
1
Fifth stage
Medicine
Lec-4
د.بشار
4/12/2016
Brain SOL
Traumatic
Subdural haematoma
Extradural haematoma
Vascular
Intracerebral haematoma
Infective
Cerebral abscess ;pyogenic ,Toxoplasma
Tuberculoma
Cysticercosis
Hydatid cyst
Schistomiasis
Inflammatory
Sarcoid mass
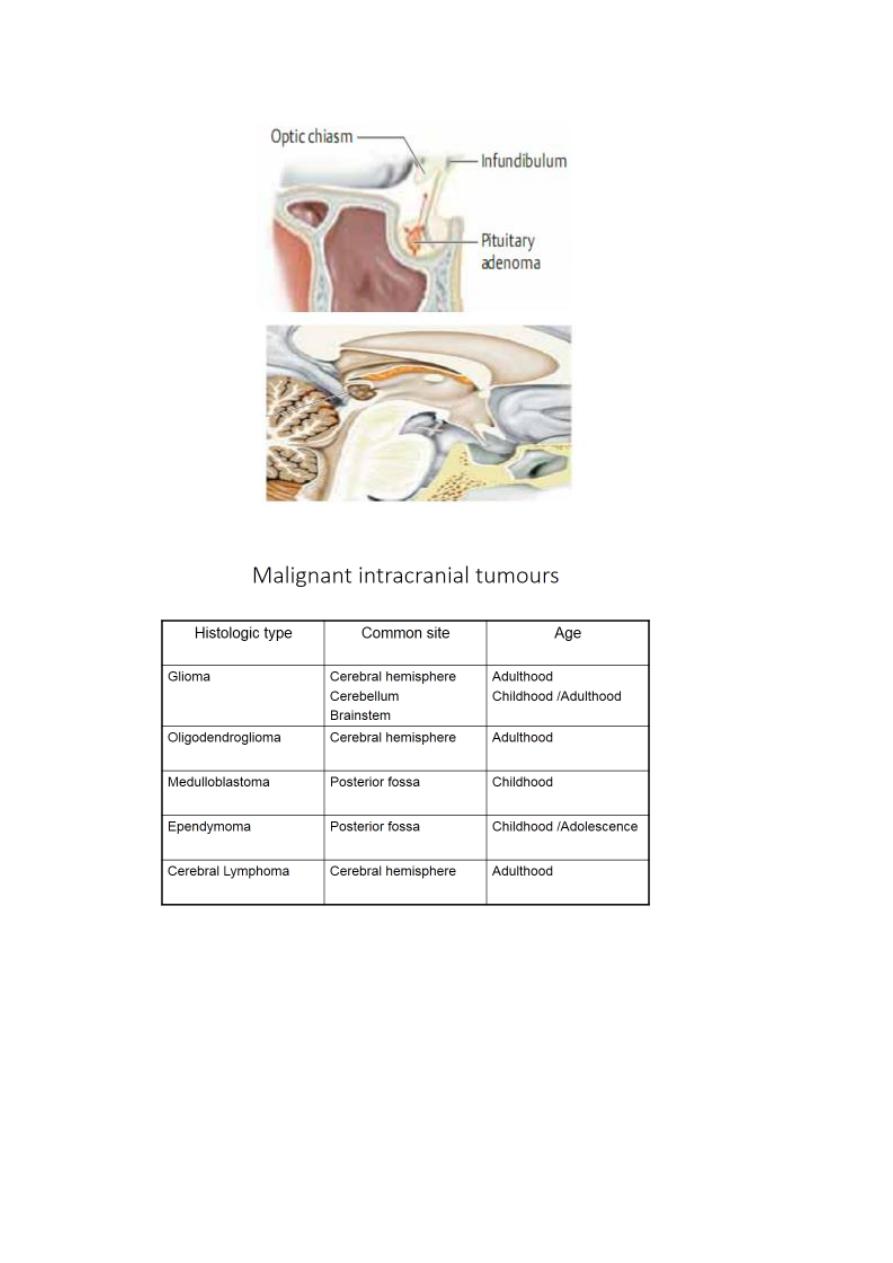
Neoplastic
Cerebral neoplasms (benign or malignant )
Other
Embryonic dysplastic lesions e.g. craniopharyngioma
&hamartomas
Arachnoid cyst
2
CNS tumours
Primary or Secondary
Account for 2% of all deaths
The majority are metastatic
Meningeomas account for 20 %of all intracranial tumours
3
Even malignant tumours don’t metastasize outside the CNS
Secondaries (metastases)
Usually located in the white matter of cerebral or cerebellar
hemispheres;common sources are bronchus ,breast &gastrointestinal
tract.

4
CLINICAL FEATURES:
• Insidious Onset = May be acute with cystic degeneration,
hemorrhage or with seizures.
• Progressive course.
• Space- occupying effect
• Site of the tumor
• False localizing signs
Space occupying effect
Raised intracranial pressure
• HEADACHE: Non specific;dull aching, eventually in most patients,
more severe in early morning in 10-15 % , aggravated by cough,
sneezing, straining &change of posture (bending,lying ).
• It is ipsilateral to supratentorial tumors in 80% of cases
• Nausea &vomiting
• Seizures : more if tumor in ant. Cranium e.g. more than 50% of
frontal lobe tumours have seizures ;generalized or partial .
• Papilloedema : more in infratentorial tumours, leading to
transient visual obscurations.
• Altered mentation.

5
SITE OF TUMOR (FOCAL SIGNS &SYMPTOMS)
• Frontal lobe : Altered mood &behavior, contra. Motor deficit,
incontinence,primitive reflexes
• Parietal lobe : Sensory s.&s. may predominate, contra. Visual field
&motor deficit
• Non dominant parietal l. :sensory or visual inattention, dressing
apraxia
• Temporal lobe : Wernicke aphasia, sup. Quadrantanopia,
temporal lobe epilepsy
• Occipital lobe : visual field abnormality
FALSEAC LOCALIZING SIGNS:
Pupillary dilatation.
6
th
cranial nerve palsy(unilateral or bilateral).
Hemiparesis (ipsilateral to the lesion ).
Bilateral extensor plantar responses.
The rise in intracranial pressure from a mass lesion is not usually uniform
within the cerebral substance and alterations in pressure relationships
within the skull may lead to displacement of parts of the brain between
its various compartments. Downward displacement of the temporal
lobes through the tentorium due to a large hemisphere mass may cause
'temporal coning
This may stretch the 3rd and/or 6th cranial nerves, or cause pressure on
the contralateral cerebral peduncle (causing ipsilateral upper motor
neuron signs).
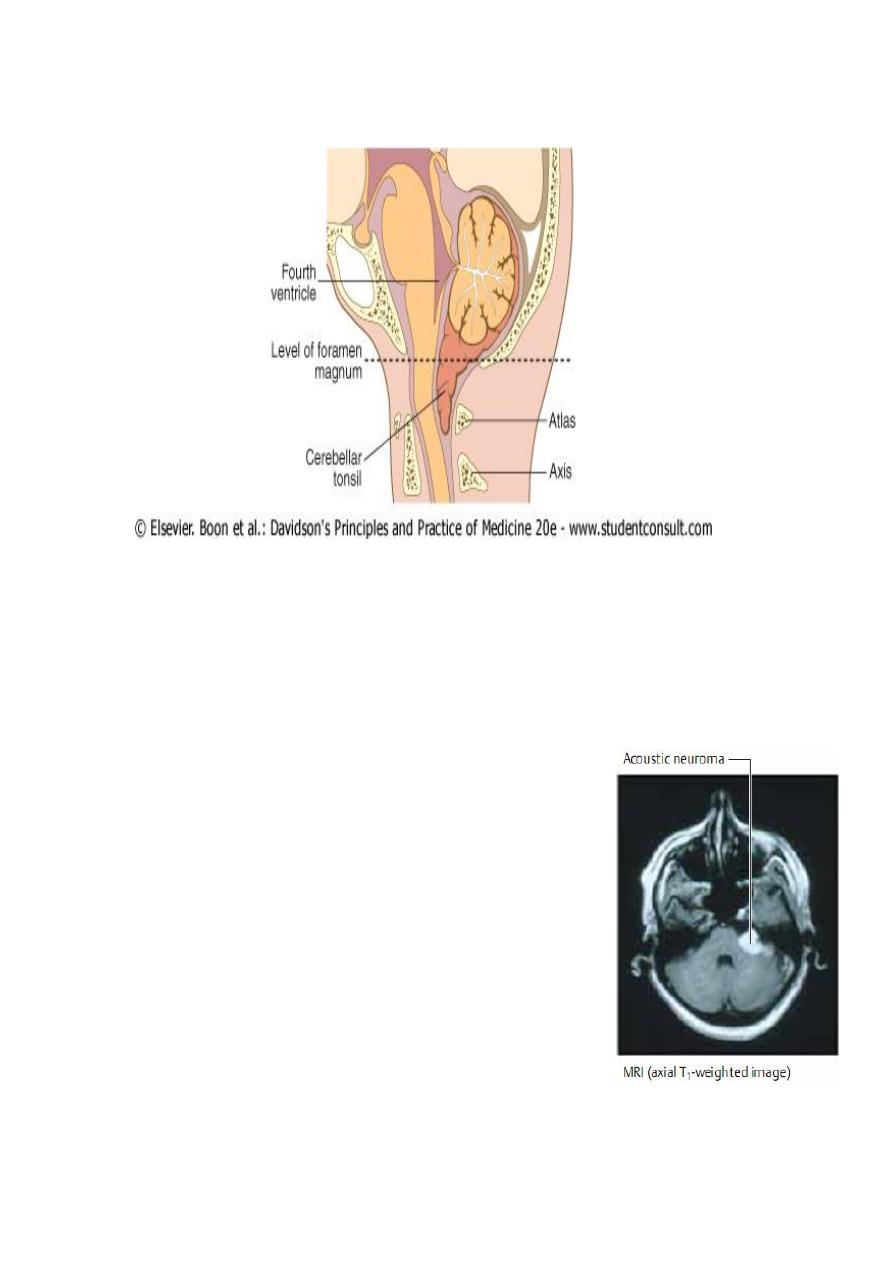
6
Downward movement of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen
magnum may compress the medulla-(tonsillar coning)
This coning may result in brain-stem haemorrhage and/or acute
obstruction of the CSF pathways. As coning progresses, the patient may
adopt a decerebrate posture and, unless rapidly treated, death almost
invariably ensues. The process may be acutely accelerated if the
pressure dynamics are suddenly disturbed by lumbar
puncture
INVESTIGATIONS
• Plain X Ray ; Signs of raised ICP, Calcification…
• EEG : Focal slowing
• CT Scan ,MRI &MRA

7
TREATMENT:
• Reduce ICP : Osmotic diuretics, Steroids
• Often required when surgery is not possible or when life is
threatened.
• Dexamethasone 8- 12 mg 12-hourly orally or by injection ;a
striking improvement in consciousness is often produced &focal
deficits may regress.
• Mannitol 0.25 – 1 mg /Kg /Dose IVI.
Surgery
Mainstay of treatment
Only partial excision may be possible if the the tumour is
inaccesible or its removal is likely to cause unacceptable damage.
Biopsy should be considered even if the tumour is not removable
?prognosis &management.
Meningeomas,acoustic neuromas &pituitary adenomas.
Radiotherapy &Chemotherapy:
Marginal effect on survival in metastases &malignant gliomas.
Combined therapy has improved prognosis in medulloblastomas
in children.
Radiotherapy reduces the risk of recurrence of pituitary adenoma
after surgery.
Ependymomas,some pineal tumours &low gradegliomas in
children &young adults are often radiosensitive.

8
Prognosis:
For benign tumours is good if removed completely.
Ependymomas &Medulloblastomas may recur with seeding via the CSF.
Oligodendrogliomas may transform to more malignant form ---- glioma .
Related to histologic grade ;
G1&2 may survive for years
G 4 –only 20 %survive for 1 year.
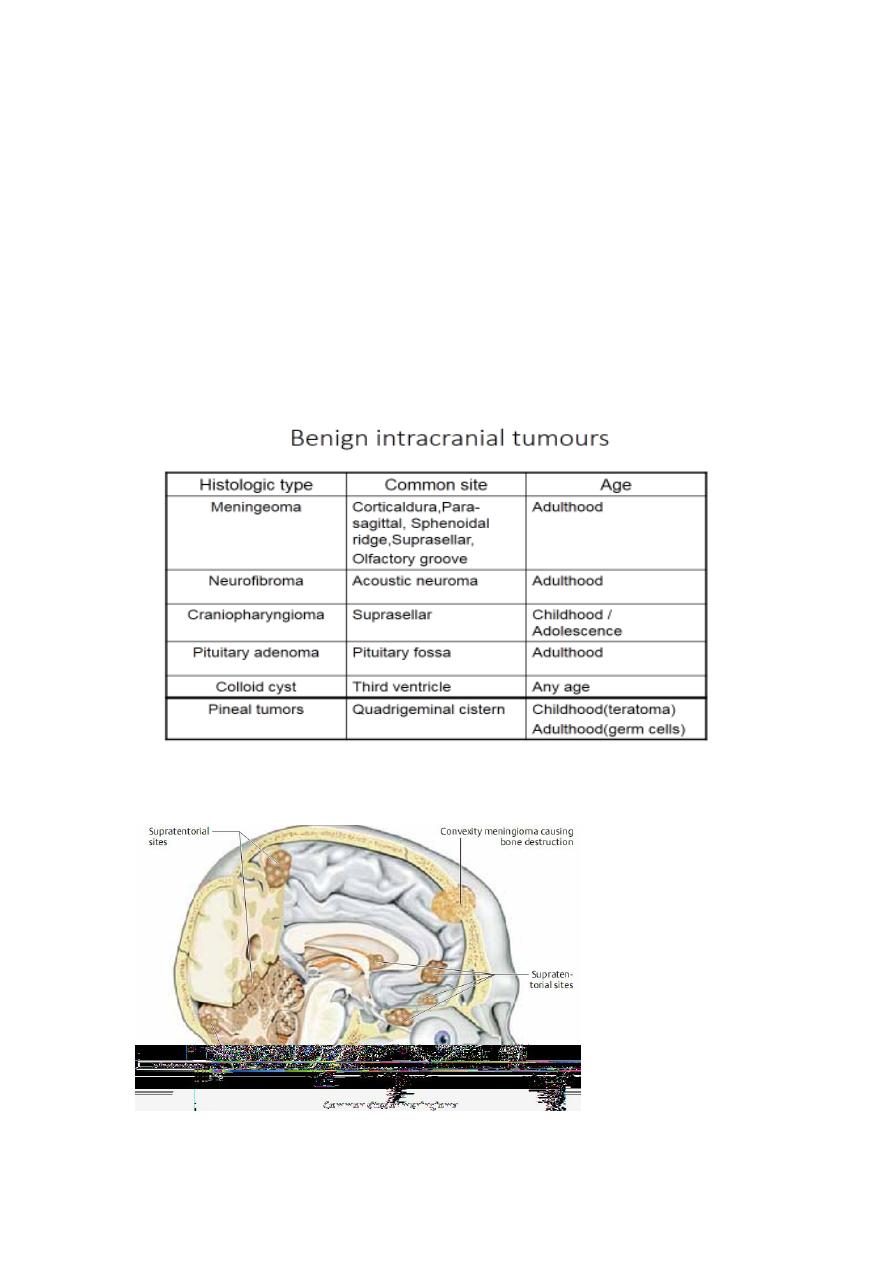
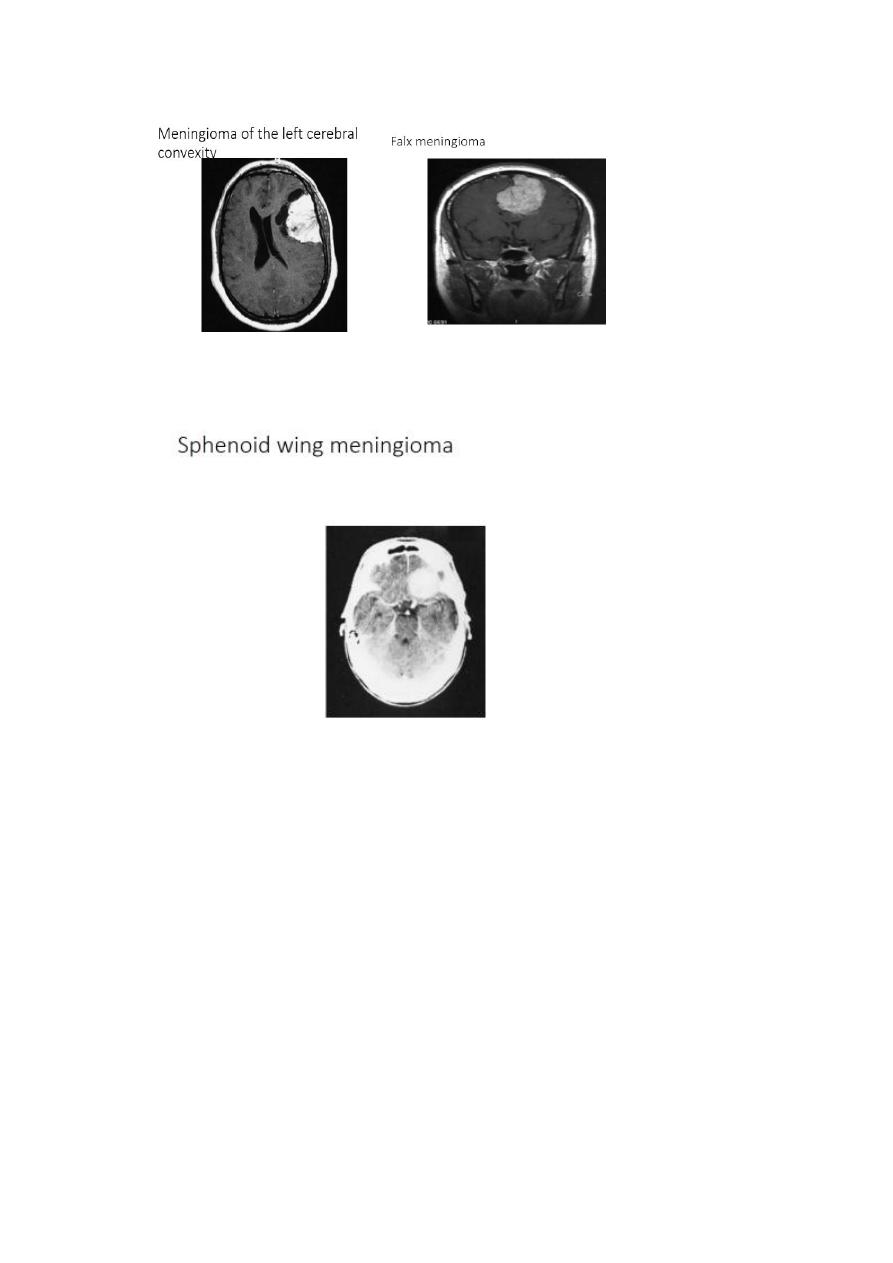
Meningiomas:
Arise from the dura mater and are nearly always benign, well-
demarcated lesions that displace rather than invade the adjacent
neural tissue as they grow.
These mesodermal tumors most often become clinically evident
between the ages of 40 and 50.
They are diagnosed by MRI or CT scanning which reveals marked,
homogeneous contrast enhancement.
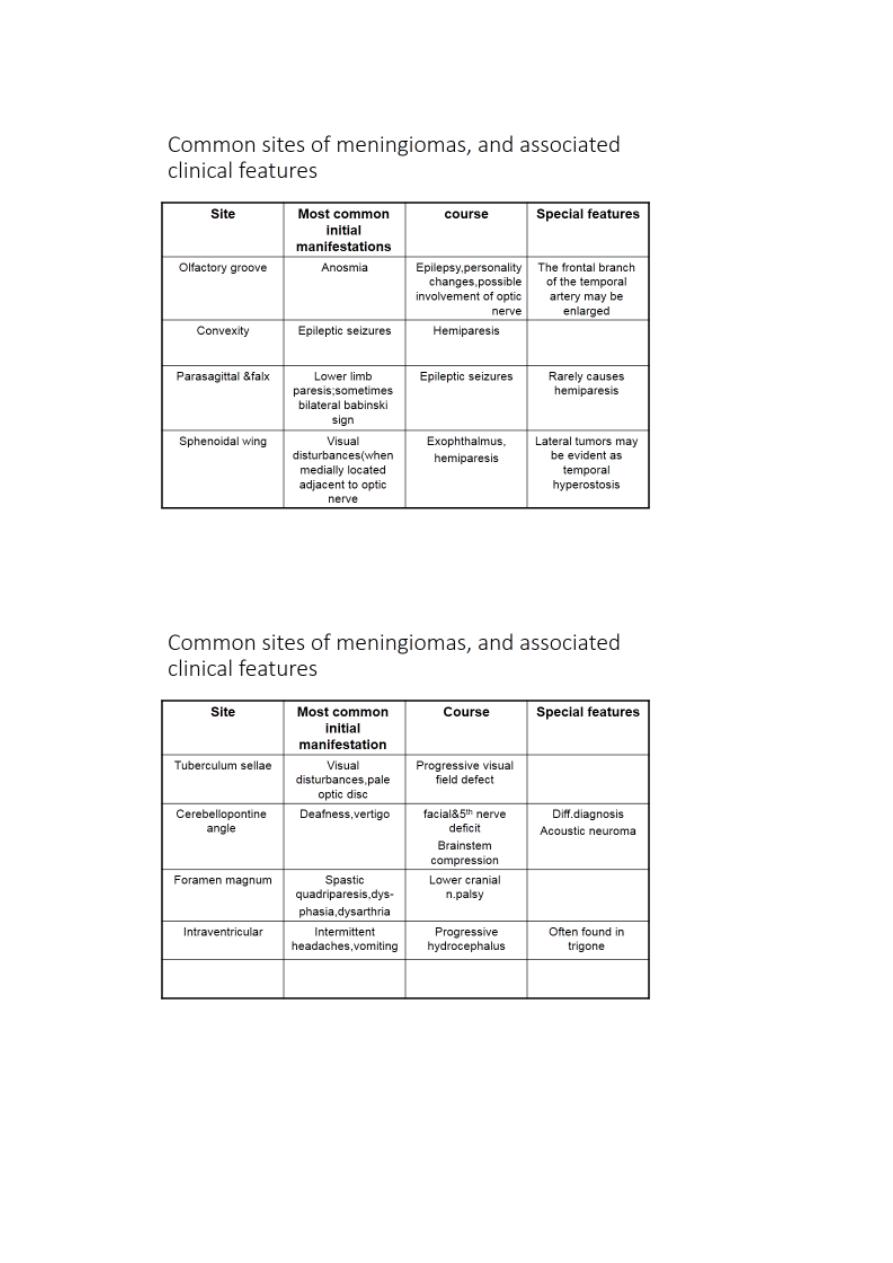
Meningiomas tend to appear in certain classic locations with
corresponding typical neurological manifestations.
They often grow very slowly and are not uncommonly discovered
as an incidental radiological finding.
The indications for treatment must then be carefully considered:
resection may be desirable in younger patients, but unnecessary
in older ones.
9
11
