
Cervical lymphadeopthy
Dr. Maitham H Kenber
General surgeon

Definition
• Lymphadenopathy
refers to nodes that are abnormal in either size, consistency
or number.
• "generalized
" if lymph nodes are enlarged in two or more noncontiguous areas
•
"localized"
if only one area is involved.
• Generalized lymphadenopathy almost always indicates the presence of a
significant systemic disease.

General principles
• Mostly diagnosed on the basis of a careful history and physical examination.
• Localized adenopathy should prompt a search for an adjacent precipitating
lesion.
• In general,
cervical, axillary lymph nodes greater than
๑ cm and inguinal >
๑.๕ cm
in diameter are considered to be abnormal.
• Generalized adenopathy should always prompt further clinical investigation.

Lymph node anatomy
• Normal lymph nodes
are composed of a
cortex and a medulla
covered by a fibrous
capsule
• Each lymph node
contains a main artery
that enters at the hilus
and branches into
multiple arterioles.
• Cortex contains tightly
packed lymphocytes and is
hypoechoic (u/s).
• Medulla is made of
trabeculae and medullary
cords and sinuses and is
echogenic (u/s)

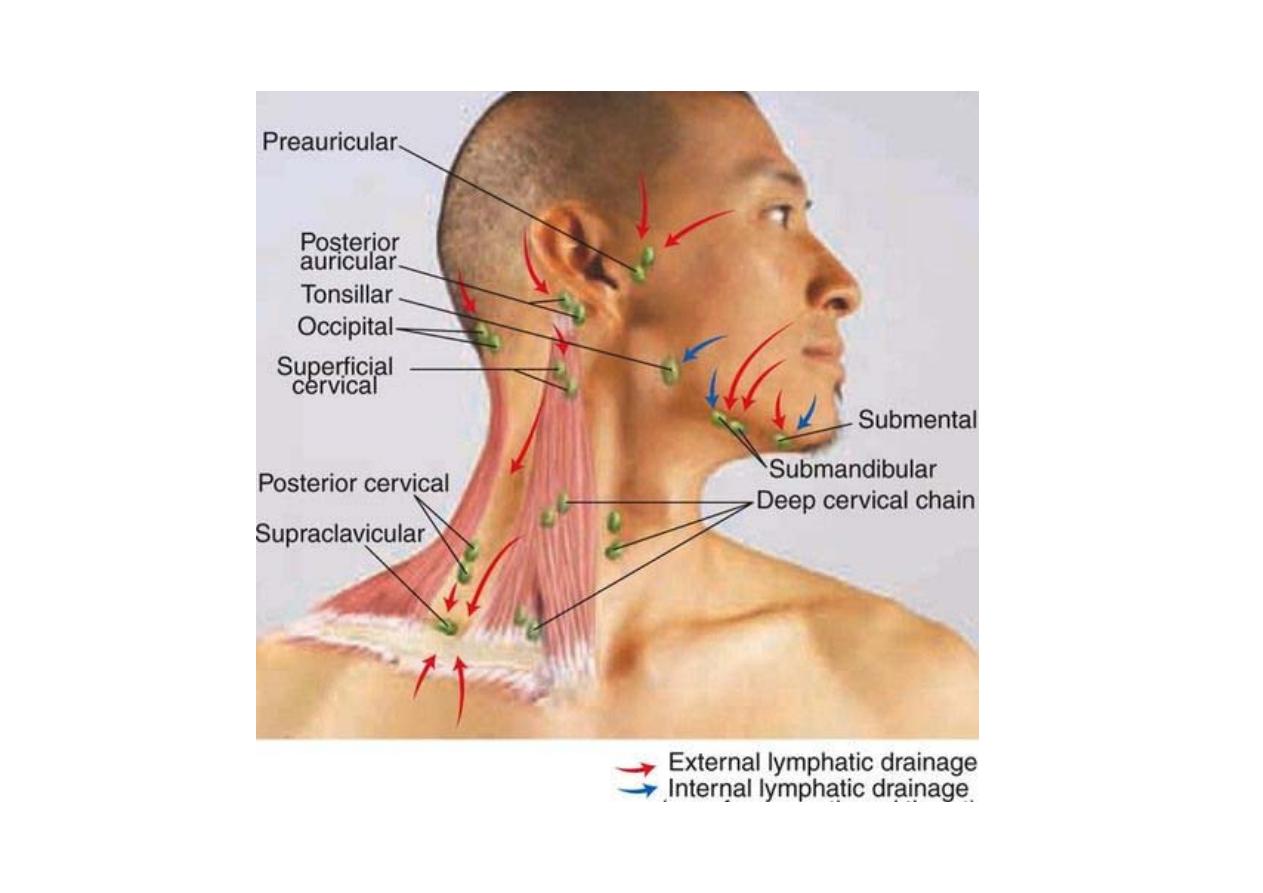
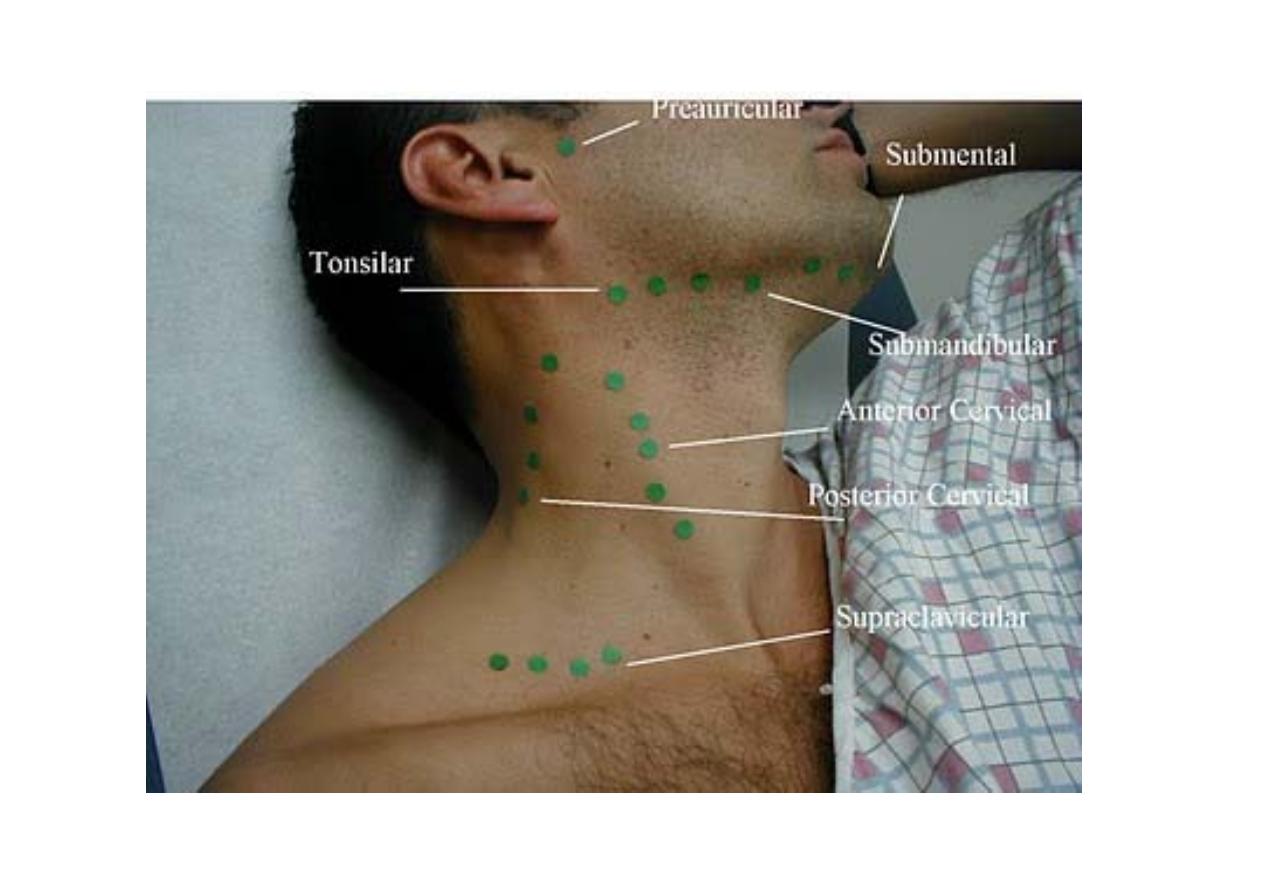
Right & left groups
each divided into: horizontal (circular) and vertical
The
horizontal group
include:
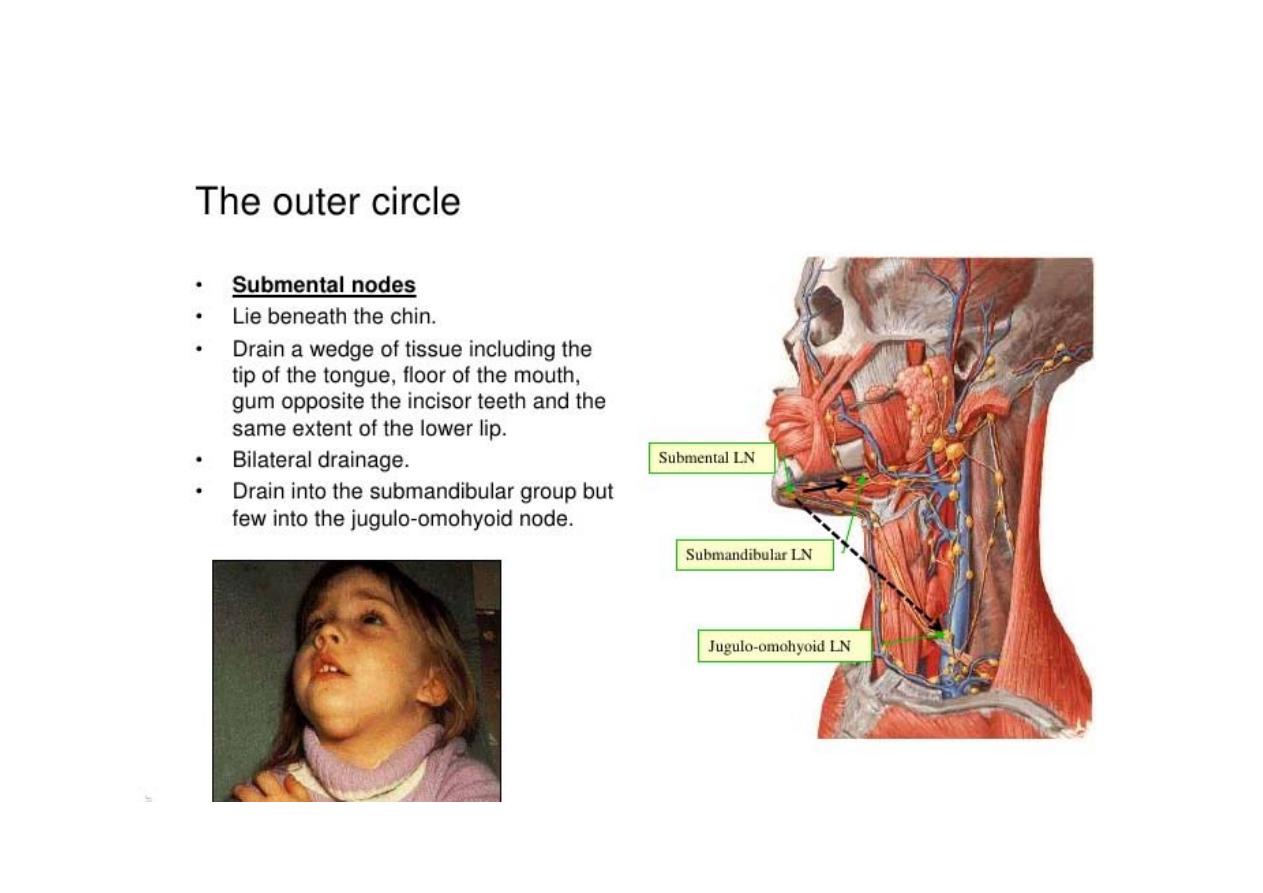
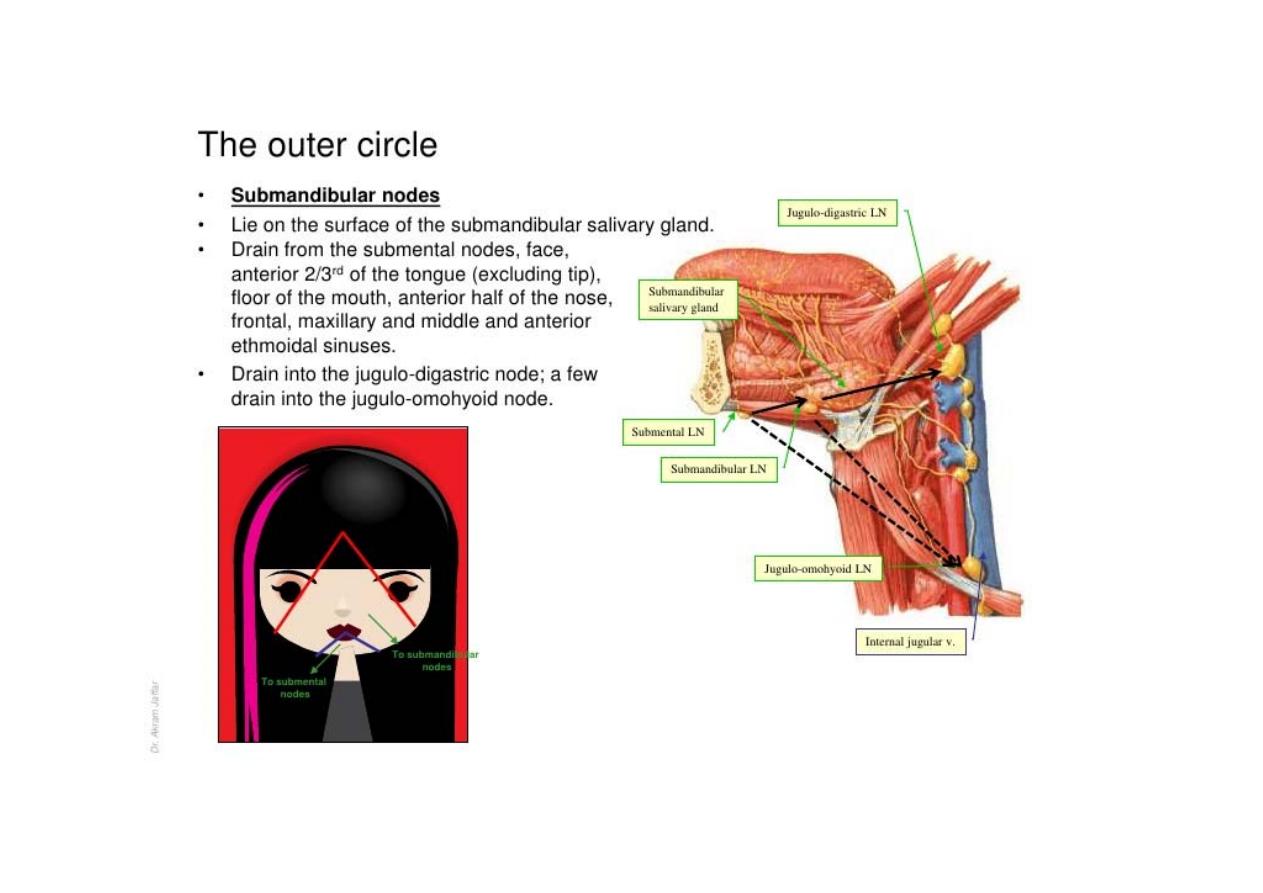
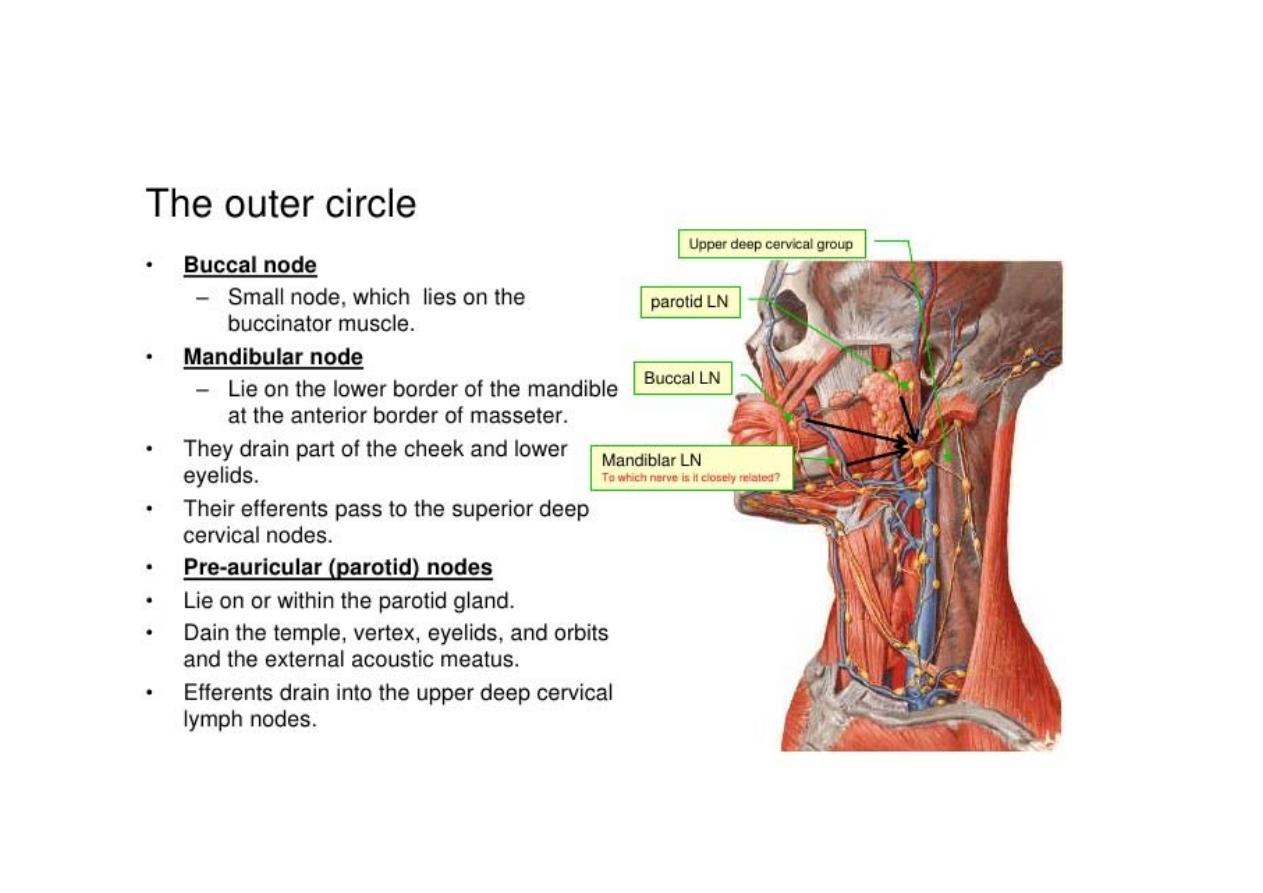
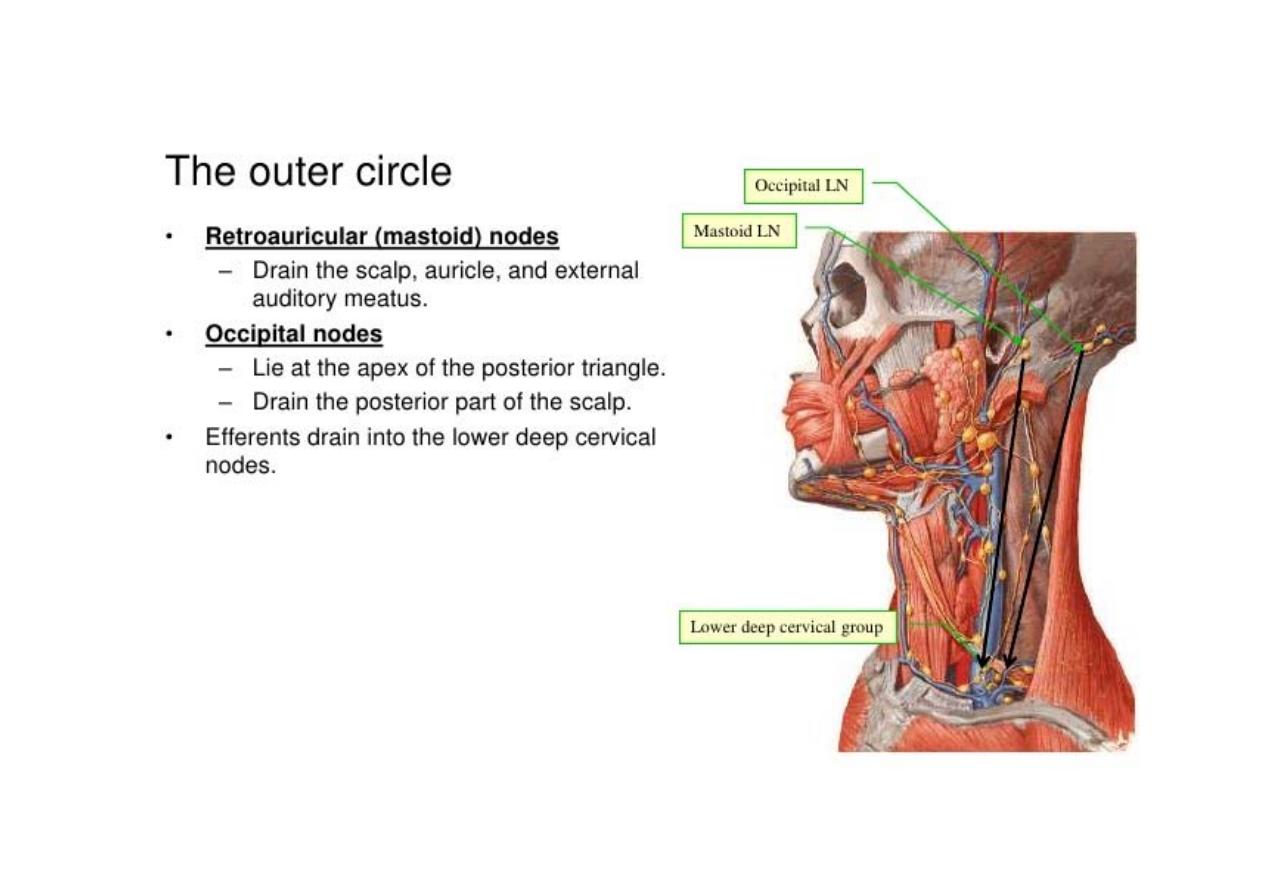
> sub-mental
> sub-mandibular
> parotid
> pre-auricular
> post-auricular
> occipital

The
vertical group
include:
> superficial (along external jugular vein)
> deep (along internal jugular vein)
> Prelaryngeal
> Pretracheal
> Paratracheal
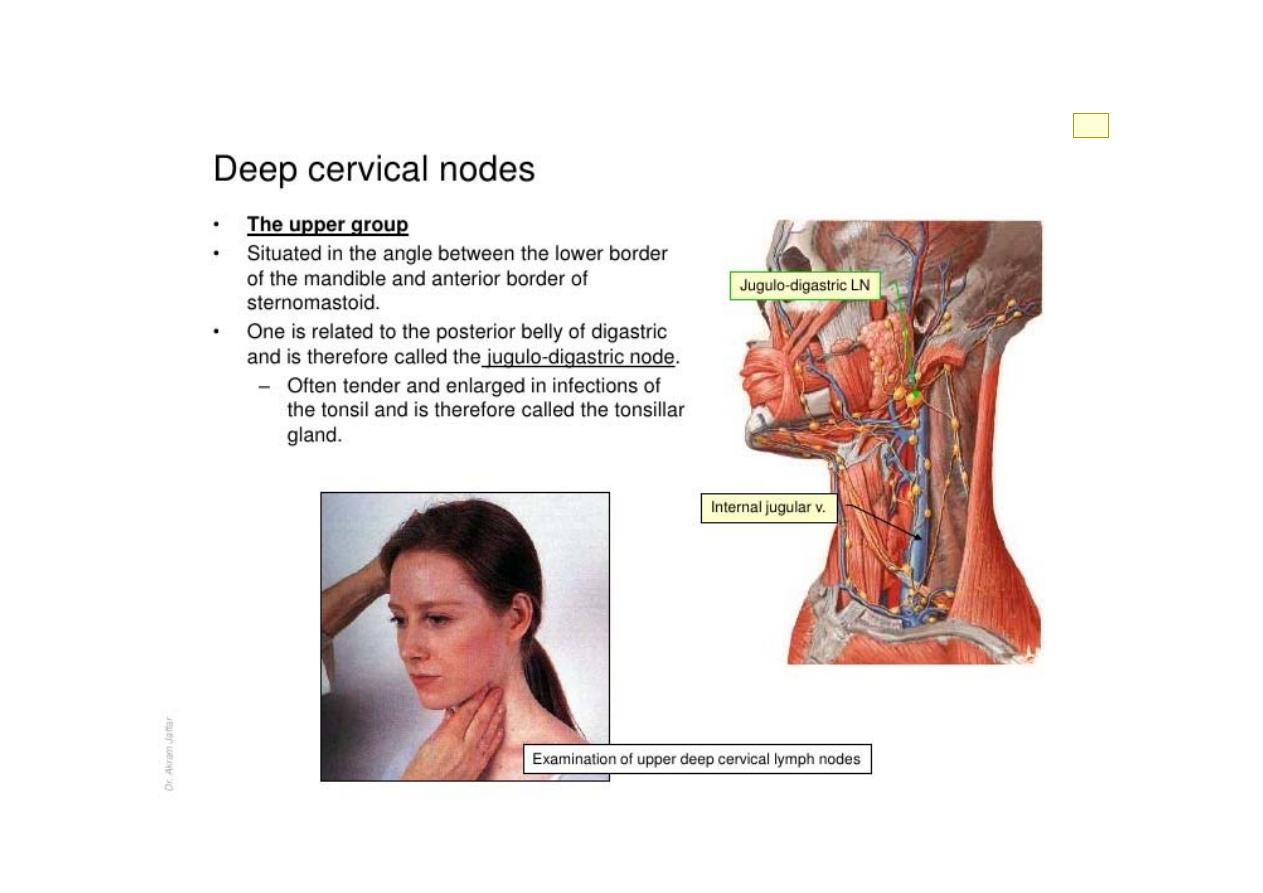
w11

الشريحة ١١
w11
wi_max 1; 03/12/2016
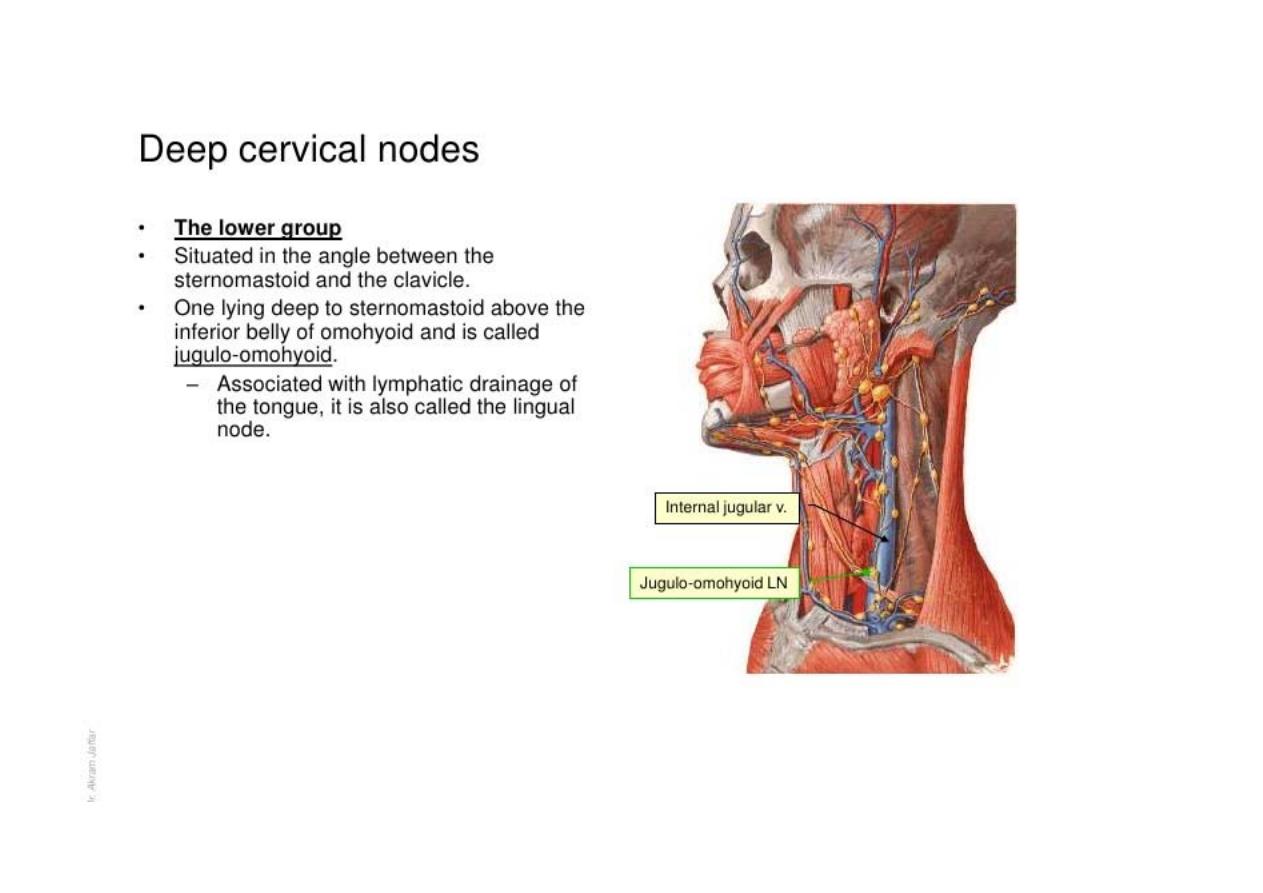
cont’d
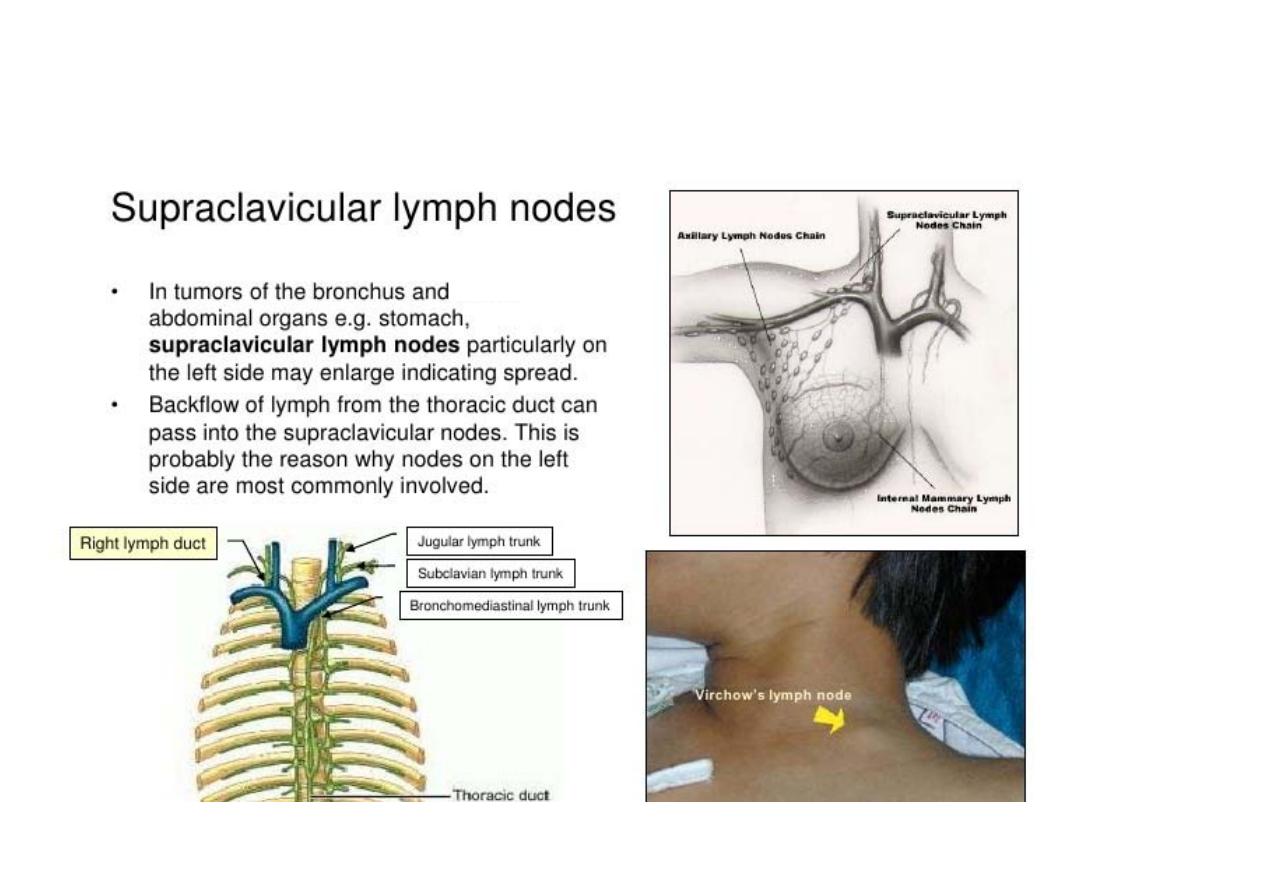
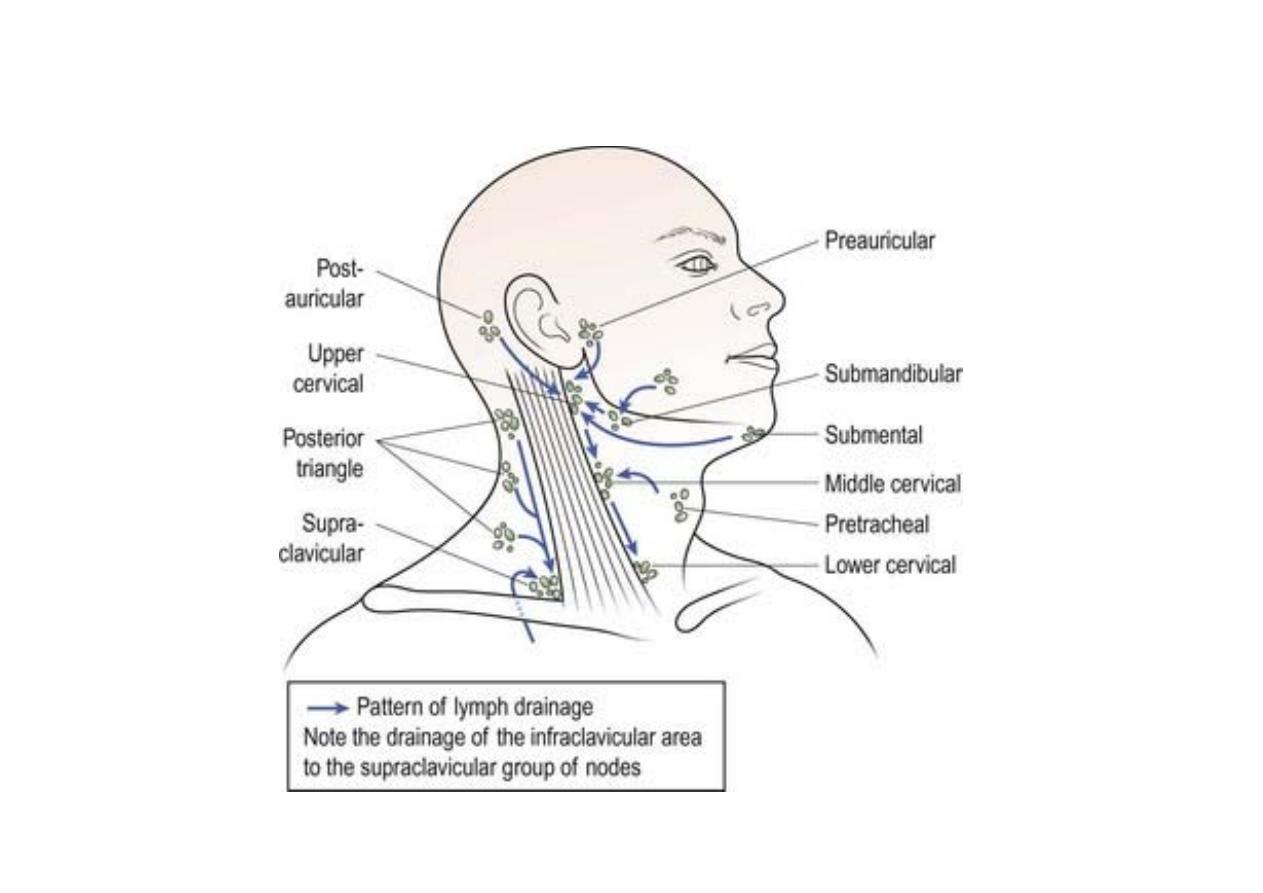
Deep cervical lymph node
cont’d
Intra‐
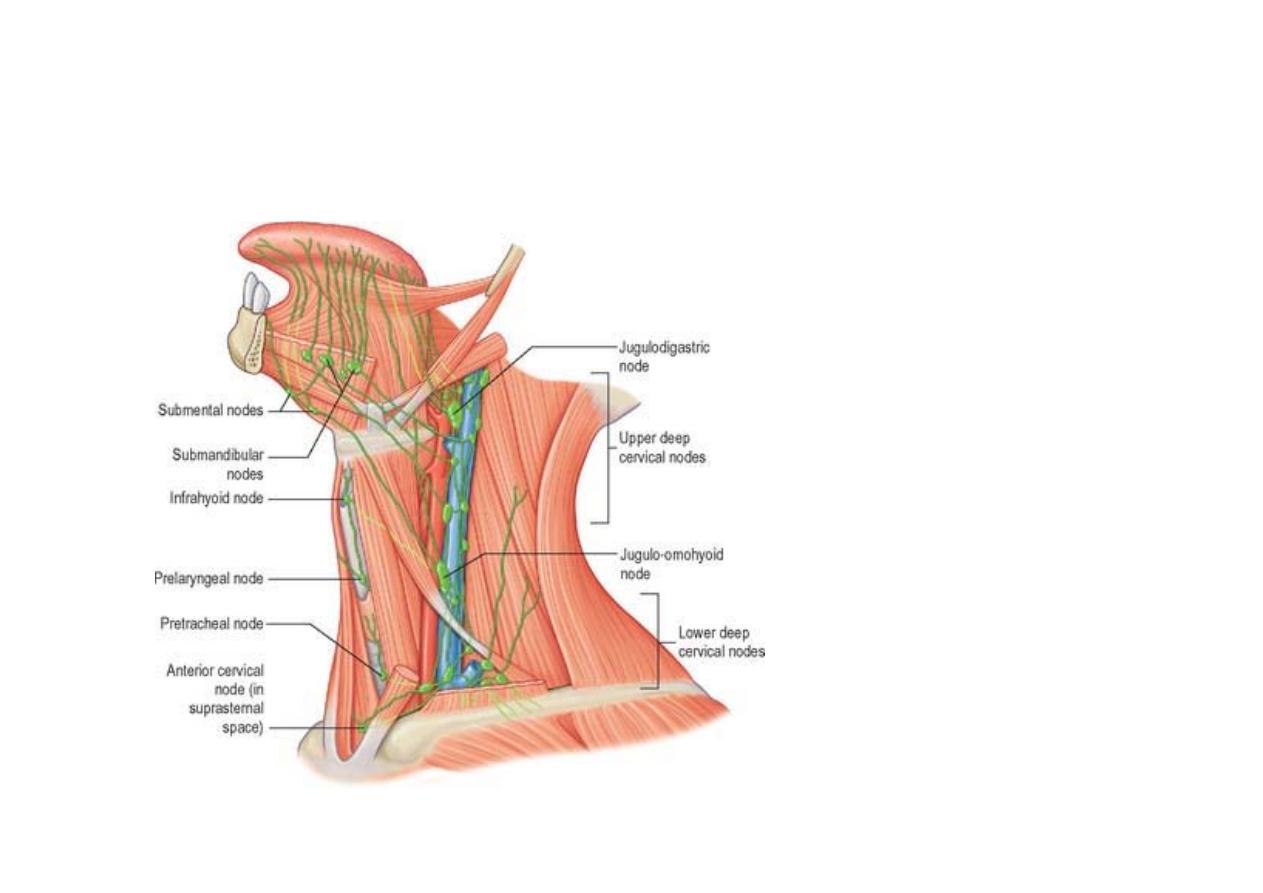
Deep cervical lymph nodes
cont’d
- Retropharyngeal
- Paratracheal
- Infrahyoid
- Prelaryngeal
- Pretracheal
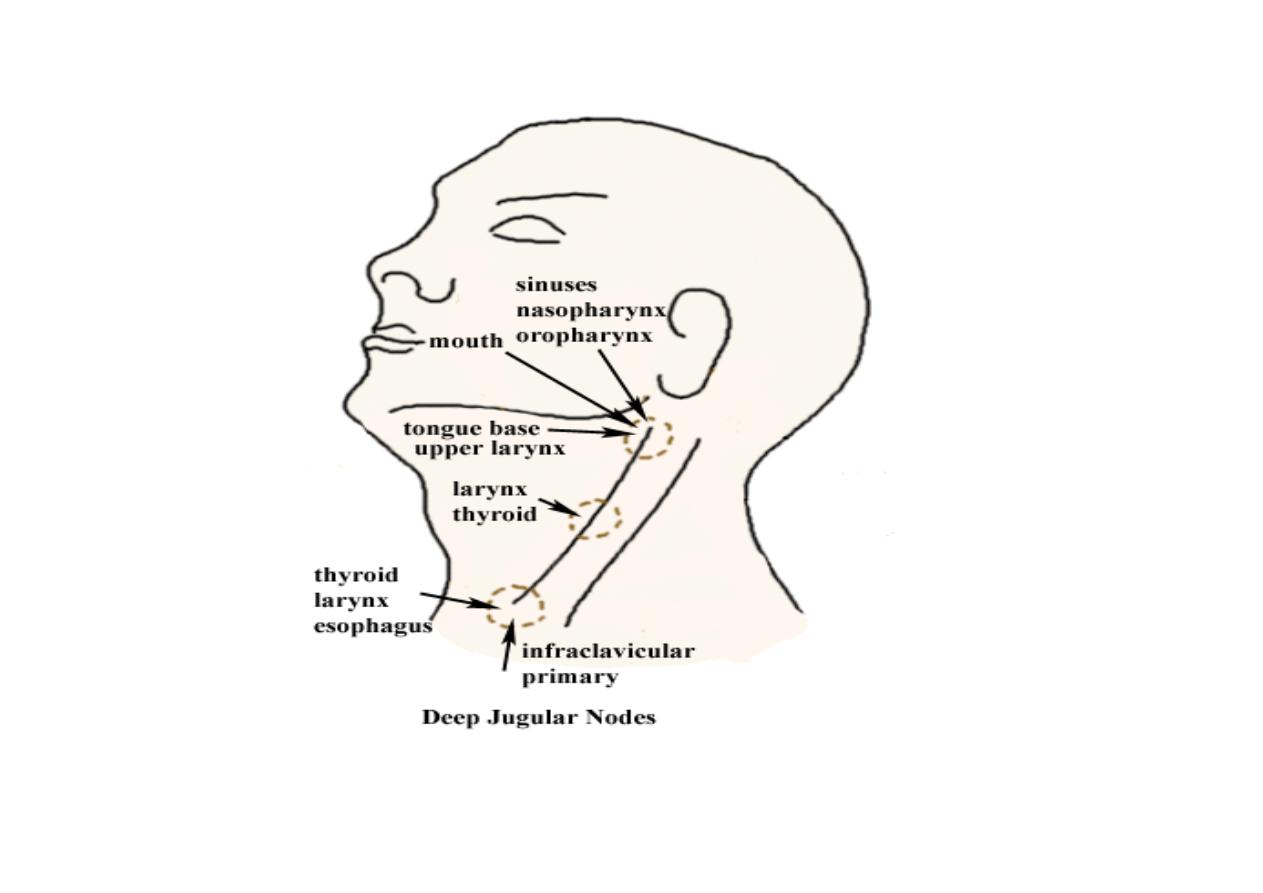
Base of skull
Bifurcation of carotid
or hyoid bone
Inferior border of cricoid
cartilage or omohyoid muscle
clavicle
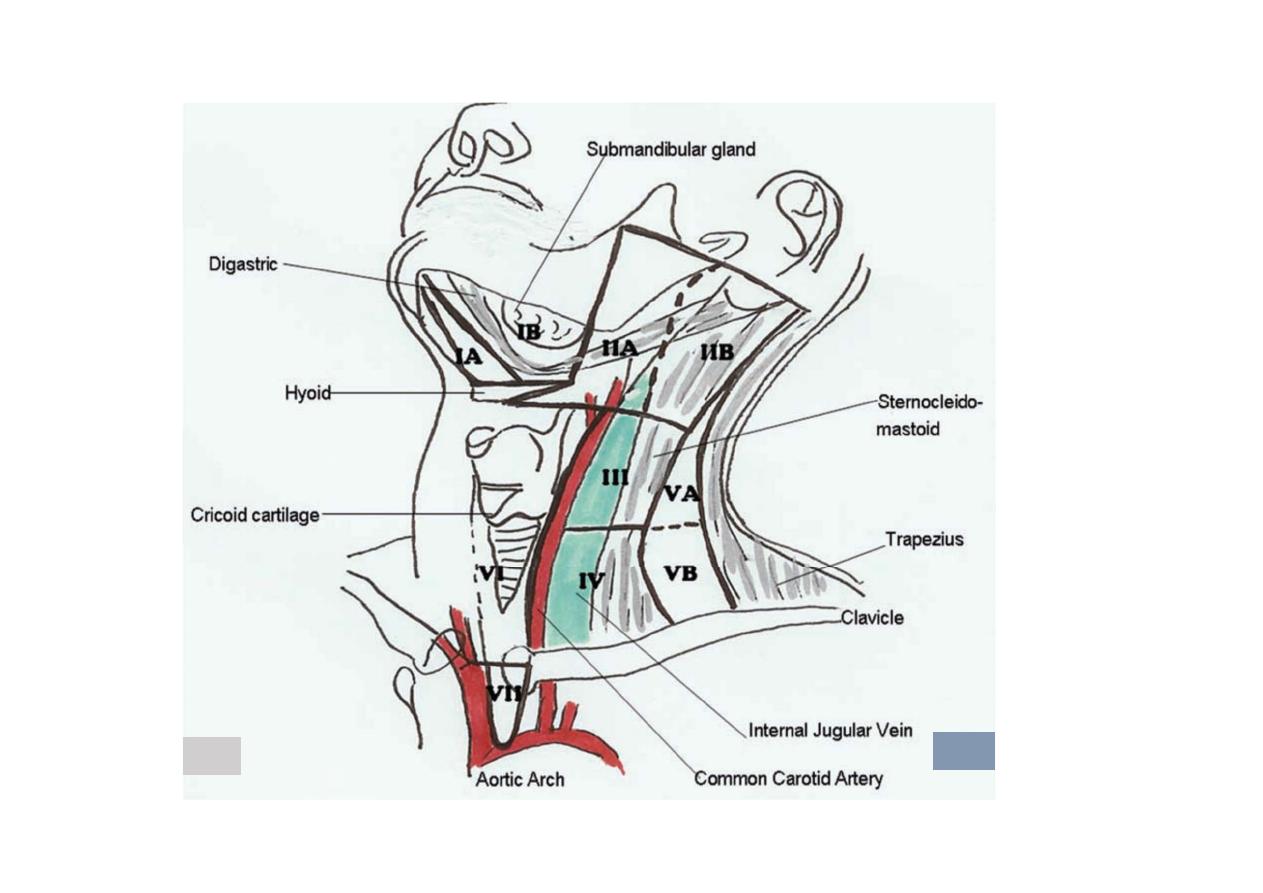

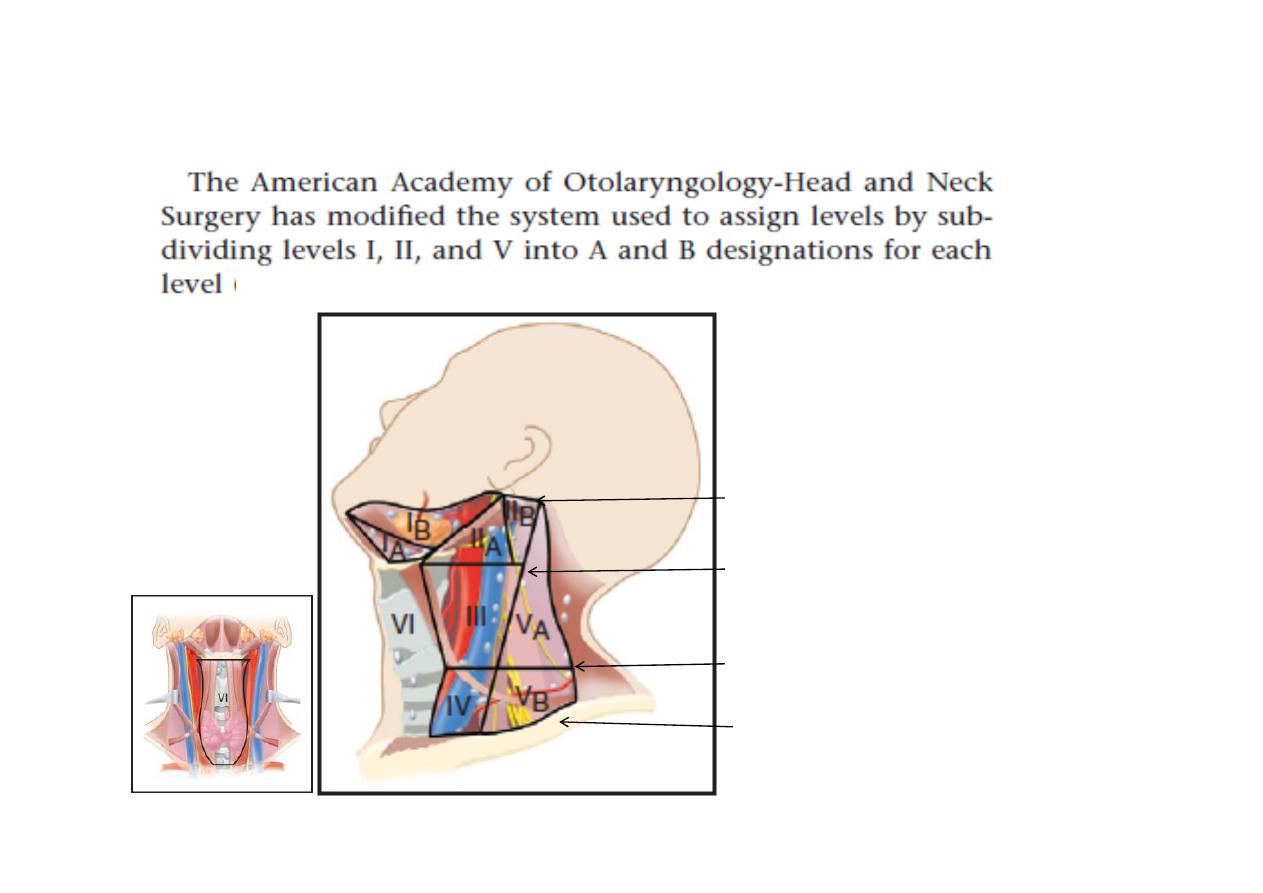
Zones Landmarks and Nodal Group
IA
Midline; anterior to the digastric muscle and superior to the hyoid bone.
Submental
-
IB
Lateral to zone IA but medial or anterior to the submandibular gland
Submandibular nodes
IIA
Anterior or medial to the internal jugular vein but lateral/posterior to the
submandibular gland; superior to the hyoid bone
Upper internal jugular
chain; more superiorly, the parotid nodes
IIB
Posterior to the internal jugular vein
Upper internal jugular chain
;
more superiorly,
the parotid nodes
III
From the level of the hyoid bone inferiorly to the cricoid arch; lateral to
the common carotid artery
Middle internal jugular chain
IV
From the level of the cricoid arch inferiorly to the level of the clavicle;
lateral to the common carotid artery
Lower internal jugular chain

VA
Posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, from the base of the
skull to the cricoid arch Supraclavicular fossa/posterior triangle
(
spinal accessory chain and transverse cervical chain
)
-
VB
Posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle from the cricoid arch
to the level of the clavicle Supraclavicular fossa/posterior triangle
(
spinal accessory chain and transverse cervical chain
)
VI
Anterior/medial to the common carotid arteries from the level of
the hyoid to the manubrium
Anterior cervical nodes, pre- and
paratracheal
VII
Anterior/medial to the common carotid arteries, inferior to the
sternal notch Anterior, upper mediastinal nodes
Supraclavicular Lateral to the common carotid artery; at or inferior
to the clavicle
Supraclavicular nodes

Causes of lymphadenopathy

Medications That May Cause Lymphadenopathy
• Allopurinol (Zyloprim)
Atenolol (Tenormin)
Captopril (Capozide)
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Cephalosporins
Gold
Hydralazine (Apresoline)
Penicillin
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Primidone (Mysoline)
Pyrimethamine (Daraprim)
Quinidine
Sulfonamides
Sulindac (Clinoril)

How to evaluate
• Thorough history and complete head and neck
examination after assuring there is no other region
involvement
to
exclude
generalized
lymphadenopathy

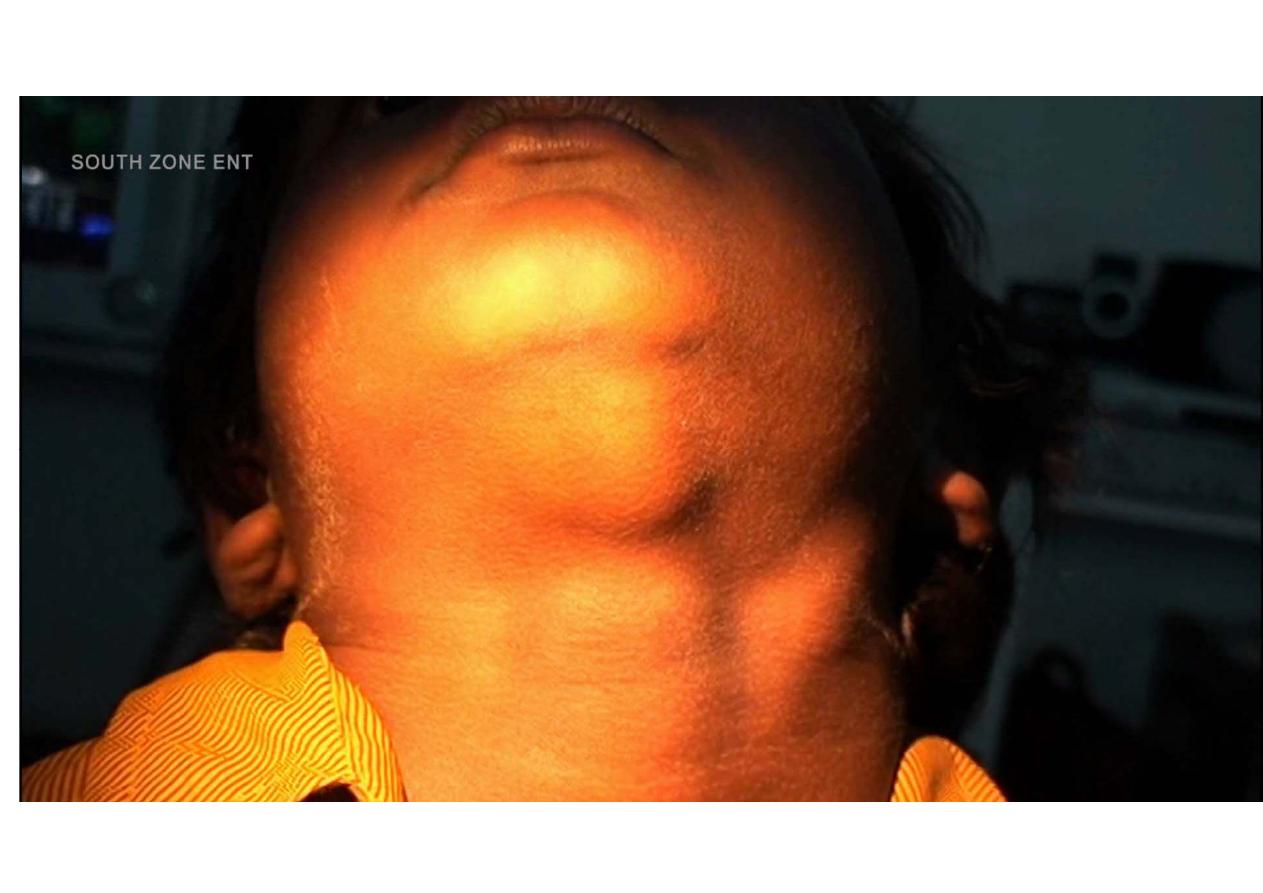
Physical examination
The following characteristics should be noted and described:
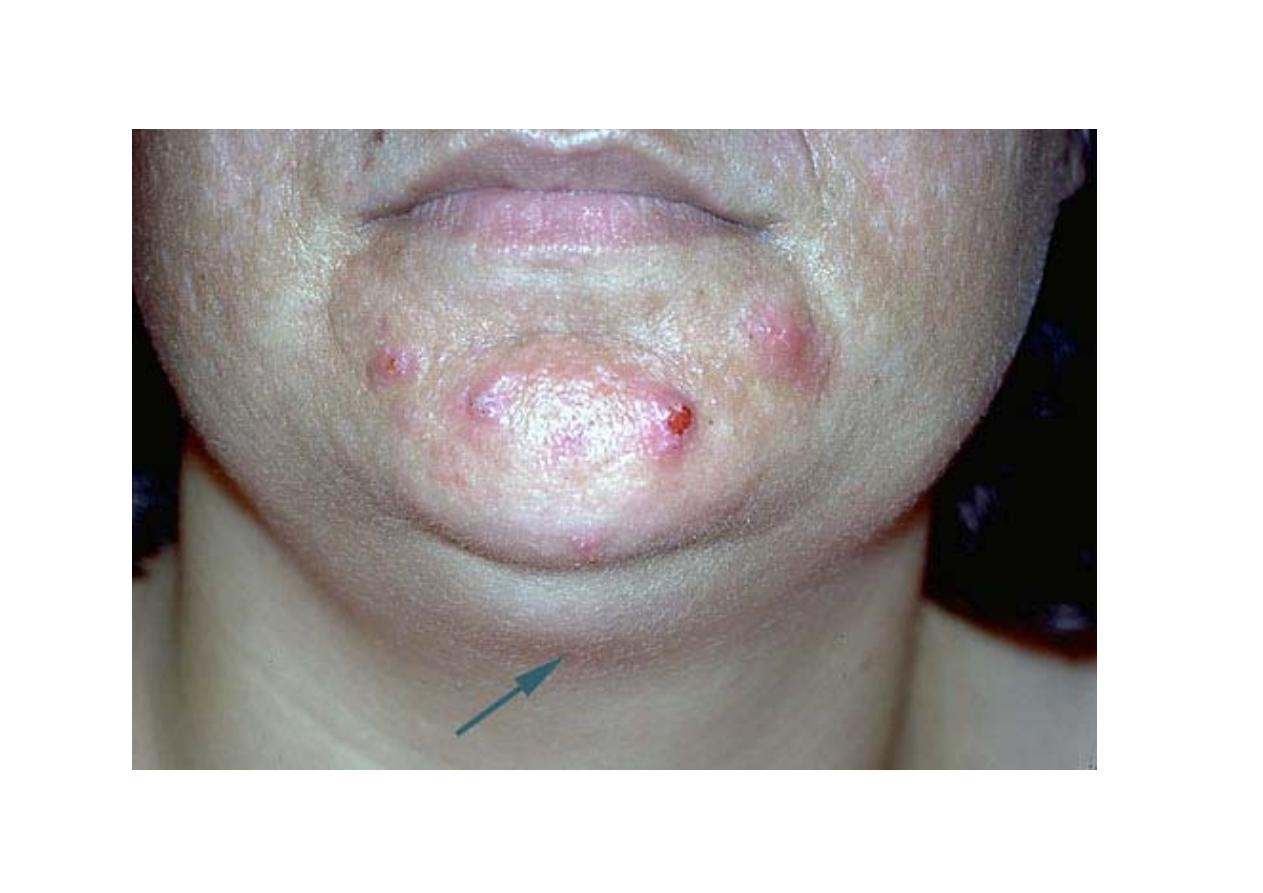
Location
• Size
. normal if <
๑ cm in diameter;
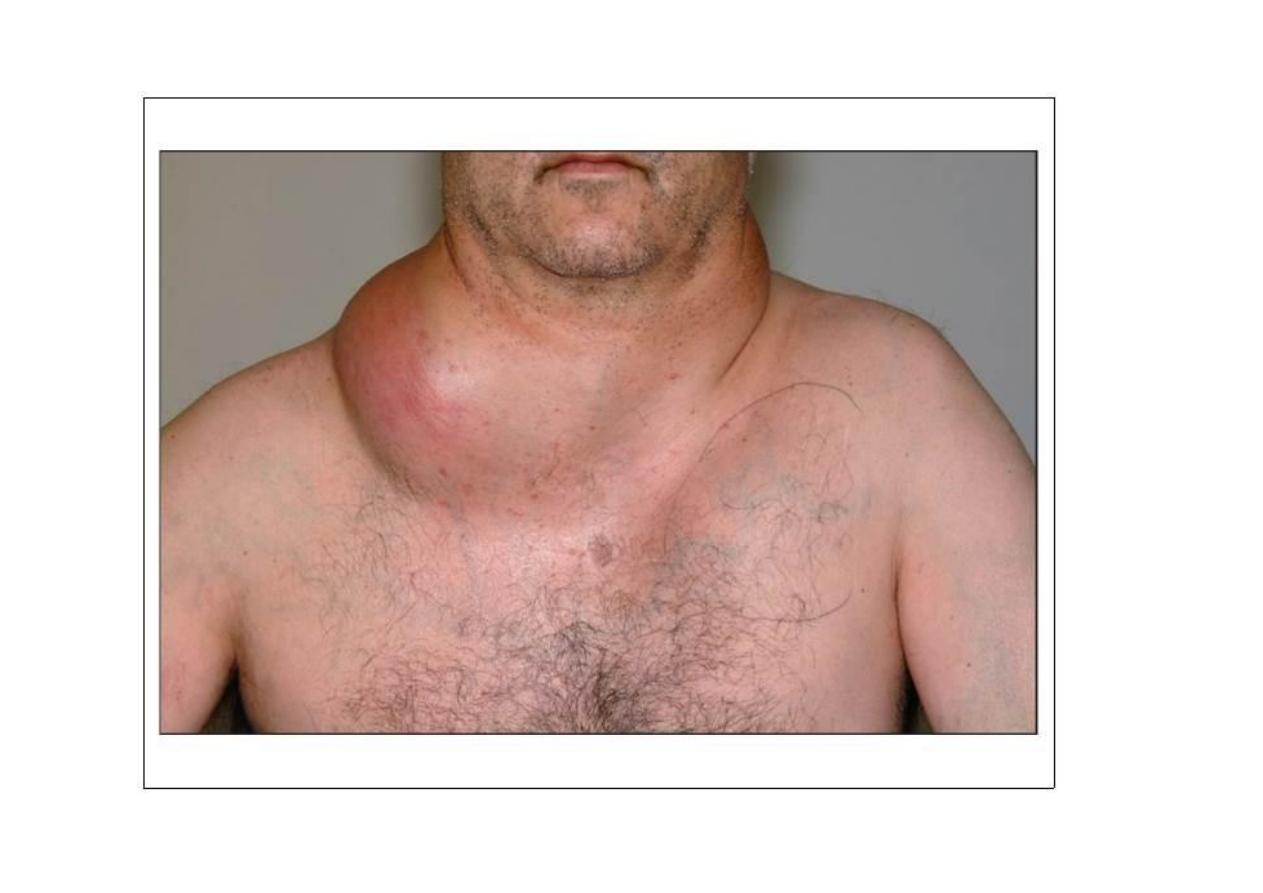
• Overlying skin color
if red indicate acute lymphadenitis
• Pain/Tenderness
. inflammatory process or suppuration, hemorrhage into the necrotic center of a
malignant node.
• Consistency
. Stony-hard nodes: cancer, usually metastatic.
Very firm, rubbery nodes: lymphoma.
Softer nodes: infections or inflammatory conditions.
Suppurant nodes may be fluctuant.
"shotty" (small nodes that feel like buckshot under the skin) cervical nodes of children with
viral illnesses.
• Matting
. benign (e.g., tuberculosis, sarcoidosis)
malignant (e.g., metastatic carcinoma ).

PALPATION
:
Number, size , tenderness , local temp , surface margins , consistency ,
fixation to underlying tissues
• Acute infection --- large, soft, painful, mobile,
• Lymphoma --- rubbery , discrete, painless and multiple
• Metastatic cancer --- hard,
fixed
to the underlying tissues, painless.
• Tuberculosis-
Stage I: Lymph nodes enlarged without matting
Stage II: Lymph nodes enlarged and matted
Stage III: Cold abscess

LYMPH NODE EXAMINATION
• Pt relaxed & unstrained position without head support
• Depending on site
• Bilateral ----
behind pt
• Unilateral ----
front of pt
• Palpation is done by placing flat surface of finger tips at same position on
both sides
• Commencing
with most superior nodes & working down to the clavicle

• Blood tests
WBC count and differential count, ESR, blood film and serology test
(e.g. AIDS , toxoplasmosis etc)
• Ultrasonography
• Upper aerodigestive tree endoscopy ( nasopharynx , larynx and
hypopharynx)
• Computed Tomography
• PET
• MRI
• FNAC +/- flow cytometry
• BIOPSY
INVESTIGATIONS

.
