NMJ DISORDERS
1- MYASTHENIA GRAVIS2- LAMBERT EATON SYNDROME
3- INFECTIVE NMJ DISORDERS
PERIODIC PARALYSES SYNDROMES
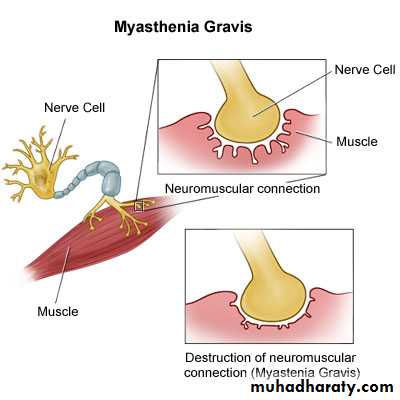
Myasthenia Gravis:
Autoimmune inflammatoryfluctuating
(diurnal rhythm & relapse & remission),
fatigueable &
painless weakness disorder
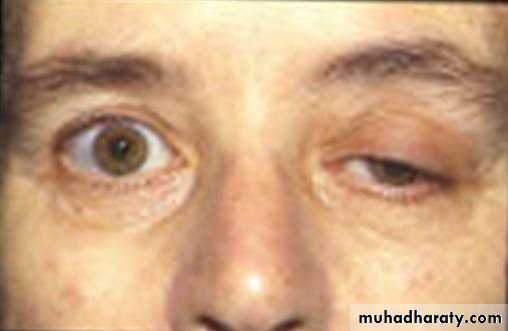
affecting particularly, ocular, masticator, facial, neck, deglutition, lingual muscles & extremity & respiratory muscles.
Epidemiology:
1st Peak:2nd peak
Pathologically
AChR Ab
AntiMusk Ab
Thymus GlandHLA & other CTD
Clinical Presentation
INVESTIGATIONS:
Clinically (Provocative Tests):
Tensilon Test
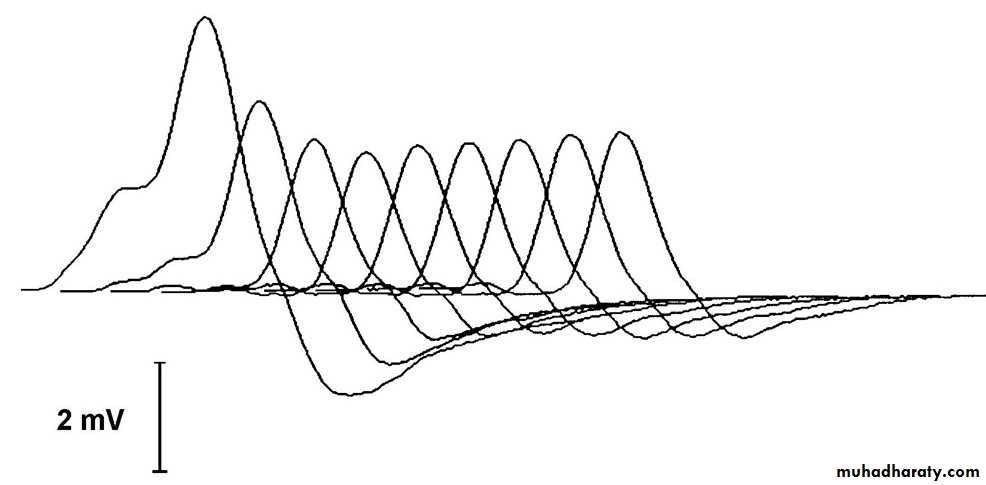
EMG
Ix
AchR Ab 80%&if negative AntiMusk Ab 40% & Anti skeletal muscle
CXR & Contrast chest CT
: Thyroid function test & Antinuclear Ab.s
Serial follow up
TREATMENT:
Aim: - Symptomatic treatment- Immune Modulation
AntiCholinestrase DrugsPyridostigmine Bromide
Immune Modulators:
CorticosteroidsAZATHIOPRIME
Mycophenolate MofetilCholinergic Crisis Treatments
EMERGENCY TREATMENTSPlasmapharesis PE
Immunoglobulin IgGThymectomy
should be offered in any:Seropositive
<45yr old
not confined to ocular
Disease duration not more than 7 years.MYASTHENiC CRISIS= ICU
Profound weakness Cn affected muscles in myasthenic :1- withdrawal of anticholinestrase drugs.
2- Withdrawal or decreasing dose or acute administration of high dose of steroid.
3- Infection.
4- Bad choice of contraindicated drugs.
Cholinergic Crisis
ACheI Overdose:Weakness in unaffected muscles too.
+Course is extremely variable
Fatality
Course
Lambert Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome LEMS:
Autoimmune NMJ Disorder, VGCC AbMalignancy Association
Clinically- spares:
- lower limbs
- ED
- Sphincter dysfunction
- Dry mouth
- Postural hypotension
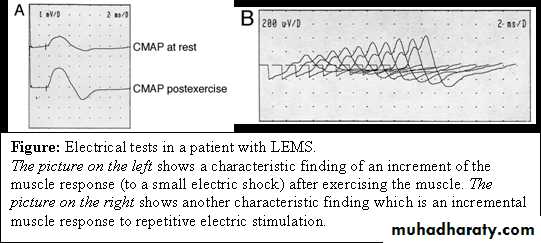
Investigations
EMGLOOK FOR MALIGNANCY
Treatment:
Treatment of associated cancerSymptomatic:
3,4 Diaminopyridine DAP or
Guanidine
Infective NMJ Disorder:
Botulism:PERIODIC PARALYSIS SYNDROMES
characterised by :Recurrent,
Episodic,
Generalised,
Painless,
fairly Rapid onset of muscle weakness
coincidental changes in serum electrolyte level, and reversal to norm in between attacks.
Hypokalaemic Periodic Paralysis:
ADAssociation with THYROTOXICOSIS
TYPICAL ATTACK
Time & provokation
Pattern
SpareDuration
Investigations:Serum K
ECG
TFT
EMG
Muscle Biopsy
Treatment:1-Acute Attack
oral or IV potassium
Prophylaxis
- Acetazolamide
- Dichlorphenamide
- Spironolactone
Course & Prognosis:
Descending Recovery
Recurence: every few weaks
Improve with ageMortality: rarely, respiratory or cardiac
Hyperkalaemic Periodic Paralysdisis (HyperKPP)AD, Na Chanelopathy
TYPICAL ATTACK:
MYOTONIAAcute Attack:
ProphylaxisInvestigations
K LevelECG.
Treatment:
Acute Attack:- IV Ca Gluconate
- IV Glucose or Glucose & Insulin
- -Diuretics
Prophylaxis
- Acetazolamide
- Dichlorphenamide
- Chlorthiazide. 0.5 mg/day
- Mexilitine
Myotonia