1
THI-QAR MEDICAL COLLEGE
2015-2016
GENERAL SURGERY
3
RD
YEAR
Surgical incisions
General principles
To select appropriate incision should be :-
1- near by the suspected target ( i.e grid iron in
appendecectomy )
2-extensiblty for exposure so in explorative laparotomy
do midline incision
3-rapidity such as top emergency or critical cases
4- less complication , (hernia , infection
-Security avoid injury to vessels or nerve or 5- avoid
important structure (nerve,
6- cosmetic skin creases
Abdominal incisions
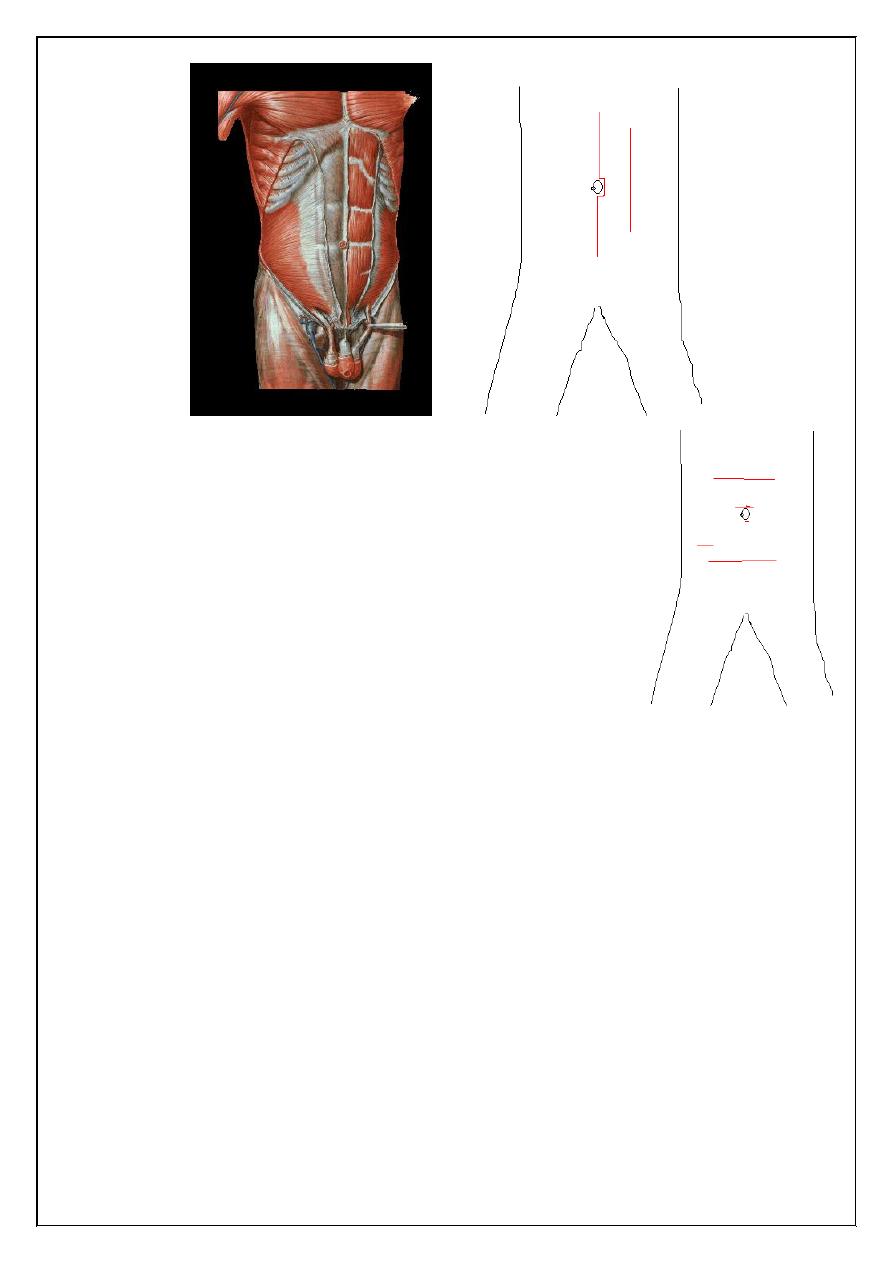
I -Vertical
1- Medline incision
Through linea alba
Advantages : a vascular field , opened readily & closed easily
Enlarged quickly , dose not damage muscles Usually used in explorative laparotomy
Disadvantage :- high post op hernia specially in lower abdomen
2-paramedian Incision
Through rectus sheath 2.5 cm from midline
can extended to thorax ( thoracoabdominal incision ) & to flank
2
II - transverse incision
1-Upper abdomen used in children , cholicystectomy , or any
upper abdominal pathology
2-Supraumbelical & infraublical :- used in paraumblical
hernia , first incision of laparoscopy
3- Pfannenstiel ´s incision :- in gynecological & pelvis
operation s
4- Lance :- is more or less transvers or oblique , its cosmotic
incision for appendicectomy
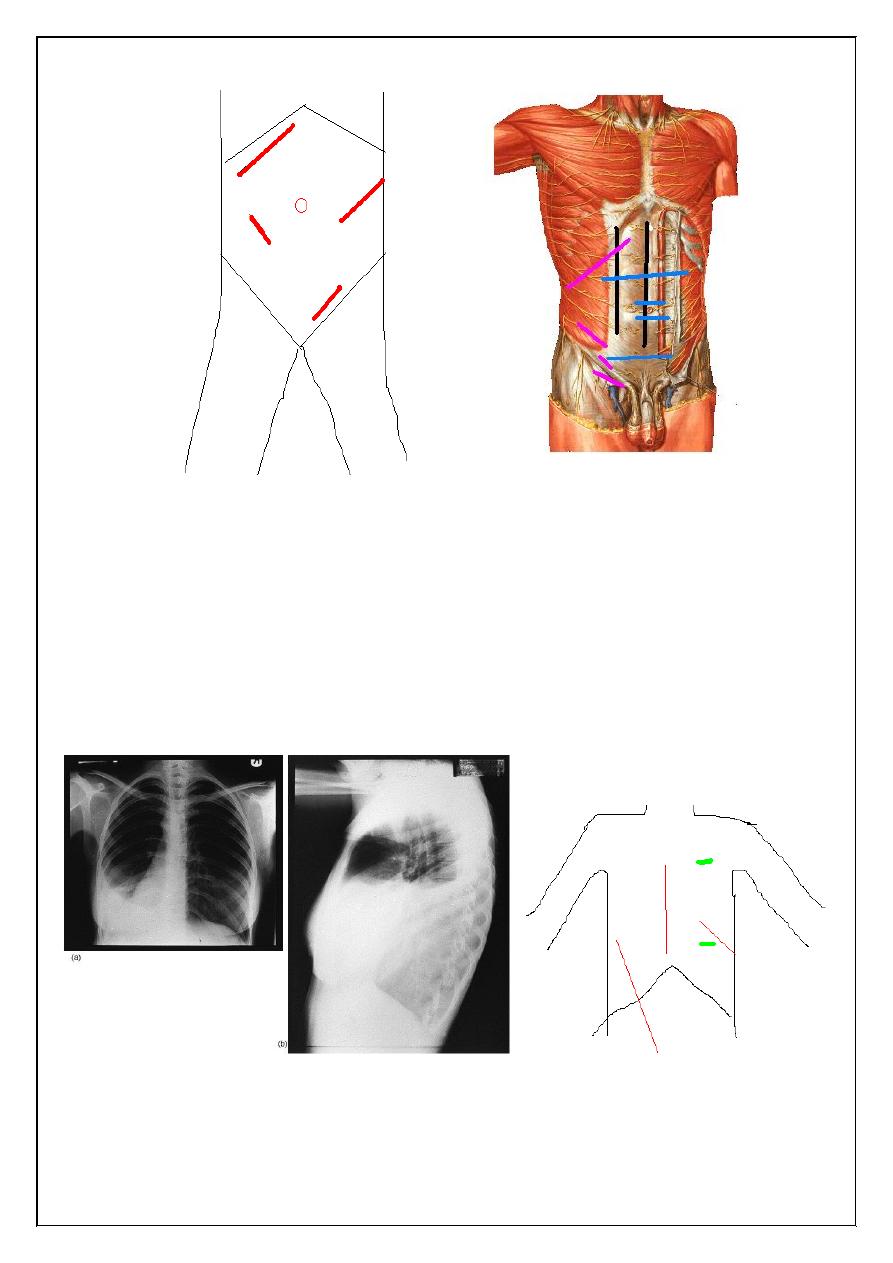
III- oblique incisions
1-Kocher(sub costal) at Rt for gallbladder & liver operation
While Lt for spleen op
2-Grid iron is incision which cruses on line between umbilical & sup. Iliac spine at Mc
Berny point lat. to rectus sheath on ext. & int. & transv . abdominal muscles usually
splitting of muscle , used in apendecectomy , its good incision less post op hernia
3- Retherford Morriss is extended grid iron up or down with muscle cutting ,
used in complicated apendecectomy
4- Lumber Moressian sub costal at lumber area used in renal & uretric surgery
5-Inguainal incision used for inguinal hernia
3
Thoracic incisions
1-Thoracostomy(chest tube )
5th ICS at ant ant. axillary line
In heamo- or pyothorax
2-Mediastenial vertical incision used for cardiac op
3-Intercostals at 5th ICS & 8th ICS
4-Thoracoabdominal extended to Rt or Lt paramedian used for oesophagial op
Breast incisions
1- Circumareolar incision : - around areola , used in lumpectomy , gynecomastia
4
2- Mastectomy incisions :- there is many types of incisions (Steward for simple
Mastectomy , Orr , Grey for radical (Halisid ) op …. )
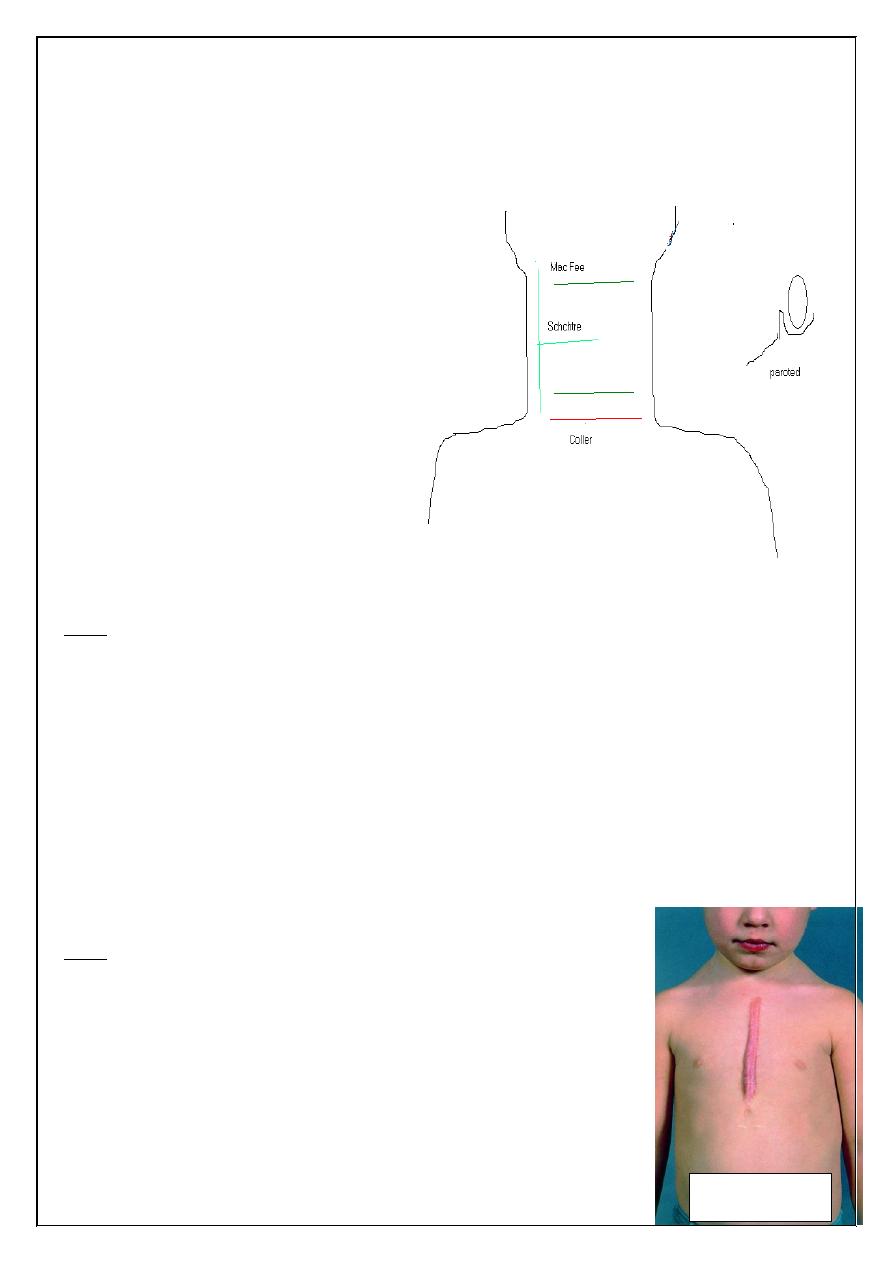
Neck & face incisions
1-Coller incision transverse incision at
lower neck 2.5 cm above suprastrnal
notch for thyroid & parathyroid surgery
2- Neck dissection for radical neck LN
dissections
a) Mac Fee incision (2 horizontal
incisions 1st from mastoid to
hyoid , 2nd above clavicle 2cm
b)
3-Periauricular for parotidectomy
Other face incisions should be with
skin creases for good cosmotics
Complications of incisional wound
Early
1-Wound infection & seroma
open stitch and evacuation of pus or serous fluid , daily dressing
2-skin allergy from plaster, dressing or content of wound discharge
3- stitch abscess ( Rx :- removal of infected stitch)
4-Wound dehiscence
if partial can use plastering and delay removal of stitches
if major should reoperation and close it again with use tension suture
5-non or bad healing due to bad technique (over lap , everted , enverted ) or poor
immunity(DM ,uremic …) or early removal
Late:
1-Incisional Hernia
2-Hypertrophic scar or kiloid
3- Chronic Pain ( specially if nerve entrapment
4-Hyper- or hypopegmentation
This complication due to :-
--Pt causes ( poor immunity , post op. cough ,near by source of
infection like colostomy
keloid

5
--Surgeon causes ( use inappropriate stitches , poor handling …)
--Nurses causes ( poor and inappropriate dressing
--Operation causes ( poor sterilization )
Suture materials
Classification according to :-
Absorbtion :-
1- Absorbable like plain or chromic catgut
2-delay Absorbable ( PDS , vicryl ,
3- Non absorbable ( silk , nylon ,metalic clips)
Biological or synthetic
--Biological like
. cutgut from sheep intestine
. silk from silkwarm larva, cotton
--Synthetic vicryl , nylon , PDS , metalic clip
Coated or non coated
Suture Packaging
6
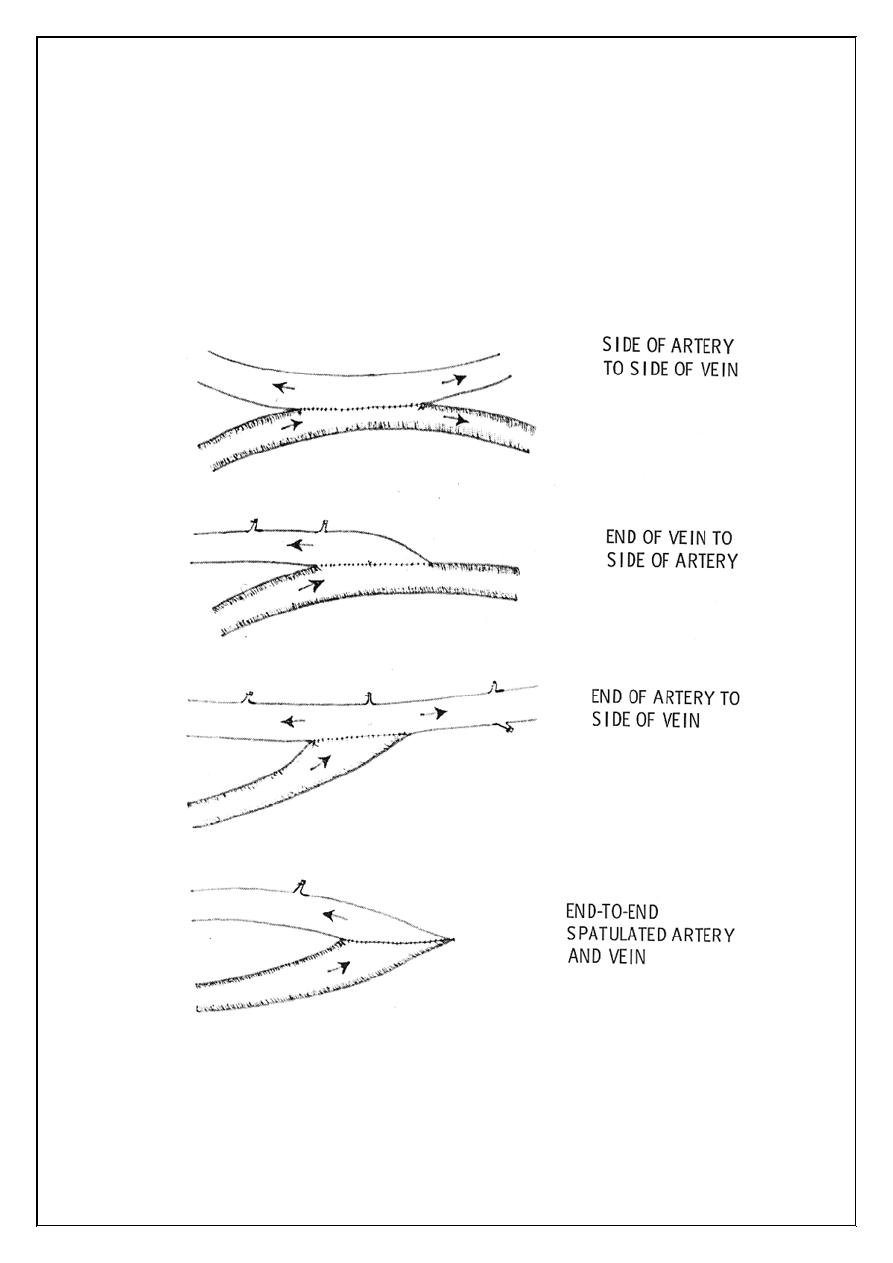
Methods of anastomosis
End to end
End to side
Side to side
Removal of suture
Early as possible , depend on
Site :- face &neck 3-5 days , while in abdomen 7-8d , In joint more
assesst.prof Dr. alaa jamel
MRCSI
C.A.B.S. MBCHB
