•
• وَقُل رَّبِّ أَدْخِلْنِي مُدْخَلَ صِدْقٍ وَأَخْرِجْنِي مُخْرَجَ صِدْقٍ وَاجْعَل لِّي مِن لَّدُنكَ سُلْطَانًا نَّصِيرًا•
• سورة الاسراء
• الآيات (80)
•
CULTURE MEDIA
andSTERILIZATION
• CULTURE MEDIA
• Contain nutrients that support microbial growth.• Isolation, growing and identification of microorganisms.
• Culture Vs culture medium?
• Common ingredients of culture media
• 1. PEPTONE• 2. Meat extract
• 3. Nacl
• 4. Agar agar
• a. Melting point 92-95 c
• b. solidifying point 42-45 c
• c. concentration 1.5-2% (solid)
• 0.4- 0.8% (semisolid)
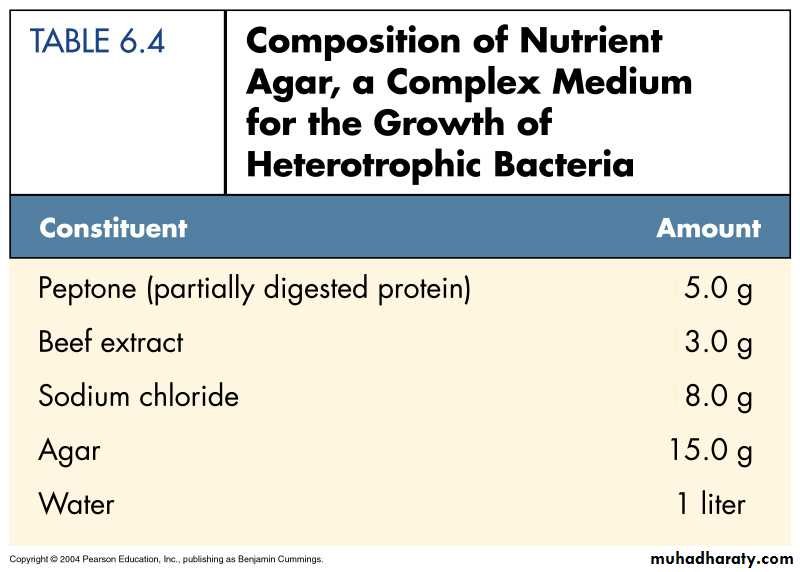
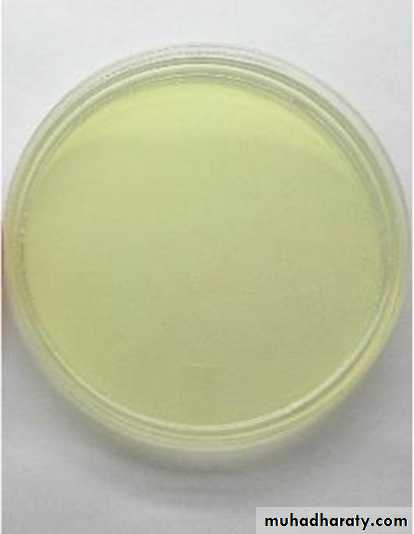
Nutrient agar
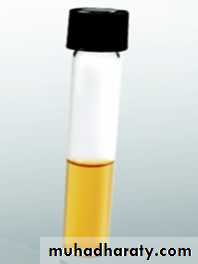
• Liquid (fluid media) e.g. nutrient broth.
• Solid media e.g nutrient agar, blood agar.• Semisolid media.
• A. PHYSICAL STATE(CONSISTENCY)OF MEDIA
• Fluid
• Nutrient broth• Peptone water
• Brain heart infusion
• Solid
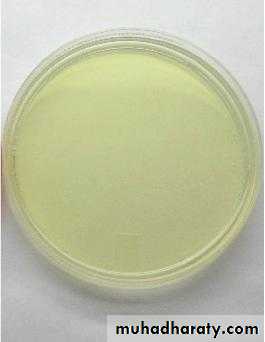
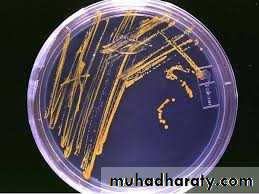
Nutrient agarBlood agar
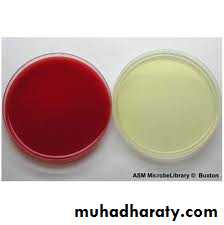
Chocolate agar
MacConkey agar
•
• Simple media e.g. nutrient agar and nutrient broth.
• 2) Special – purpose mediaB. Use of the media
• Simple media enriched with appropriate substance ,e.g. Blood ,glucose ,serum and ascetic fluid , most commonly used to cultivate fastidious microorganism like Streptococci.
• Special – purpose media
• A) Enriched media
• Contain inhibitory substance ( e.g. bile salt , antibiotic, dyes … etc) which favour the growth of concerned microorganism and inhibit the growth of other . e.g. Mannitol Salt agar and MacConkey's agar.
• Special – purpose media
• B) selective media
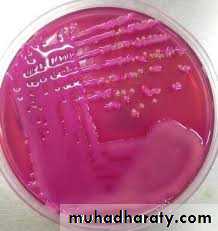
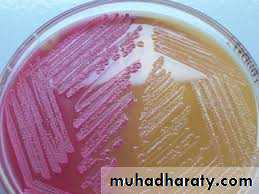
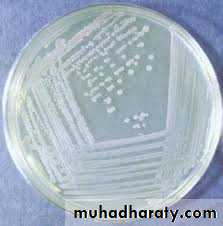
Mannitol Salt Agar
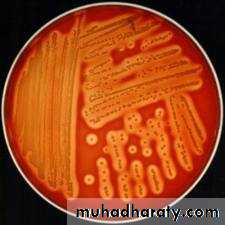
• Selective medium for gram negative bacilli (contains bile salts which inhibit the growth of gram positive microorganisms)• Certain species produce characteristic growth that can be easily recognized, or can produce certain effects in the media e.g. hemolytic and non-hemolytic species on blood agar ,MacConkeys agar differentiates between lactose fermenter and non lactose fermenter gram negative bacilli, nutrient agar differentiates between species of genus Staphylococcus
2) Special - Purpose medium
C) Differential media
Mannitol Salt Agar
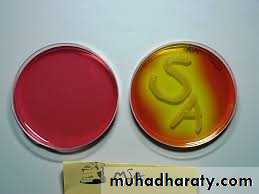
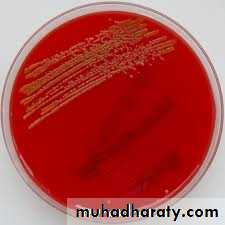
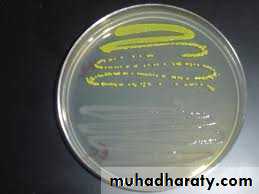
• Non haemolytic
• bacteria on blood agar• Staphylococcus citreus (lemon yellow colonies) on nutrient agar
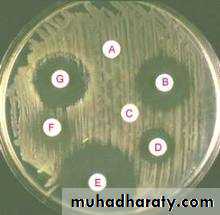
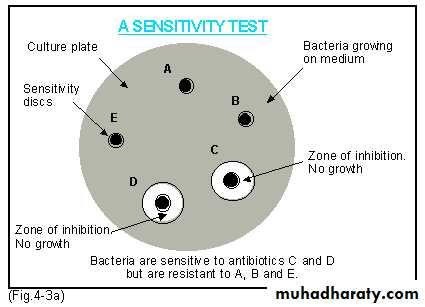
• Antibiotic sensitivity test on Mueller-Hinton agar
•
• Is the destruction or removal of all living organisms in or on an object
• DISINFECTION• Is the destruction of pathogenic microorganism only
• 1. PHYSICAL METHODS
• 2. CHEMICAL METHOD
• PHYSICAL METHOD
•• a. At a temperature below 100 c e.g. pasteurization of milk
• b. At a temperature of 100 c• I. Boiling at 100 c for 5-10 min
• II. Steaming at 100 c e.g. Tyndallization
• c. At a temperature above 100 c e.g. auto clave
• 1)Direct sun light
• 2)Ultra violet light
• 3)Ionizing radiation
• A-DISINFECTANTS e.g. acids(toxic to living tissue)
• B-ANTISEPTICS e.g. chlorine and iodine(safely applied to living (tissue• 1.Chemical indicators
• Control tubes Browne’ s sterilization• 2.Adhesive tape
• Bowie ---dick auto clave tape test