Spigelian hernia
These hernias are uncommon.Men and women equally affected, are most common in the elderly.
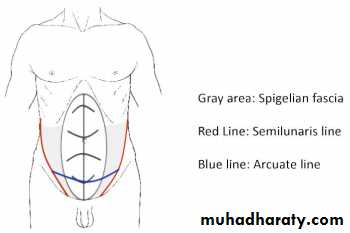
They arise through a defect in the spigelian fascia which is the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis muscle.
Often these hernias advance through the internal oblique as well and spread out deep to the external oblique aponeurosis.
Most Spigelian hernias appear below the level of the umbilicus near the edge of the rectus sheath. But they can be found anywhere along the ‘Spigelian line’.
the defect is almost always above the arcuate line.
In young patients they usually contain extraperitoneal fat only but in older patients there is often a peritoneal sac and they can become very large indeed.
They have also been described in infants and may be congenital, reflecting incomplete differentiation of the mesenchymal layers within the abdominal wall.
Clinical features
Young patients usually present with intermittent pain.
A lump may or may not be palpable as the fatty hernia is small and the overlying external oblique is intact.
Older patients generally present with a reducible swelling at the edge of the rectus sheath and may have symptoms of intermittent obstruction.
The diagnosis should be suspected and is confirmed by CT.
Ultrasound scanning should be performed in the upright patient as no defect may be visible with the patient lying down.
Treatment
Surgery is recommended as the narrow and fibrous neck predisposes to strangulation. Surgery can be open or laparoscopic.Lumbar hernia
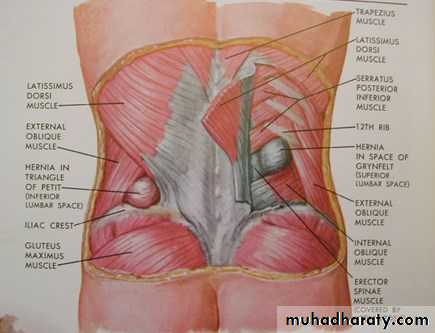
Most primary lumbar hernias occur through the inferior lumbar triangle of Petit bounded below by the crest of the ilium, laterally by the external oblique muscle and medially by the latissimus dorsi.Less commonly, through the superior lumbar triangle, which is bounded by the 12th rib above, medially by the erector spinalis and laterally by the posterior border of the internal oblique muscle.
Primary lumbar hernias are rare.
Differential diagnosis of lumbar hernia
• a lipoma;• a cold (tuberculous) abscess pointing to this position.
• pseudo-hernia due to local muscular paralysis. E.g injury to the subcostal nerve during a renal operation.
Treatment is by surgery with mesh repair
Parastomal hernia Is a hernia induced by surgery by bringing bowel out through the abdominal wall in a process called colostomy or ileostomy
Traumatic hernia
- Hernias through abdominal stab wound sites
- Hernias protruding through splits or tears in the abdominal muscles following blunt trauma.
-Abdominal bulging secondary to muscle atrophy which occurs as a result of nerve injury or other traumatic denervation.
Rare external hernias
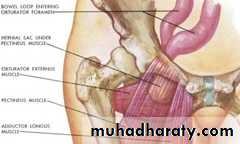
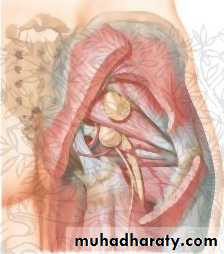
Perineal hernia postoperative hernia through a perineal scar, which may occur after excision of the rectum.Obturator hernia Obturator hernia, which passes through the obturator canal, occurs six times more frequently in women than in men.
Gluteal and sciatic hernias A gluteal hernia passes through the greater sciatic foramen, either above or below the piriformis. A sciatic hernia passes through the lesser sciatic foramen.
Obturator hernia
Gluteal and sciatic herniaUMBILICAL CONDITIONS IN THE ADULT
Chronic infectionIn patients with poor hygiene, the obese and when a paraumbilical hernia is present. It can be due to a plug of keratin causing chronic irritation.
A range of bacteria and fungi can be involved.
A rapid onset, superficial cellulitis occurs even after minor surgery in this region.
It is normally a streptococcus and treated with penicillin or other appropriate antibiotic.
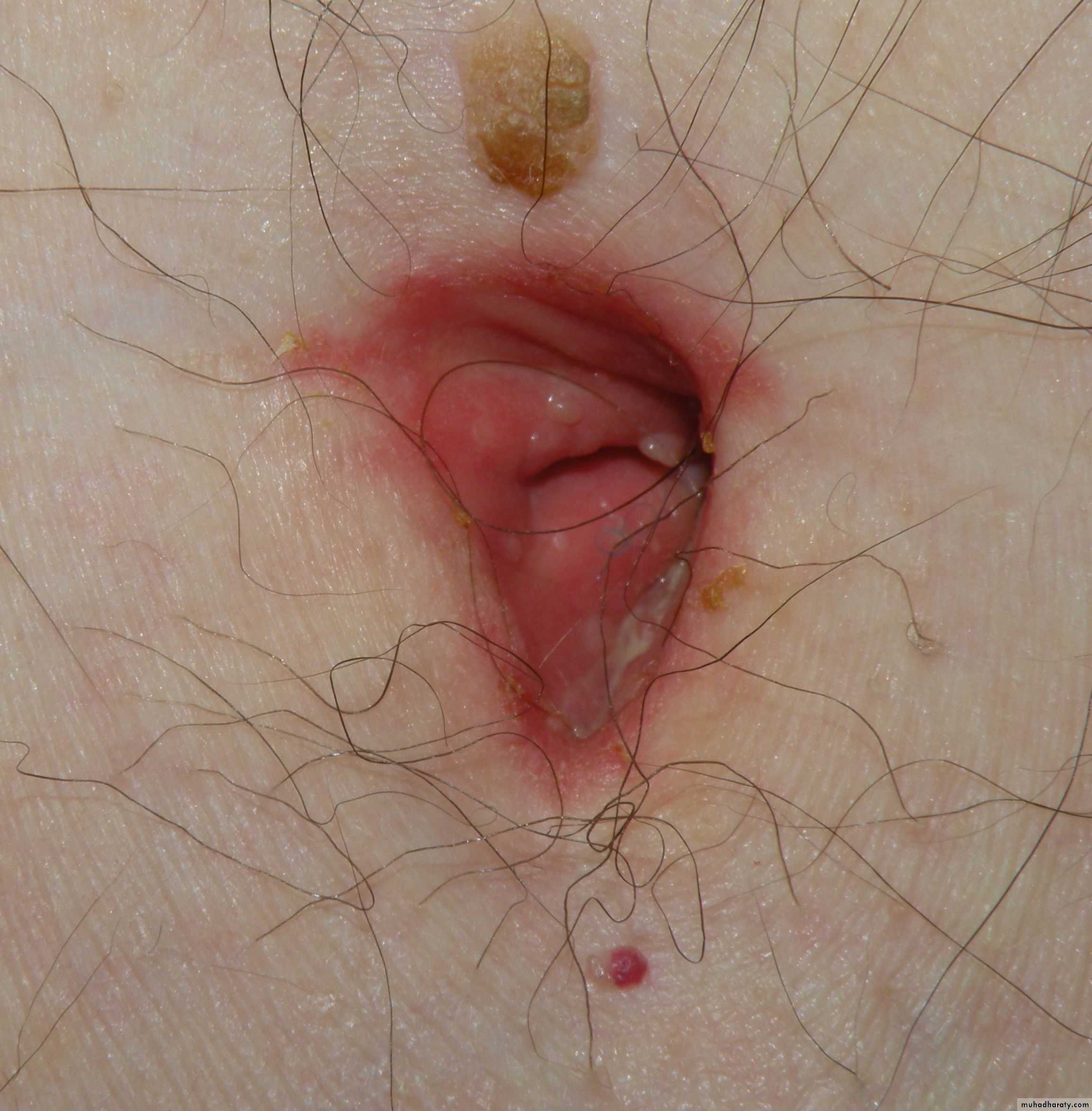
Chronic fistula
Patients may present with a persistent discharge from the umbilical area.Causes:
1- Simple, superficial infection
2- Possibly an infected epidermoid cyst within the umbilicus.
3- Or sinus or a fistulous connection to deeper structures.
4- Complication of umbilical hernia repair due to chronic infection of a mesh or around non-absorbable suture material.
fetal life the umbilicus was also connected to the gut by the vitellointestinal duct
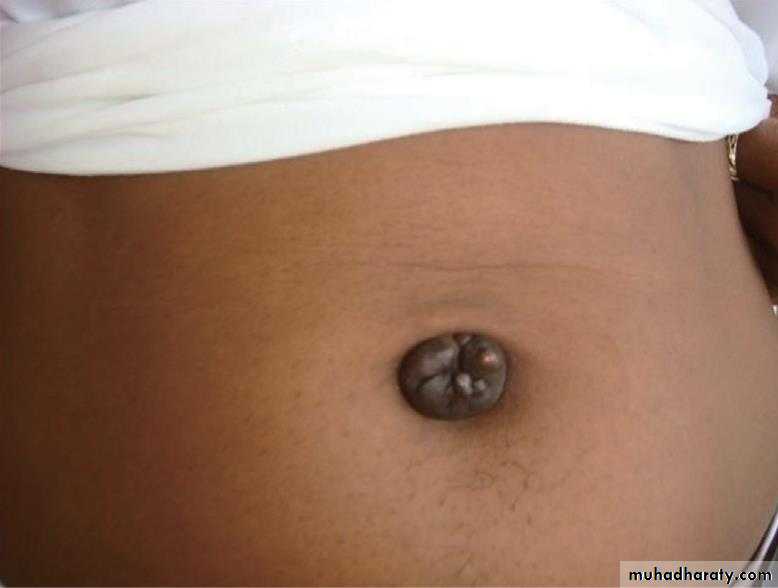
In normal patients, the umbilicus is connected to the liver, bladder and gynaecological organs by various ligaments. Diseases of these organs, such as infection or malignancy, can extend along these ligaments to appear at the umbilicus as a mass or fistulous discharge. E.g sister joseph’ nodule
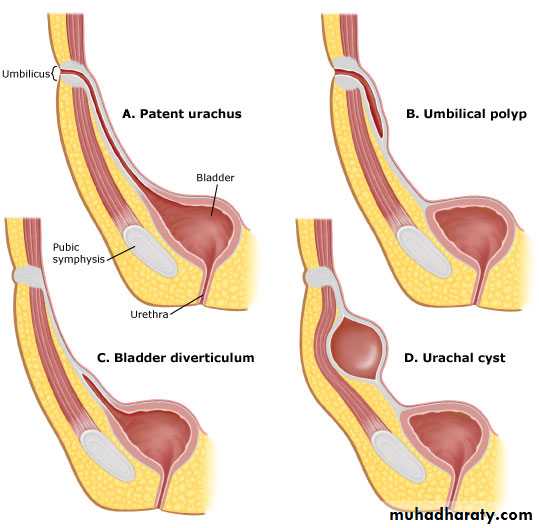
Patent urachus
A connection between the urinary bladder and umbilicus usually presents in later life. This is due to increased pressure in the bladder as a result of obstruction from conditions such as prostatic hypertrophy. The cause of obstruction should be dealt with initially but if the problem persists then surgical excision of the patent urachus might be considered.
Sister Joseph’s nodule----- indicates internal malignancy
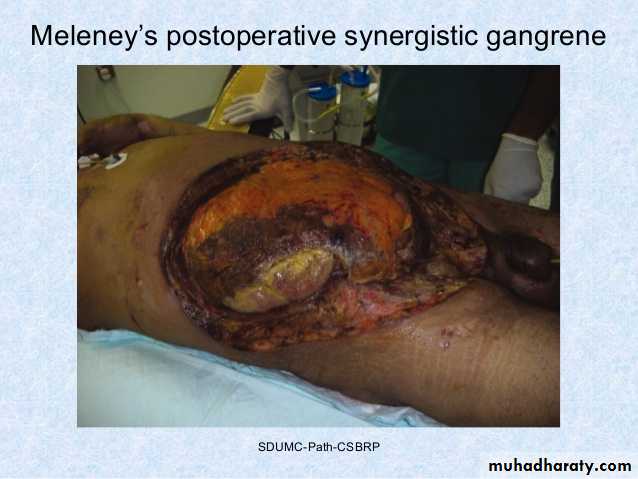
Necrotising fasciitis of the abdominal wall
Necrotising fasciitis results from a polymicrobial, synergistic infection, most commonly a streptococcal species (group A b haemolytic) in combination with Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Proteus, Bacteroides or Clostridia.80%have a history of previous trauma/infection or surgery
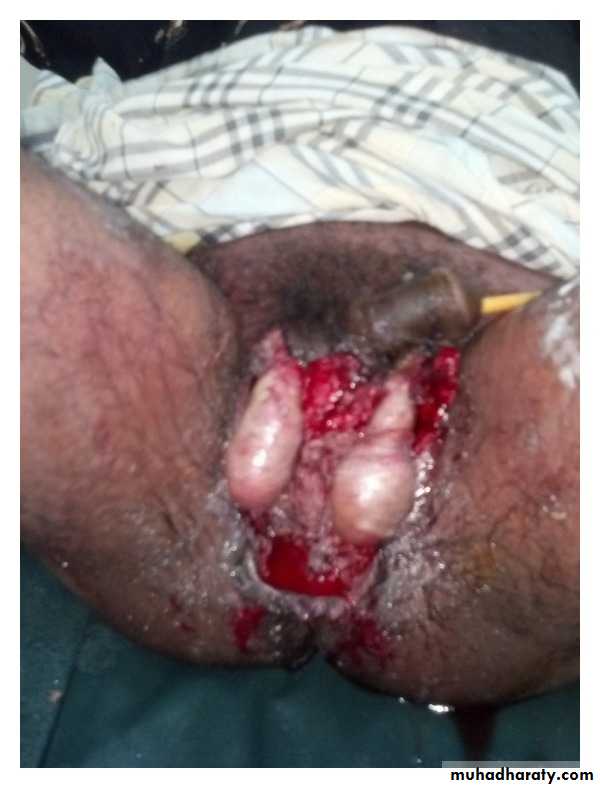
Meleney’s synergistic gangrene(abdominal wall) and Fournier’s gangrene(perineum) are all variants of a similar disease process.
It causes rapid tissue necrosis and overwhelming systemic infection that requires immediate administration of high-dose of broad spectrum powerful antibiotics, aggressive wound and dead tissue debridement.
Predisposing conditions include:
diabetes;
smoking;
penetrating trauma;
pressure sores;
immunocompromised states;
intravenous drug abuse;
perineal infection (perianal abscess, Bartholin’s cysts);
skin damage/infection (abrasions, bites, boils).
Fournier’s gangrene(perineum
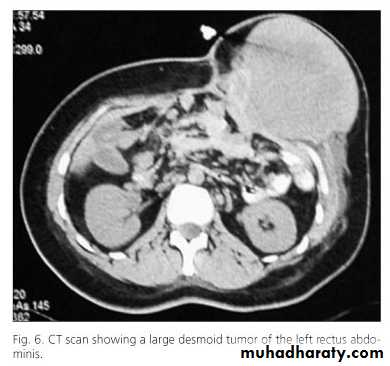
Desmoid tumor
This is usually considered by pathologists to be a hamartoma or a fibroma due to repeated trauma.Is more common in women.
Histologically they contain plasmoidal cell masses resembling giant cells. They undergo central myxomatous change.
Surgical excision with a wide margin is required to prevent recurrence which is a frequent problem.