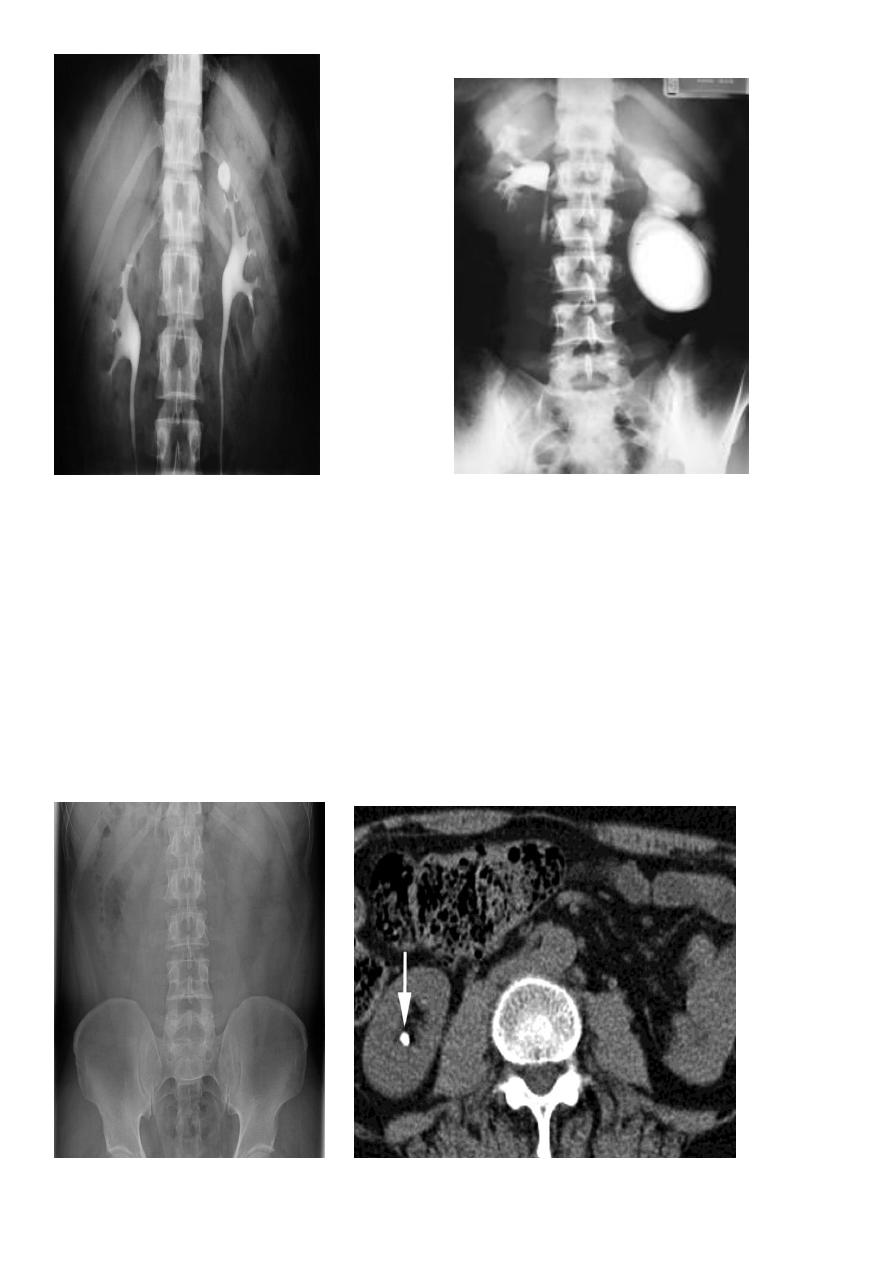
Renal TB:
GU tract second most common site of tuberculous infection after lungs, 2ndry to TB
infection everywhere.
Spread is hematogenous
Features :
Plain films may show large globular, a morphous calcifications
IVU :
Cortical scarring
"Smudged" papillae (moth-eaten) –irregular due to inflammation and necrosis
Infundibular strictures
Hydrocalyces without dilatation of renal pelvis or Hydronephrosis
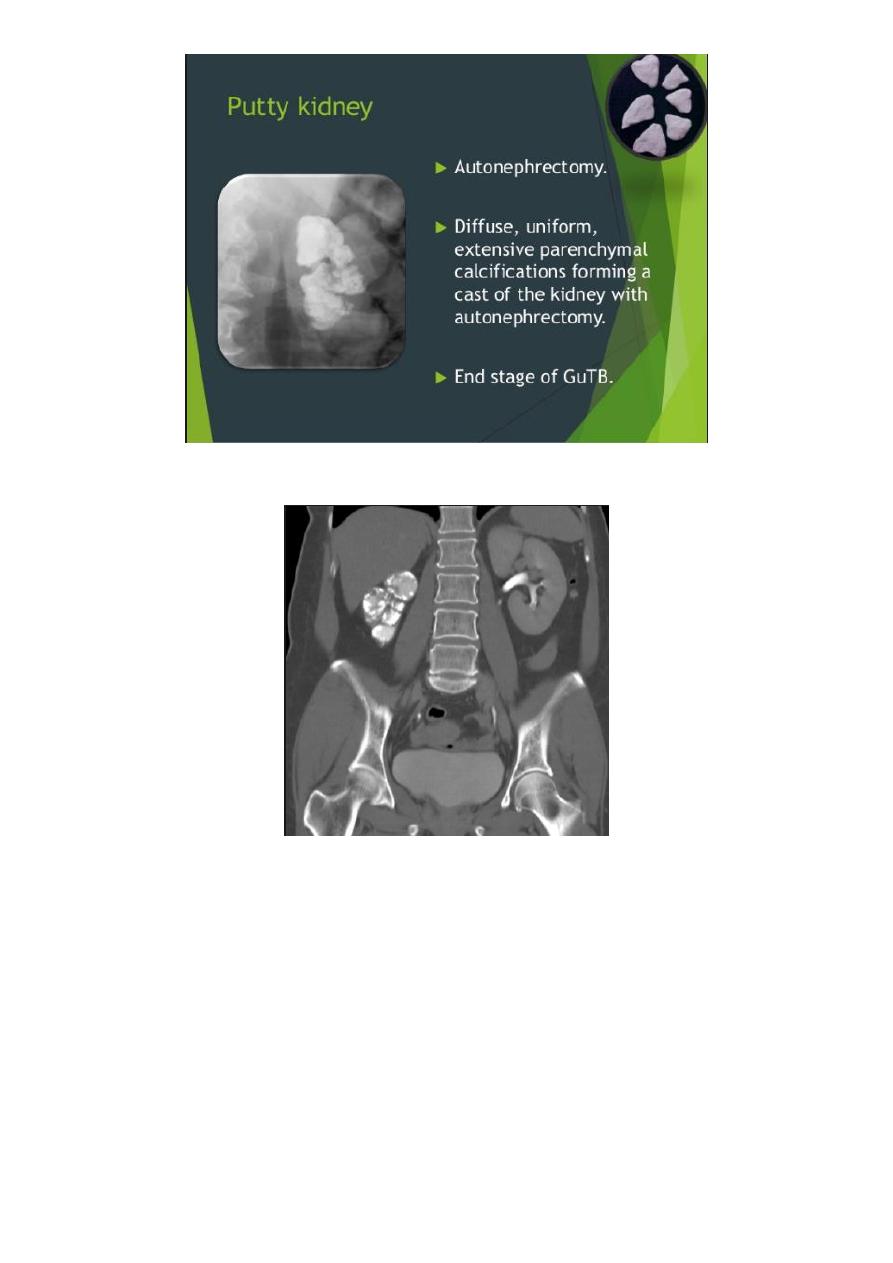
Autonephrectomy – small, shrunken kidney with dystrophic calcification
When ureters are involved, usually the upper or lower third (more common)
Bladder involvement rarely leads to calcification of wall (think histosomiasis)
8
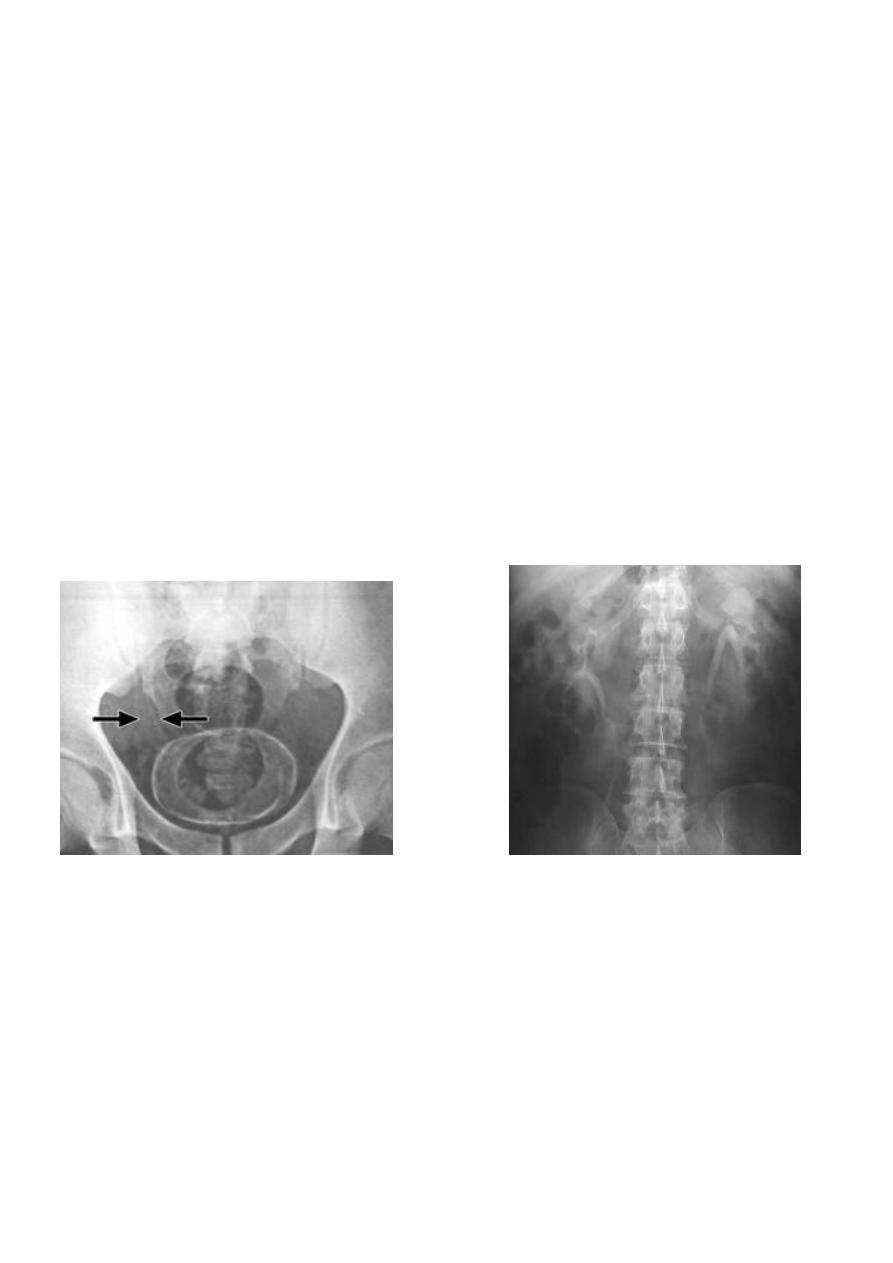
Schistosomiasis
Infestation by s.hematobium
Calcification is most important feature, mainly in bladder & lower ureters , but may involve
whole ureters .
In early stage inflammation may cause cobble stone appearance.
Bladder capacity not affected.
Ddx of bladder calcification :
1. schistosomiasis .
2. tumor , TB …
9
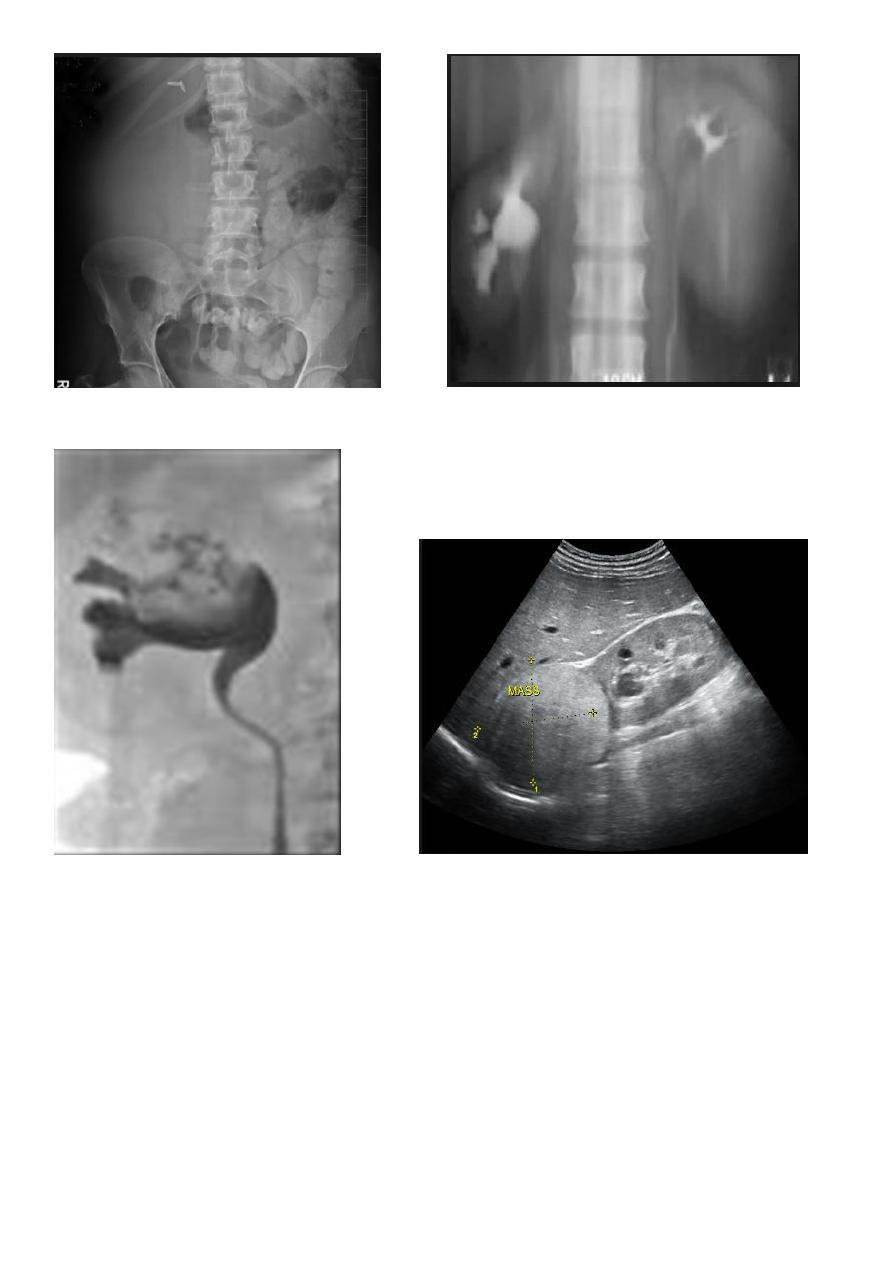
Tumor
Renal cell carcinoma:
Comprise 85% of renal malignancy
Features
1. Soft tissue mass on KUB.
2. 2. Irregular filling defect with destruction of calyces
.
11
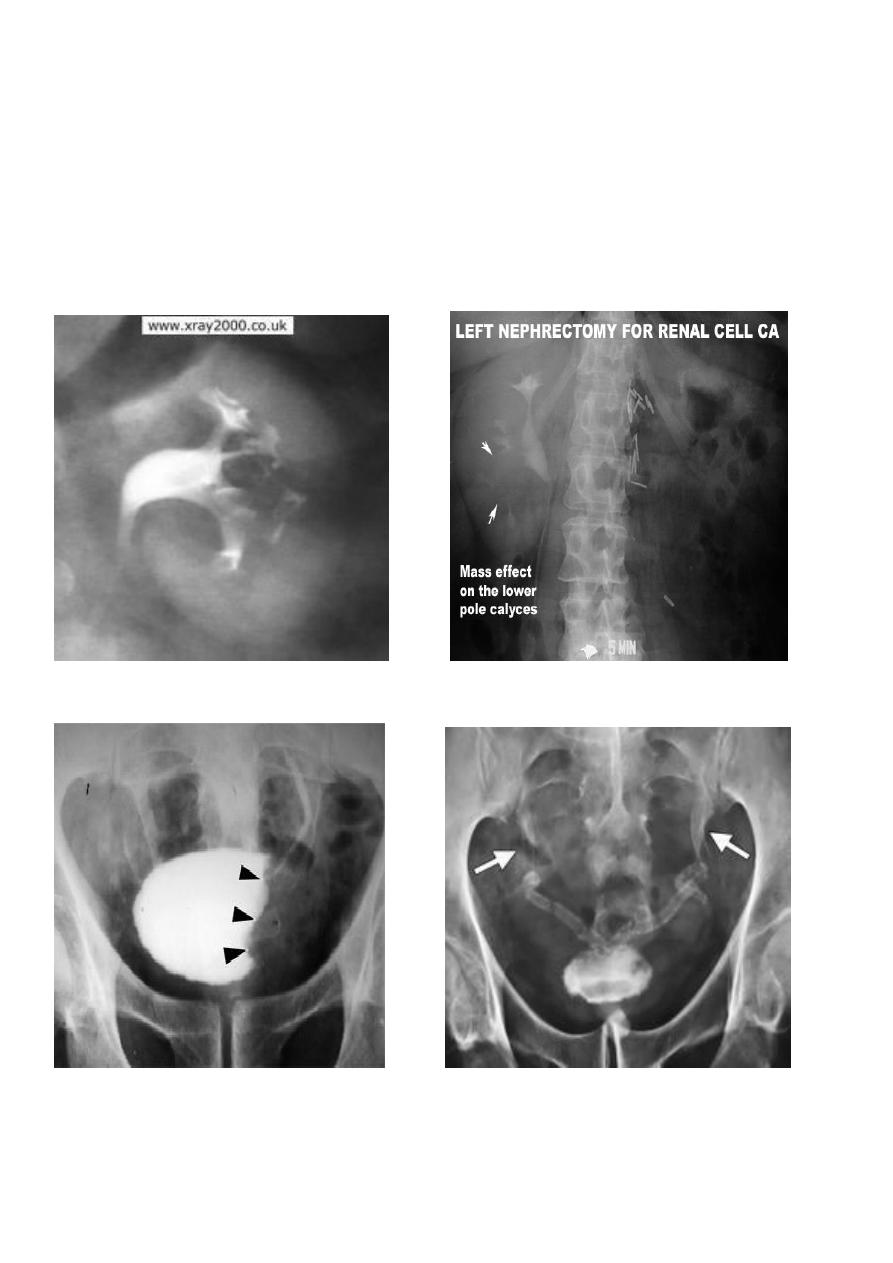
Urothelial tumors
85.90% of tumors arising within the collecting systems of the kidneys are
transitionalcellcarcinomas(TCC)
May occur at multiple sites, so pelvicalyceal system, ureter and bladder must be
well examined .
IVU plays an important role in displaying upper tract tumors.
They appear as radiolucent filling defects projecting into the lumen, within the
collecting system.
11
Must be differentiated from
blood clots or radiolucent calculi
if confused with overlying gas shadow, then tomography may be required during an
Ivu to solve this problem.

12
A.L.Y

13
