Tyrosine
• A• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Tyrosine is a non essential Amino Acid synthesized from hydroxylation of phenylalanine by the phenylalanine hydroxylase
• phenylalanine
• Tyrosine
Metabolism of Tyrosine was divided into 2 parts:
1. Transamination Pathway.2. Synthesis of specialized products.
A- Thyroid Hormones T3. T4.B- Adrenalin & nor adrenalin.
C-Melanin pigment of the skin
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Transamination of Tyrosine
oxidase
Schematic presentation of Tyrosine Metabolism
parahydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
The end result of tyrosine metabolism are
1.Fumarate …………. Citric Acid cycle
2.Acetoacetate& Acetate……………..Fatty Acid Synthesis
Tyrosine is both glucogenic & KetogenicFumarate Glucogenic
Acetoacetate Ketogenic• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
• Inborn Error diseases of Tyrosine (Metabolic disorders)
• Type 2 Tyrosinemia
• Neonatal Tyrosinemia
• Alkapotoneuria
• Type 1 Tyrosinemia
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Type 2 Tyrosinemia
#Deficiency of tyrosine transaminase.
# mild to severe keratitis.erosive lesion of the palm,,
# Skin lesions, hyperkeratosis of the palm and the hand.
#Mental retardation.
# High level of tyrosine in the blood.
# harmful untreatable disease.
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Neonatal Tyrosinemia
#Deficiency of parahydroxyphenyl pyruvate hydroxylase.
# Accumulation of parahydroxyphenyl pyruvic acid (Toxic).
# Hepatosplenomegally.#Harmful untreatable Death before the age of 6 months
• A• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
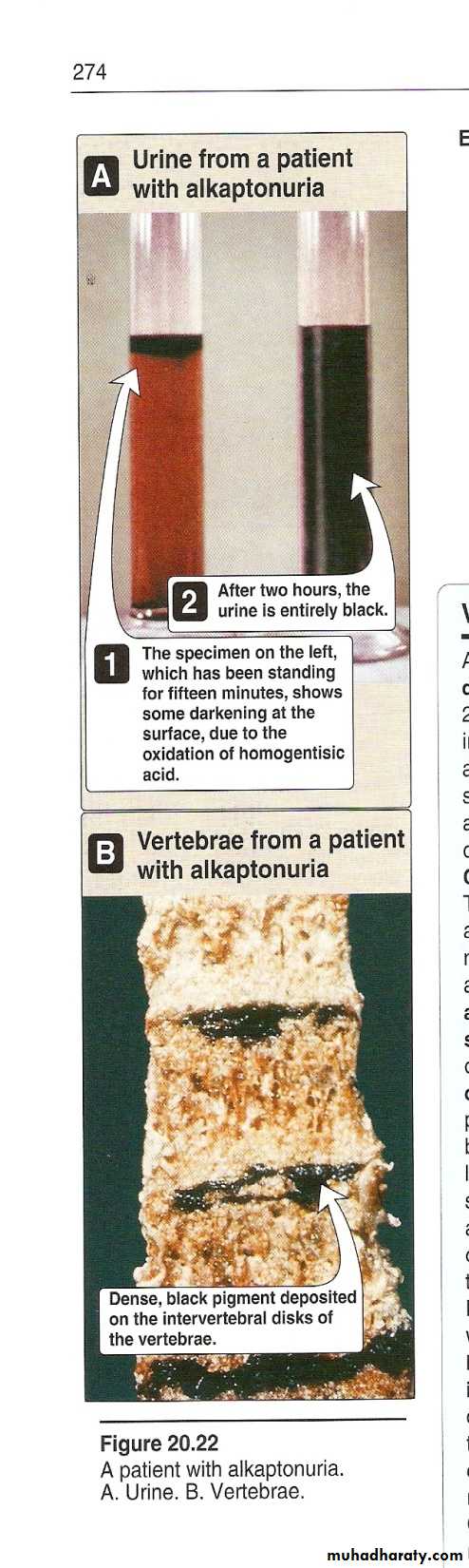
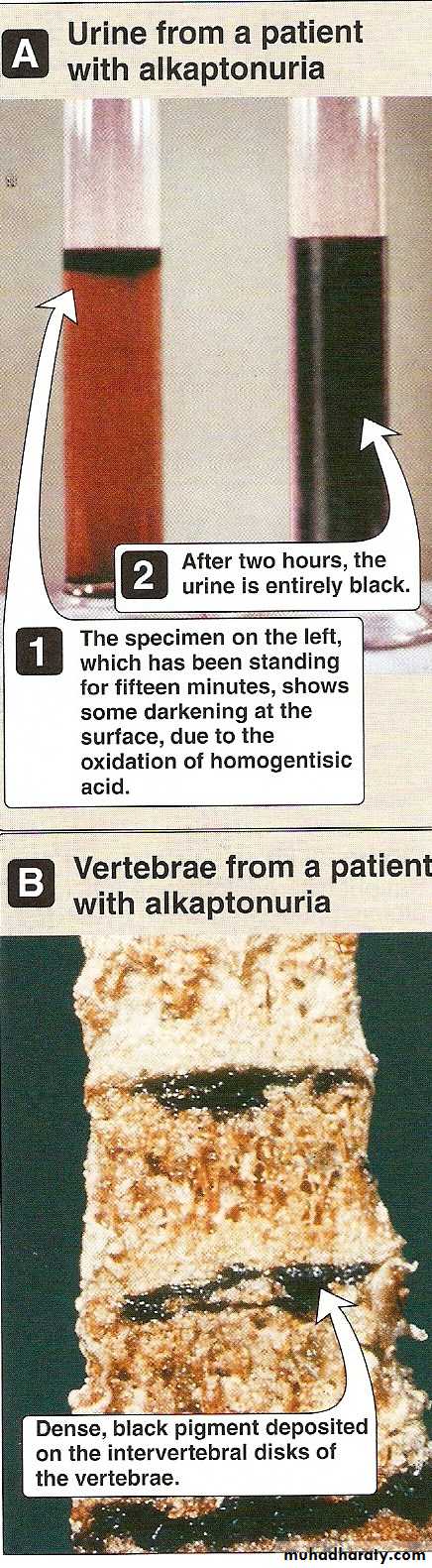
Alkaptonuria
# Autosomal recessive.
#Deficiency of homogentisic acid oxidase.
#Increase homogentisic acid in blood and urine.
#Homogentisic acid on standing become black pigment. .(Alkapotonuria)
#It may be precipitate in the cartilage specially in the ear.
#Harmless.
#Diagnosis: Black color urine.
#Ferric chloride test is positive.
• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Type1 Tyrosinemia (Tyrosinosis)
# Acute form lead to vomiting&diarrhoea.#Failure to thrive.
#Deficiency of Fumaryl acetate hydroxylase.
#Mostly die before age of 6-8 months (Acute form).
#Death due to liver failure.
#Chronic form similar but milder ,death usually before age of 10 Years.
#Example of harmful untreatable diseases.
• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Metabolism of tyrosine in melanocyte(skin)
Schematic presentation of Tyrosine metabolism in the skin
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Metabolism of Tyrosine in the melanocyte(Skin)
1.Hydroxylation of tyrosine by tyrosinase enzyme to form dihydroxyphenylalanine(L-Dopa).
2. Dihydroxyphenylalanine is converted to Dopaquinone.
3.Dopaquinone is converted to melanin pigment.4. L-Dopa is decarboxylated in the brain to form Dopamine.( epinephrine and nor epinephrine.)
5.Dopamine is deficient in brain patient with parkinsonism.
6.Minor pathway is that tyrosine is decarboxylated to form tyramine a vasopressor agent.• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Inborn Error (Metabolic disease)of Tyrosine in the skin.
Albinism.
# Deficiency of tyrosinase enzyme of melanocytes.#Failure of melanocyte to form melanin pigments.
#Whitish skin, Whitish eye lashes, whitish hair#Intolerance to sunlight.
#Harmless condition.• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Parkinson disease is linked with decrease production of dopamine .The disease is due to degeneration of certain part of the brain leading to impairment synthesis of dopamine.
Treatment: dopamine can not enter the brain hence its administration is of no use.
L- dopa or levodopa is used in the treatment of Parkinson . In the brain DOPA is decarboxylated to dopamine which alleviates the symptoms but dopamine synthesis occurs in various tissue causing side effect, such as nausea, vomiting hypertensionSinemet contain L=Dopa 250mg and carbidopa 25mg act as peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor to prevent decarboxylation in various tissue and decrease the side effect
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Tissue Proteins
Diet
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
DOPA
Melanin
DA
(dopamine)
NE
(norepinephrine)
p-hydroxy-
phenlypyruvate
homogentisic
acid
thyroxine
phenyl-
pyruvic acid
PAH
The main metabolic pathways of phenylalanine and tyrosine in the human
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Tissue Proteins
Diet
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
DOPA
Melanin
DA
(dopamine)
NE
(norepinephrine)
phenyl-
pyruvic acid
PKU
Albinism
p-hydroxy-phenlypyruvate
homogentisic
acid
thyroxine
Alkaptonuria
goitrous
cretinismTyrosinosis
Schematic presentation of main inborn error of metabolism of Tyrosine• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M