1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
Lec-2
.د
بسام
23/11/2015
BIRTH INJURIES
Avoidable and unavoidable mechanical and anoxic trauma affects the baby during labor.
The incidence is about 2-7 / 1000 live birth
predisposing factors includes macrosomia,prematurity, cephalopelvic disproportion,prolong
labor and breach presentation.
5-8/100 000 infants die of traumatic birth injuries.
25/100 000 die because of anoxic injuries.
Some injuries may be latent initially but later result in severe sequele.
Cranial injuries
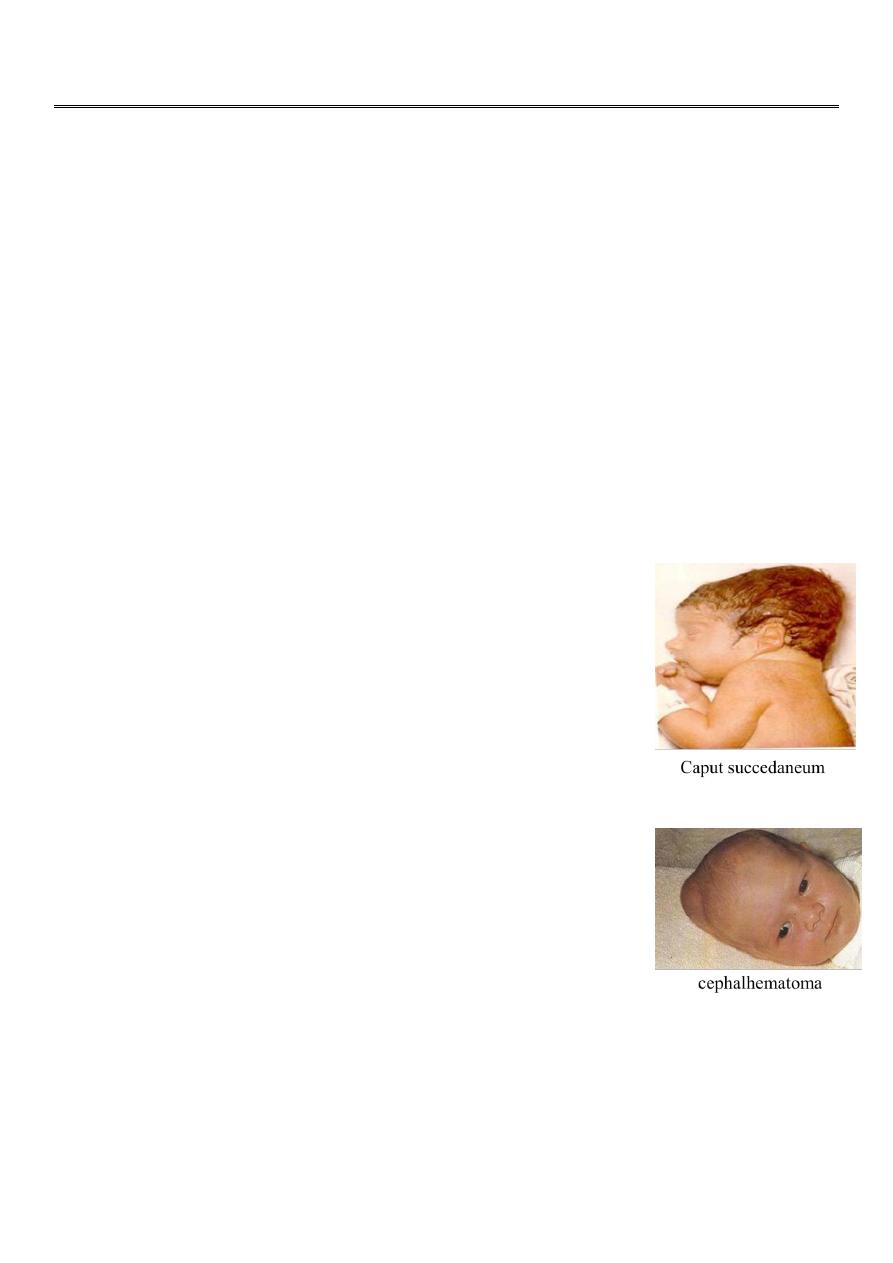
Caput succedaneum:
Is a diffuse sometimes ecchymotic edematous swelling of the soft
tissues of the scalp involving the portion presenting during labor.
It may extent across the midline & across the suture lines.
The edema disappear during the 1st few days of life. No specific
treatment is needed.
Cephalhematoma:
is a subperiosteal hemorrhage , it is always limited to the surface of
one cranial bone
It does not cross the suture lines. No discoloration of the overlying
scalp. The swelling starts after several hours after birth. Occasionally
an underlying linear skull fracture is associated with
cephalhematoma.
It takes 2wks to 3 mo to be resorbed.
No treatment is needed but may be photo- therapy to ameliorate hyperbilirubinemia.
A massive cephalhematoma may rarely result in blood loss severe enough to require
transfusion.

2
Fractures of the skull:
linear skull fractures are the most common cause no symptoms and requires no treatment.
Depressed fractures by the use of forceps delivery, it is advisable to elevate severe
compression to prevent cortical injury from sustained pressure.
Subconjunctival and retinal hemorrhage are frequent, petechiae of the skin of the head and
neck are common.
Peripheral Nerves Injuries
Erb’s palsy: is an injury to C 5,6, there is failure of abduction of the arm
from the shoulder unability for external rotation of the arm and to
supinate the forearm.
The characteristic position is adduction and internal rotation of the arm
and pronation of the forearm.
The biceps reflex is absent. The Moro reflex is absent on the affected side.
Klumpks paralysis:
It is rare injury to C 7, 8 and T1. It produce a paralyzed hand and ipsilateral ptosis and meiosis
if the sympathetic fibers of T1 are injured.
Phrenic nerve paralysis:
C 3, 4, 5 injury result in dyspnea, cyanosis and irregular breathing.
Facial nerve injury:
results from pressure over the facial nerve in utero, from efforts during labor, or from
forceps during delivery,rarely it is due to nuclear agenesis of facial nuclei.
When the infant cry:
there is movement only on the non paralyzed side of the face, and the mouth is drawn to
that side.On the affected side the forehead is smooth, the eye cannot be closed, the
nasolabial fold is absent.
Visceral Injuries:
The liver is ruptured and there is formation of subcapsular hematoma which may tamponade
furthur bleeding. The infant appears normal in the initial 1-3 days non specific signs related
to loss of blood in the hematoma may appear as poor feeding irritability, pallor, jaundice,
tacchypnea, and tacchycardia. A mass may be palpable in the right hypochondrium and
abdomen may appear blue, the hematoma may be large enough to cause anemia.

3
Shock and death may occur if the hematoma breaks into through the capsule into the
peritoneal cavity.
Rupture of the spleen may also occur alone or in association with the liver.
Fractures:
Clavicles: usually results when there is difficulty in the delivery of the shoulder in vertex
presentation and of the extended arms in breach deliveries. The baby is unable to move the
arm freely on the affected side, bony irregularity may be palpated, occasionally discoloration
may be visible over the fracture side. The Moro reflex is absent on the affected side.
Extremities: fracture of the humerus and the femur. Spontaneous movement and Moro
reflex is absent on the affected extremity.
Intracranial hemorrhage:
Intracranial hemorrhage may result from:
1. Trauma and it is usually epidural subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage, it occur when
there is cephalopelvic disproportion, prolonged labor, breach delivery, or in mechanical
intervention.
2. Asphyxia.
3. Thrombocytopenia.
4. DIC
5. Vit. K deficiency.
6. Other bleeding tendency or vascular malformation,these results in subarachnoid or
intracerebral hemorrhage.
