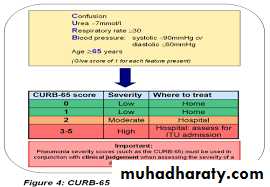
Clinical Pharmacology for Respiratory Diseases
Dr Mudher Z.H. Al-khairallaConsultant in Respiratory Medicine
MBChB MRCP (UK) CCT Resp&GIM FRCP
Aims…
Basic clinical pharmacology for common respiratory diseasesPDF at the end of the series
x4 one –hour sessions
Terms…
Clinical PharmacologyPharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Generic Vs Brand
In Latin!
Montelukast 10mg P.O. nocte 28 days
Common Diseases
Diseases of the airwaysASTHMA
COPD
Infection
PNEUMONIA
CAP
HAP
TUBERCULOSIS
BRONCHIECTASIS
Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILD)
Lung Cancer
Respiratory Failure
OXYGEN
Pulmonary Embolism
Elsewhere!Common Drugs/Group of Drugs!
Bronchodilators (SABA/LABA)Corticosteroids
Antimuscarinic
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
Mucolytics
Methylxanthines
Magnesium sulphate
Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Macrolides
Tetracyclines
Quinolones
Anti-pseudomonal
Anti-Tuberculosis
Pirfenidone
Oxygen
Anti-IgE (Monoclonal antibody)
Methotrexate
Azathioprine
Anti-fungal
Lung Cancer (NSCLC & SCLC)
Palliative Care
Anticoagulation
Common Drugs/Group of Drugs!
Bronchodilators (SABA/LABA)Corticosteroids
Antimuscarinic
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
Mucolytics
Methylxanthines
Magnesium sulphate
Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Macrolides
Tetracyclines
Quinolones
Anti-pseudomonal
Anti-Tuberculosis
Pirfenidone
Oxygen
Anti-IgE (Monoclonal antibody)
Methotrexate
Azathioprine
Anti-fungal
Lung Cancer (NSCLC & SCLC)
Palliative Care
Anticoagulation
Warfarin
Next…
Respiratory Condition
Brief Pathophysiology
Treatment Goals
Drug (Generic names)
Mechanism of Action
Indications
Contraindications/Cautions
Side effects
Dosage
Note(s)/Interactions
Next…
Respiratory ConditionBrief Pathophysiology
Treatment Goals
Drug (Generic names)
Mechanism of Action
Indications
Contraindications/Cautions
Side effects
Dosage
Note(s)/interactions
Drug Class
GenericMechanism
Indication(s)Caution(s)
Contraindication(s)Side Effects
DoseNote/Interaction
Diseases of the Airways
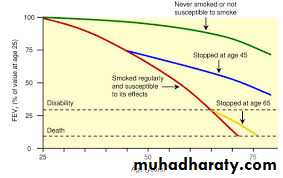
AsthmaUncontrolled Vs Severe
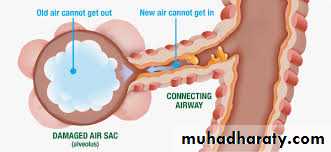
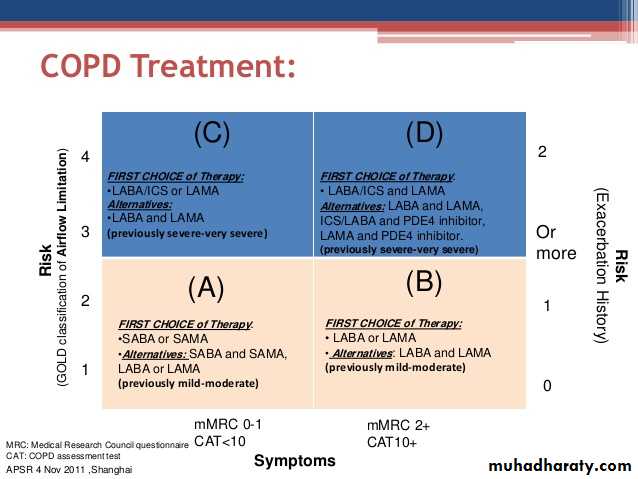
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseSABA
Short Acting Beta AgonistDrug Class – Selective Beta2 Agonists
GenericSalbutamol, Formoterol
Mechanism
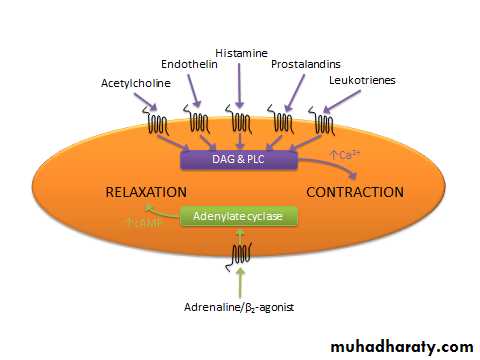
bronchodilatation
Indication(s)
Asthma (mild), Reliever, Exercise induced
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Hypokalaemia, tachyarrhythmia, Thyrotoxicosis
Side effects
Tremor, palpitations, headache, tachyarrhythmia, hypokalaemia
Dose
e.g. Salbutamol 100-200mcg 1-2 puffs as required
Note
• Interaction(s)
Usually, Inhaled via MDI or Nebuliser
LABA
Long Acting Beta AgonistDrug Class – Selective Beta2 Agonists
GenericFormoterol, Salmeterol, Indacaterol
Mechanism
bronchodilatation
Indication(s)
Asthma and COPD (usually in combination with ICS)
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Hypokalaemia, tachyarrhythmia, Thyrotoxicosis
Side effects
Tremor, palpitations, headache, tachyarrhythmia, hypokalaemia
Dose
e.g. Formoterol 12mcg b.d. inhaler
Note
• Interaction(s)
Usually, Inhaled via MDI or Nebuliser
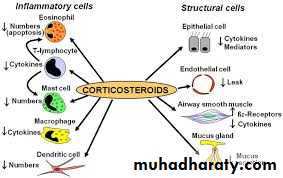
ICS
Inhaled Corticosteroid
Systemic Steroids
OralIntravenous
Drug Class – Corticosteroids
GenericBeclomethasone, Fluticasone, Budesonide
Mechanism
Reduce airway inflammation (edema) and mucous
Indication(s)
Asthma Prophylaxis, COPD (usually in combination with LABA)
Caution
Contraindication(s)
-
Side effects
Oral thrush
Dose
e.g. Budesonide Turbohaler 200mcg b.d. inhaled
Note
• Interaction(s)
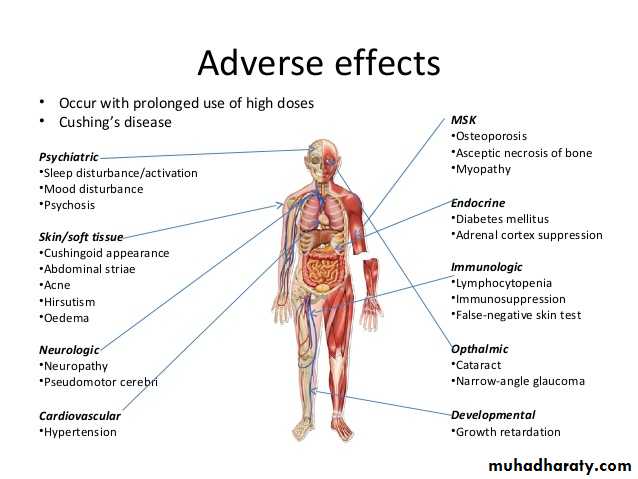
Inhaled corticosteroids are the cornerstone of asthma maintenance. Systemic side effects are exceedingly rare
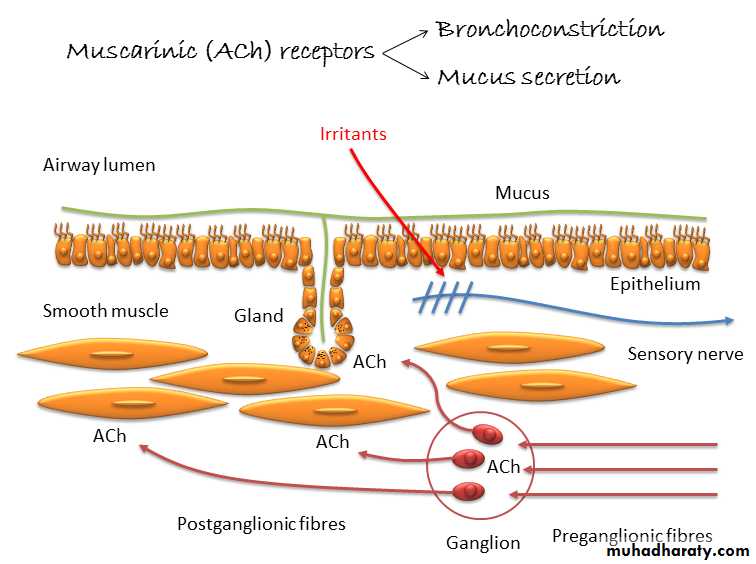
LAMA
Long Acting Antimuscarinic Agent
Drug Class – Antimuscarinic
GenericTiotropium, Ipratropium, Aclidinium
Mechanism
bronchodilatation
Indication(s)
COPD, Step 4-5 Asthma
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Angle closure glaucoma
Side effects
Dry mouth
Dose
e.g. Tiotropium handihaler 18mcg od
Note
• Interaction(s)
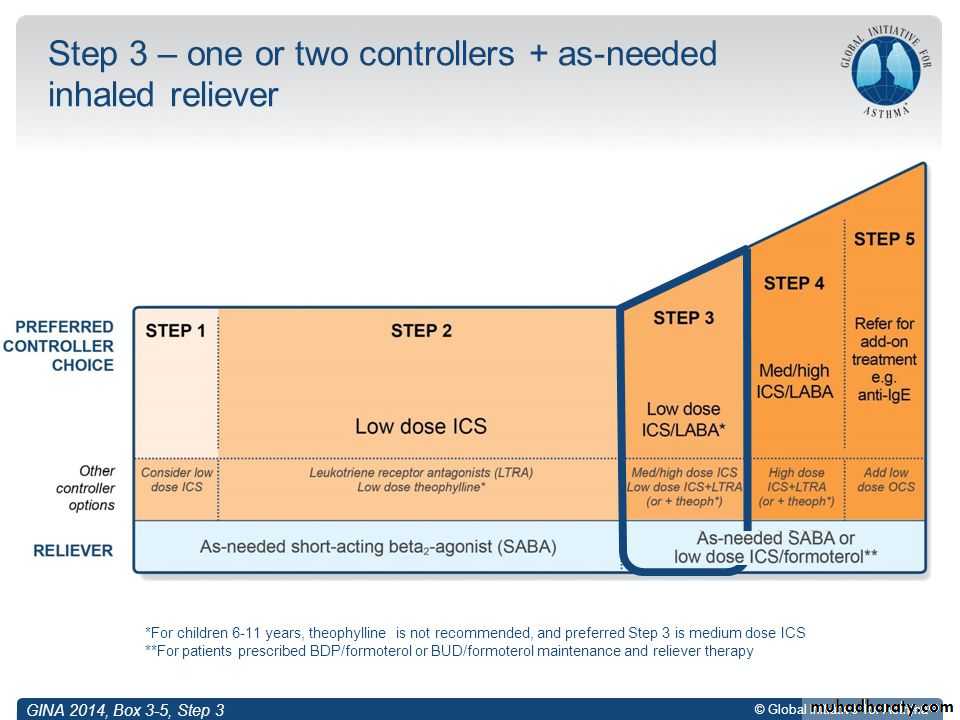
ICS/LABA
Dual Combination therapy
SABA & LABA
SABA & LABA
LRA
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist
Drug Class – Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist
GenericMontelukast
Mechanism
Blocks cysteinyl leukotrienes in the airway
Indication(s)
Asthma prophylaxis
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Churg-Strauss Syndrome
Side effects
Abdominal pain, thirst, somnolence
Dose
e.g. Montelukast 10mg nocte P.O.
Note
• Interaction(s)
Useful if concomitant Rhintis
Methylxanthines
Drug Class – Methylxanthines
GenericAminophylline
Mechanism
bronchodilatation
Indication(s)
Asthma and COPD
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Hypokalaemia
Side effects
Nausea, vomiting, tachyarrhythmia, convulsions
Dose
e.g. Aminophylline (Phyllocontin) 225mg MR P.O. B.D.
Note
• Interaction(s)
Narrow therapeutic window
Should measure plasma levels
Infections
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP)
Mycobacterial Tuberculosis (MTB)
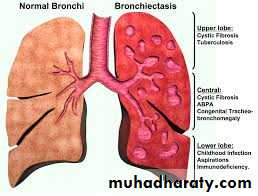
Bronchiectasis
CAP
HAP
48 Hours after hospital admission
MTB
Bronchiectasis
Drug Class – Penicillins
GenericBenzylpenicillin, Amoxicillin, Co-amoxiclav
Mechanism
Bactericidal, interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis
Indication(s)
Respiratory tract infections, other infections
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Hepatic dysfunction
Hypersensitivity 1-10% (anaphylaxis in 0.05%).
Side effects
Diarrhoea, cholestatic jaundice
Dose
e.g. Co-amoxiclav 625mg t.d.s. P.O.
Note
• Interaction(s)
Co-amoxiclav (Amoxicillin with Calvulanic acid) used for beta-lactamase-producing strains
Drug Class – Cephalosporins
Generic
1st Generation: Cefalexin, 2nd Generation: Cefuroxime, 3rd Generation: Cefpodoxime, Ceftazidime & Ceftriaxone
Mechanism
bactericidal
Indication(s)
Respiratory tract infections, other infections
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Hepatic dysfunction
Hypersensitivity (in 0.5-6.5% in those allergic to penicillin)
Side effects
Diarrhoea, cholestatic jaundice, N+V
Dose
e.g. Cefuroxime 1.5g t.d.s. i.v.
Note
• Interaction(s)
Drug Class – Macrolides
GenericAzithromycin, Clarithromycin, Erythromycin
Mechanism
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis
Indication(s)
Respiratory Tract infection, particularly atypicals. Other infections
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Can prolong QT interval
Side effects
NV&D, Abdominal discomfort, Prolongation of QT interval
Dose
e.g. Azithromycin 500mg P.O. o.d.
Note
• Interaction(s)
Avoid using with Warfarin and Quinolones
Drug Class – Quinolones
Generic
Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Levofloxacin
Mechanism
Impairs bacterial replication
Indication(s)
Respiratory Tract Infections
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Epilepsy, G6PD deficiency, avoid in pregnancy (arthropathy)
Side effects
Tendon Rupture, QT prolongation, NV&D, Dizziness
Dose
e.g. Levofloxacin 500mg P.O. o.d.
Note
• Interaction(s)
Avoid with macrolides
Drug Class – Tetracyclines
GenericDoxycycline, Tetracycline
Mechanism
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis
Indication(s)
Respiratory Tract infection especially H.Influenzae in COPD Exacerbation. Other infections (Acne, Lyme disease)
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Acute Porphyria. Pregnancy.
Side effects
N,V+D
Dose
e.g. Doxycyclince 200mg day one then 100mg daily P.O.
Note
• Interaction(s)
Drug Class – Antipseudomonal penicillin
Generic
Piperacillin
Mechanism
• Bactericidal, interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis
Indication(s)
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa infectionGram +ve, -ve and anaerobic Bacteria
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Hypernatraemia
Hypersensitivity
Side effects
Diarrhoea, hypernatraemia
Dose
e.g. Piperacillin with Tazobactam (Tazocin) 4.5g t.d.s i.v.
Note
• Interaction(s)
With beta-lactamase inhibitor Tazobactam. Not active against MRSA
Drug Class – Antituberculous
Generic
Rifampicin
Mechanism
Inhibits bacterial RNA synthesis
Indication(s)
MTB, other infections
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Jaundice, hypersensitivity
Side effectsDiscolouration of bodily fluids. Liver toxicity, Flu like, N,V&D
Dose
Weight dependent and in combination with other drugs
Note
• Interaction(s)
Potent inducer of liver enzymes (contraception, anicoagulation & steroids)
Drug Class – Antituberculous
GenericIsoniazid
Mechanism
Impairs bacterial cell wall synthesis
Indication(s)
MTB
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Hepatic disorder
Side effects
Liver toxicity, peripheral neuropathy (add Pyridoxine 10mg daily in those at risk), N,V&D
Dose
Weight dependent and in combination with other drugs
Note
• Interaction(s)
Drug Class – Antituberculous
GenericPyrazinamide
Mechanism
Unknown! May inhibit enzymes responsible for cell synthesis
Indication(s)
MTB
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Acute porphyria
Side effectsLiver toxicity, photosensitivity, N&V
Dose
Weight dependent and in combination with other drugs
Note
• Interaction(s)
Drug Class – Antituberculous
Generic
Ethambutol
Mechanism
Unknown! Bacteriostatic?
Indication(s)
MTB
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Avoid in renal impairment
Side effects
Rarely, retinal toxicity
Dose
Weight dependent and in combination with other drugs
Note
• Interaction(s)
Notes
Initial phase 2 monthsRifampicin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide & Ethambutol
Continuation phase 4 months
Rifampicin & Isoniazid
Combination treatment to reduce resistance
Add streptomycin is Isoniazid resistance confirmed/suspected
Pulmonary TB and TB pleuritis (6 months duration of Rx)
Directly Observed Treatment (DOT) is different
Rifater (depending on weight)
Liver function at baseline
Snellen chart at baseline
MDR-TB
XDR-TB
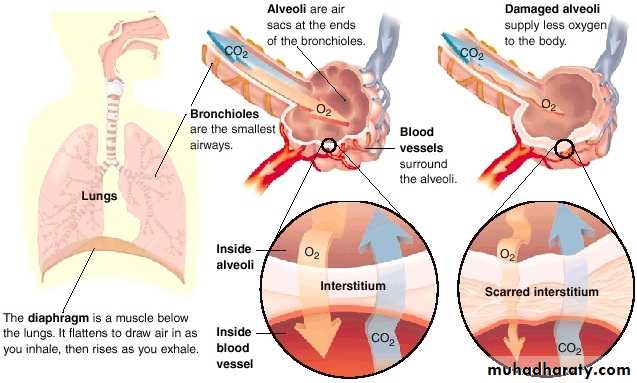
ILD
Interstitial Lung Disease
Common Drugs/Group of Drugs!
Bronchodilators (SABA/LABA)Corticosteroids
Antimuscarinic
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
Mucolytics
Methylxanthines
Magnesium sulphate
Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Macrolides
Tetracyclines
Quinolones
Anti-pseudomonal
Anti-Tuberculosis
Pirfenidone
Oxygen
Anti-IgE (Monoclonal antibody)
Methotrexate
Azathioprine
Anti-fungal
Lung Cancer (NSCLC & SCLC)
Palliative Care
Anticoagulation
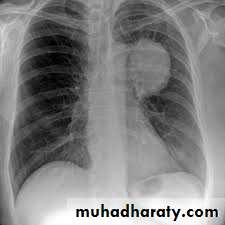
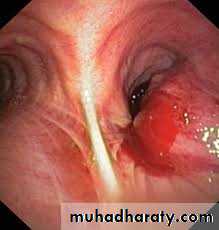
Lung Carcinoma
Assessing suspected Lung Cancer
3Important Questions…
Suspected Lung Cancer Assessment
FitnessFEV1
ECOG PS
Disease staging
Histology
NSCLC (Non small cell cancer)
SCLC (small cell cancer)
Outcome
Curable
Palliative
Surgery
Radical RTH
OncologyNon-Curable
Chemotherapy
NSCLCPemetrexed/Cisplatin
SE: Hair loss, myelosuppression, GI upset
Erlotinib/Gefitinib
SCLC
Etoposide + Cisplatin/Carboplatin
SE: Hair loss, myelosuppression, GI upset
Best supportive Care (Palliative)
PainParacetamol, NSAID, Opiate, Palliative RTH
Constipation
Osmotic laxatives e.g. Macrogol, Lactulose
Nausea
Metoclopramide, Ondansetron, Domperidone
Hypercalcaemia, SIADH other paraneoplastic syndromes
Haemoptysis
Tranexamic acid, palliative RTH
SVCO
Dexamethasone, stent
Dyspnoea
Endoscopic/pleural intervention, Benzodiazepines, Opiates
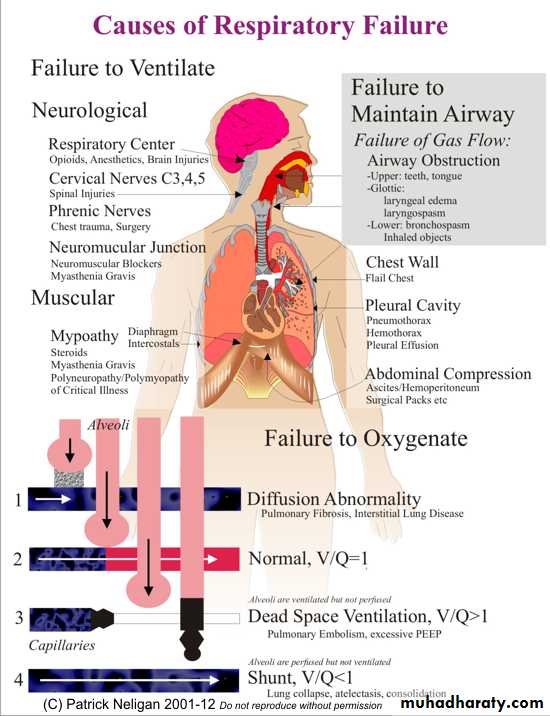
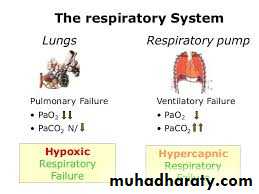
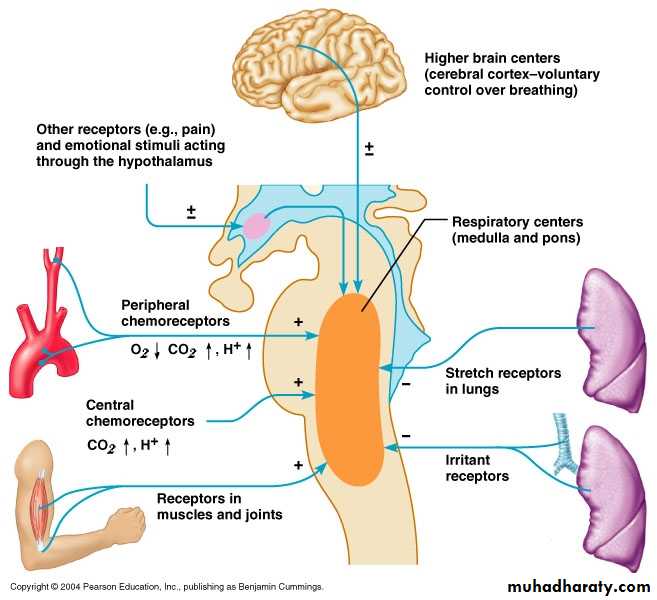
Respiratory Failure
Oxygen
Is a Drug!High Flow
Targeted Oxygen
Sats 88-92%
Sats >94%
LTOT
Palliative
Drug Class – Oxygen
GenericOxygen
Mechanism
Supplements the amount of oxygen in the blood stream and cells
Indication(s)
Hypoxaemia/respiratory failure
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Type 2 Respiratory Failure
Side effects
Lung toxicity (ICU), nasal irritation (cannulae), respiratory depression
Dose
e.g. Oxygen low flow target Saturation 88-92%
Note
• Interaction(s)
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Treatment
Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH)Heparin
Warfarin
Newer Oral Anticoagulants
Dabigatran
Rivaoxaban
Apixaban
Drug Class – Low molecular weight heparin
GenericEnoxaparin, Dalteparin
Mechanism
Binds and potentiates anti-thrombin III
Indication(s)
VTE, ACS/MI, Prophylaxis against VTE
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Renal dysfunction, bleeding diatheses, hyperkalaemia
Side effects
Bleeding, HIT (Heparin induced thrombocytopenia)
Dose
e.g. Enoxaparin 150units/kg s/c o.d. (if patient 70kg 10,500units)
Note
• Interaction(s)
Safer than unfractionated heparin. Requires no monitoring
Drug Class – Coumarins
GenericWarfarin
Mechanism
Antagonises the effect of vitamin K
Indication(s)
VTE, AF & Prosthetic cardiac valves
Caution
Contraindication(s)
Liver dysfunction
Hypersensitivity, Bleeding Diatheses, N,V&D
Side effects
Haemorrhage, INR monitoring
Dose
e.g. Warfarin o.d. p.o. as per INR target range (2-3)
Note
• Interaction(s)
Takes 48-72H for the anticoagulation effect
Many interactions!
Questions
x20
Question 1
The following drug is the best at providing maintenance treatment in step 2 asthma (mild-persistent Asthma)• Salbutamol
• Inhaled Beclomethasone
• Montelukast
• Warfarin
• Phyllocontin
Question 2
64 years-old male is a heavy smoker and presents with progressive dyspnoea (MRC 3). Spirometry confirms obstructive airflow defect with no reversibility to short acting beta agonist.Which of the following drugs may help improve his symptoms best?
• Tiotropium• Ipratropium
• Prednisolone
• Amoxicillin
• Doxycycline
Question 3
32 years-old female presents with fever, cough and green sputum over 3 days. She had crackles at the right base of the lung. She was otherwise well. She is allergic to trimethoprim (rash). Blood Urea was elevated and her systolic blood pressure was 85 mmgh. Respiratory rate was 32 breaths per minute.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
• Mild Community Acquired Pneumonia• Severe Hospital Acquired Pneumonia
• Bronchiectasis
• Severe Community Acquired Pneumonia
• Mesothelioma
Question 4
32 years-old female presents with fever, cough and green sputum over 3 days. She had crackles at the right base of the lung. She was otherwise well. She is allergic to trimethoprim (rash). Blood Urea was elevated and her systolic blood pressure was 85 mmgh. Respiratory rate was 32 breaths per minute.What is the best treatment option?
• Oral Moxifloxicin• i.v. Co-amoxiclav & Clarithromycin
• Rifampicin and Isoniazid p.o.
• i.v. Amoxicillin
• i.v. Ceftriaxone
Question 5
The following side effect can cause petechiae in patients taking Low Molecular Weight Heparin• Hyperkalaemia
• Headache
• Sleepiness
• Dizziness
• Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia
Question 6
Which of the following anti-Tuberculosis drugs causes discolouration of bodily fluids
• Streptomycin
• Pyrazinamide
• Isoniazid
• Rifampicin
• Ethambutol
Question 7
Question 7
44 years-old male presents with haemoptysis, cough and loss of appetite for one month. Sputum revealed alcohol-acid fast bacilli.What is the best regime we should use to start treating the most likely underlying condition?
• Rifampicin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide & Ethambutol
• Rifapmicin, Isoniazid & Ethambutol
• Rifampicin
• Levofloxacin
• Rifampicin and Isoniazid
Question 8
A patient was diagnosed with metastatic lung cancer. He developed hypercalcaemia. He then developed abdominal discomfort.
Which group of drugs may help him?
• NSAID• Paracetamol
• Anti-spasmodic
• Laxatives
• Benzodiazepines
Question 9
Pemetrexed can cause the following side effect• Hair loss
• Myelosuppression
• Vomiting
• None of the above
• All of the above
Question 10
Which of the following drugs, in carefully selected patients, can help reduce the progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis• Prednisolone
• Carbocisteine
• Azithromycin
• Perfenidone
• All of the above
Question 11
In asthma and COPD, which of the following drugs has both short acting and long acting bronchodilator properties?
• Formoterol
• Salmeterol
• Indacaterol
• Aclidinium
• Salbutamol
Question 12
The following categories/clinical features are used to determine the appropriate step in managing COPD patients..• Exacerbation Rate
• Functional Capacity
• FEV1
• None of the above
• All of the above
Question 13
22 years-old female presents with recurrent bronchial sepsis. Investigations including CT scan of the chest confirms Bronchiectasis. She has grown Pseudomonas Aeruginosa which of the following drugs could help treat her infection?• Tazobactam and Piperacillin
• Ceftriaxone
• Gentamycin
• Doxycycline
• Erythromycin
Question 14
22 years old heavy smoker presents with acute respiratory distress and was wheezy on chest auscultation. He received bronchodilator therapy initially but then became tired. His oxygen saturation on room air on arrival was 86%
What is the most appropriate next step?
• Intravenous theophylline• Intravenous Hydrocortisone
• Oxygen high flow non re-breather mask 100%
• Hudson mask oxygen at 60% concentration
• 2litres per minute Oxygen via nasal cannulae with target saturation of 88-92%
Question 15
Which of the following drugs can cause insomnia?• Montelukast
• Lorazepam
• Diazepam
• Nitrazepam
• Prednisolone
Question 16
Patients on inhaled corticosteroids who suffer from controlled bronchial asthma and then develop allergic rhinitis many benefit from …• Switching to a combination inhaler containing corticosteroid and long acting beta agonist
• Adding Tiotropium
• Adding Montelukast
• Discontinuing the inhaled corticosteroid
• Adding Aspirin
Question 17
Which of the following inhaler devices are hardest for the patients to use and coordinate?
• Pressurised metered dose inhaler
• Turbohaler
• Pressurised metered dose inhaler with a spacer device
• Accuhaler
• Handihaler
Question 18
An elderly lady with COPD and Connective Tissue Disease who is on long term oral corticosteroids. She develops a chest infection. Which of the following drugs should be avoided most?• Amoxicillin
• Clarithromycin
• Ciprofloxacin
• Ceftazidime
• Doxycycline
Question 19
A 33-years-old woman is 20 weeks gestation. She has presented with symptoms in keeping with uncontrolled asthma.Which of the following drugs should be avoided in pregnancy?
• Budesonide• Fluticasone
• Prednisolone
• Tetracycline
• Azithromycin
Question 20
Amoxicillin 500mg P.O. t.d.s.
Is given to the patient..
• Once daily
• Twice daily
• Thrice daily
• Four times daily
• Five times daily
Questions
x20Question 1
The following drug is the best at providing maintenance treatment in step 2 asthma (mild-persistent Asthma)• Salbutamol
• Inhaled Beclomethasone
• Montelukast
• Warfarin
• Phyllocontin
Question 2
64 years-old male is a heavy smoker and presents with progressive dyspnoea (MRC 3). Spirometry confirms obstructive airflow defect with no reversibility to short acting beta agonist.Which of the following drugs may help improve his symptoms best?
• Tiotropium• Ipratropium
• Prednisolone
• Amoxicillin
• Doxycycline
Question 3
32 years-old female presents with fever, cough and green sputum over 3 days. She had crackles at the right base of the lung. She was otherwise well. She is allergic to trimethoprim (rash). Blood Urea was elevated and her systolic blood pressure was 85 mmgh. Respiratory rate was 32 breaths per minute.What is the most likely diagnosis?
• Mild Community Acquired Pneumonia• Severe Hospital Acquired Pneumonia
• Bronchiectasis
• Severe Community Acquired Pneumonia
• Mesothelioma
Question 4
32 years-old female presents with fever, cough and green sputum over 3 days. She had crackles at the right base of the lung. She was otherwise well. She is allergic to trimethoprim (rash). Blood Urea was elevated and her systolic blood pressure was 85 mmgh. Respiratory rate was 32 breaths per minute.What is the best treatment option?
• Oral Moxifloxicin• i.v. Co-amoxiclav & Clarithromycin
• Rifampicin and Isoniazid p.o.
• i.v. Amoxicillin
• i.v. Ceftriaxone
Question 5
The following side effect can cause petechiae in patients taking Low Molecular Weight Heparin• Hyperkalaemia
• Headache
• Sleepiness
• Dizziness
• Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia
Question 6
Which of the following anti-Tuberculosis drugs causes discolouration of bodily fluids
• Streptomycin
• Pyrazinamide
• Isoniazid
• Rifampicin
• Ethambutol
Question 7
Question 7
44 years-old male presents with haemoptysis, cough and loss of appetite for one month. Sputum revealed alcohol-acid fast bacilli.What is the best regime we should use to start treating the most likely underlying condition?
• Rifampicin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide & Ethambutol
• Rifapmicin, Isoniazid & Ethambutol
• Rifampicin
• Levofloxacin
• Rifampicin and Isoniazid
Question 8
A patient was diagnosed with metastatic lung cancer. He developed hypercalcaemia. He then developed abdominal discomfort.
Which group of drugs may help him?
• NSAID• Paracetamol
• Anti-spasmodic
• Laxatives
• Benzodiazepines
Question 9
Pemetrexed can cause the following side effect• Hair loss
• Myelosuppression
• Vomiting
• None of the above
• All of the above
Question 10
Which of the following drugs, in carefully selected patients, can help reduce the progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis• Prednisolone
• Carbocisteine
• Azithromycin
• Perfenidone
• All of the above
Question 11
In asthma and COPD, which of the following drugs has both short acting and long acting bronchodilator properties?
• Formoterol
• Salmeterol
• Indacaterol
• Aclidinium
• Salbutamol
Question 12
The following categories/clinical features are used to determine the appropriate step in managing COPD patients..• Exacerbation Rate
• Functional Capacity
• FEV1
• None of the above
• All of the above
Question 13
22 years-old female presents with recurrent bronchial sepsis. Investigations including CT scan of the chest confirms Bronchiectasis. She has grown Pseudomonas Aeruginosa which of the following drugs could help treat her infection?• Tazobactam and Piperacillin
• Ceftriaxone
• Gentamycin
• Doxycycline
• Erythromycin
Question 14
22 years old heavy smoker presents with acute respiratory distress and was wheezy on chest auscultation. He received bronchodilator therapy initially but then became tired. His oxygen saturation on room air on arrival was 86%
What is the most appropriate next step?
• Intravenous theophylline• Intravenous Hydrocortisone
• Oxygen high flow non re-breather mask 100%
• Hudson mask oxygen at 60% concentration
• 2litres per minute Oxygen via nasal cannulae with target saturation of 88-92%
Question 15
Which of the following drugs can cause insomnia?• Montelukast
• Lorazepam
• Diazepam
• Nitrazepam
• Prednisolone
Question 16
Patients on inhaled corticosteroids who suffer from controlled bronchial asthma and then develop allergic rhinitis many benefit from …• Switching to a combination inhaler containing corticosteroid and long acting beta agonist
• Adding Tiotropium
• Adding Montelukast
• Discontinuing the inhaled corticosteroid
• Adding Aspirin
Question 17
Which of the following inhaler devices are hardest for the patients to use and coordinate?
• Pressurised metered dose inhaler
• Turbohaler
• Pressurised metered dose inhaler with a spacer device
• Accuhaler
• Handihaler
Question 18
An elderly lady with COPD and Connective Tissue Disease who is on long term oral corticosteroids. She develops a chest infection. Which of the following drugs should be avoided most?• Amoxicillin
• Clarithromycin
• Ciprofloxacin
• Ceftazidime
• Doxycycline
Question 19
A 33-years-old woman is 20 weeks gestation. She has presented with symptoms in keeping with uncontrolled asthma.
Which of the following drugs should be avoided in pregnancy?
• Budesonide• Fluticasone
• Prednisolone
• Tetracycline
• Azithromycin
Question 20
Amoxicillin 500mg P.O. t.d.s.Is given to the patient..
• Once daily
• Twice daily
• Thrice daily
• Four times daily
• Five times daily