Tooth-colored restoration
Tooth-colored restoration
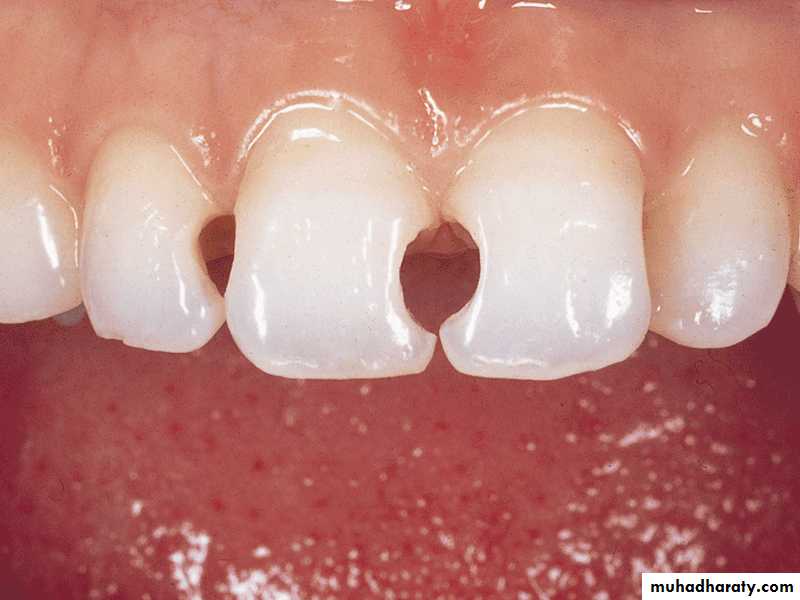
For Class Ⅲ,Ⅳ and Ⅴ,Esthetic Dentistry
For Class Ⅰand Ⅱ,
What are Tooth-colored materials?What is their working mechanism?
What are the cavity preparation futures for tooth-colored restoration?
What are steps for tooth-colored
restoration?What are the advantage & disadvantage
of tooth-colored restoration?
Tooth-Colored Materials
Composite resin
Glass ionomer cement
CompomerComposite Resin
Traditional compositesHybird composites
Flowable composites
Condensable composites
Packable
Universal composites
Glass Ionomer
Chemical adhesion to dentinRelease Fluoride
Compomer
Compomer =Composite
+
Ionomer
Dental Adhesionor Dental Bonding
Adhesion is a process of solid and/or
liquid interaction of one material with
another at a single interface.
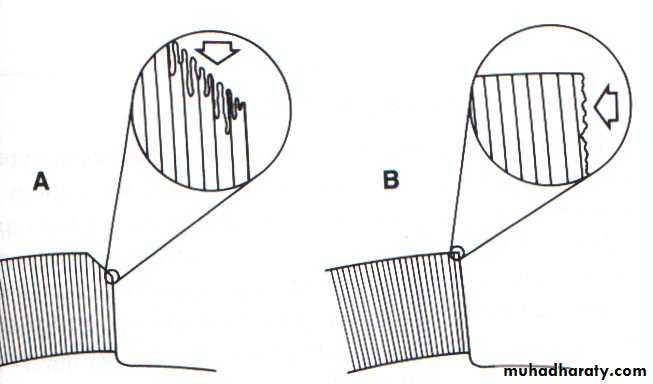
Enamel bonding system
Enamel bonding depends on resin tagsbecoming interlocked with the surface
irregularities created by etching.
Macrotags: form between enamel rod
peripheries.Microtags: smaller tags form across
the end of each rod.
Macrotags and microtags are the basis
for micro-mechanical bonding.
Dentin bonding system
The difficulties of dentin bonding:More water---wet bonding
Lower calcification
Richer organic---collagen network
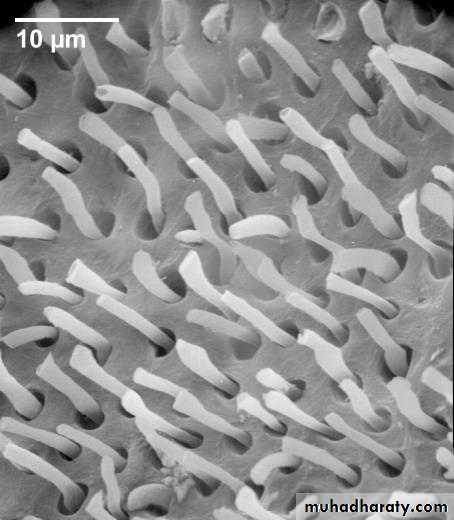
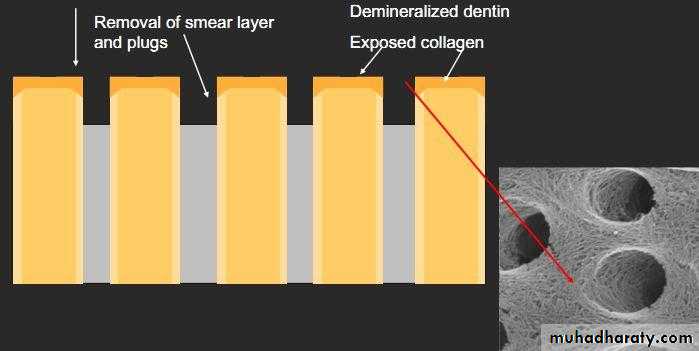
Smear layer
The bond strength is primarily related
to micro-mechanical bonding to the
intertubular dentin which occures
between tubules along the cut dentin
surface.
Dentin Bonding Agent, DBA
Early DBA were hydrophobic, bondeddirectly to the dentin smear layer.
Bond strengths<6MPa.
Later DBA removed the smear layer but
tended to over-etch dentin.
Bond strengths≈10~12MPa.
DBA were chemically modified to be
more hydrophilic.Bond Strengths≈18~20MPa.
Careful dentin conditioning,
Coupled with hydrophilic primer,
Bond Strength≈22~35MPa.
The Development of DBA
Enamel etch (1955)
Dentine etch (1960)
Treatment of smear layer (1980)
Wet Bonding technique(1990)
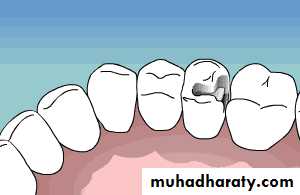
Cavity Preparation
Three designs of cavity preparation:1.Conventional
2.Beveled conventional
3.Modified
Beveled conventional cavity preparations
are similar to conventional preparation,in that the outline form has external,
“box-like” walls, but with beveled
enamel margin.
Beveled enamel margin
Beveled conventional cavity designs for
Class Ⅲ, Ⅳ and Ⅴ preparationsThe advantages :
The ends of enamel rods are more etchedThe increase in etched surface results in
a stronger bond
Increase the retention and reduce marginal
leakage and discoloration.
More esthtically
Modified cavity preparation
Have neither specified cavity wall structurenor specified pulpal depth, and have enamel
margins.
Conserve more tooth structure.
Modified cavity preparation
Initial Clinical Procedure
Local anesthesia
Preparation of the operating site
Shade selection
Isolation of the operating site
with rubber dam or cotton rolls
Rubber dam
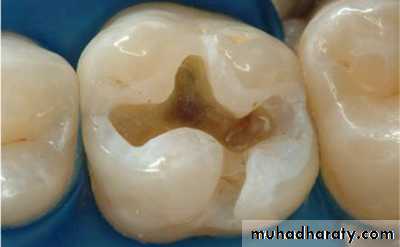
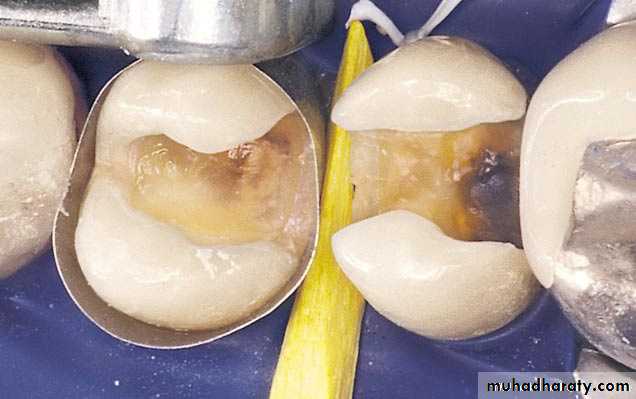
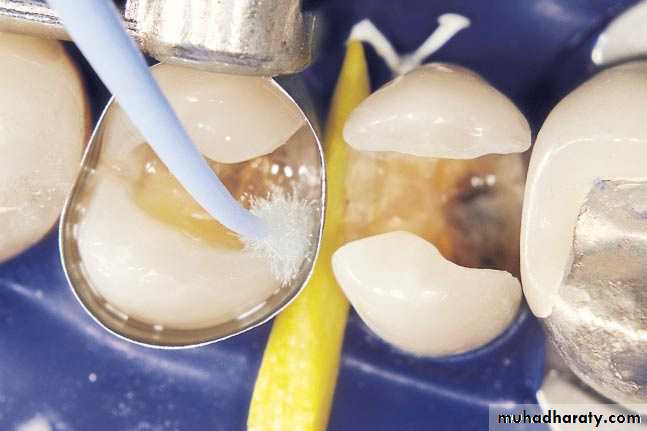
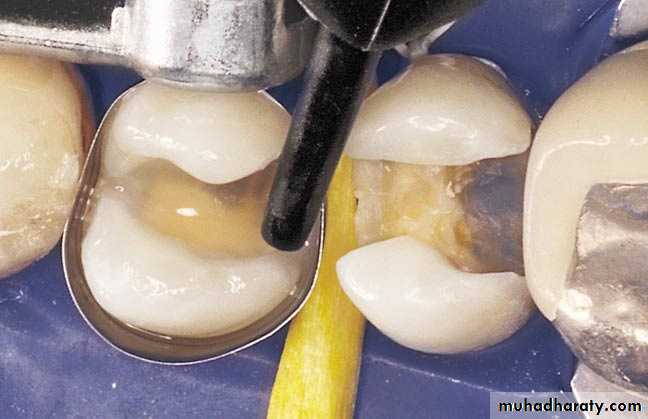
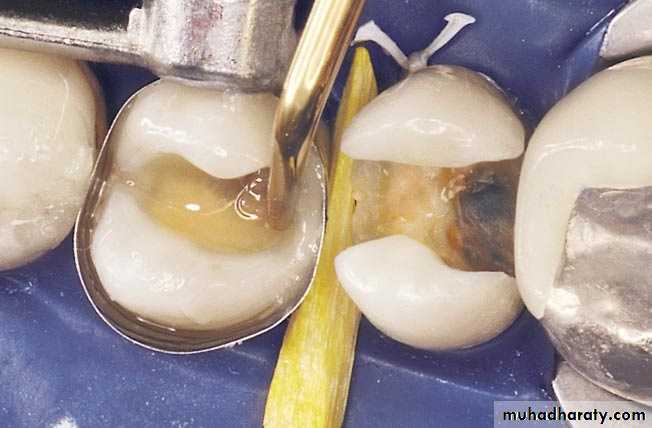
Clinical ProcedureCavity preparation
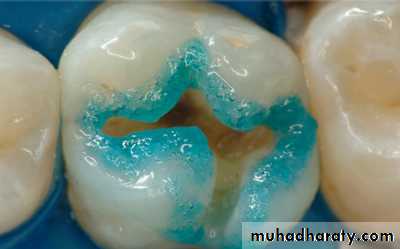
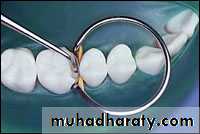
Acid etching enamel & conditioning dentin
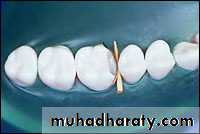
Matrix application
Application of bonding agent
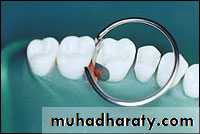
Insertion of composite
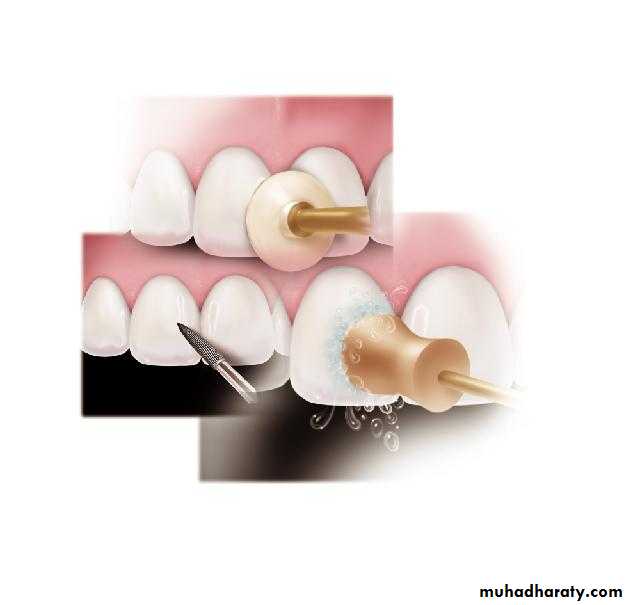
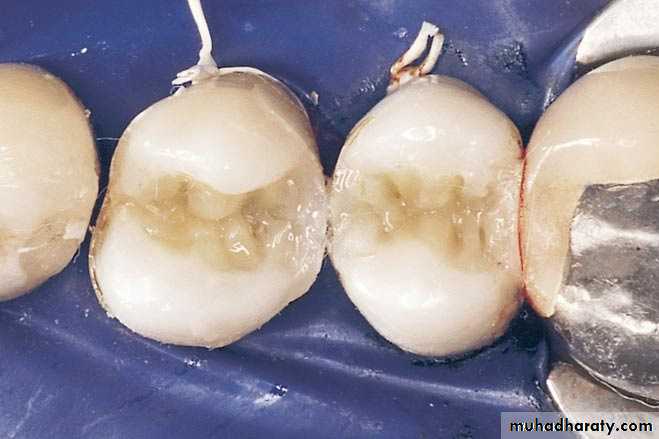
Finishing procedures
Matrix application
Final procedures
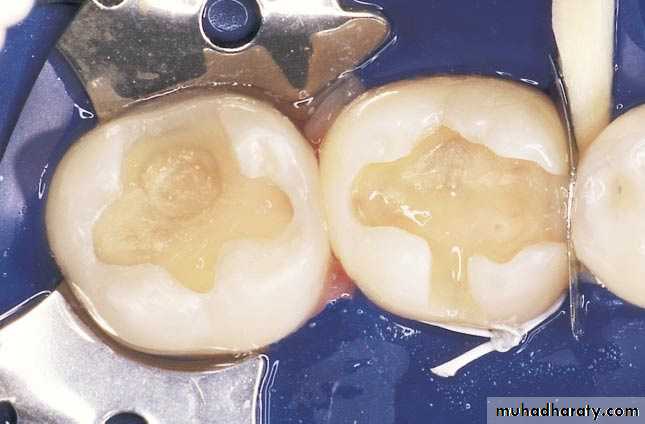
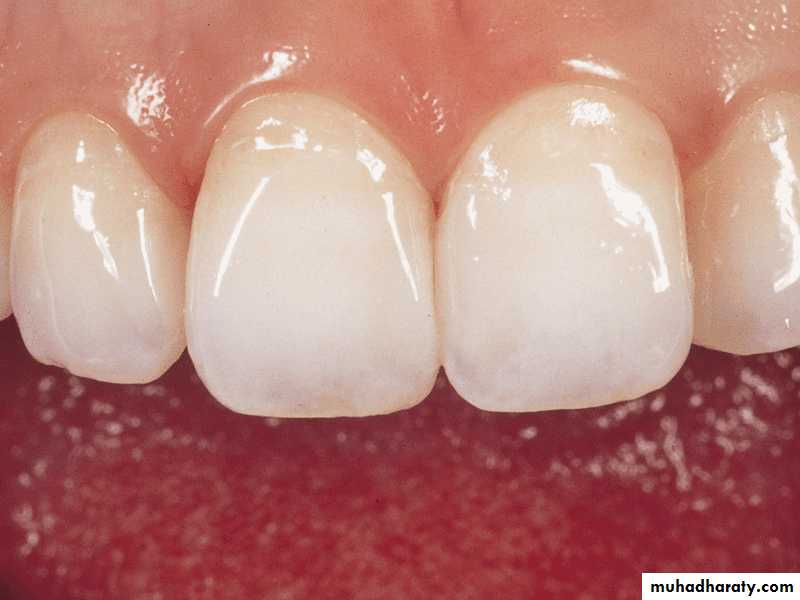
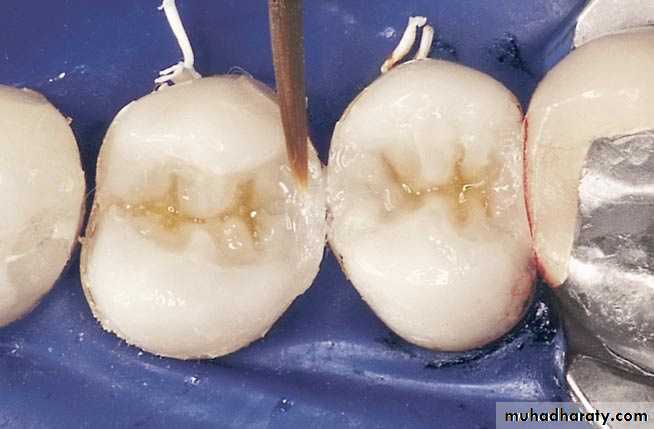
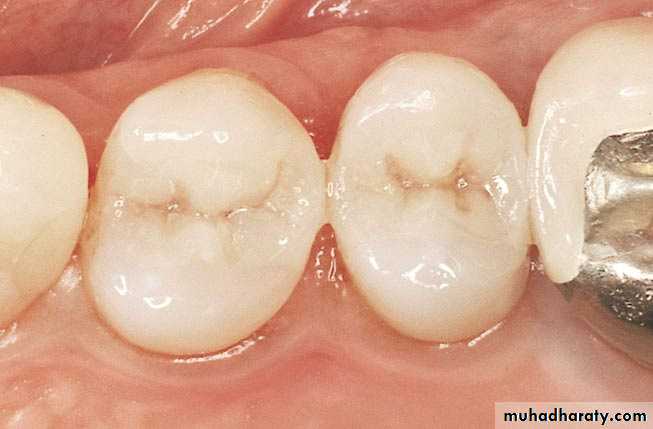
Cases
Conservative Operative Dentistry
Minimal intervention dentistry• is regards as a main stream in caries treatment in the 21st century.
Principles of Minimal Intervention dentistry
• Remineralization of early lesions• Reduction in cariogenic bacteria, to elminate the risk of further demi-neralization and cavitation
• Repair rather than replacement of defective restorations