
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
1
FEVAR AND RASH
MEASLES
Agent that cause the infection
Agent- RNA virus (Paramyxo virus family, genus Morbillivirus)
Source of infection-cases of measles,
but not carriers.
No animal reservoir
Infective material- Nasal secretion, Respiratory tract &Throat
Communicability- Highly infectious during prodromal period and at the
time of eruption.
Secondary attack rate- > 80%
Clinical features
- Prodromal stage
- Eruptive stage
- Post-measles stage
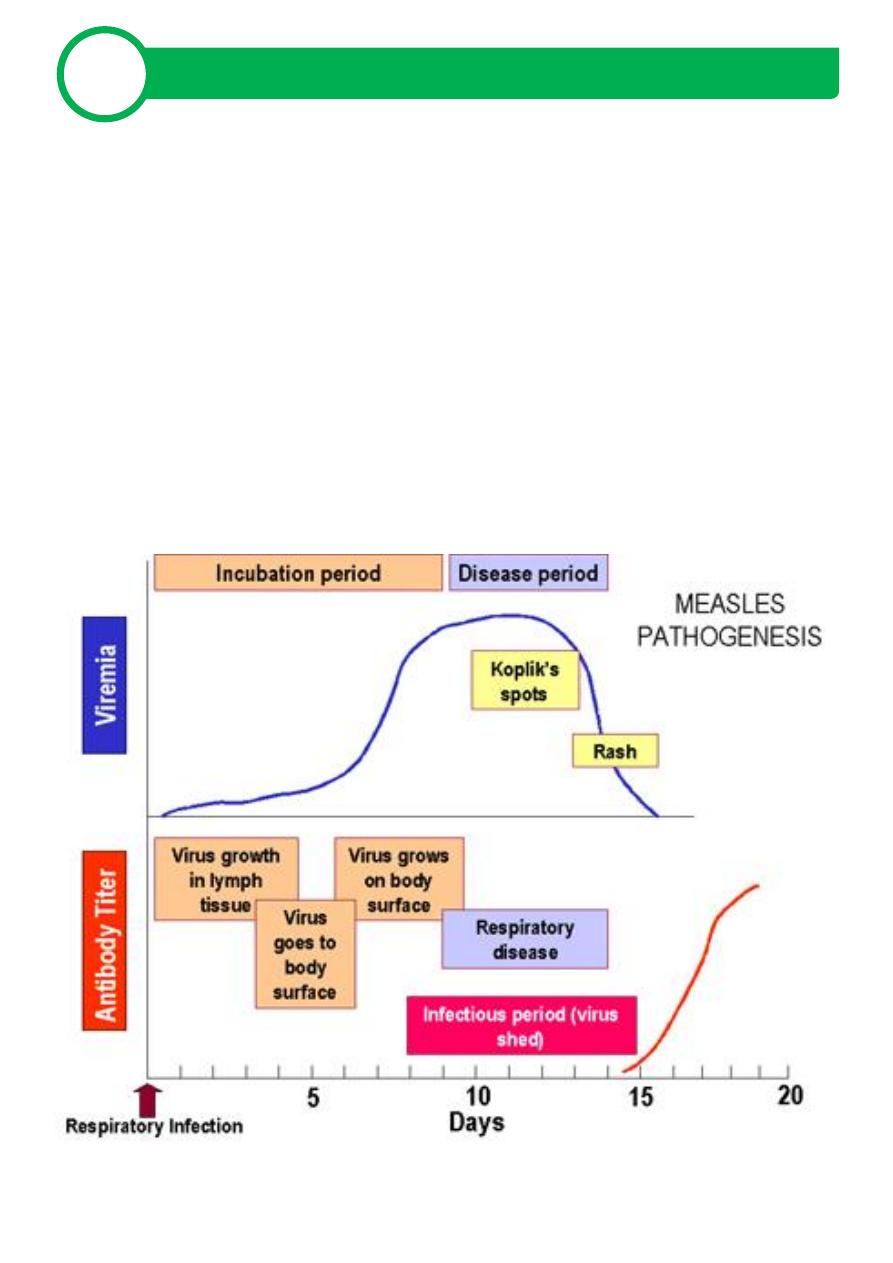
I. P 1-2 wks. Prodromal symptoms - fever, malaise, dry (occasional
croupy) cough, coryza, conjunctivitis c clear d/c, marked photophobia
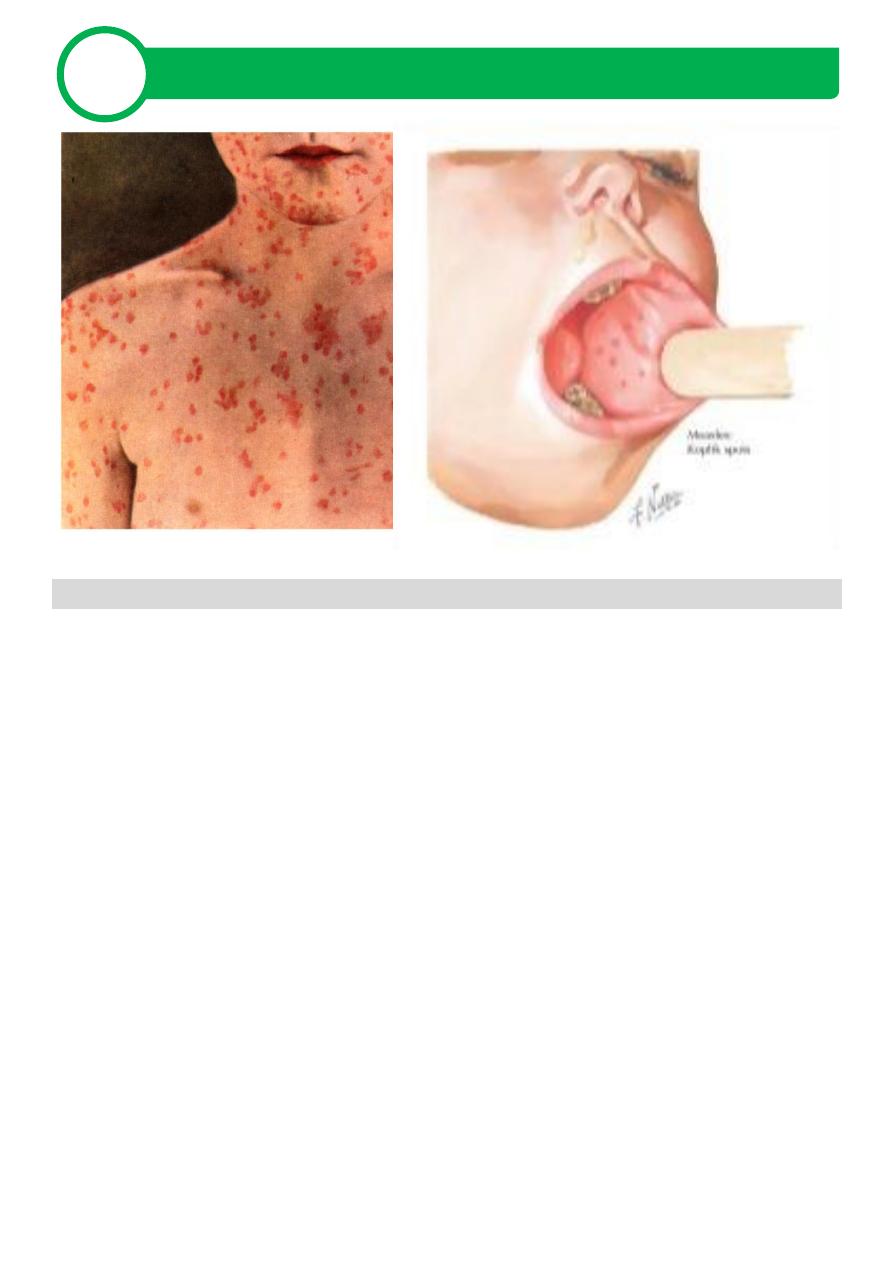
1-2 days’ prodromal symptoms - Koplik spots on the buccal mucosa
Koplik spots - tiny, bluish-white dots surrounded by red halos opposite
to 2
nd
molar teeth.
Day 4-7 blotchy, erythematous, blanching, maculopapular exanthem
appears
Rash begins at the hairline and spreads cephalocaudally and involves
palms and soles
Rash typically lasts 5 - 6 days
Can see desquamation in severe cases
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
2
Patients can be systemically ill
Patients contagious from 4 days prior to the rash until 4 days after
the resolution of the rash
Highly contagious - 90% for susceptible people
High morbidity and mortality common in children in underdeveloped
countries
Peak season is late winter to early spring
Potential complications - OM, PNA, obstructive laryngotracheitis,
acute encephalitis
Vaccination is highly effective in preventing disease
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
3
Rubella (german measles)
Little or no prodrome in children
In adolescents - 1-5 days of low-grade fever, malaise, headache,
adenopathy, sore throat, coryza
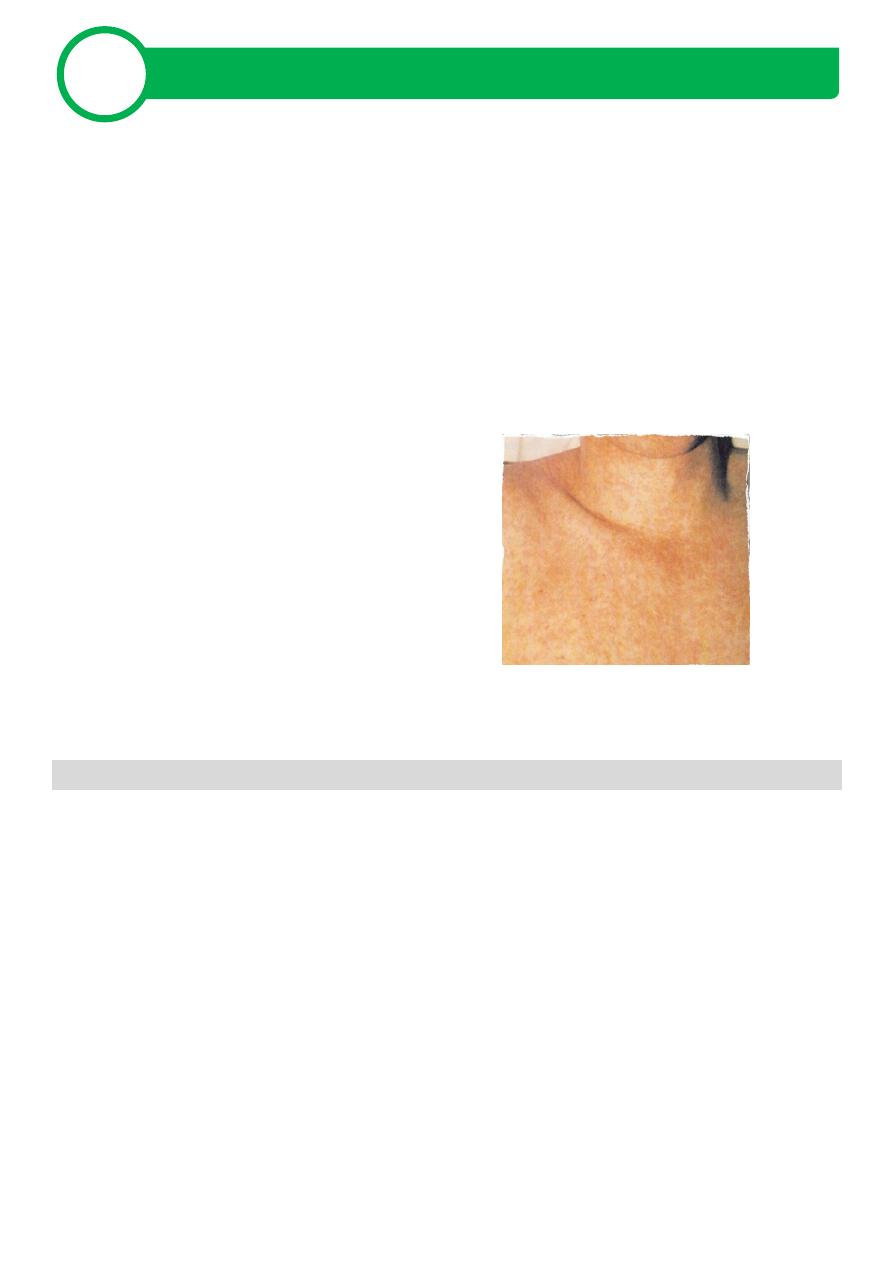
Exanthem - discrete, pinkish red, fine maculopapular eruption - begins
on the face and spreads cephalocaudally
Rash becomes generalized in 24 hours and clears by 72 hours
Forchheimer spots - small reddish spots on the soft palate - can
sometimes be seen on day 1 of the rash
Arthritis and arthralgias - frequent in adolescents and young women -
beginning on day 2 or 3 lasting 5-10 days
Up to 25% of patients are asymptomatic - serology testing may be
necessary to establish the diagnosis
Important in establishing the diagnosis if the patient is pregnant or has
been in contact c a pregnant woman
Peaks in late winter to early spring
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
4
Contagious from a few days before the rash to a few days after the
rash
Incubation period 14-21 days
Complications - rare in childhood - arthritis, purpura c or s
thrombocytopenia, mild encephalitis
Congenital rubella syndrome
Infection of seronegative mother during pregnancy
Risk of fetal infection
– I. trimenon: 75-90%
– II. trimenon: 20-40%
– III.trimenon: 25-50%
– Fetal lesion
» 1-8. gest. week: 80%
» 9-12. gest. week: 30%
» 13-20. gest. week: 10%
Varicella (chickenpox)
Caused by varicella-zoster virus
Highly contagious
Brief prodrome of low-grade fever, URI symptoms, and mild malaise
may occur
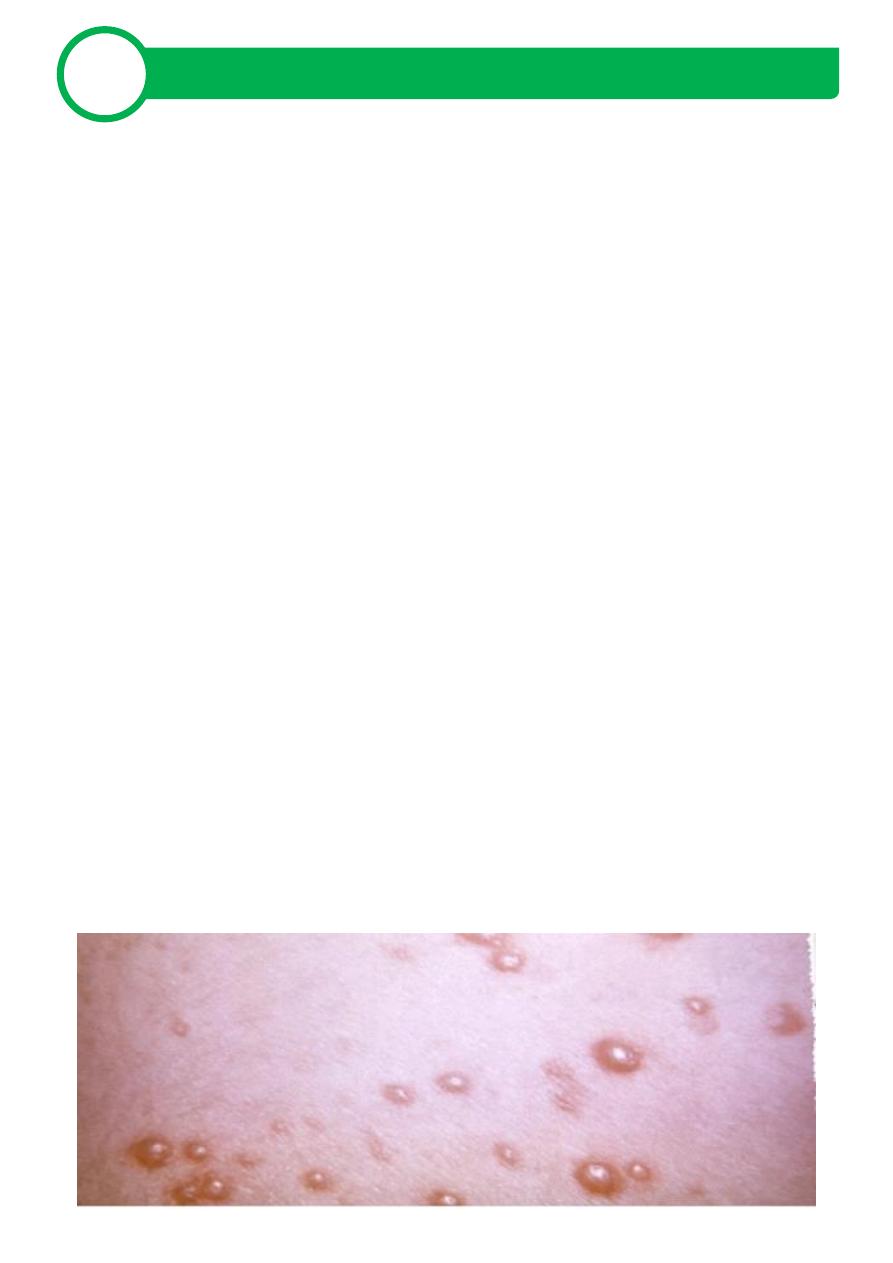
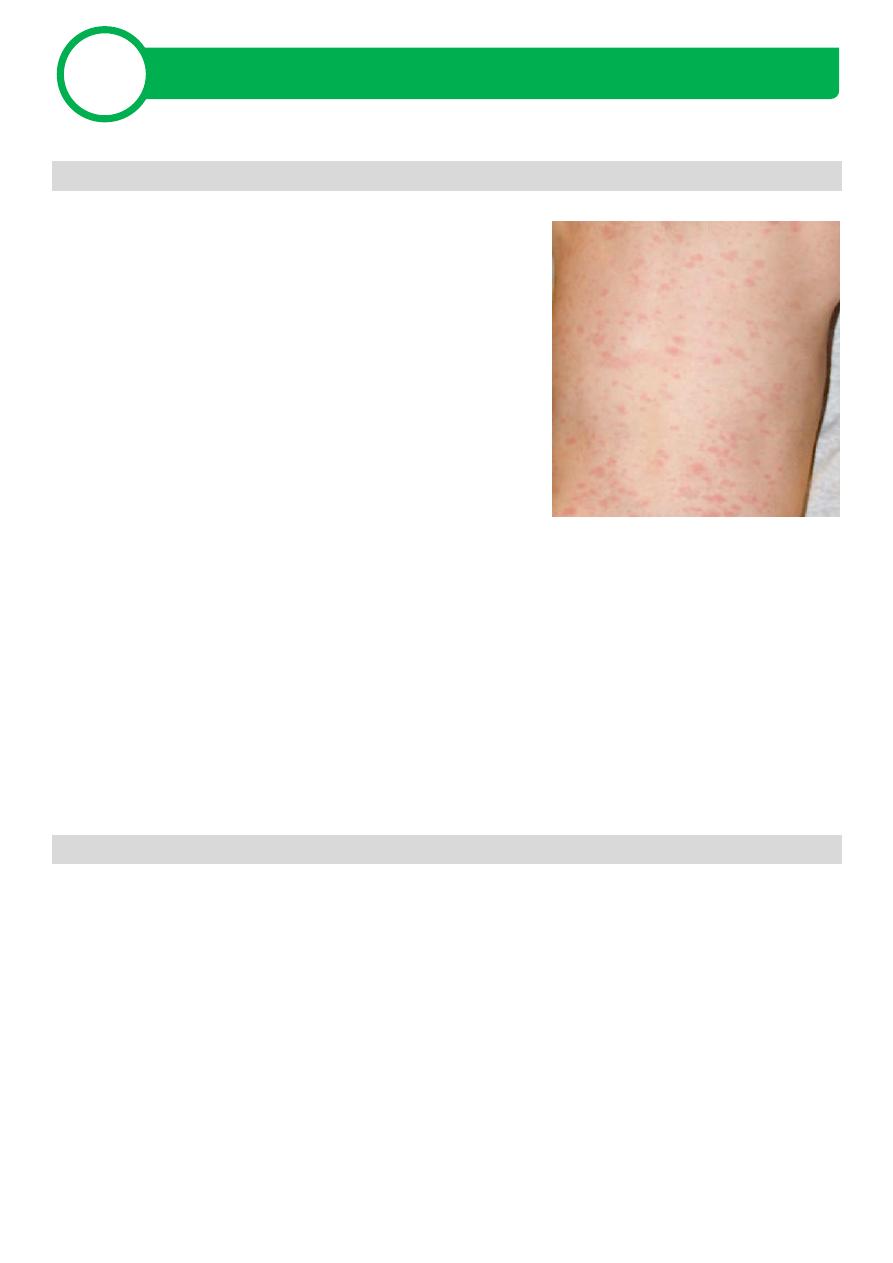
Rapid appearance of pruritic exanthem
Lesions appear in crops - typically have 3 crops
Crops begin in trunk and scalp, then spread peripherally
Lesions begin as tiny erythematous papules, then become vesicles
surrounded by red halos
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
5
Lesions began to dry - umbilicated appearance, then surrounding
erythema fades and a scab forms
Hallmark - lesions in all stages of evolution
All scabs slough off 10-14 days
Scarring not typical unless superinfected
Cluster in areas of previous skin irritation
Puritic lesions on the skin
Painful lesions along the oral, rectal, and vaginal mucosa, external
auditory canal, tympanic membrane
Occurs year-round, peaks in late autumn and late winter through early
spring
Incubation period ranges from 10-20 days
Contagious 1-2 days prior to rash until all lesions are crusted over
Complications - secondary bacterial skin infections (GAS),
pneumonia, hepatitis, encephalitis, Reye syndrome
Severe in the immunocompromised host - can be fatal
Can have severe CNS, pulmonary, generalized visceral involvement
(often hemorrhagic)
Need to get varicella-zoster immunogloblin 96 hours post-exposure to
possible varicella
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
6
Roseola infantum (exanthem subitum)
Febrile illness affecting children 6-36
months
Human herpesvirus 6 is causative agent
Symptoms include:
– fever, usually >39
– anorexia
– irritability
– these symptoms subside in 72
hours
As fever subsided, usually an erythematous, maculopapular rash that
appear on the trunk and then spread to the extremities, face, scalp,
and neck
Occurs year-round
More common in late fall and early spring
Incubation period thought to be 10-15 days
Scarlet fever
Introduction
1- A kind of acute infectious disease of respiratory tract
2-
Group A β-hemolytic streptococcus
3- Main clinical manifestation:
- acute fever
- pharyngitis
- diffuse and red exanthem(rash)

Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
7
desquamation and hyperpigmentation
- 2~3weeks later
- rheumatic fever
- glomerulonephritis
- arthritis
Etiology
Group A β-hemolytic streptococci
1- Morphology and structure
- Gram-positive spherical cocci
-
Diameter: 0.6~1.0 μm
- Capsule (+) flagellum and spore (-)
- Streptococcus groups: A~H & K~U on the basis of C-carbohydrate
within the cell wall
- Group A: more than 80 immunologically distinct types that are based
on differences in the M protein.
2- Pathogenecity
- M protein: resists phagocytosis
- resist phagocytosis,
- promote Schwartzman
- reaction
- Streptokinase
- Streptodornase
- Streptolysin O & S: WBC, RBC & platelet
- Hyaluronidase: hyaluronic acid
Epidemiology
1- Source of infection:
- Patients in scarlet fever or pharyngitis

Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
8
- Carriers with streptococci in nasal and pharyngeal
2- Route of transmission:
- droplet, skin lesion, food, milk and water and so on.
3- Susceptibility of population
– Anti-bacterium immunity anti-M
– Anti-pyrogenic toxin immunity
4- The feature of epidemiology
- season, age, endemic area, variation of this disease
Pathogenesis
1- Suppurative change
- Pathogenepithelial cellsdiffusion in local tissue
LTA hyaluronidase
M protein streptokinase, streptodornase
capsule streptolysin
Suppurative change
- pharyngitis, tonsillitis
- peritonsillar abscess
- retropharyngeal abscess
- otitis media, sinusitis
- lymphangitic-----lymphadenitis
- bacteremia (sepsis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia)
2- Toxic change
pyrogenic exotoxin (erythrogenic exotoxin)
fever
scarlatina rash other toxic symptoms

Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
9
3- Allergic reactive change 2~3weeks later,
Heart-------rheumatic fever
Kidney-----glomerulonephritis
joint---------arthritis
Reason:
1- similar antigencrossed immune reaction
2- immune complex
Clinical manifestation
- Incubation period 2~3days(1~7days)
Character of clinical manifestation:
Fever, Pharyngitis, scarlatina rash
1- Fever
a- feature: persistent, fever & rash
b- temperature.: 39~40
℃
c- accompanied symptoms: headache, weakness, poor appetite
d- course: 1 week
2- Pharyngitis
- Symptom
- sign
3- Rash
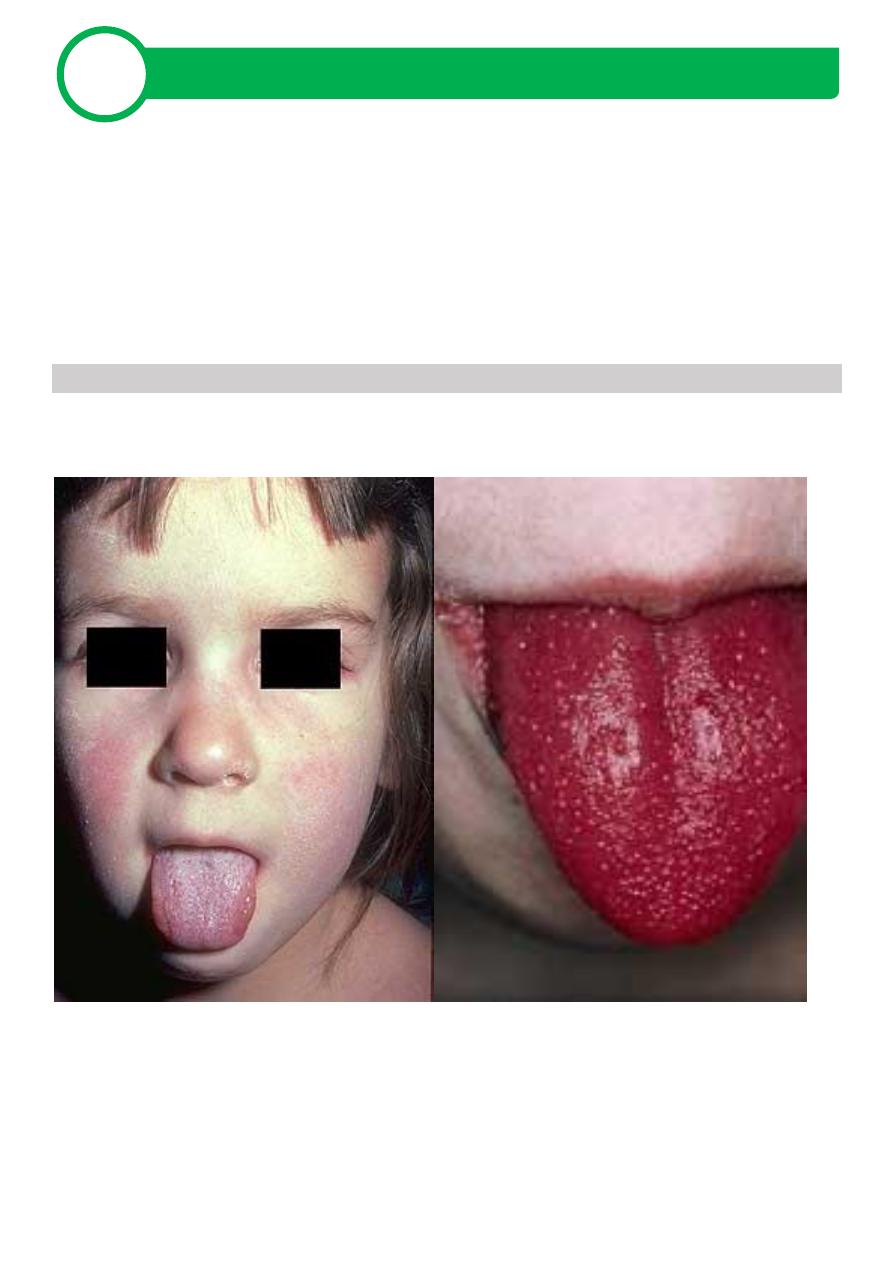
a- fever & rash: 24 hours
b- initial position: ear, neck, upper chest
c- feature: diffuse papular (punctate or finely), miliary sudamina (not so
many), circumoral pallor, strawberry tongue, red strawberry tongue,
Pastia lines(antecubital fossate), desquamation and hyperpigmenta-
tion
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
10
Type of clinical manifestation
- light type
- toxic type
- sepsis type
- surgery type
- obstetrics type
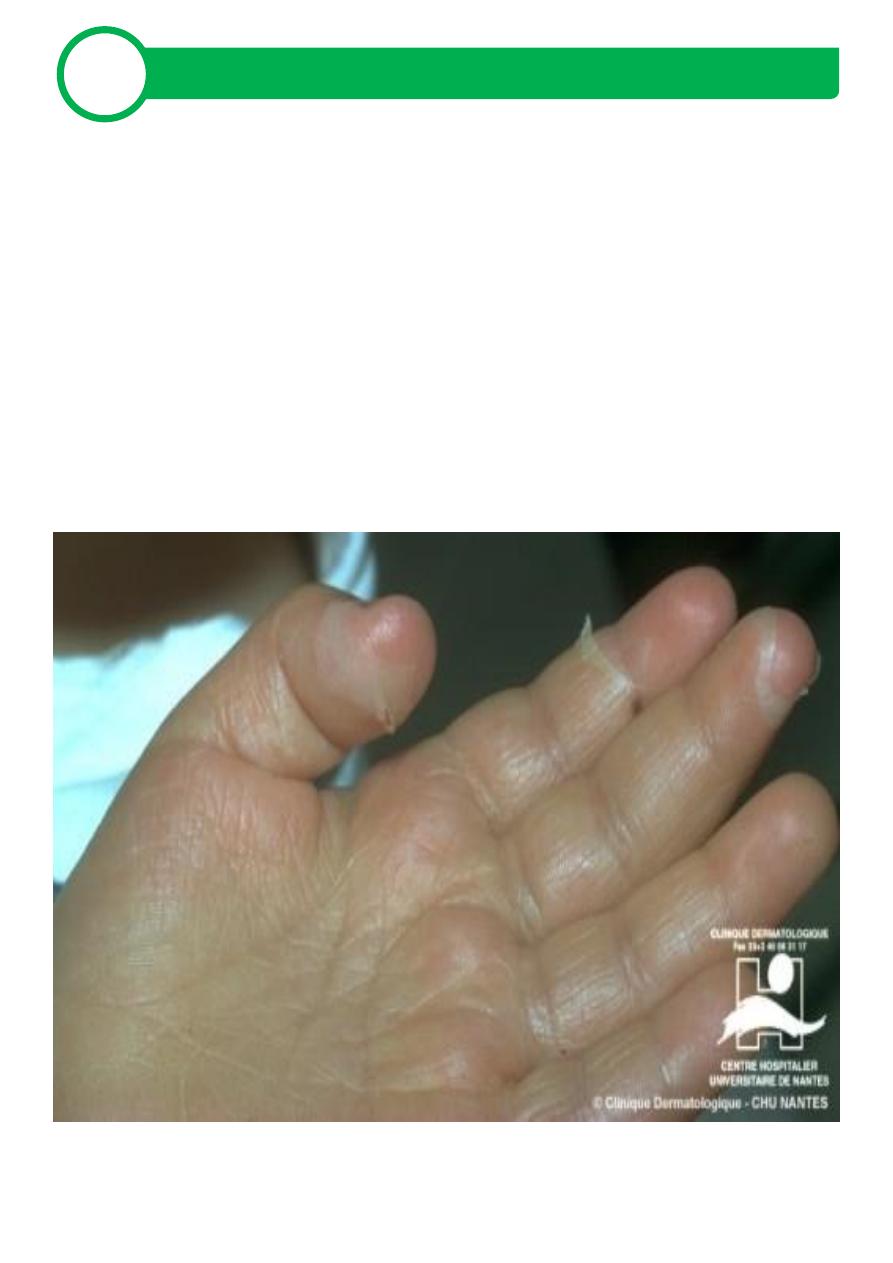
Scarlat fever
(Group A Streptococcus, erythrogenic toxin, fine papular exanthem,
palmar/ plantar peeling).
Laboratory examination
1- peripheral picture: WBC, neutrophil 80%
2- Urine allergic reaction: protein RBC, WBC, cylindruria
3- bacteriology test: Immunological fluorescence, assay(IFA), bacteria
culture
Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
11
Complication 2~3 weeks later
- rheumatic fever
- glomerulonephritis
- arthritis
Diagnosis
1- clinical data: fever, pharyngitis, rash
2- laboratory test: peripheral picture,
- Urine
- Bacteriology test
- Dick test (pyrogenic test)
3- epidemiology data

Pediatrics Fifth Stage – G:E FEVAR AND RASH
12
Differential diagnosis
1- staphylococcus infection
2- drug rash
3- Virus rash: measles, rubella etc.
Treatment
A. Supportive
B. Specific
1- penicillin
- adult: 80万U/ time, bid 5~7days.
- child:20万U/ (kg d), 10days
- 800万U/d(adult)
2- erythromycin
Prevention
1. Isolation: patients in scarlet fever
2. protection:
