Proper diagnosis is vital for treatment
planning.DIAGNOSIS:
PREVENTION:
To prevent any recurrence of the
causative disease and their defect.
INTERCEPTION:
Preventing further loss of tooth structure
by stabilizing an active disease process.
PRESERVATION:
Preservation of the vitality and
periodontal support of remaining tooth
structure.
RESTORATION:
Includes restoring form, function,
phonetics, and esthetics.
Purposes of Operative Dentistry
Clinical procedures for Operative Treatment
3
Steps in operative/ restorative procedures
• Evaluate the tooth to be restored
• Obtain local anesthesia
• Determine the type of moisture control to be used during the procedure:
• Cotton roll (partial Isolation)
• Dental rubber dam (complete isolation)
4
Steps in operative/ restorative procedures
• 4. Prepare the tooth for the restoration
• 5. Determine the type of dental materials
• to be used
• 6. Apply dental material
5
Steps in operative/ restorative procedures
• 7. Burnish, carve or finish the dental material
• 8. Check the occlusion of the restoration
• 9. Finish and polish the restoration
6
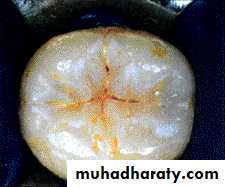
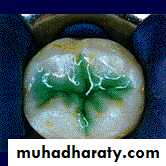
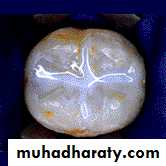
1. Evaluate the tooth to be restored Diagnostic phase
• a. Clinical examinations
• Percussion, pain
• Deep caries
• b. Radiographic examinations
• - Periapical radiograph
• - Bitewing
• c. Vitality test
7
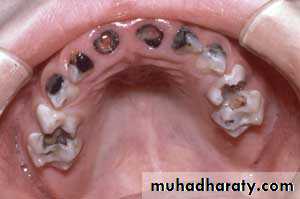
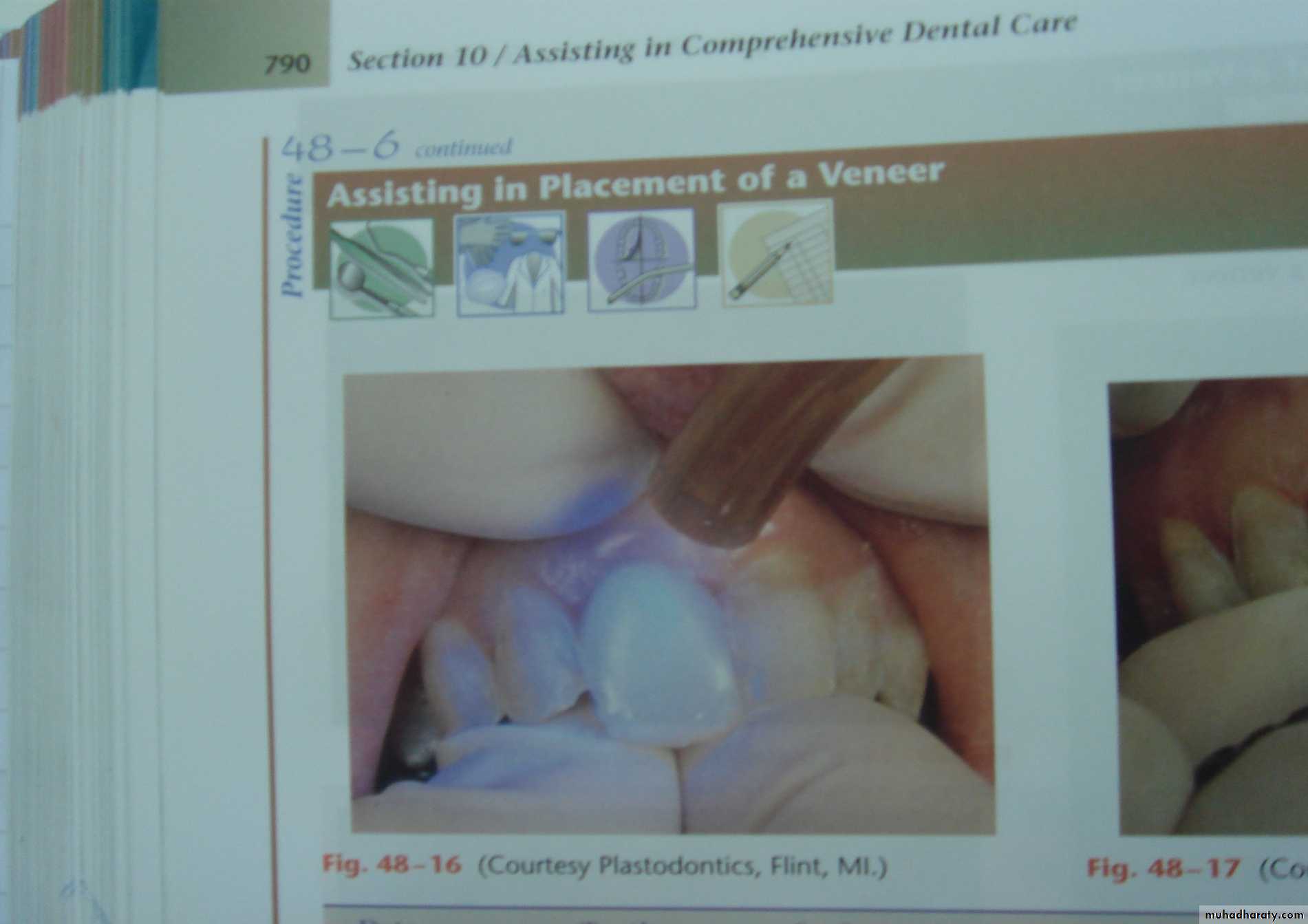
a. Clinical examination
8
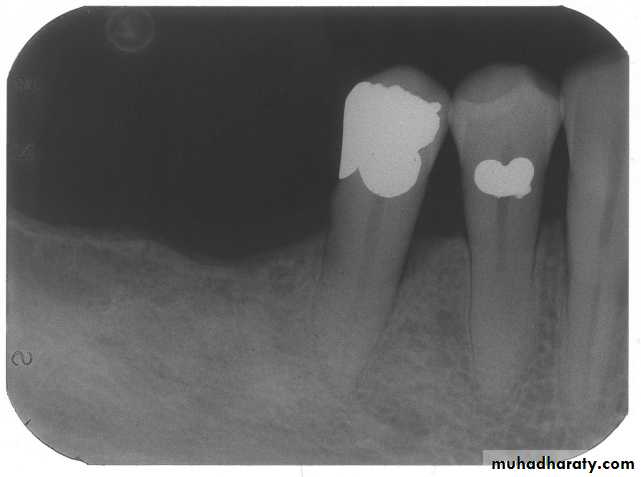
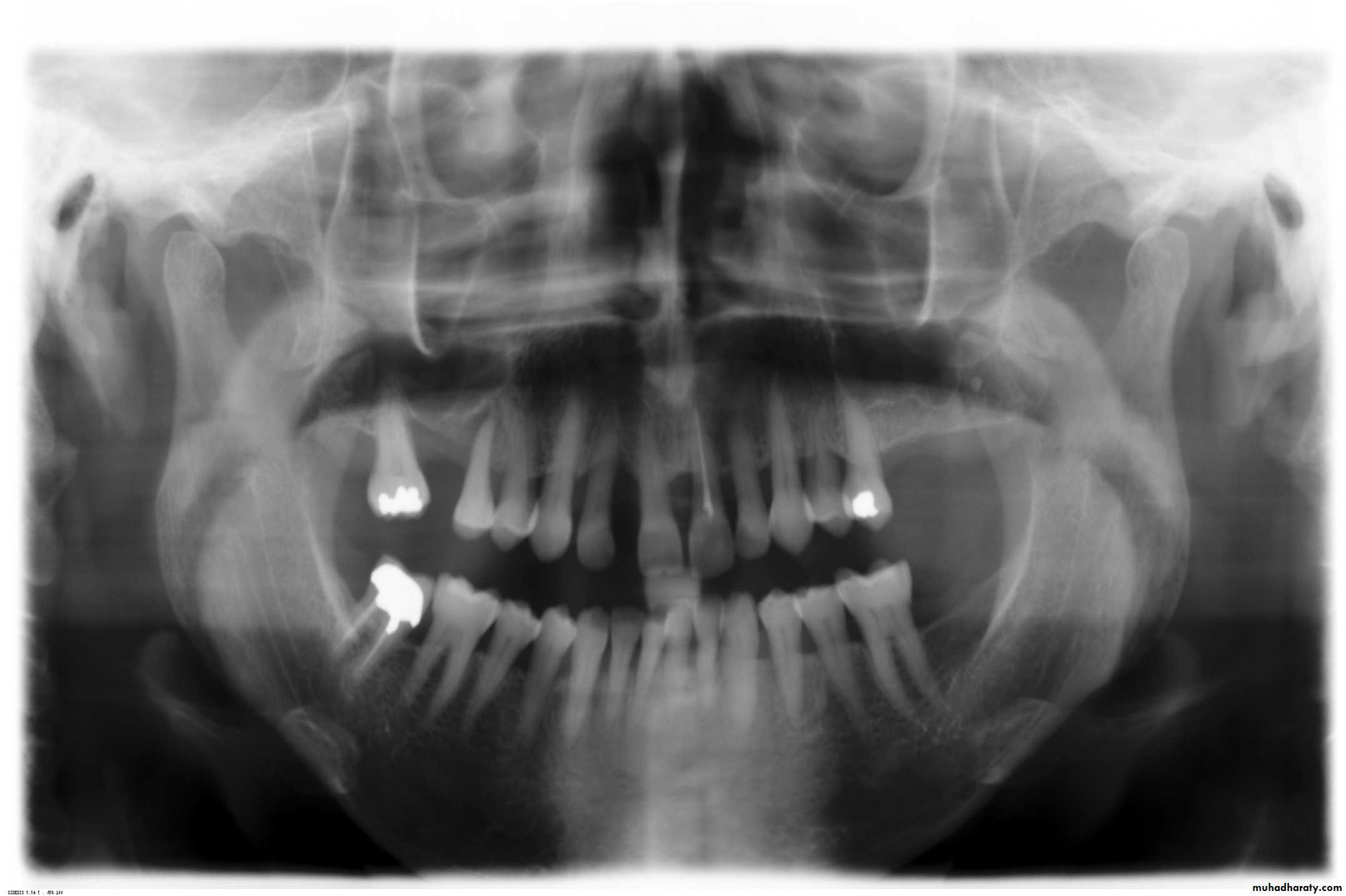
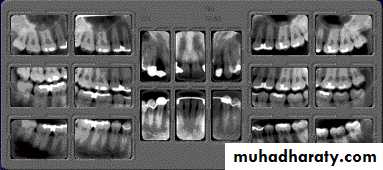
b. Radiographic examination
Panoramic radiograph, OPGPeriapical
Bitewing
9
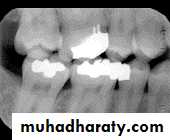
Full mouth intra oral radiographs
Bitewings+ periapicals
Radiographic examination
10
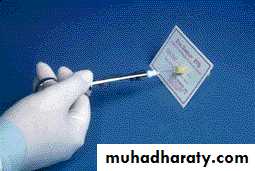
c. Vitality test
Electric pulp tester(EPT):
tests the vitalty of the Pulp by passing low electric current throw the tooth painCompare the reading with the opposing or adjacent normal tooth
11
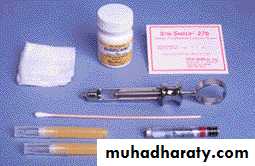
Anesthetic Gel
• Anesthetic solution= carpule
GauzeSyringe
Cotton tipNeedles
ShortLong
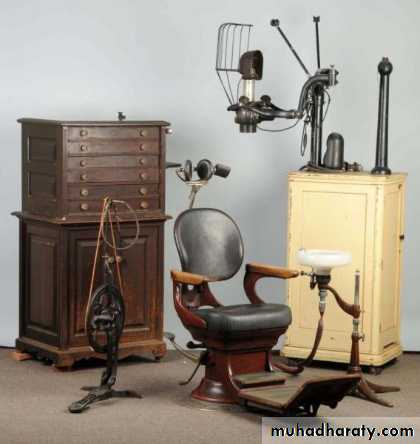
local anesthesia kit
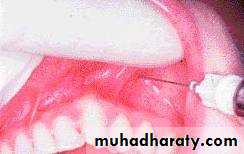
122. Obtain local anesthesia
Upper teeth
Infiltration
• Lower teeth
• Nerve block13
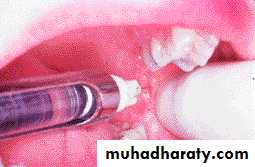
After local anesthesia
Sharping container
Cardboard needle cap-holding device makes recapping needles safer14
Never leave the patient after local anesthesia
15
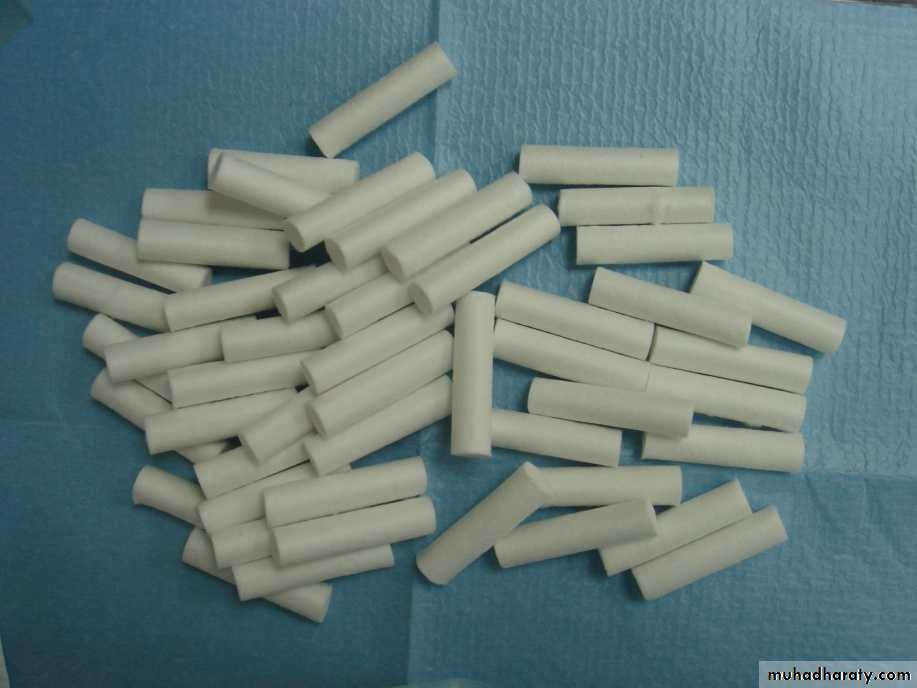
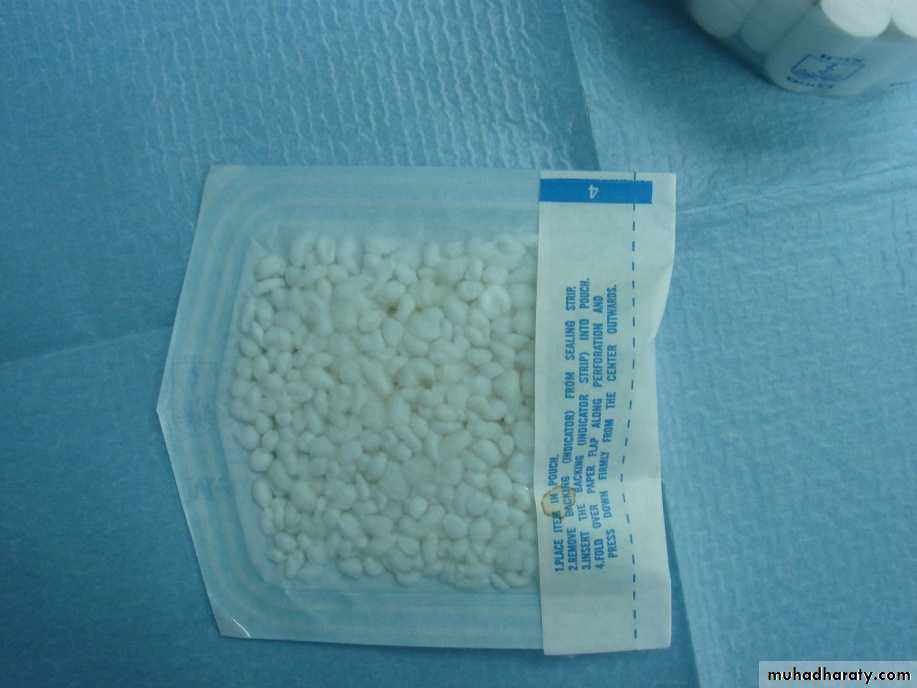
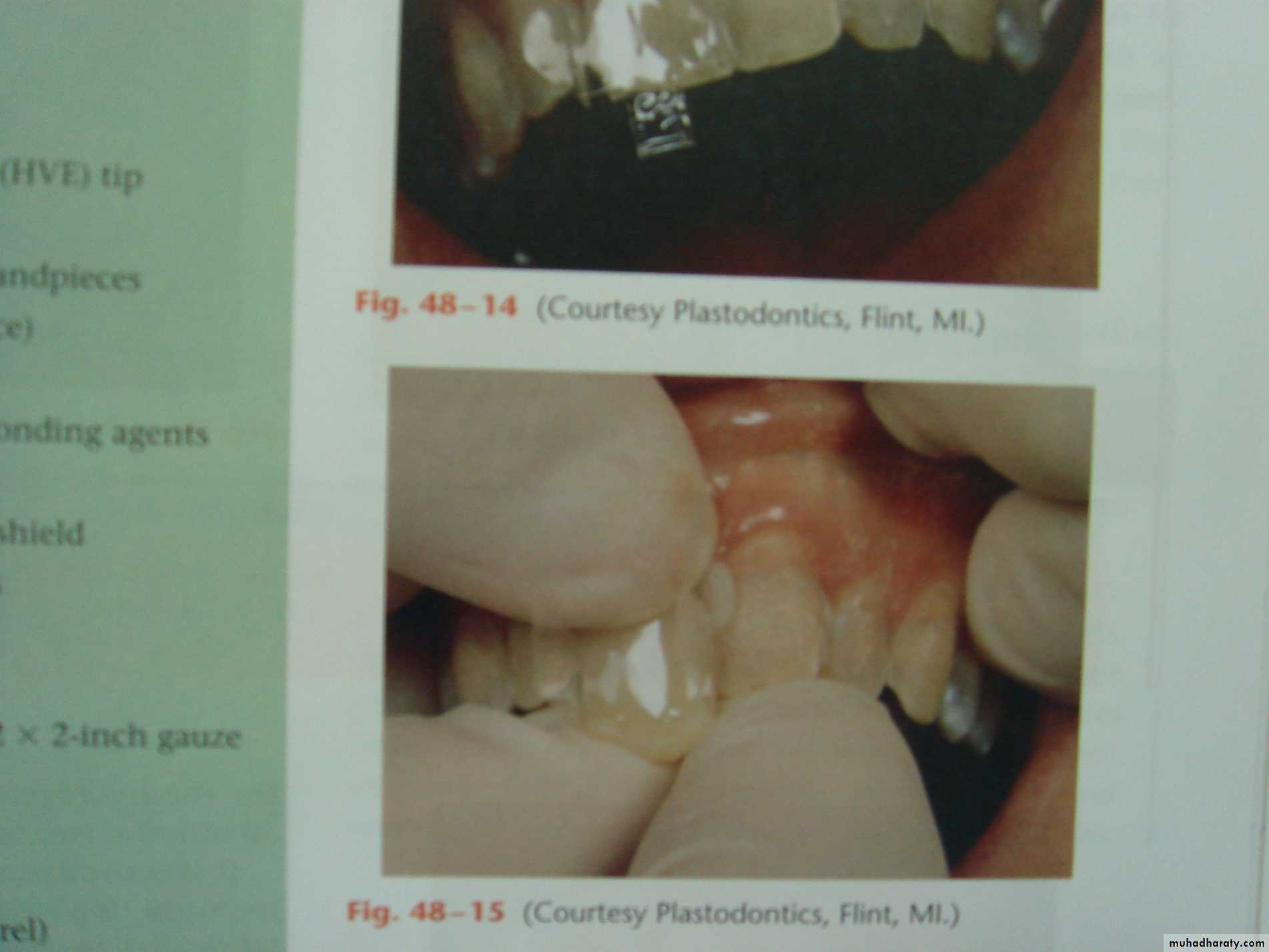
3. Moisture control
• Cotton rolls
• Cotton pellets
• Gauze
• Dental rubber dam
• Saliva ejector
• High-volume oral evacuator tip
16
A. Cotton rolls B. Cotton pellets
17
C. Gauze
18
19
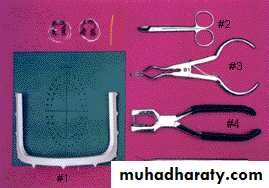
D. Dental Rubber Kit
20
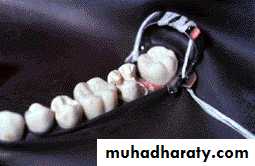
D. Dental Rubber dam
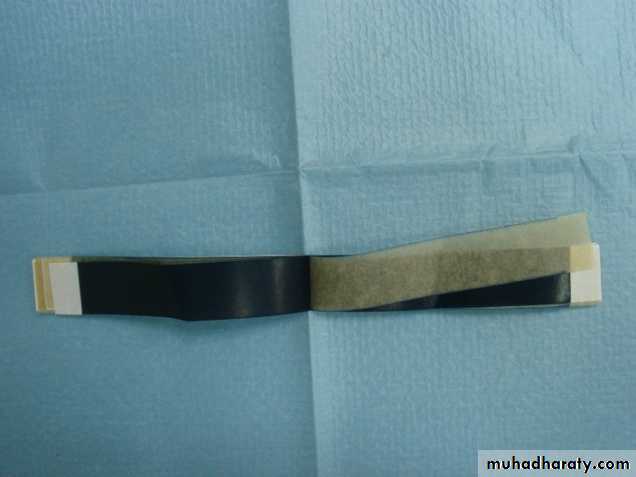
Rubbere dam over the area to isolate the tooth, keep it clean and free of saliva during the dental procedure
21
E. Saliva ejector
22
F. High-volume oral evacuator tip
23
The difference??
24
Suction tips
High-volume oral evacuator=high volume suction
Saliva ejector
= low volume suction
25
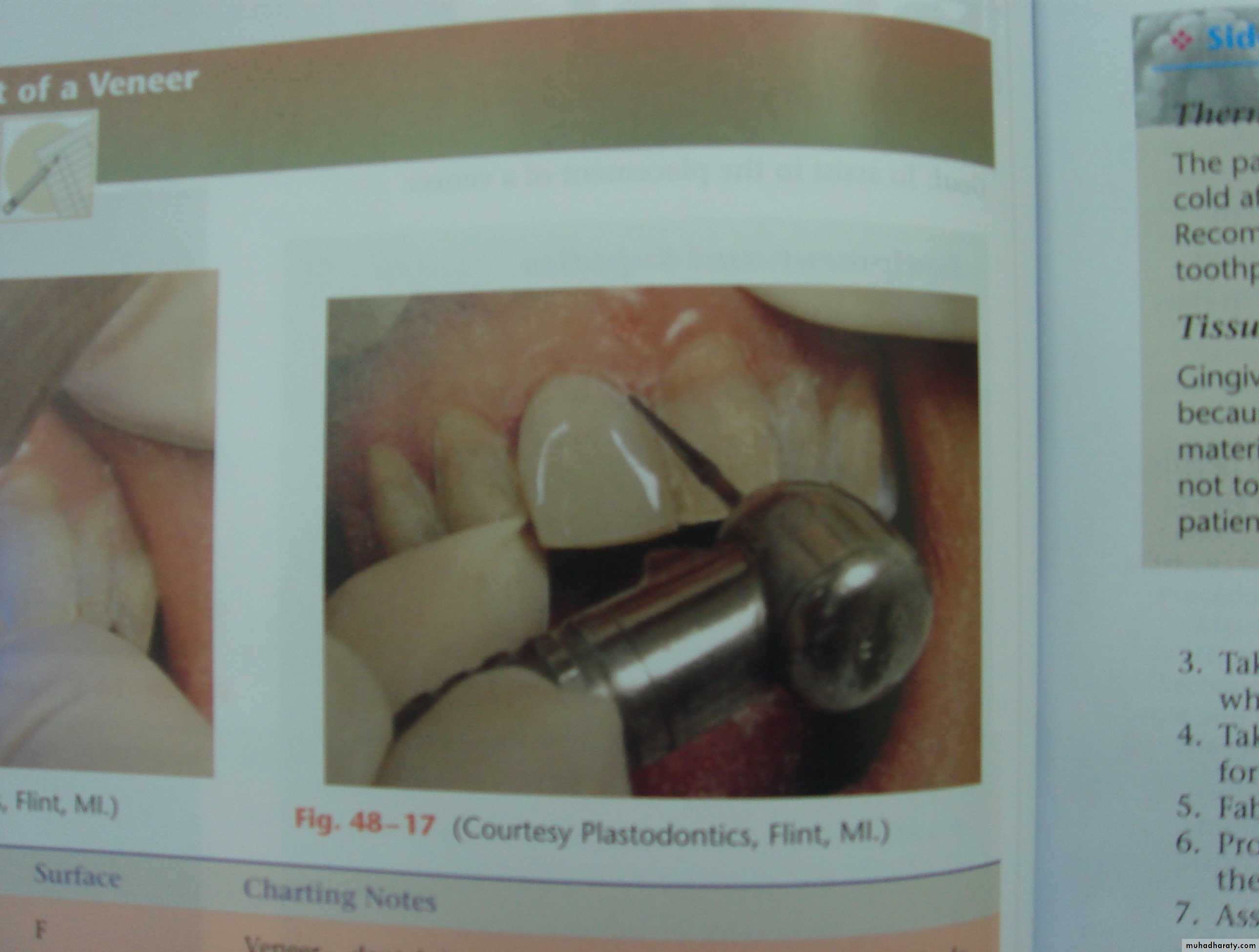
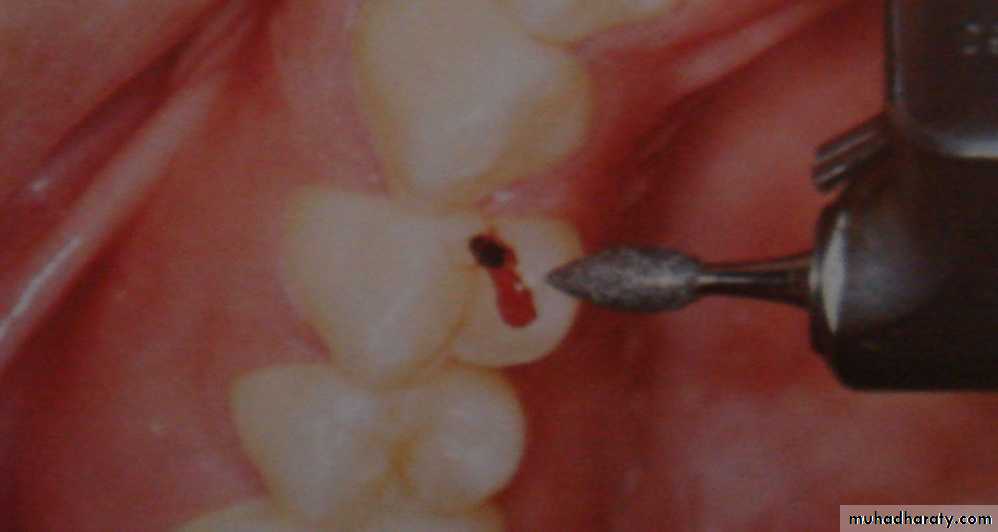
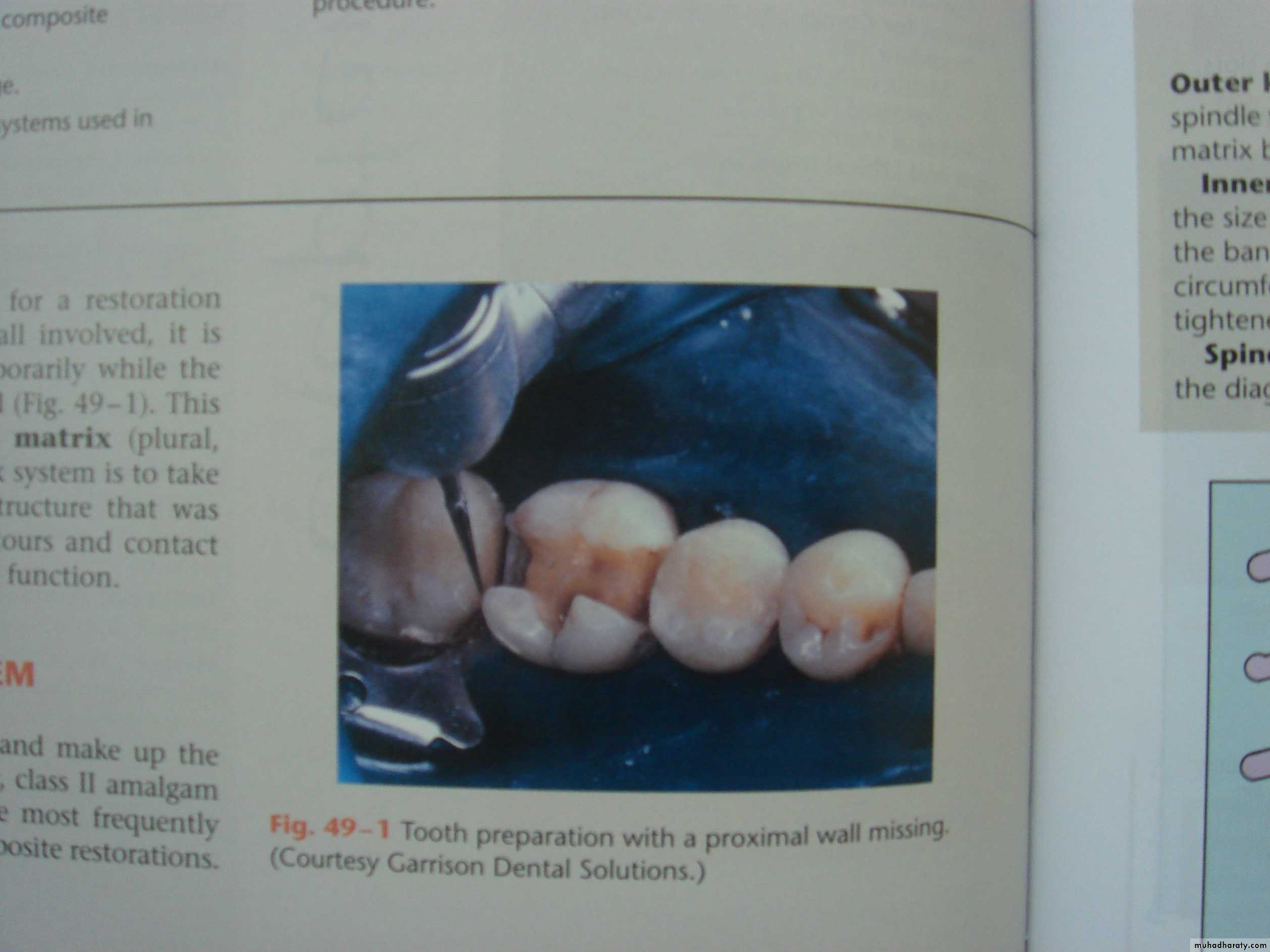
4. Prepare the tooth for the restoration
Rotary instruments
Hand instruments
26
Rotary instruments
LOW SPEED HAND PEICE
HIGH SPEED HAND PEICE27
28
Burs holder
29
Hand instruments
30
5. Determine the type of dental materials
a. Amalgam
b. Composite
31
c. Glass ionomer
Contains Fluoride/ Release Fluoride in the Oral cavity.
White /light gray in color.
Bond to the tooth structure.
32
d. If no time, or deep caries you can apply temporary filling
33
6. Apply the dental material
34
Amalgam
Alloy of mercury and one or more other metals.
Contents:
Silver
Tin
Copper
Zinc
35
a. Application of amalgam
Amalgamator
Amalgam capsule36
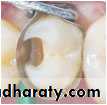
a. Application of amalgam
Amalgam carrierDappen dish
37Application of amalgam
Amalgam condenser
Burnisher
Matrix
Retainer
Wedge
38
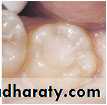
APPLICATION OF AMALGAM
39
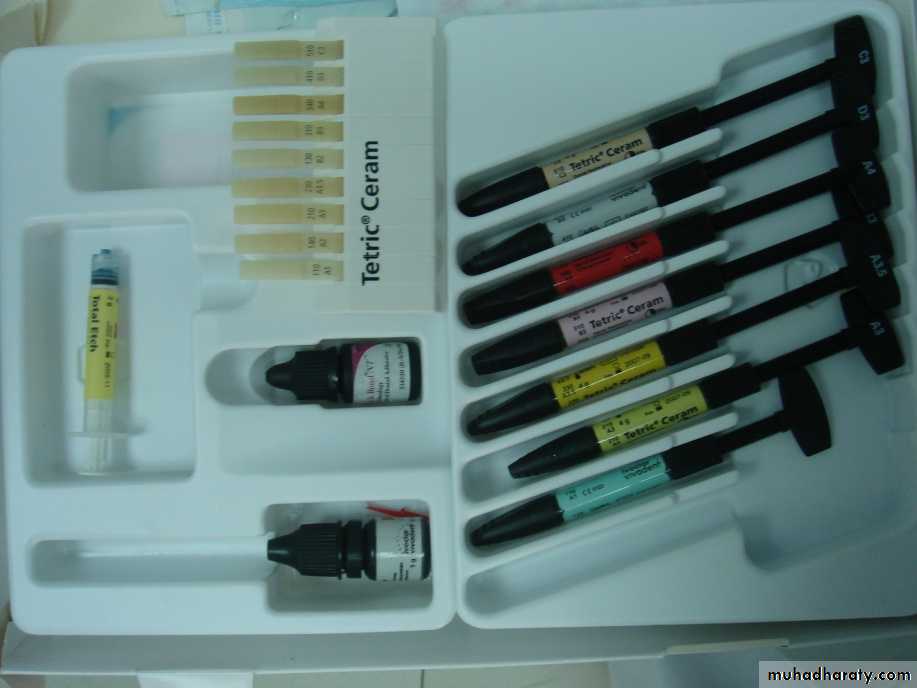
Composite
Resin composites
Bond to the tooth structure by Bonding agentSuperior aesthetic properties and to health concerns about the mercury in dental amalgams
Have found increasing application in the repair and rebuilding of teeth.
Chemical cure or light cure restoration.
40
Composite kit
Shade guide
Acid etchant
Bonding material
Composite
41
Composite
• Select the shade
• Dry the tooth
• Acid etchant
• Wash
• Dry
• Bonding
• Light cure
• Composite in layers 2mm
42
Application of Composite
Light cure
Dry the tooth
Acid itchant43
Application of Composite
44
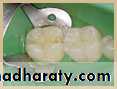
7. Burnish, carve or finish the dental material
45
8. Check the occlusion of the restoration
Articulating paper
High speed hand pieceDiamond bur
High point removal
46
9. Finish and polish the restoration
Amalgam
Composite finishing strips
47
48
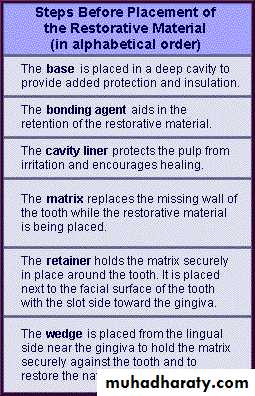
Before placement of the restorative material
Base: placed in deep cavities to provide pulp protection and insulation
Cavity liner: protects the pulp from irritation and encourages healing
Bonding agent: retention of the composite
49
Before placement of the restorative material
Cavity base: placed in deep cavities to provide pulp protection and insulation
e.g. Glass ionomer cement
Zink oxide eugenol cement
Cavity liner: protects the pulp from irritation and encourages healing
e.g. Dycal= under amalgam, composite
Varnish= under amalgam ONLY
Bonding agent: retention of the composite
50
Varnish under Amalgam
Dycal under amalgam orcomposite
Cavity liners
51
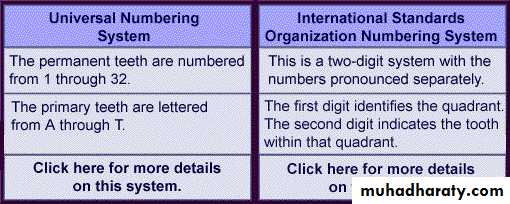
Teeth numbering systems
52
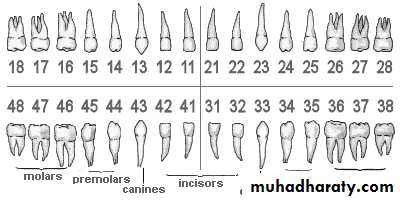
FDI two-digit tooth numbering systemTeeth numbering chart for adult teeth
53
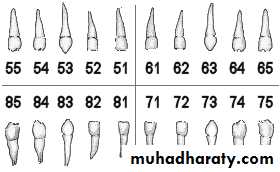
FDI two-digit tooth numbering systemTeeth numbering chart for primary teeth
54
Tooth #16 : Upper Right 1st Molar
Tooth #46: Lower Right 1st Molar
Tooth #25: Upper Left 2nd Premolar
Tooth #34: Lower Left 1st Premolar
Tooth #11: Upper Right central incisor
Tooth #32:……………
Tooth #23:……………
Tooth #44:…………....
Teeth numbering systemsISO, FDI
55
Cavity Classification
Class I
Class II
Class III
Class IV
Class V
Class VI
56
Class I
57
Class II
Occluso-distal
Occluso-mesial
58
Occluso-mesio-distal MOD
59
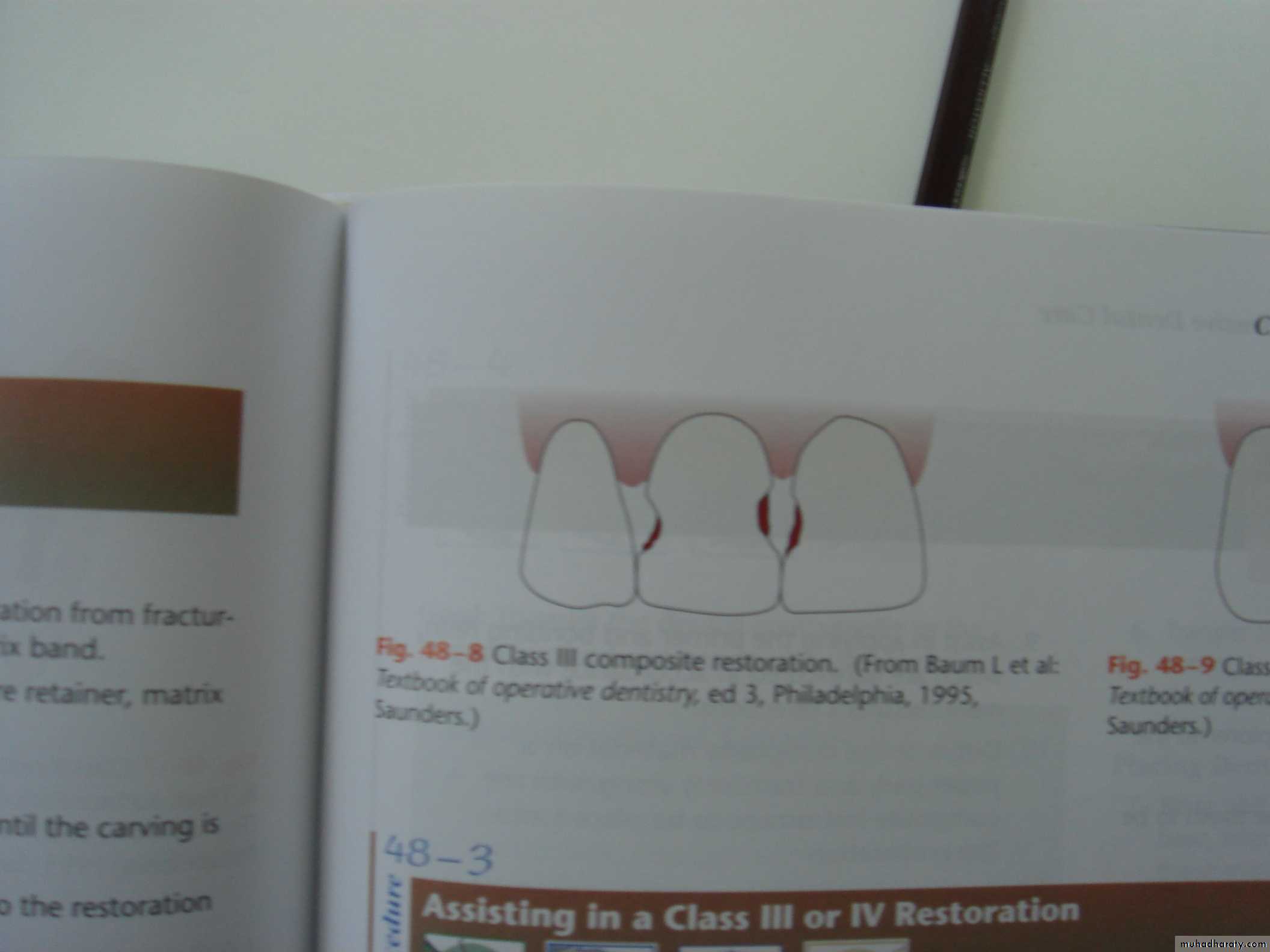
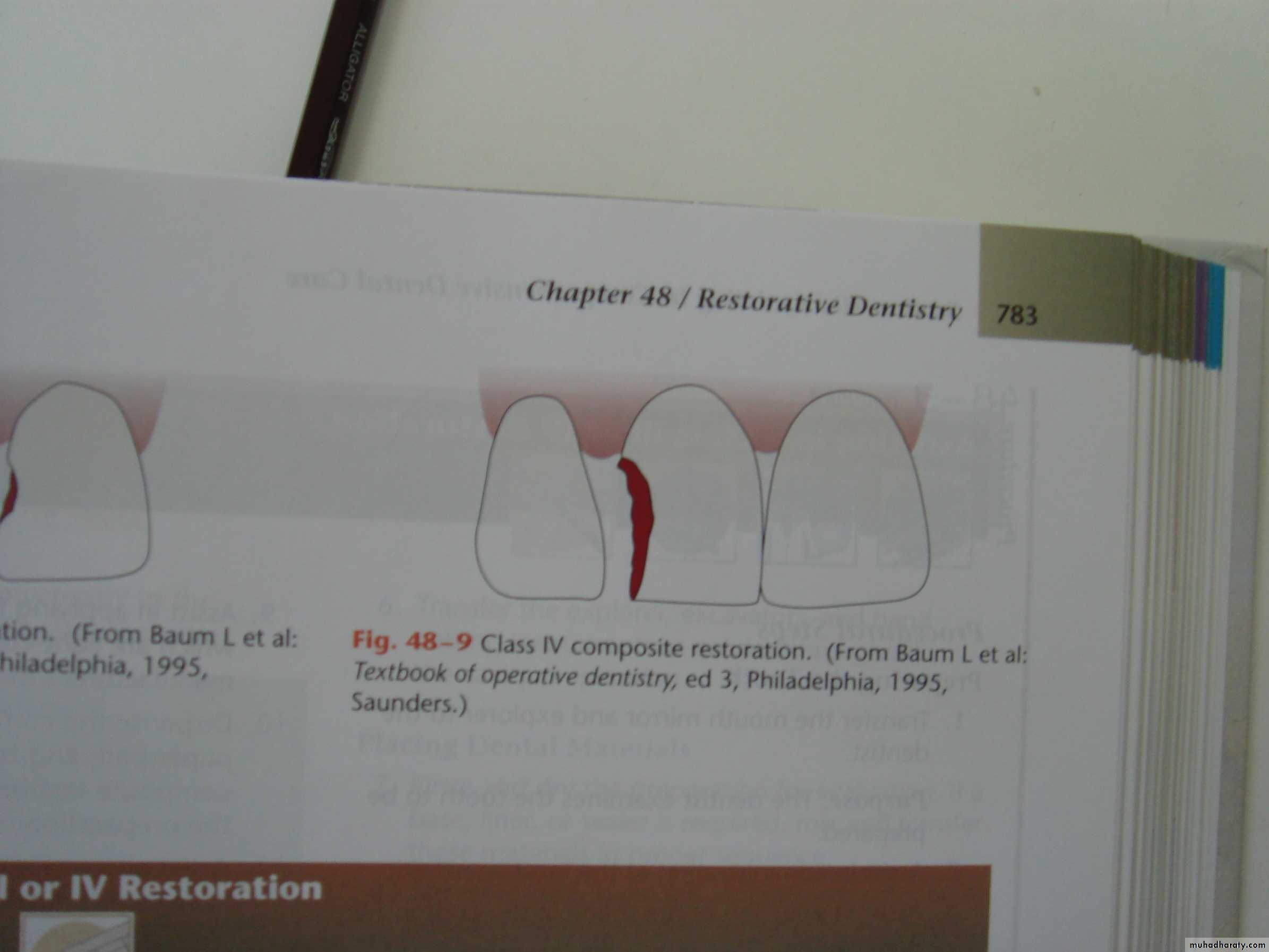
Class III
Class IV
60THANK YOU!